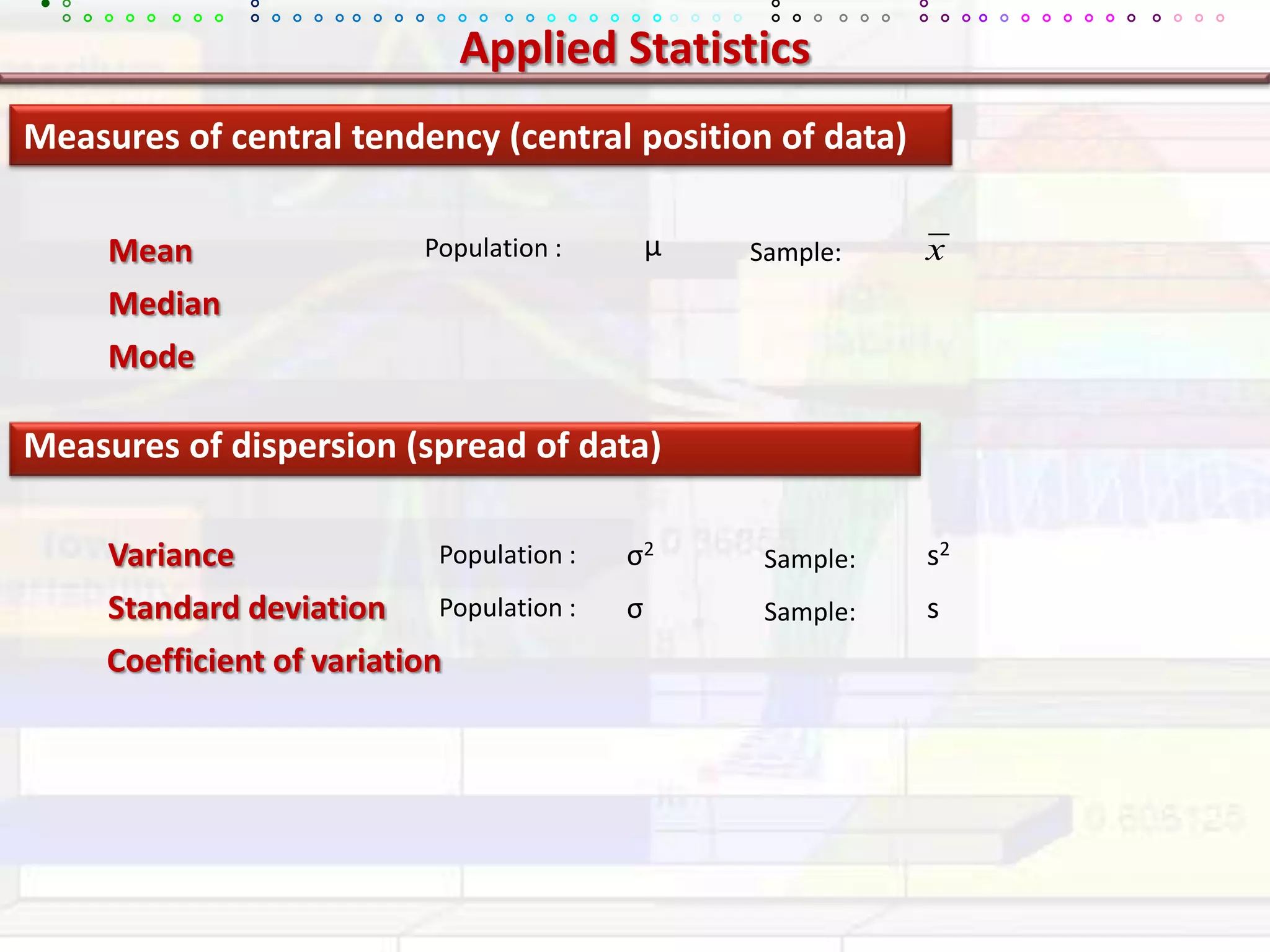
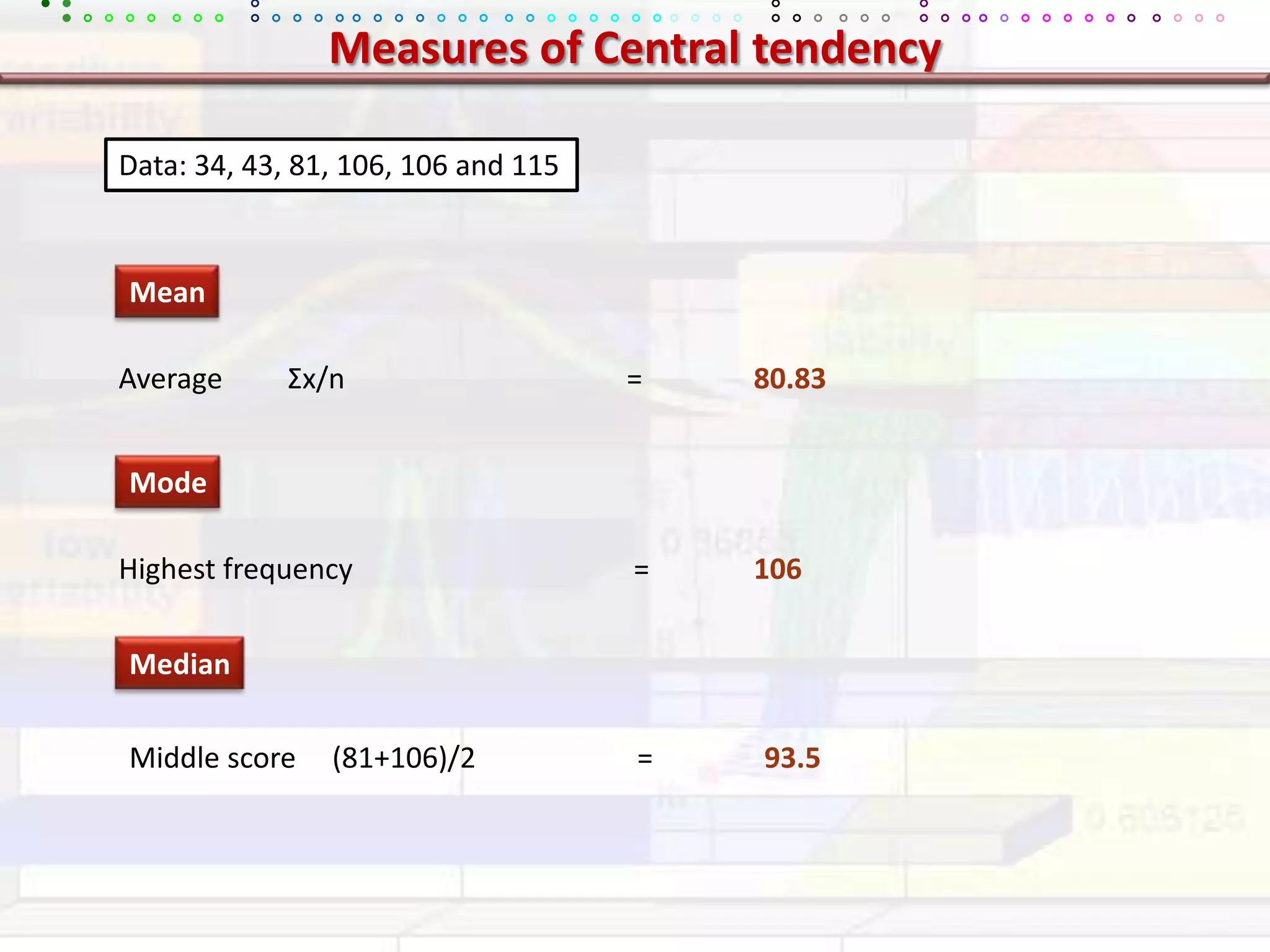
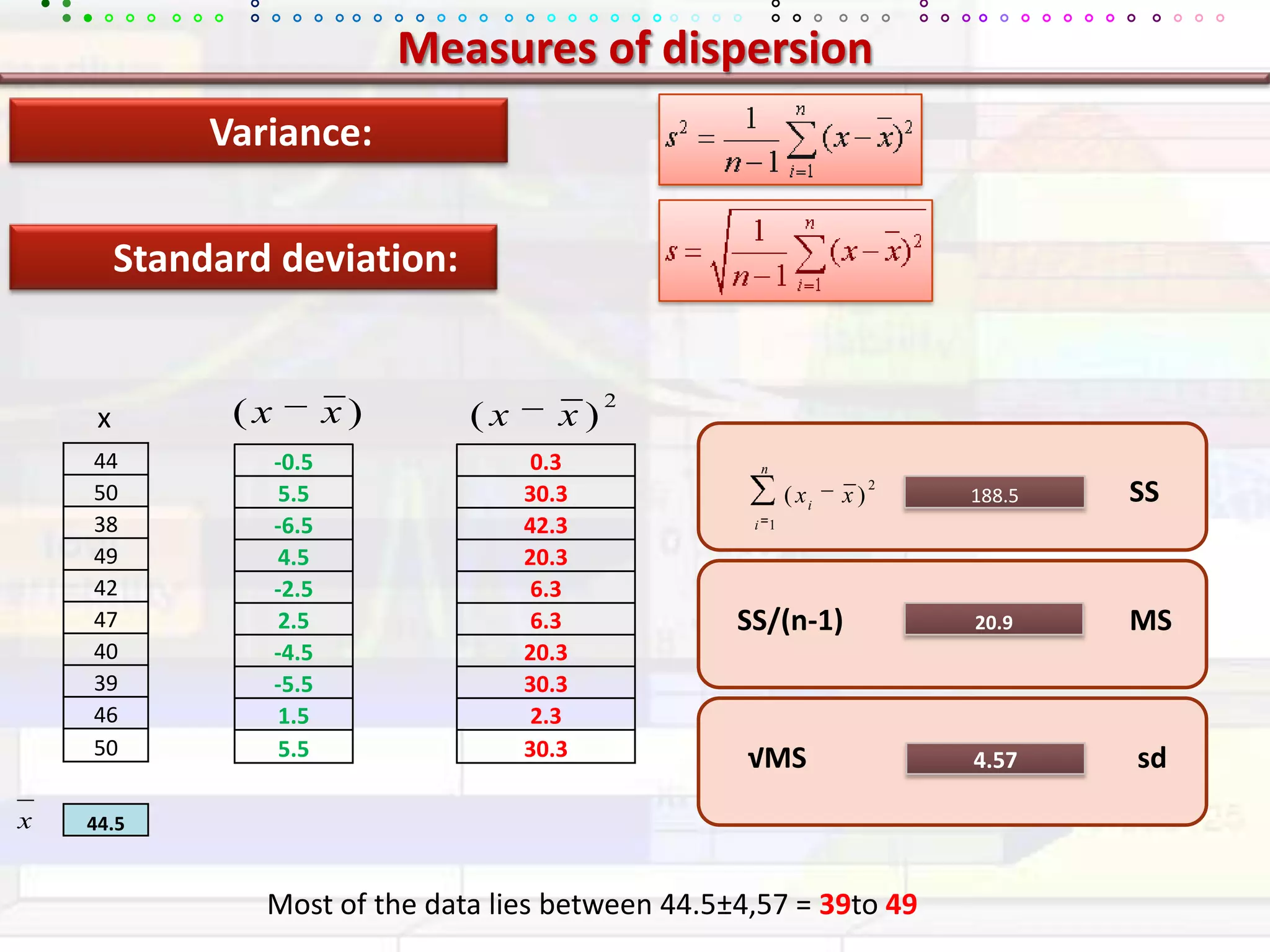
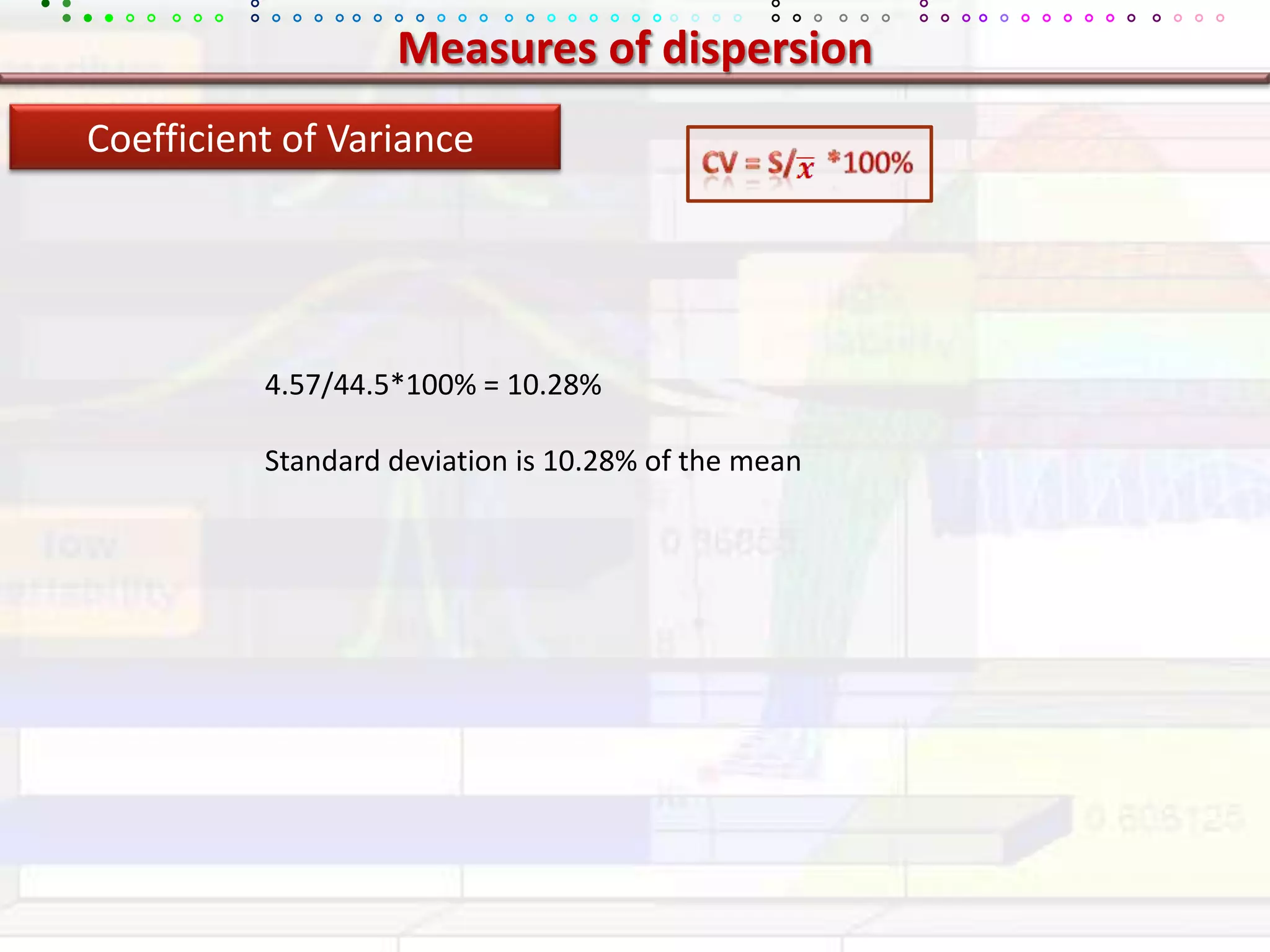
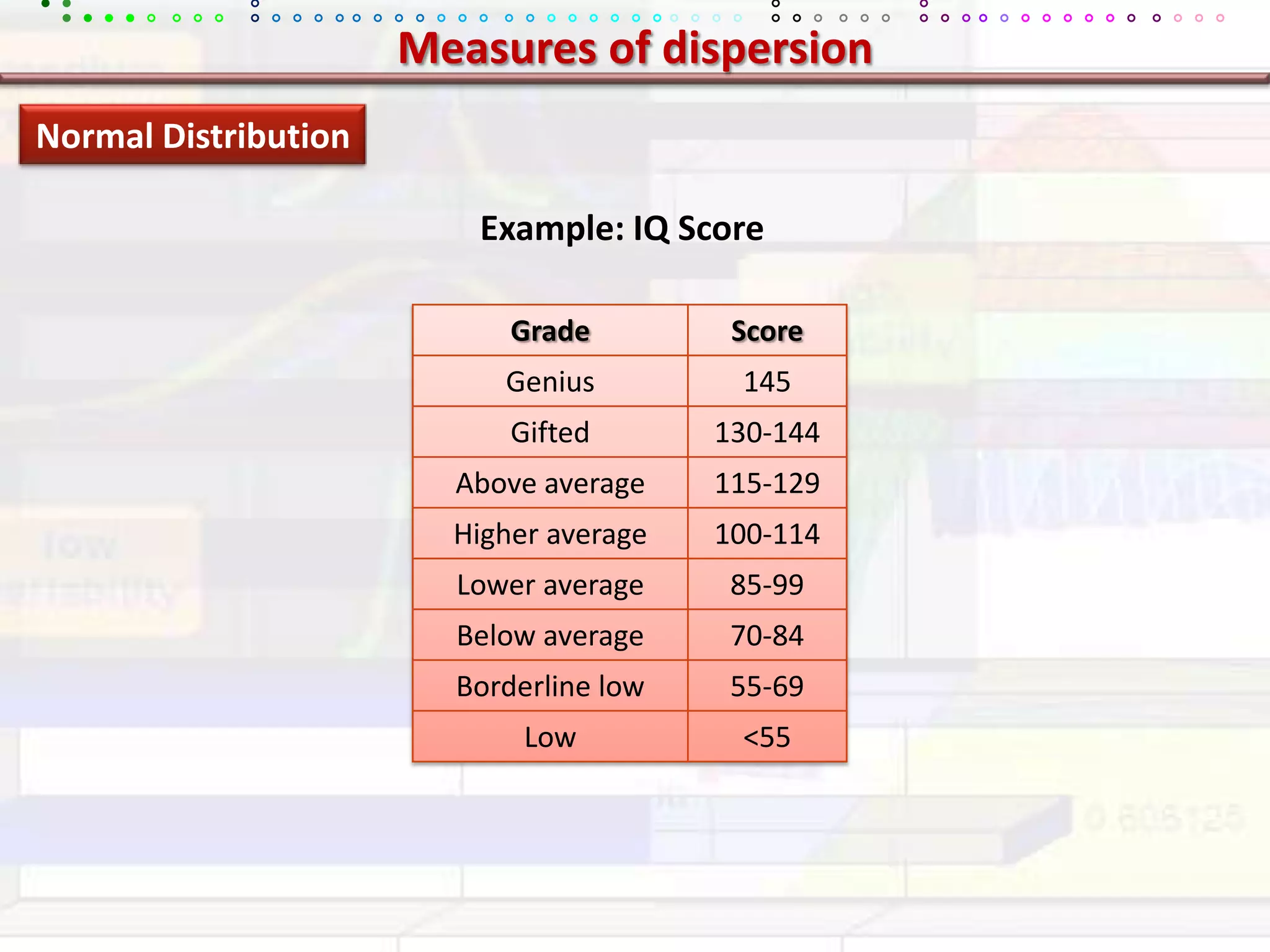
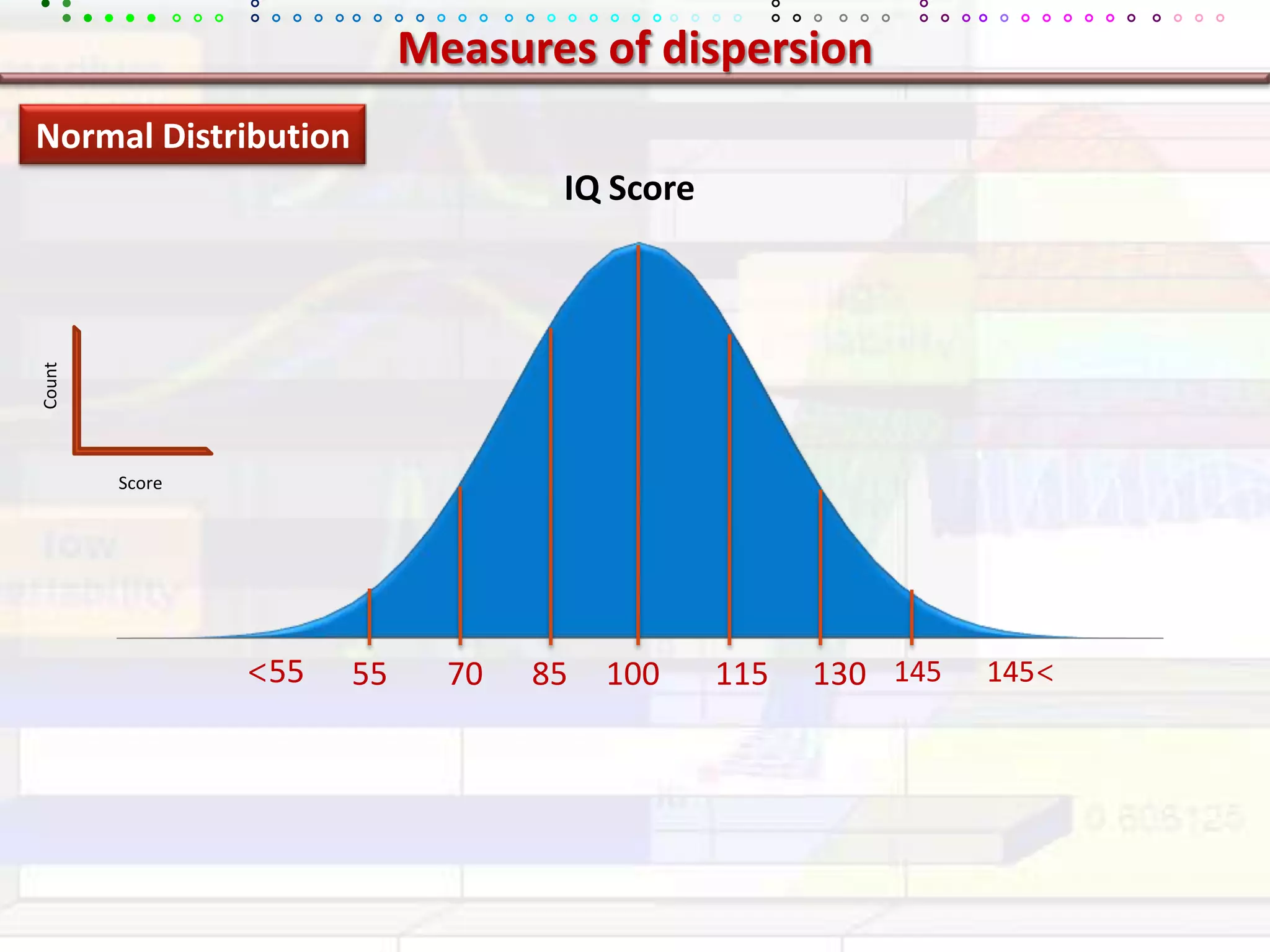
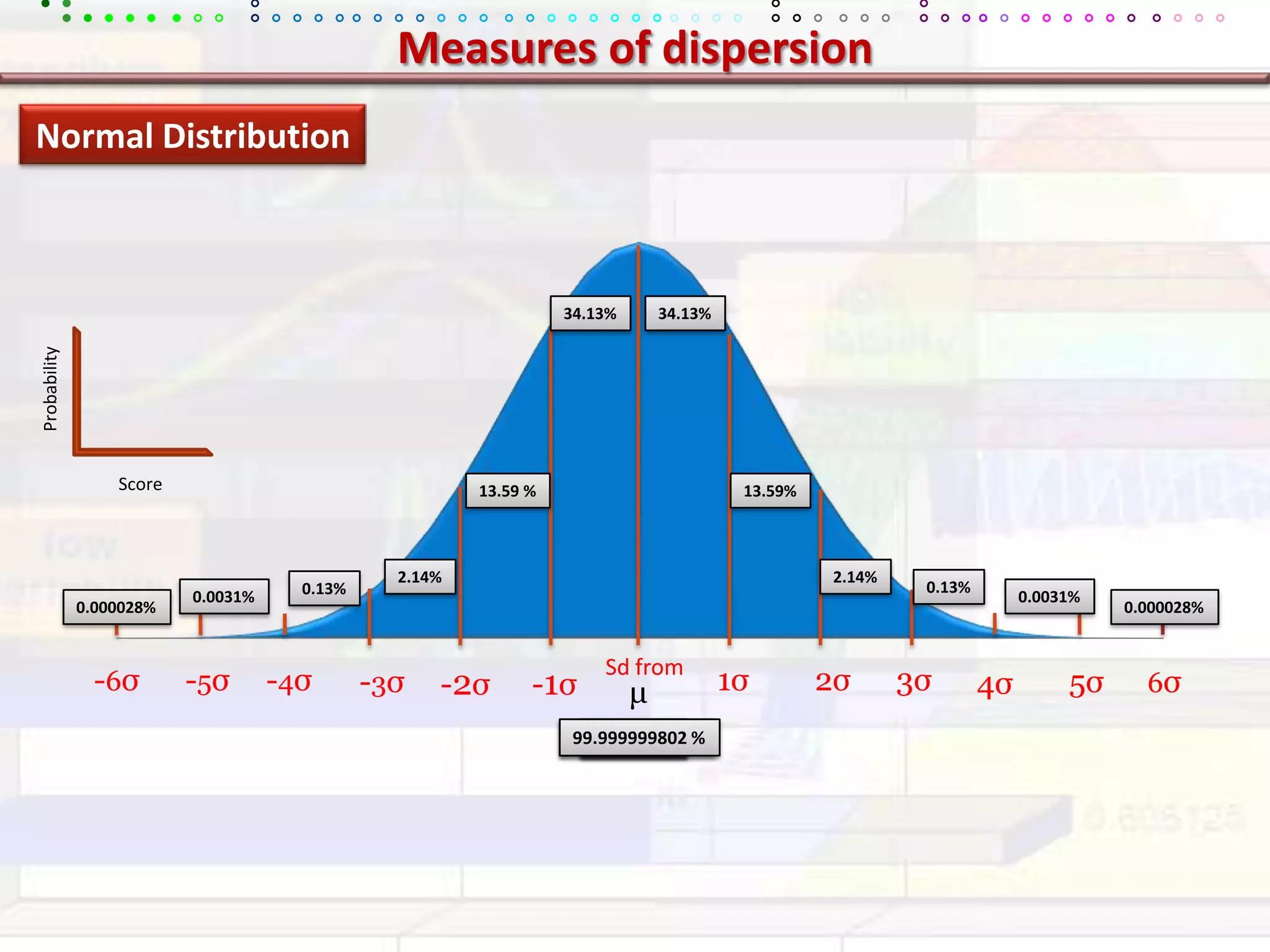
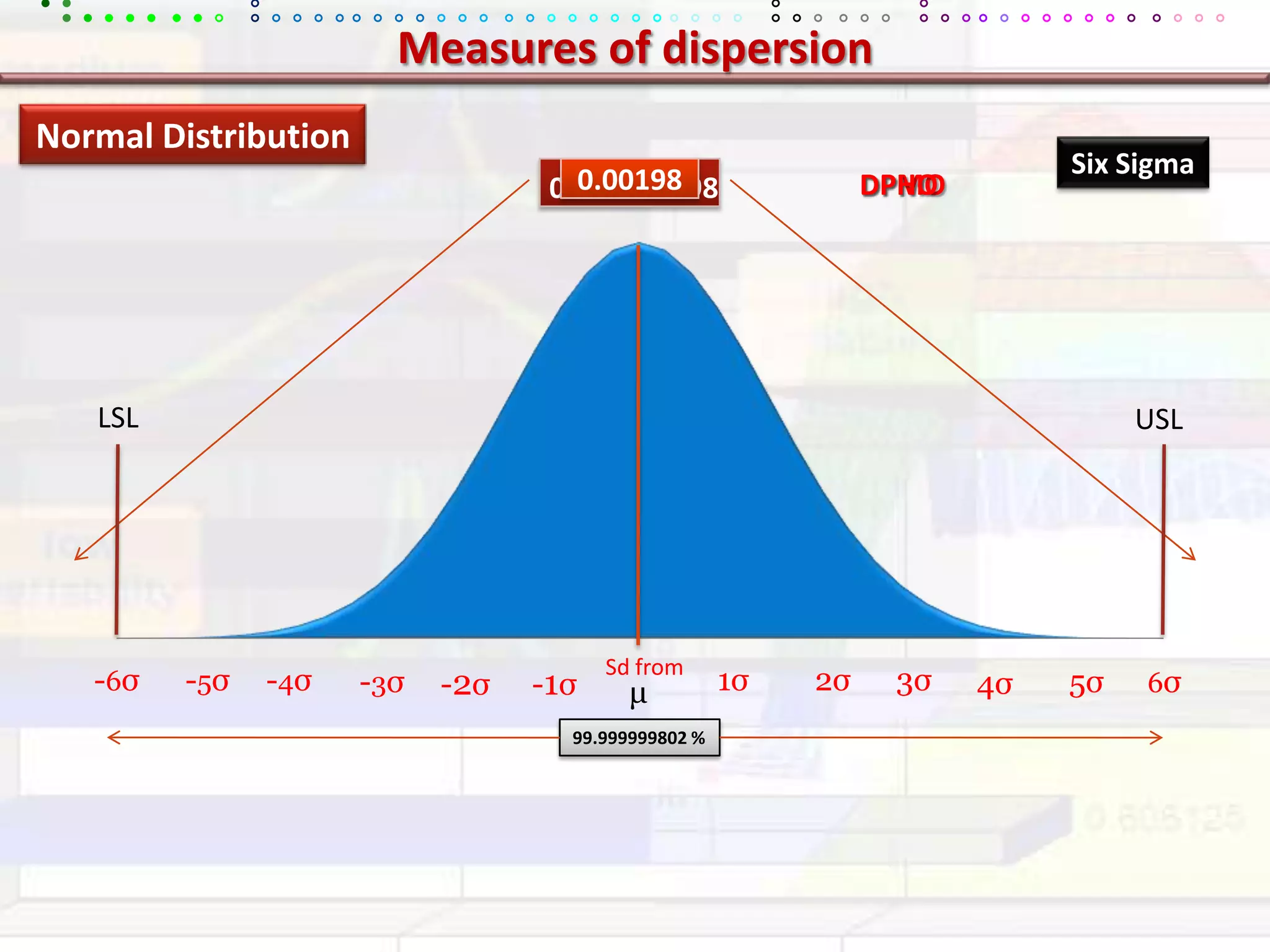
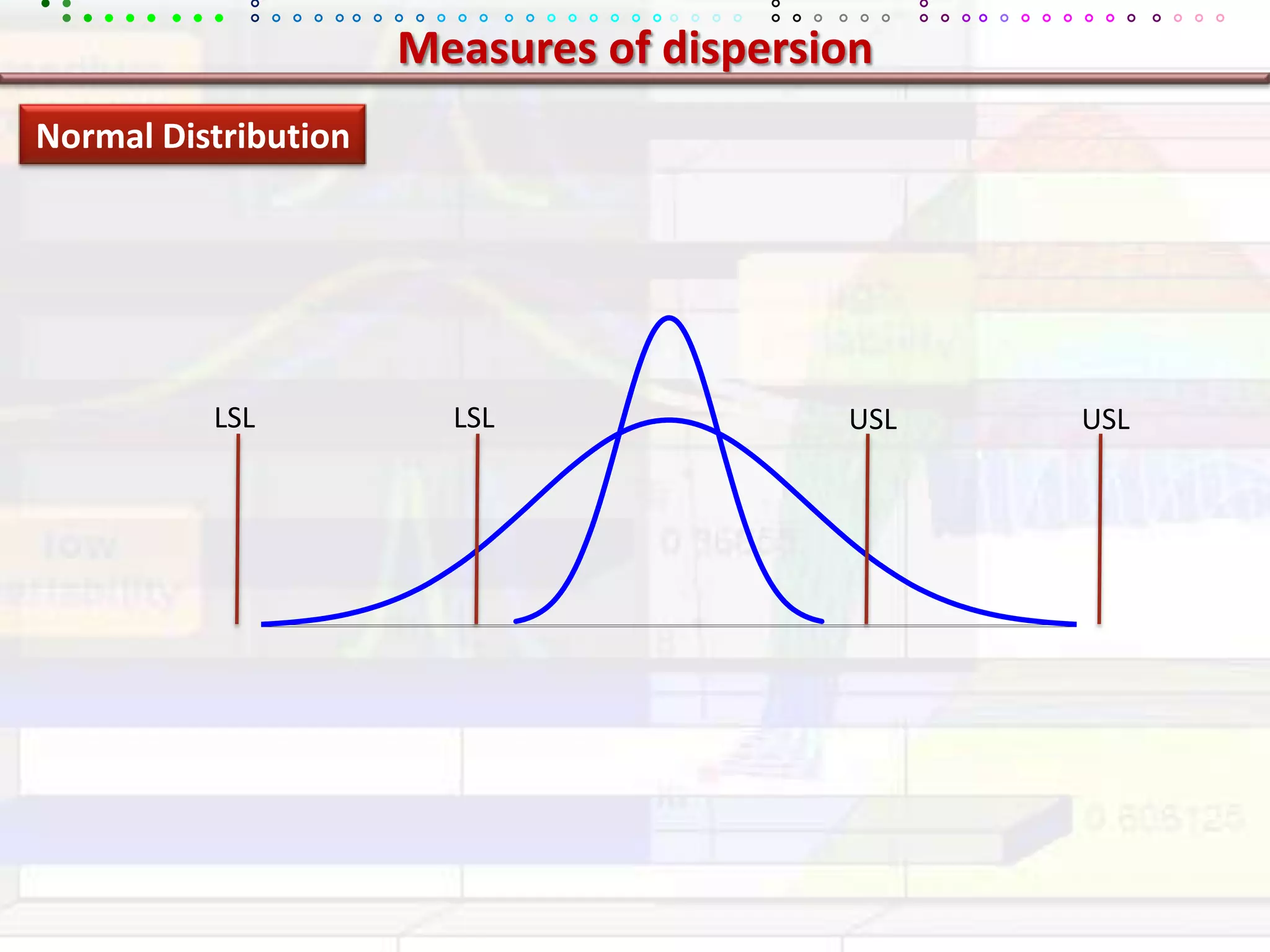
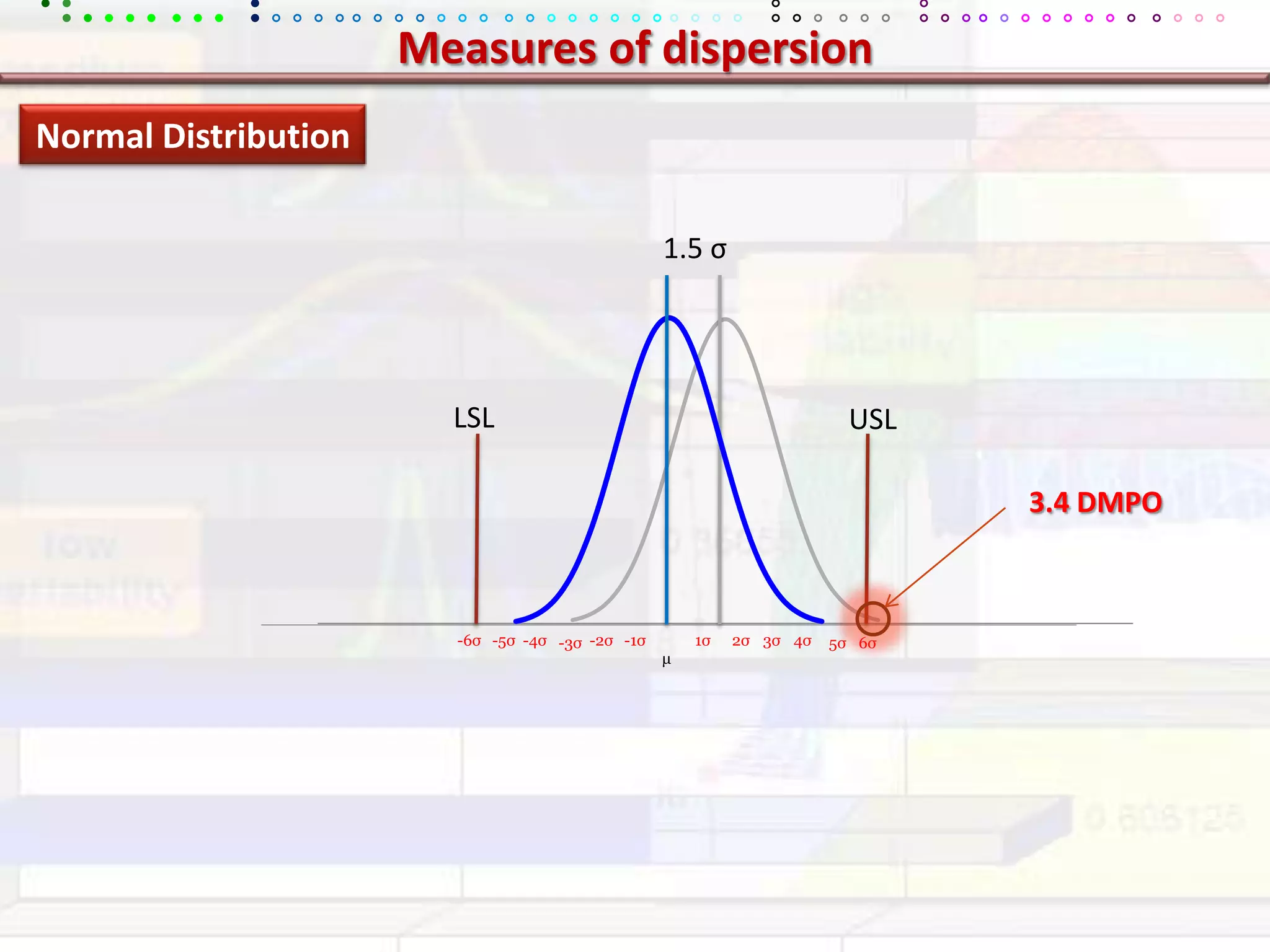
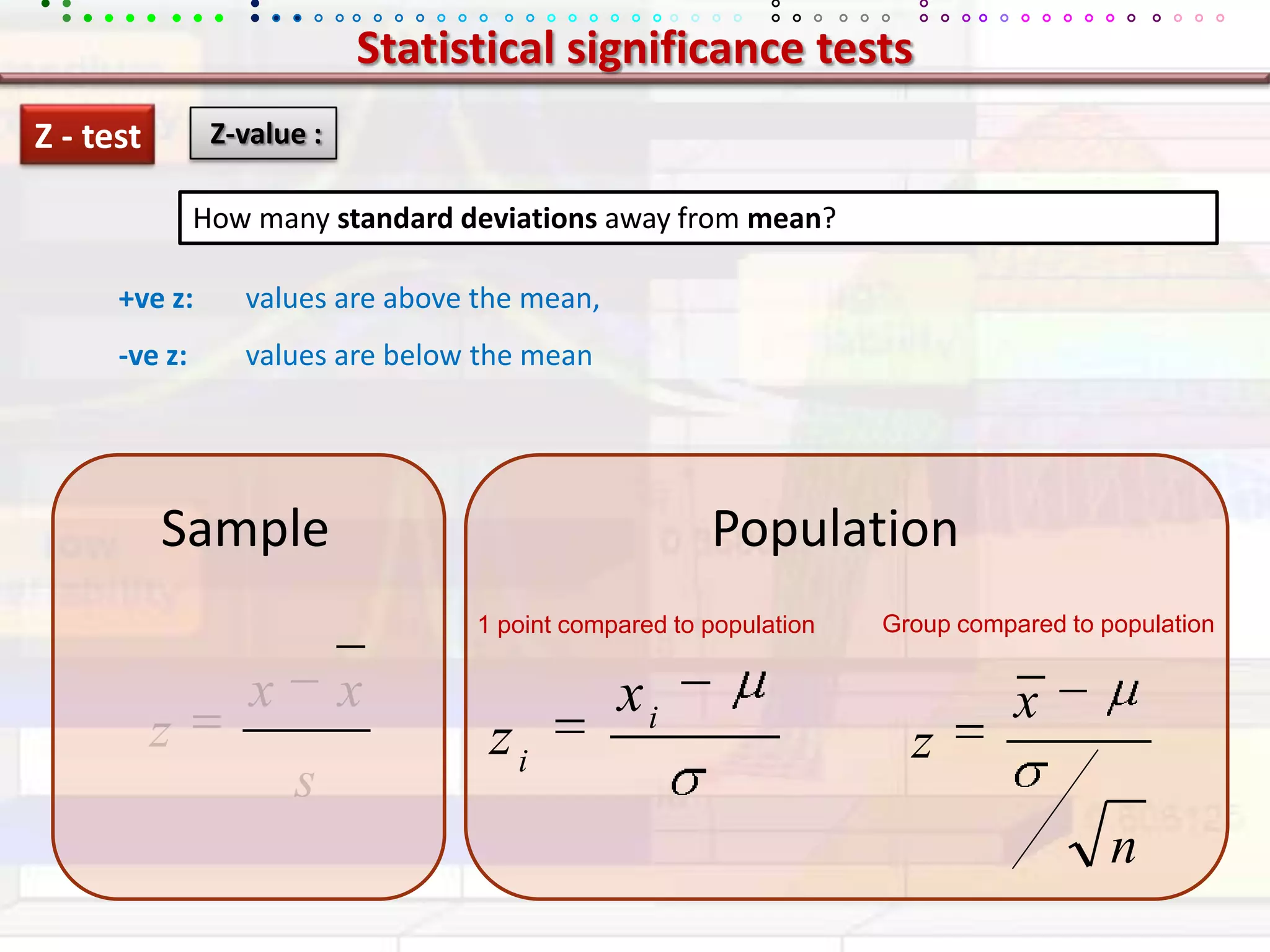
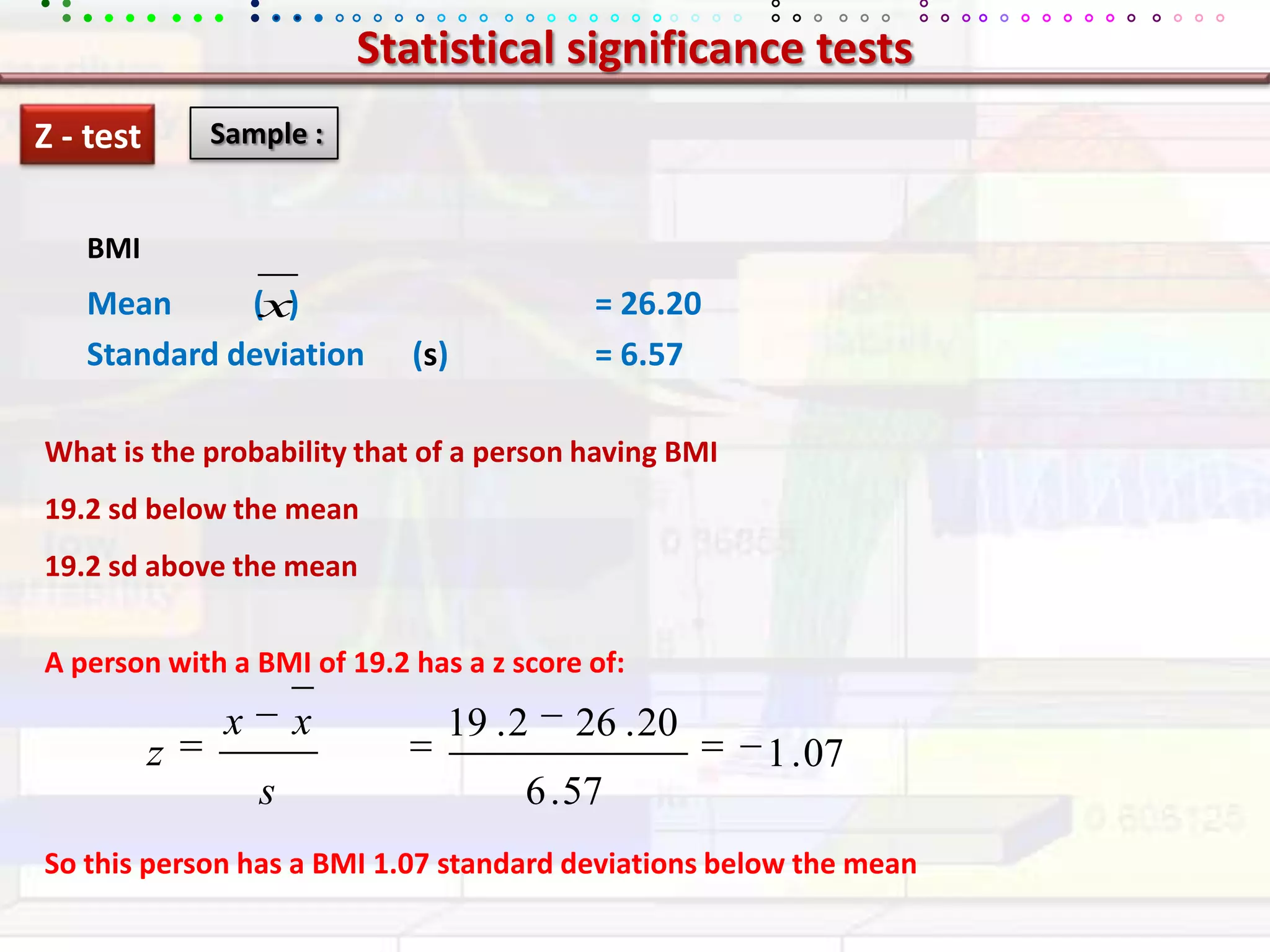
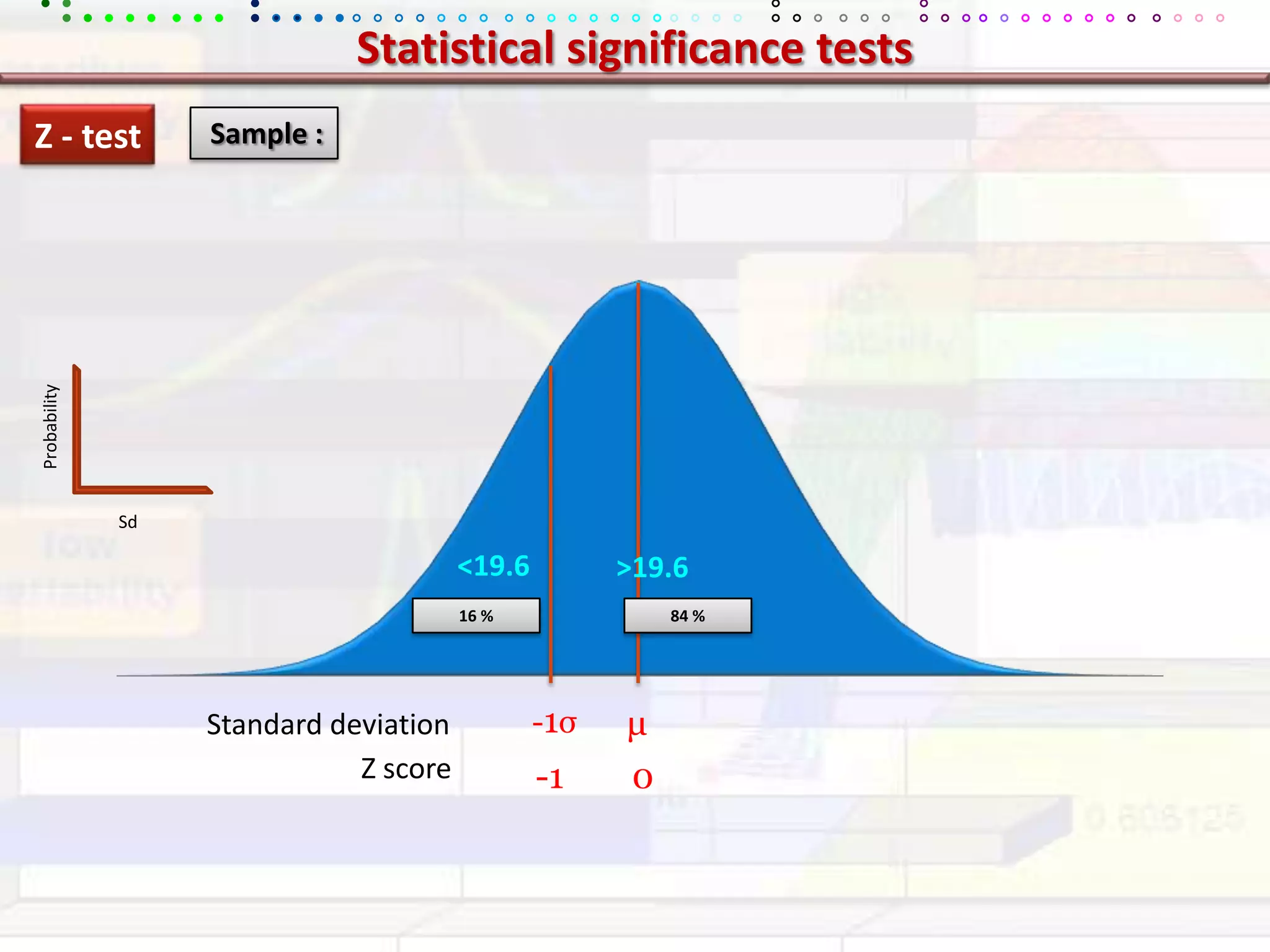
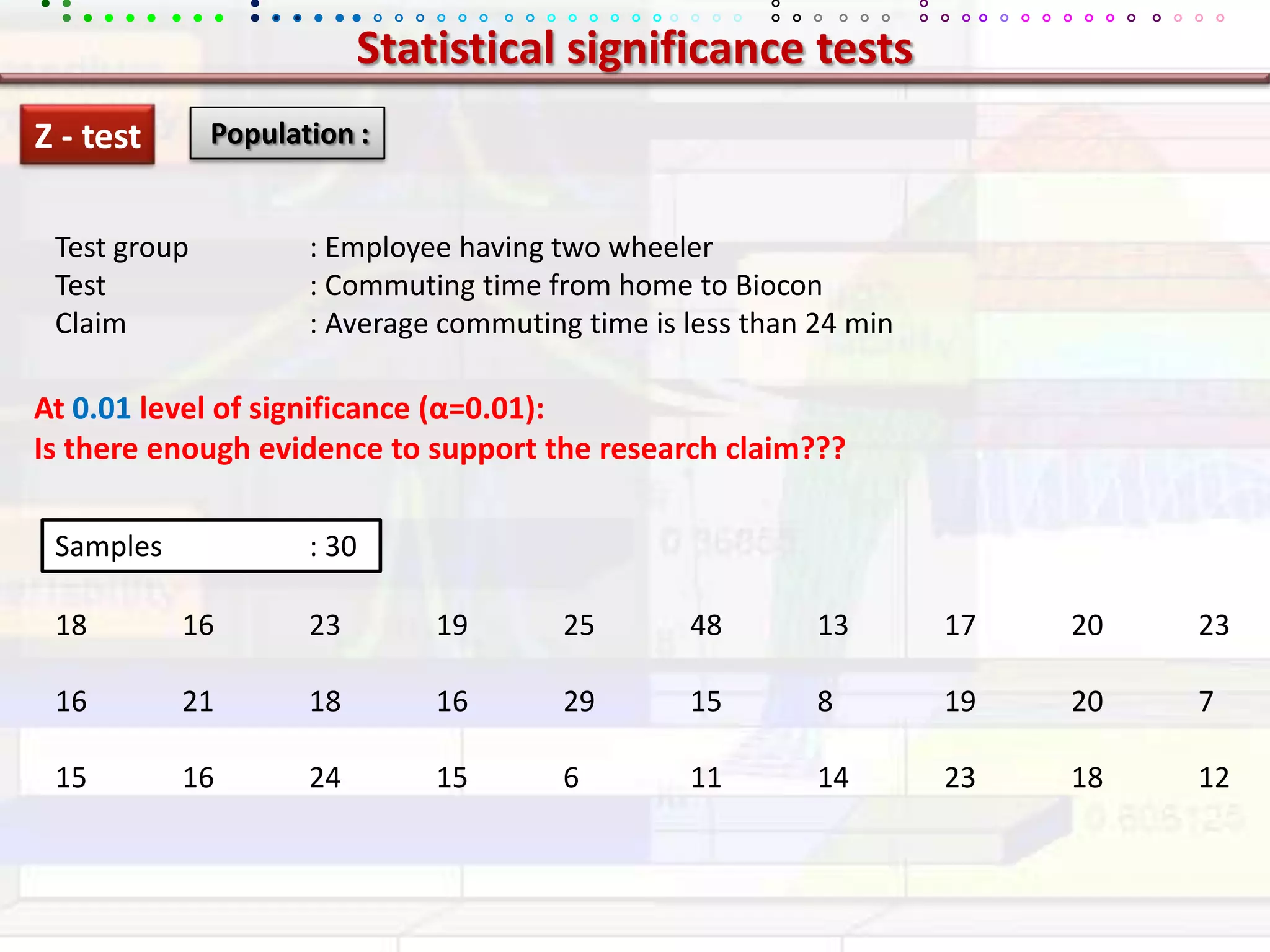
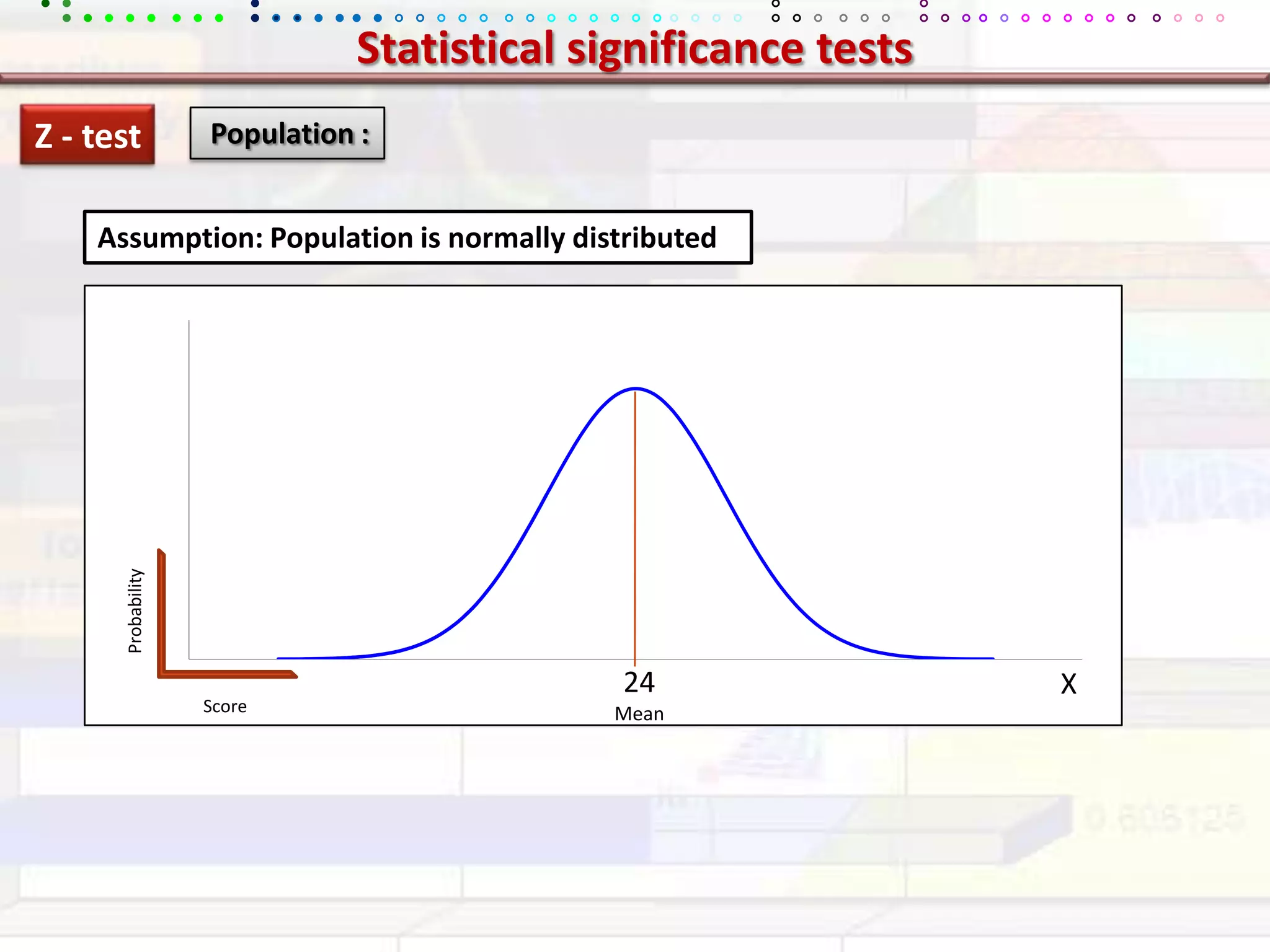
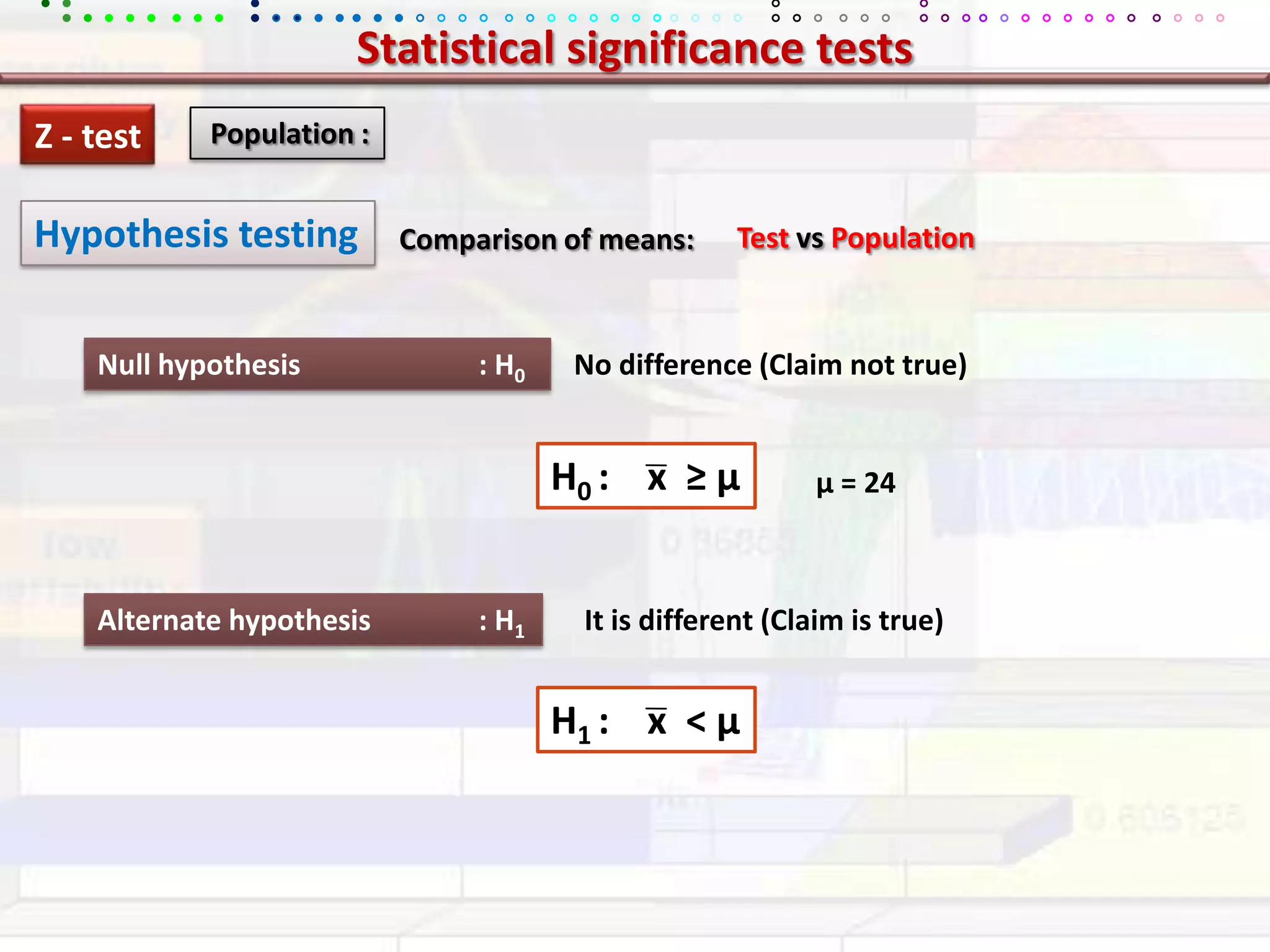
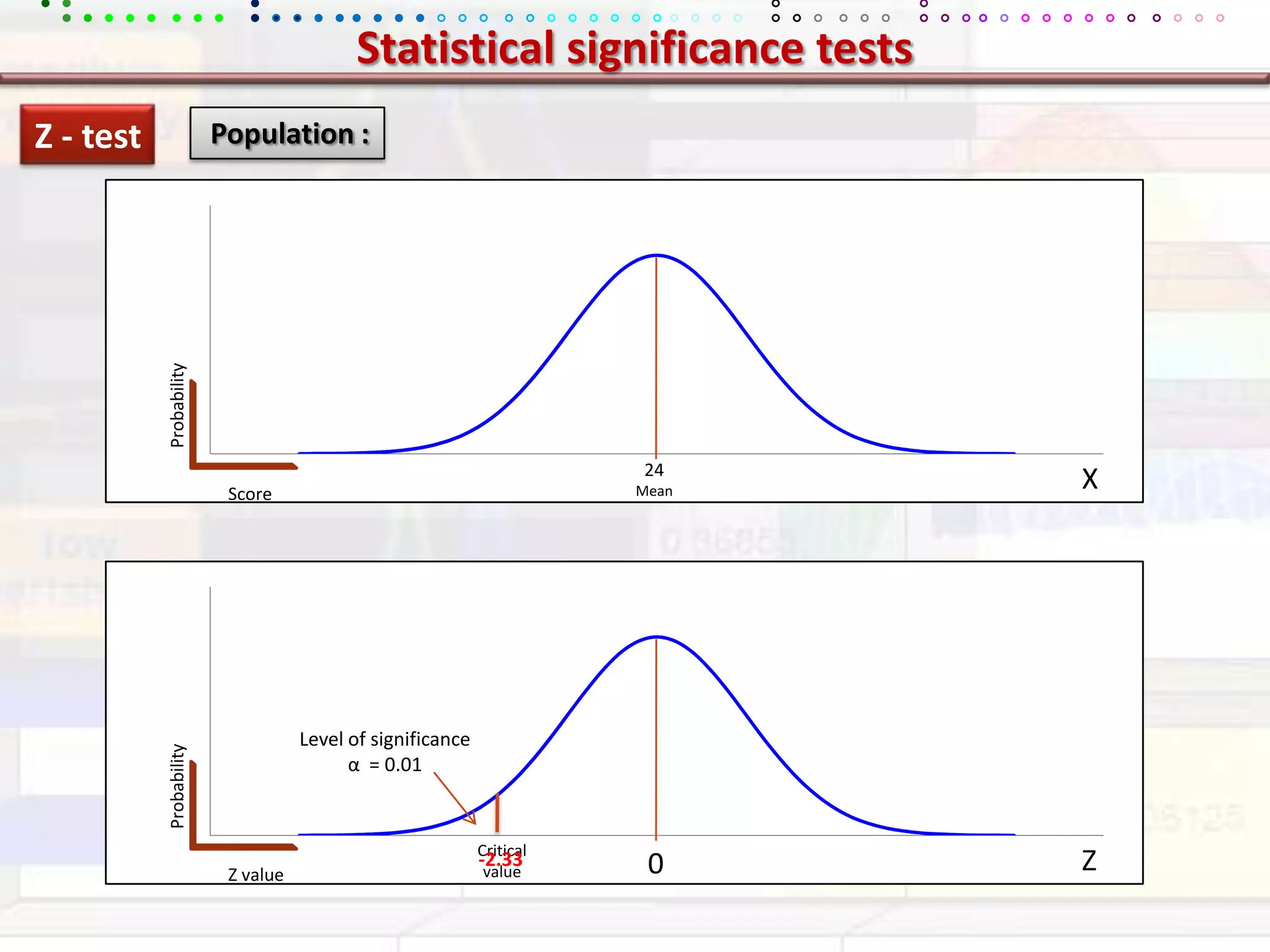
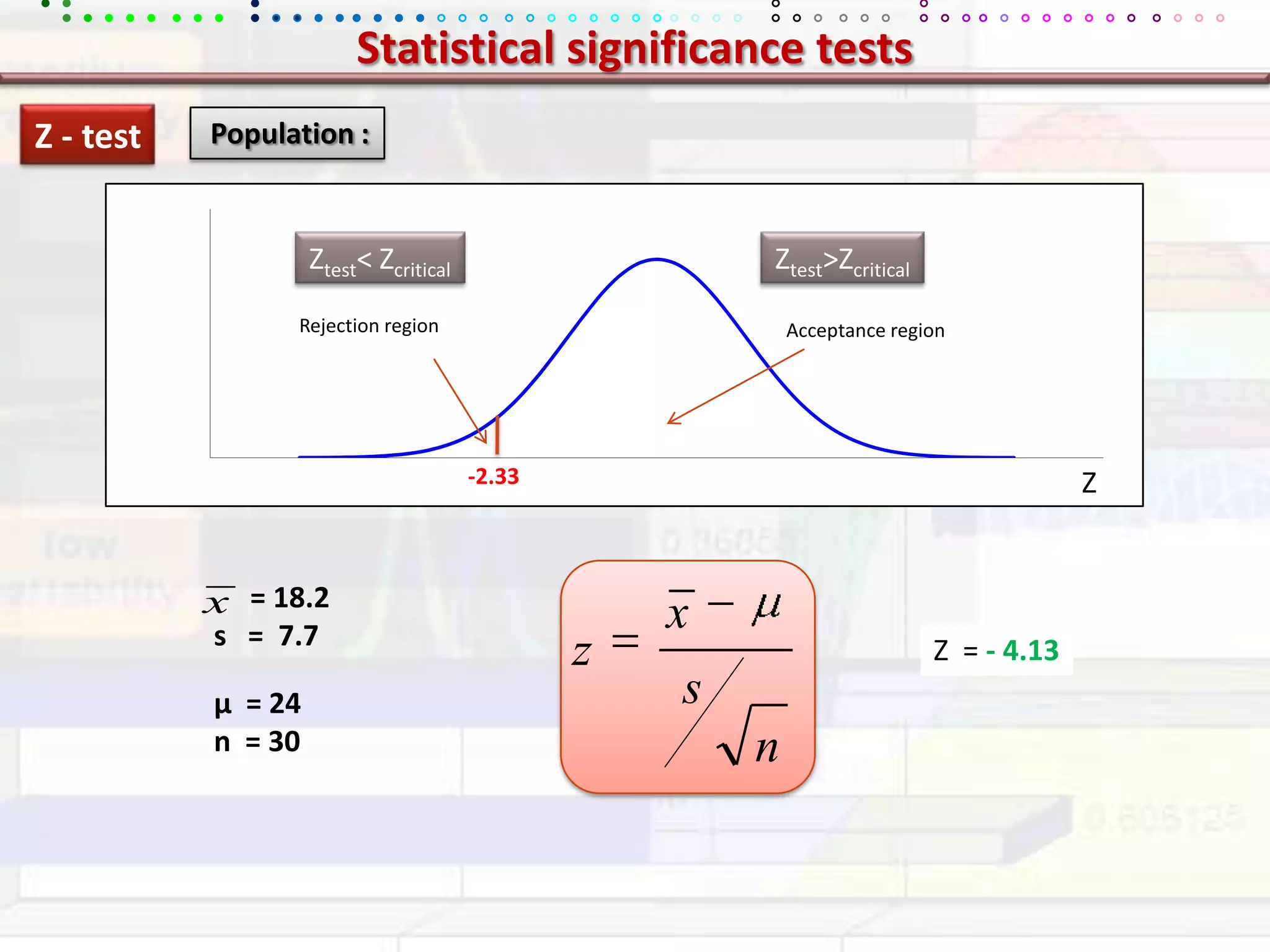
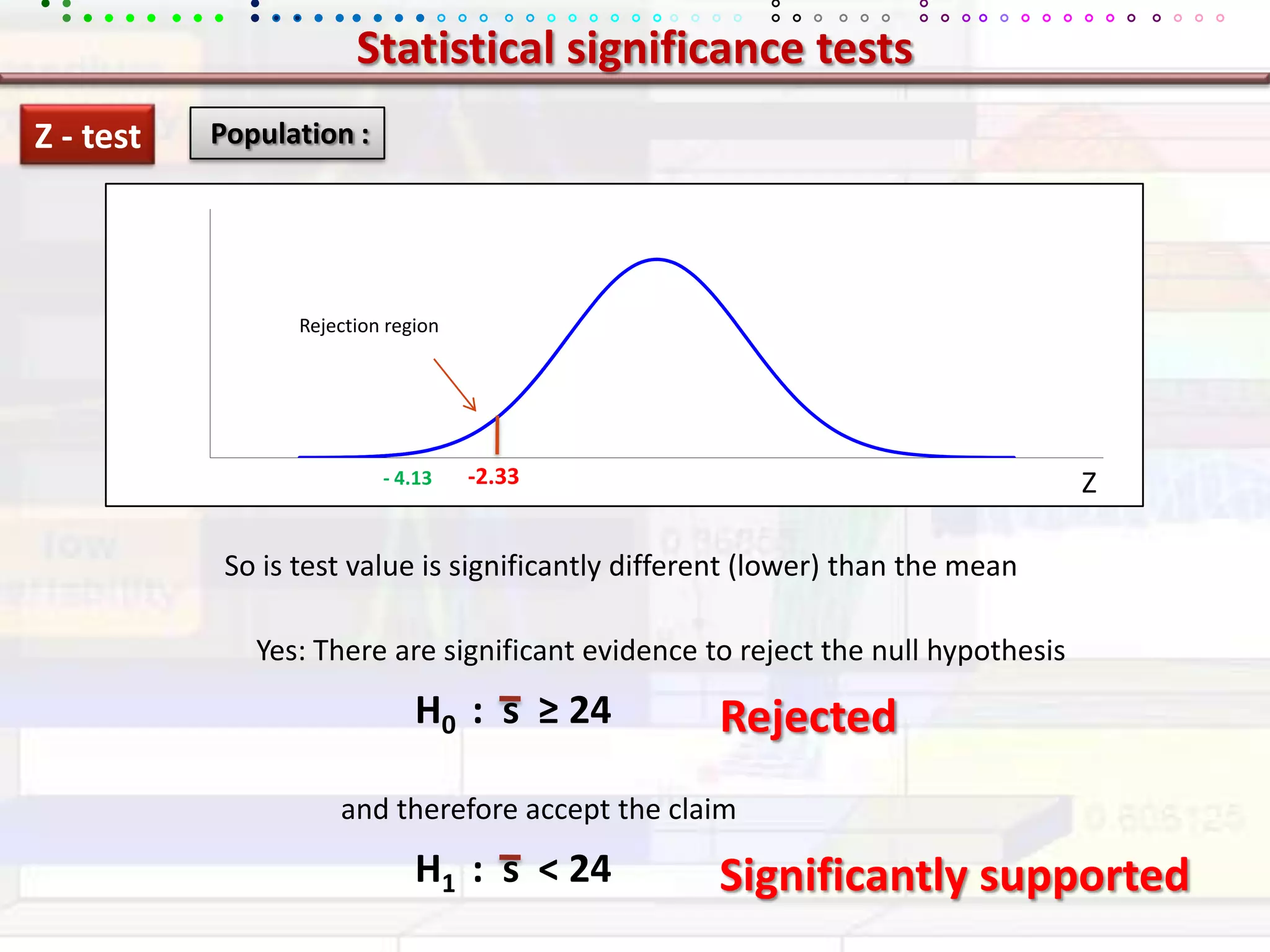
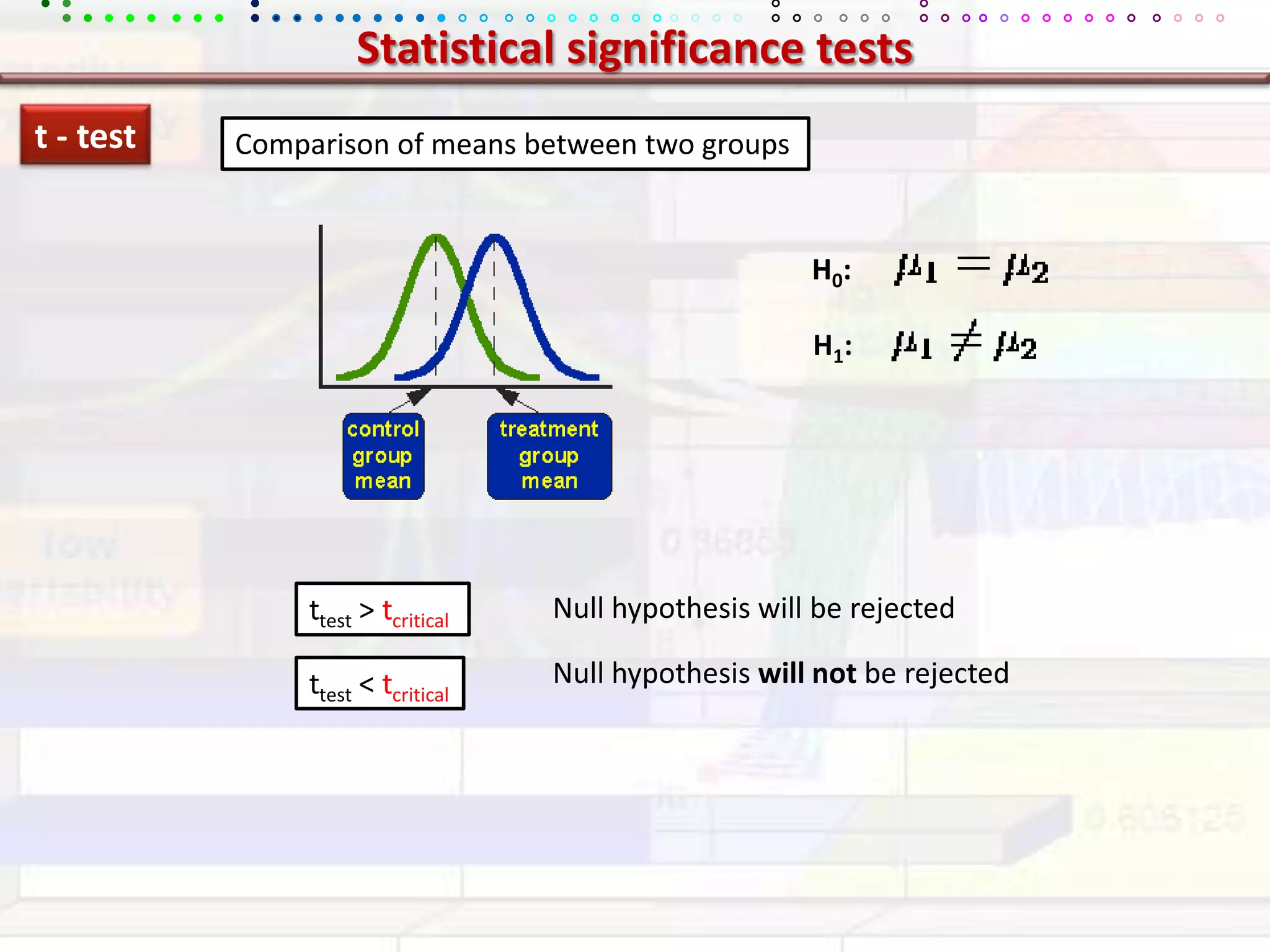
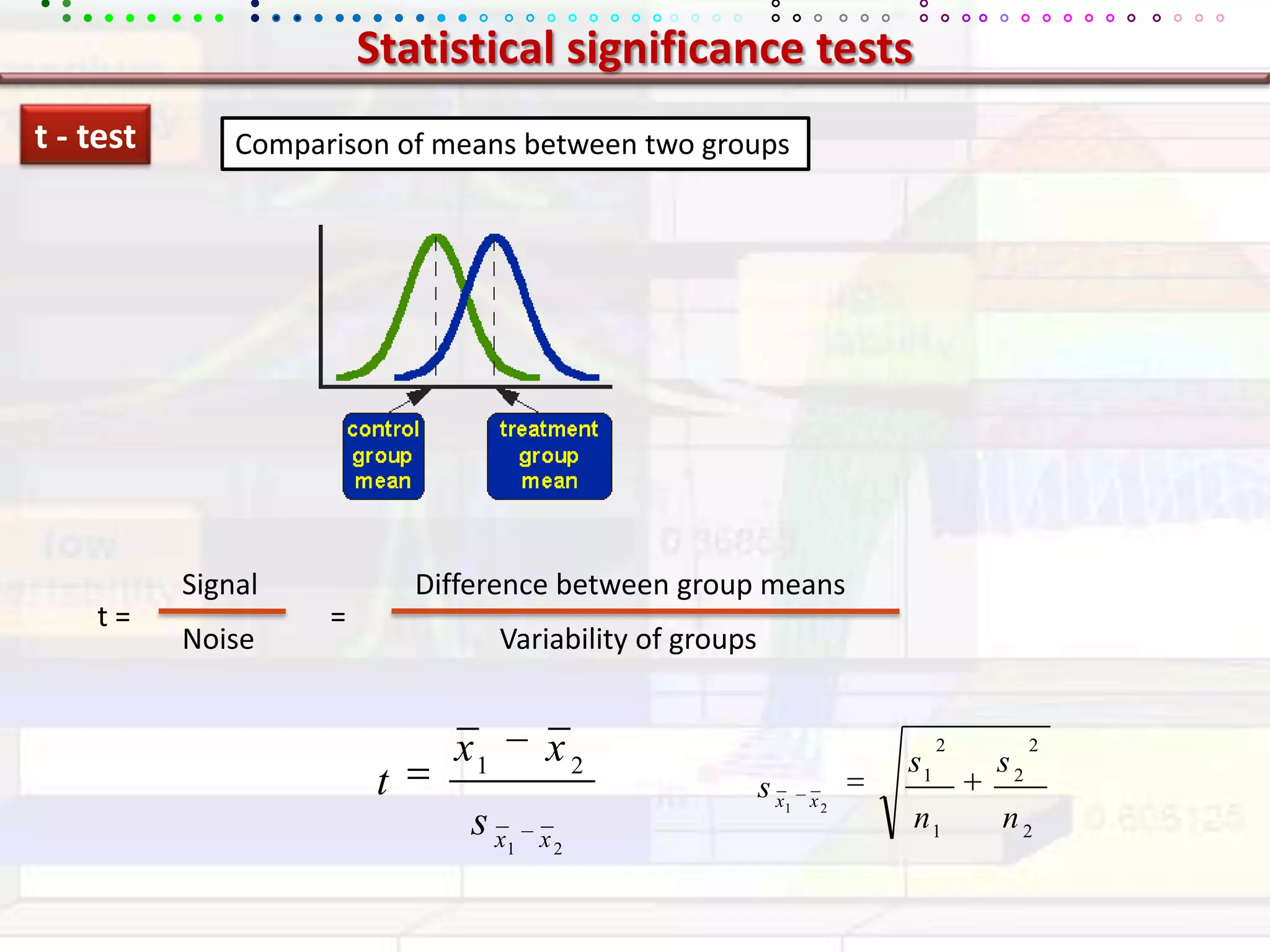
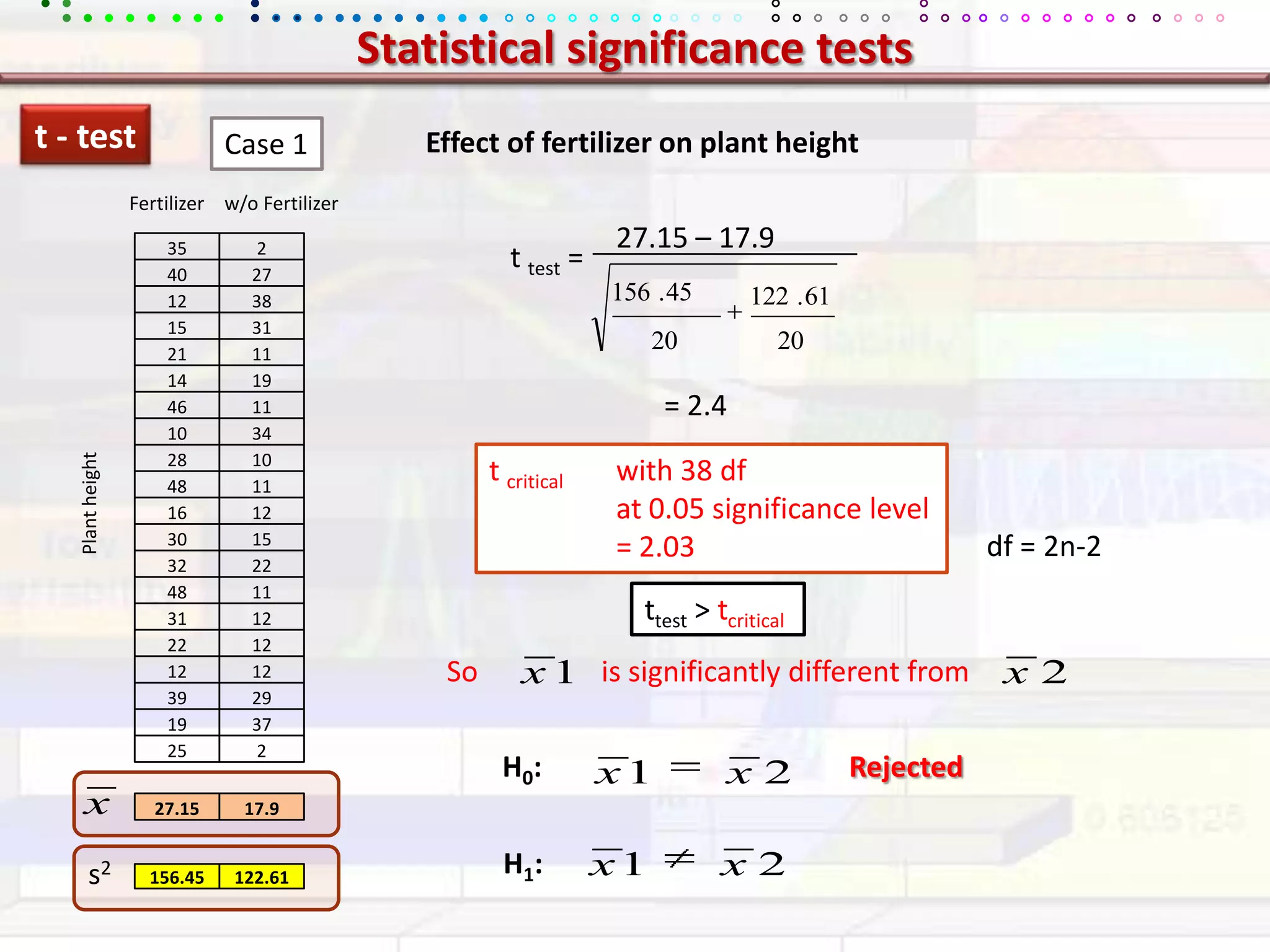
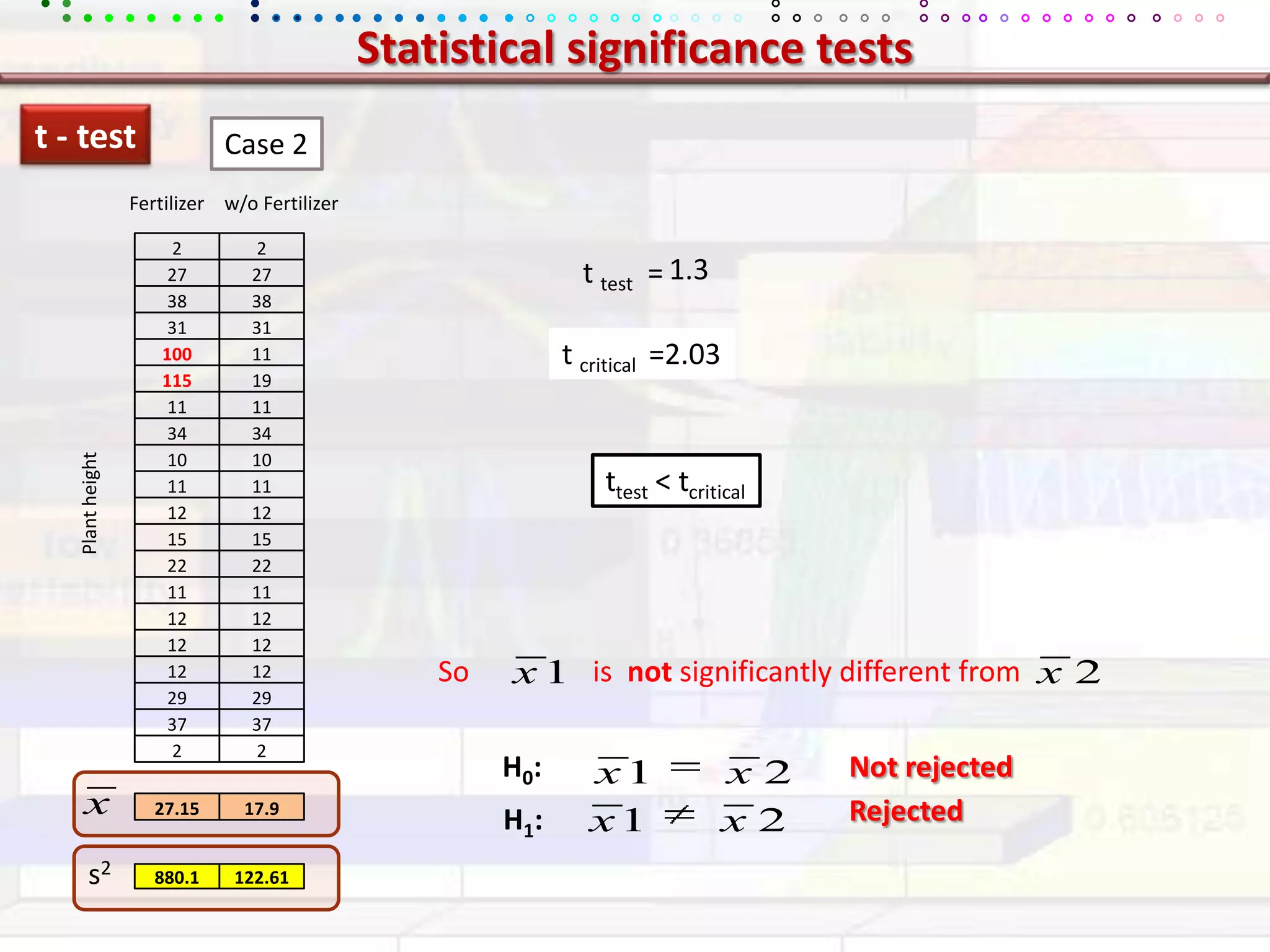
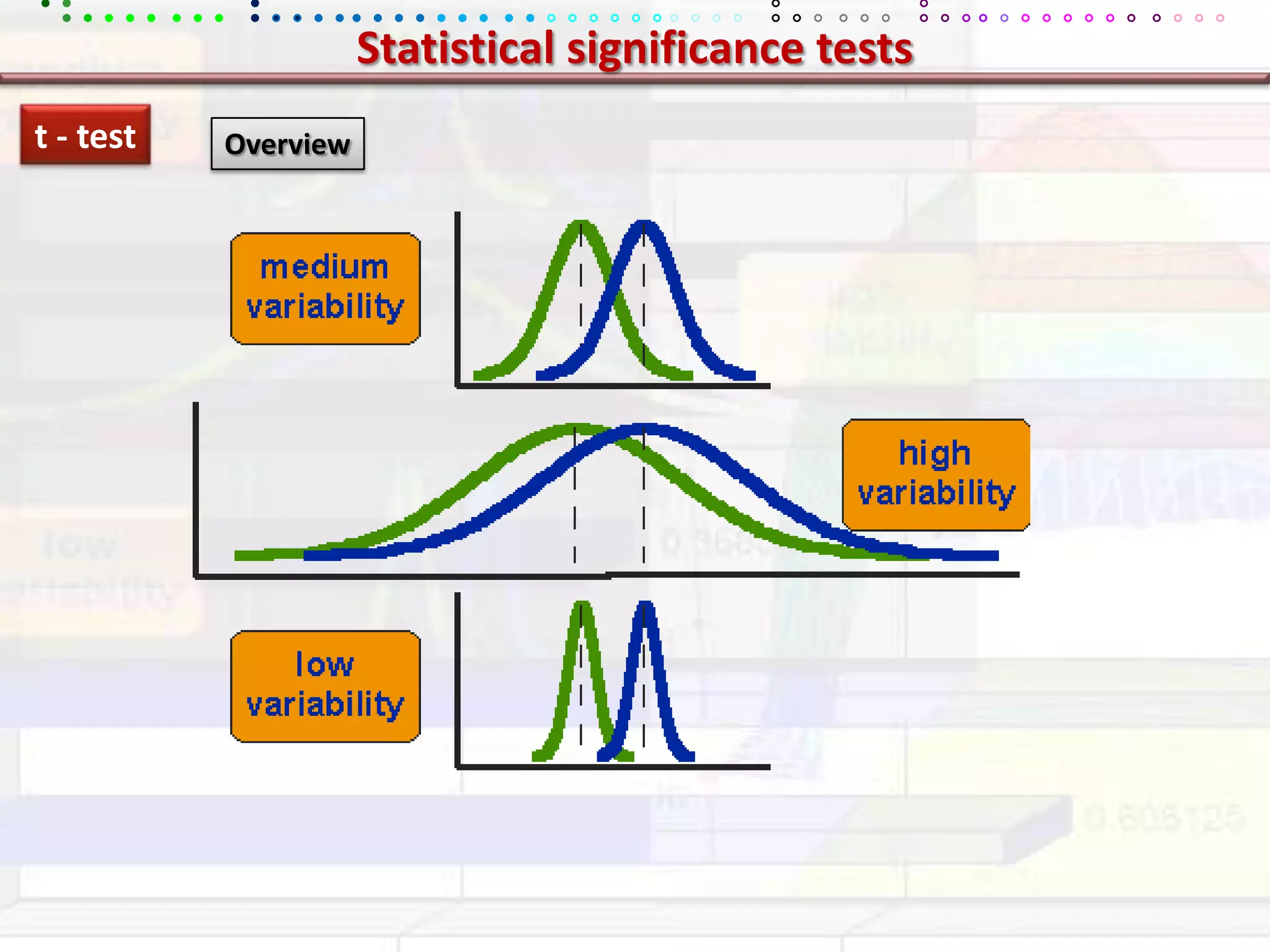
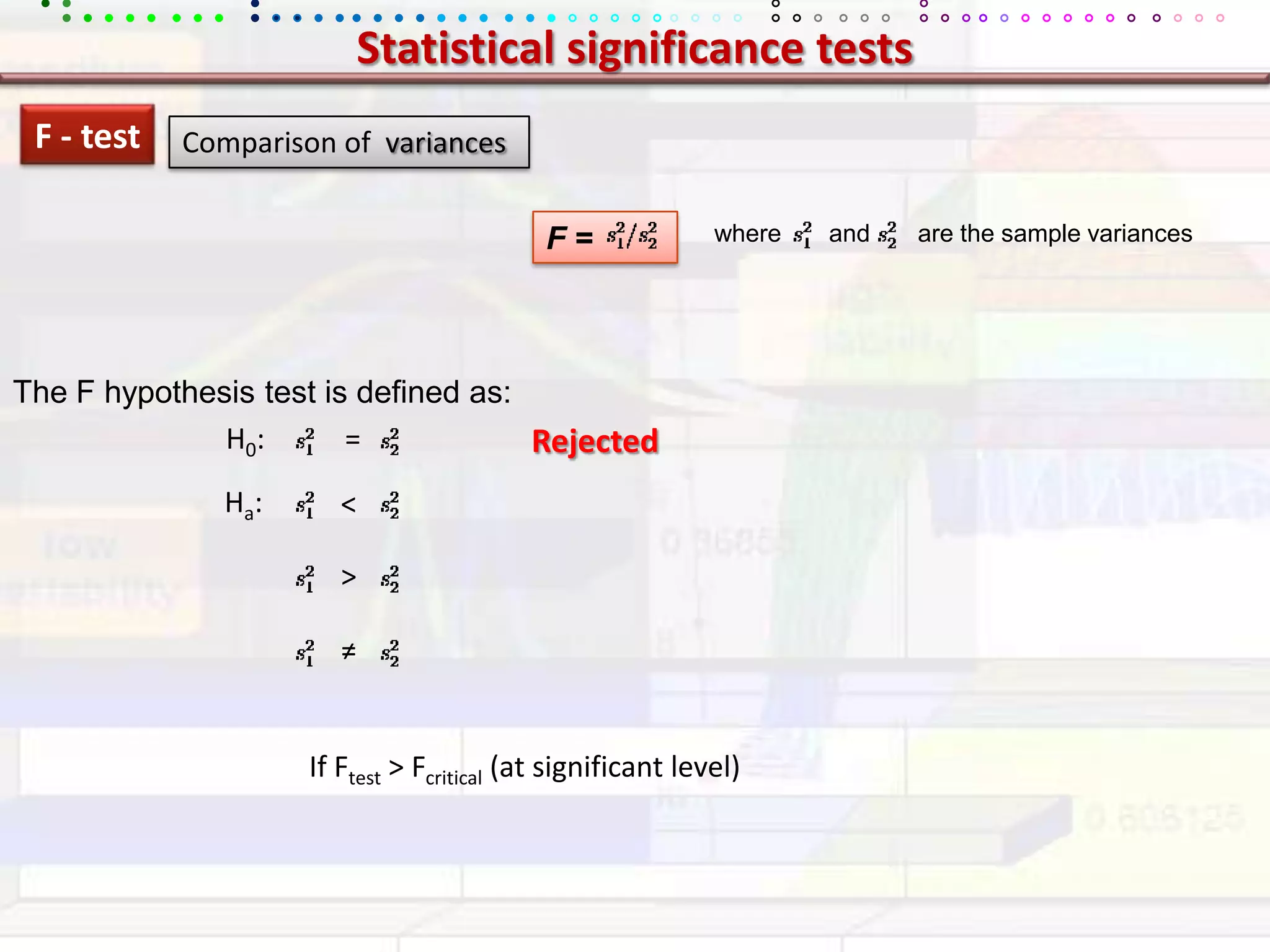
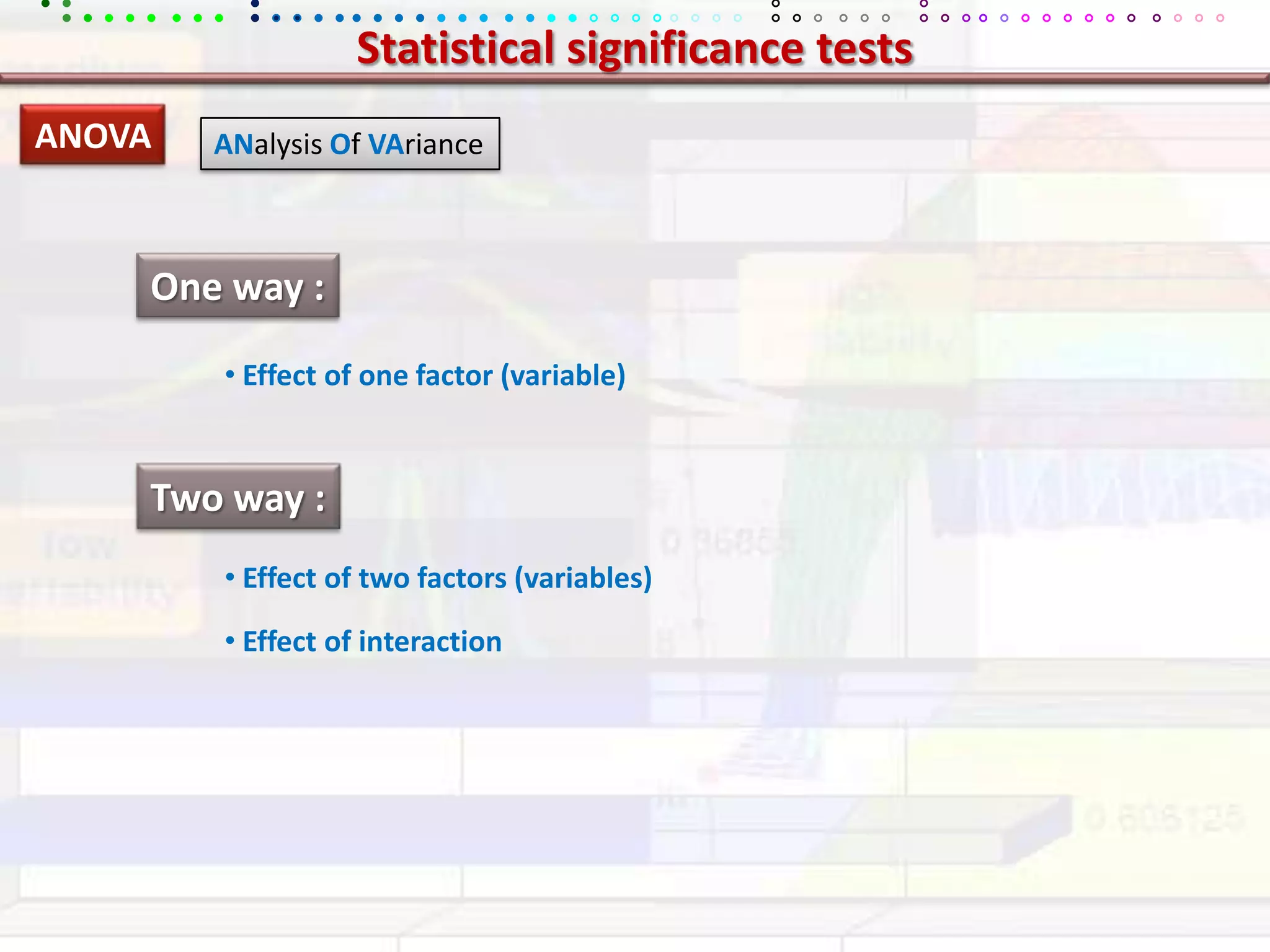
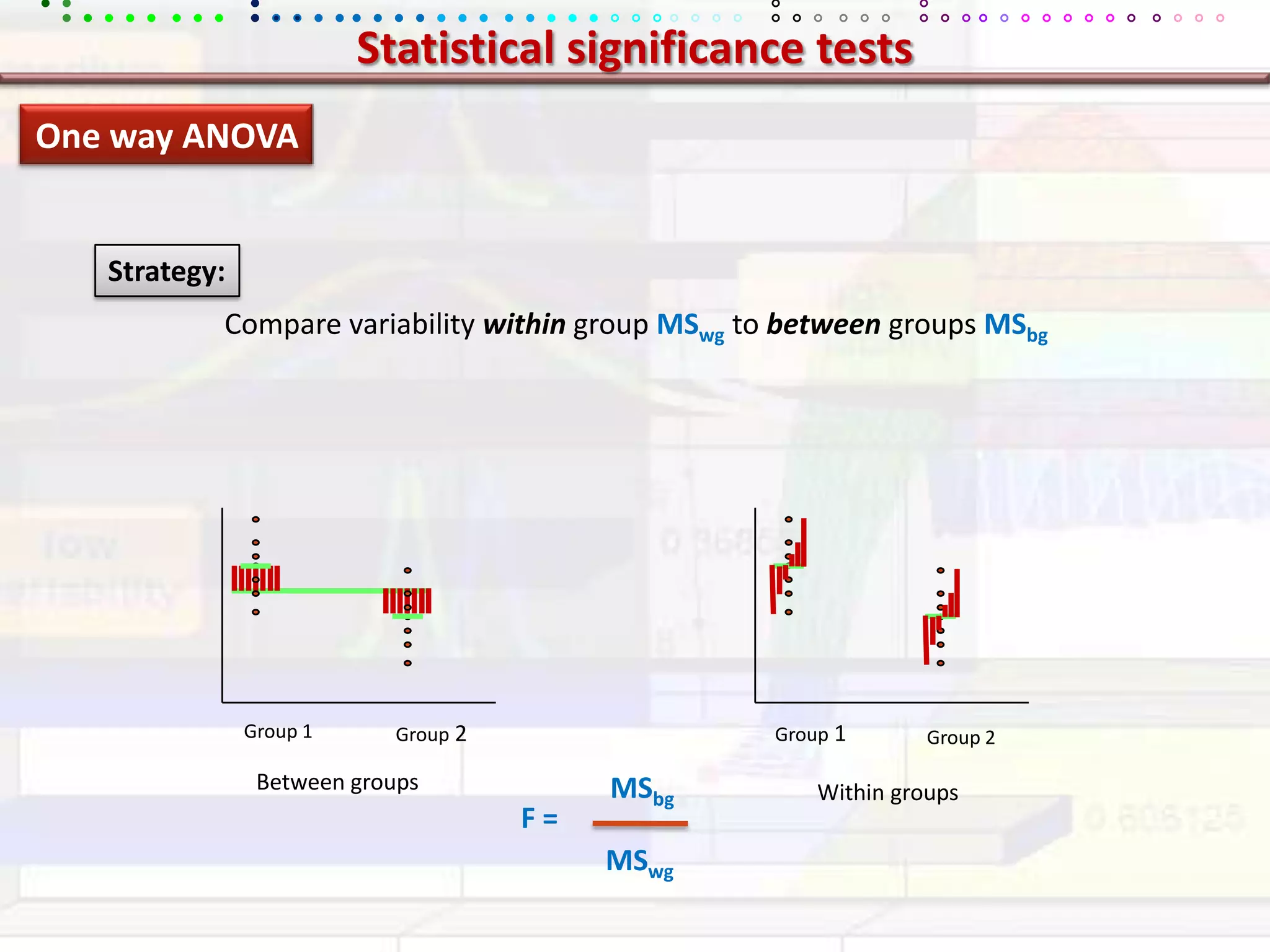
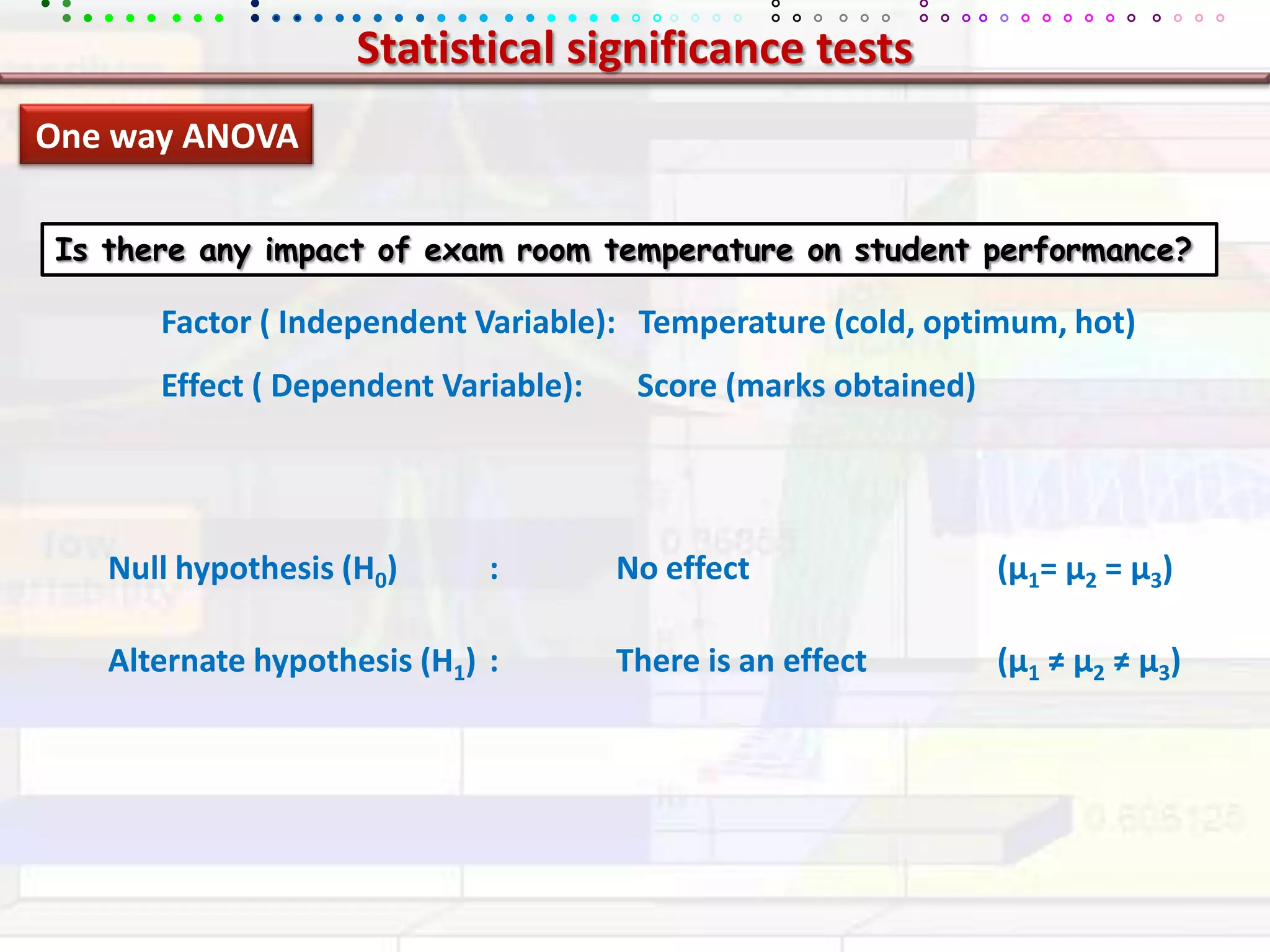
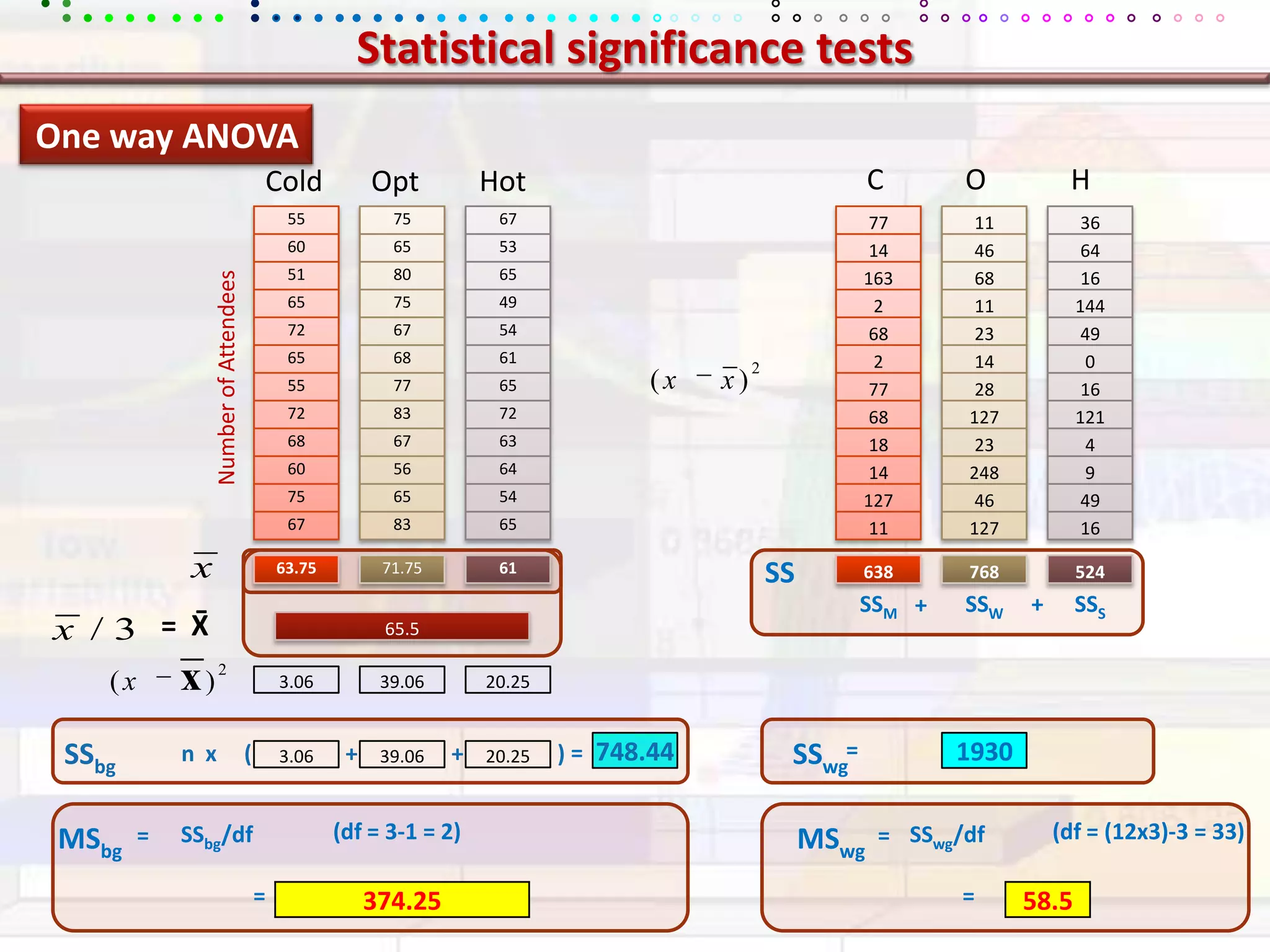
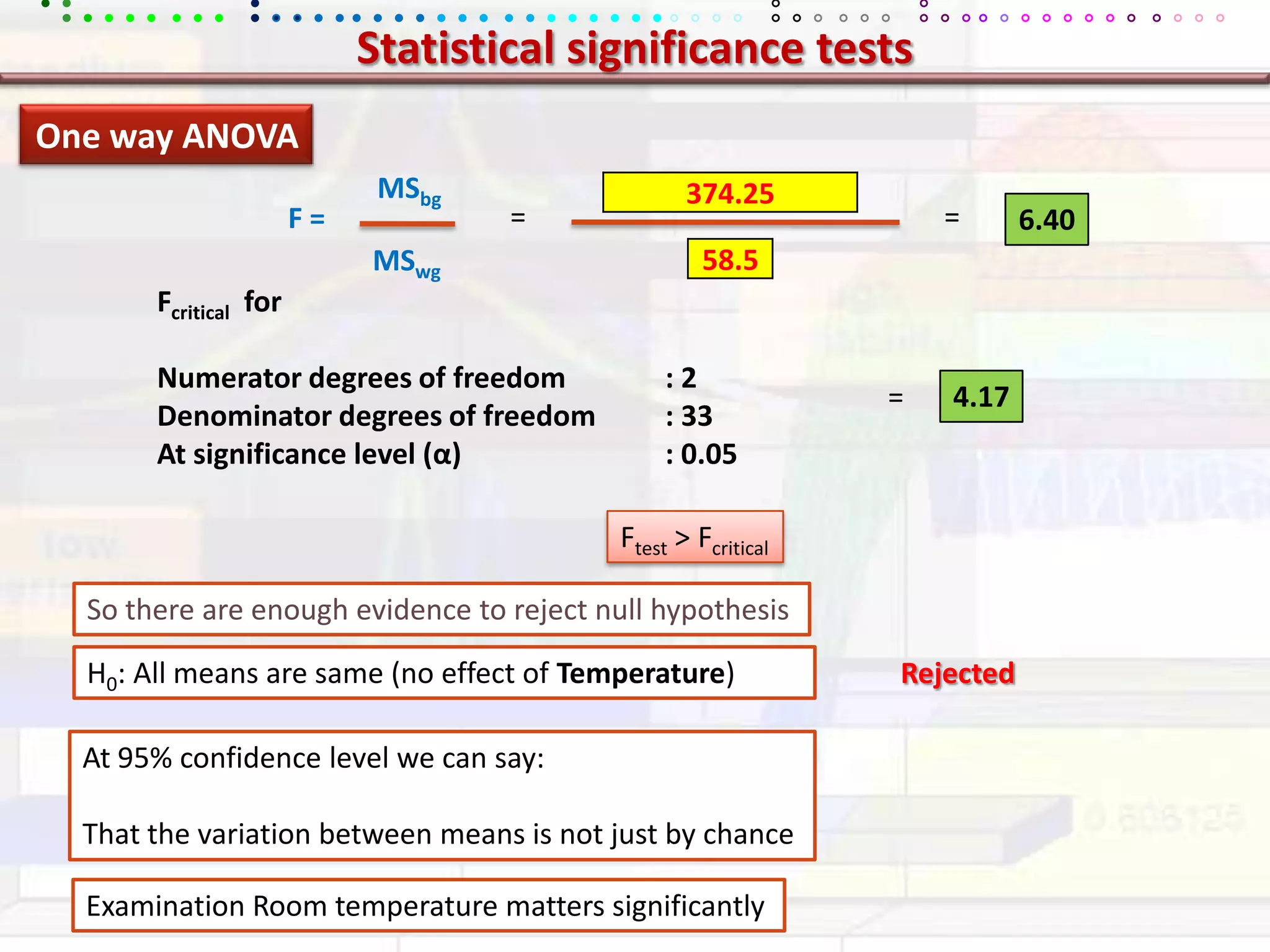
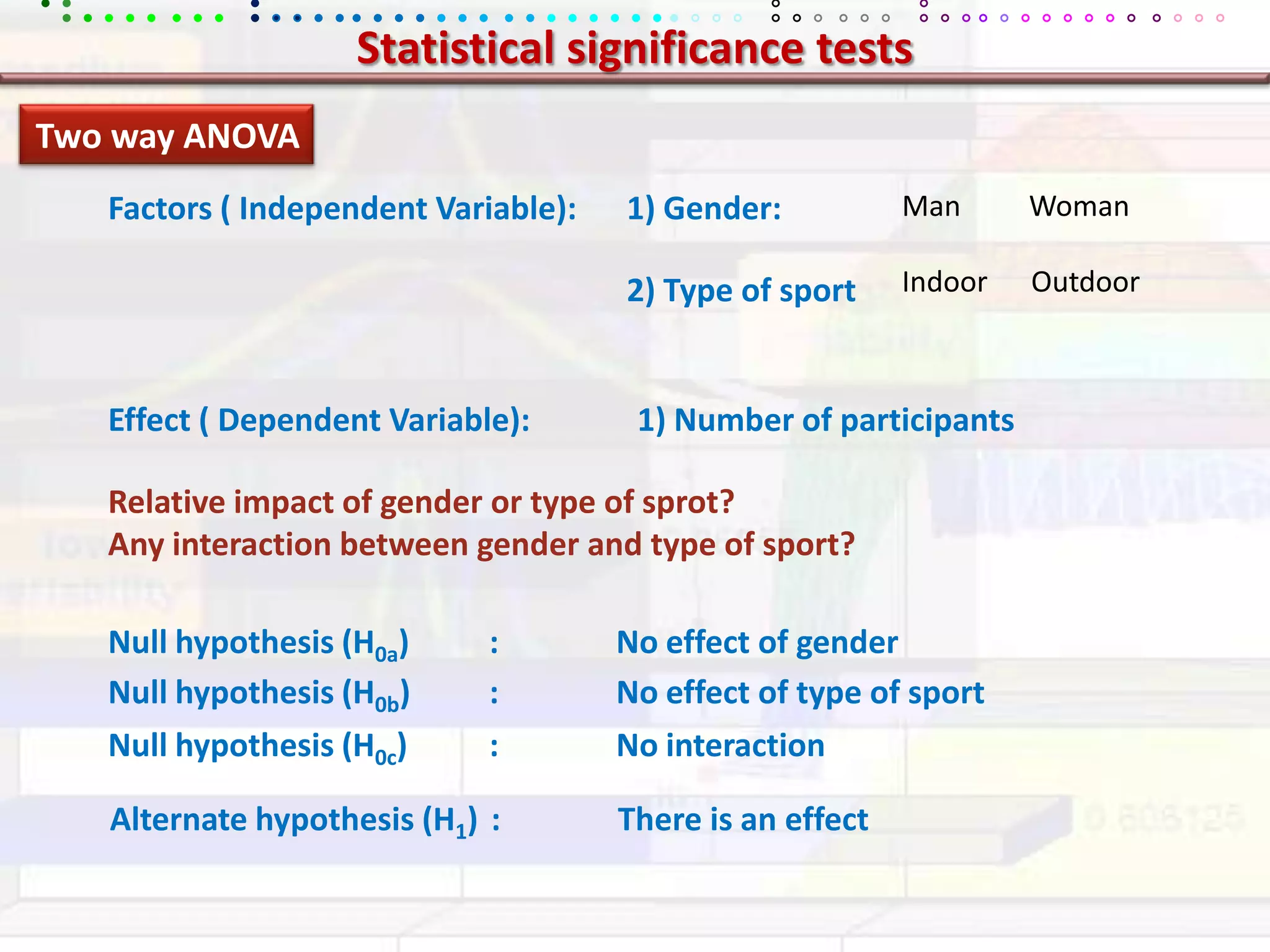
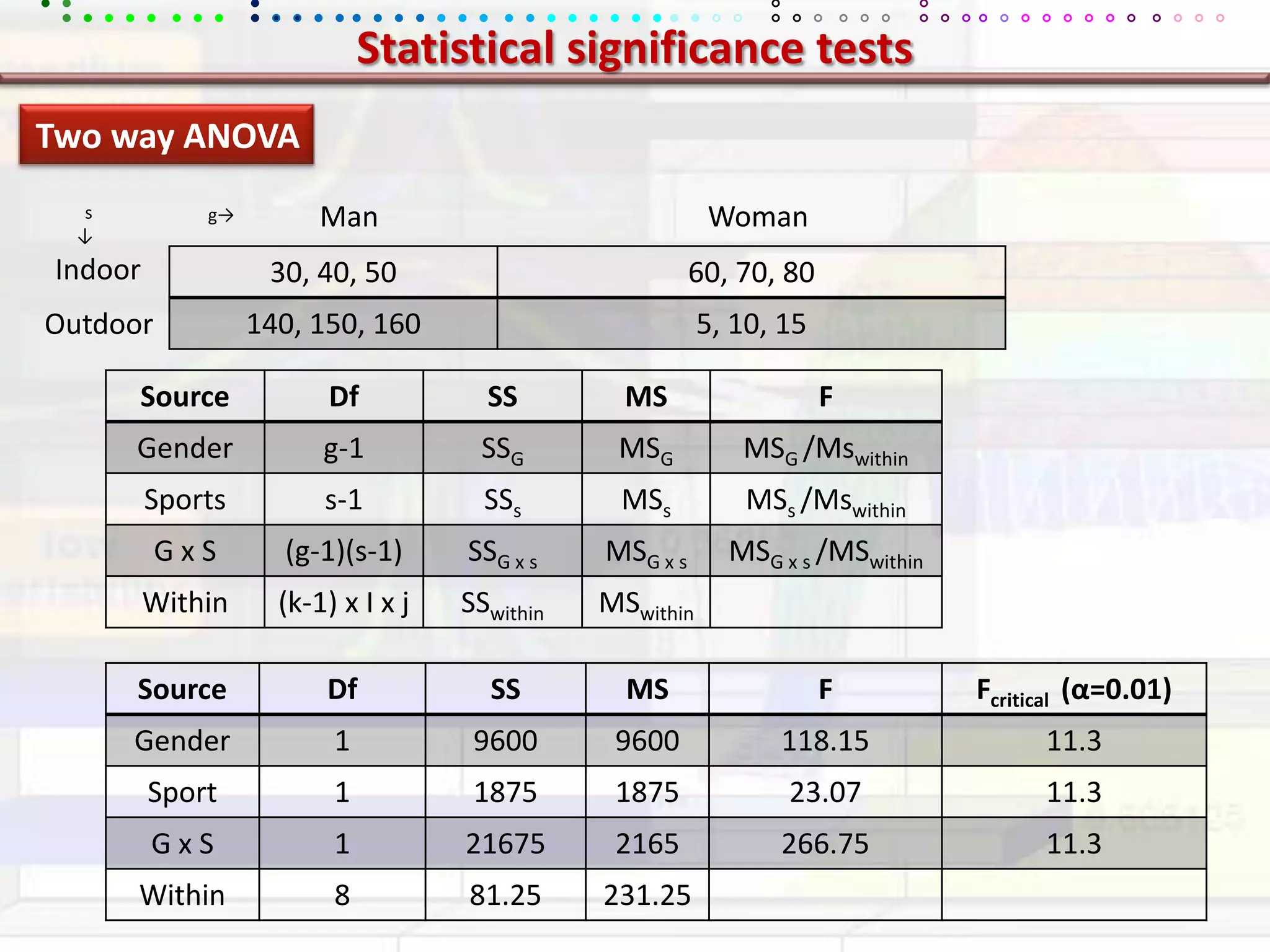
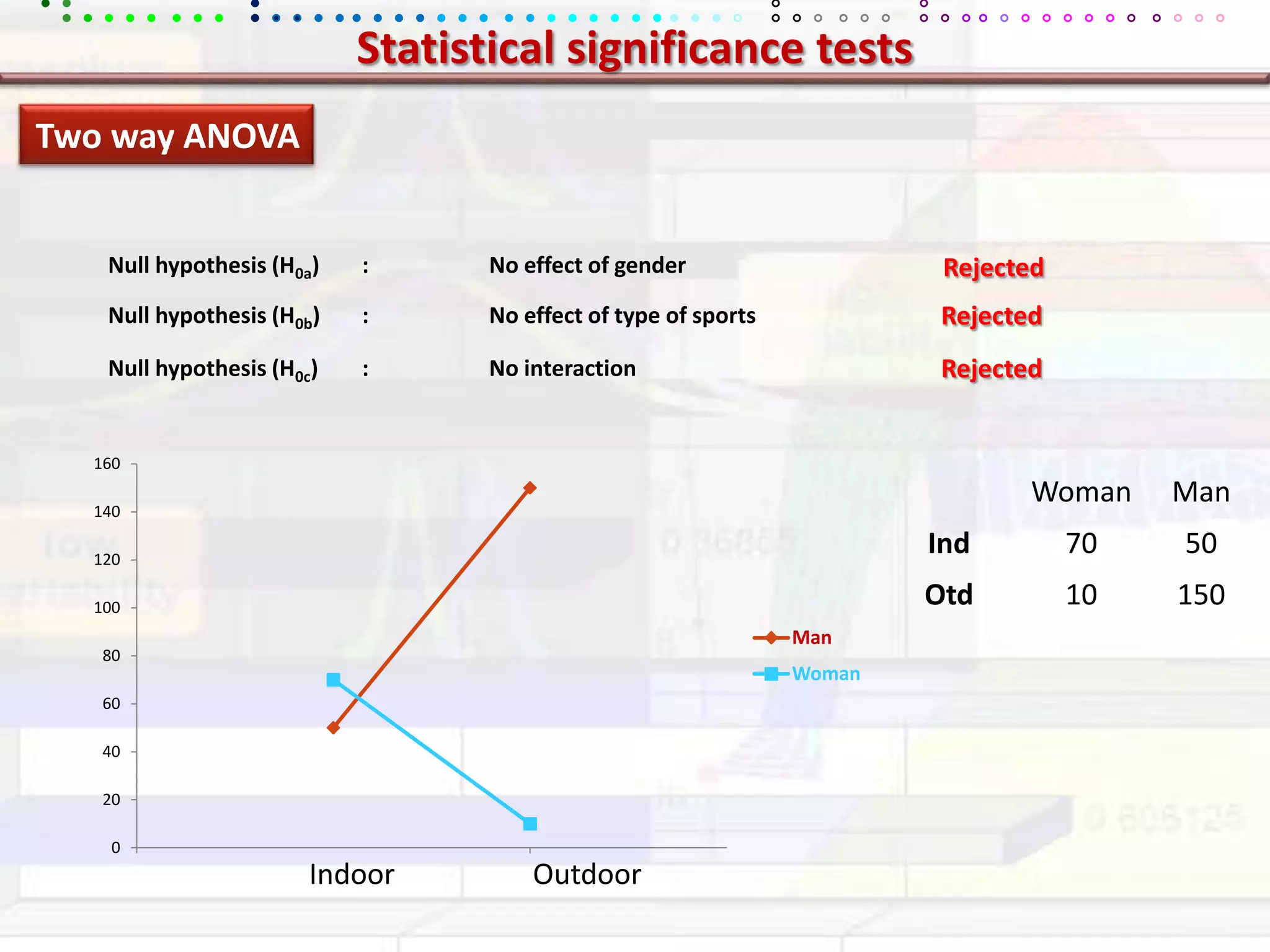
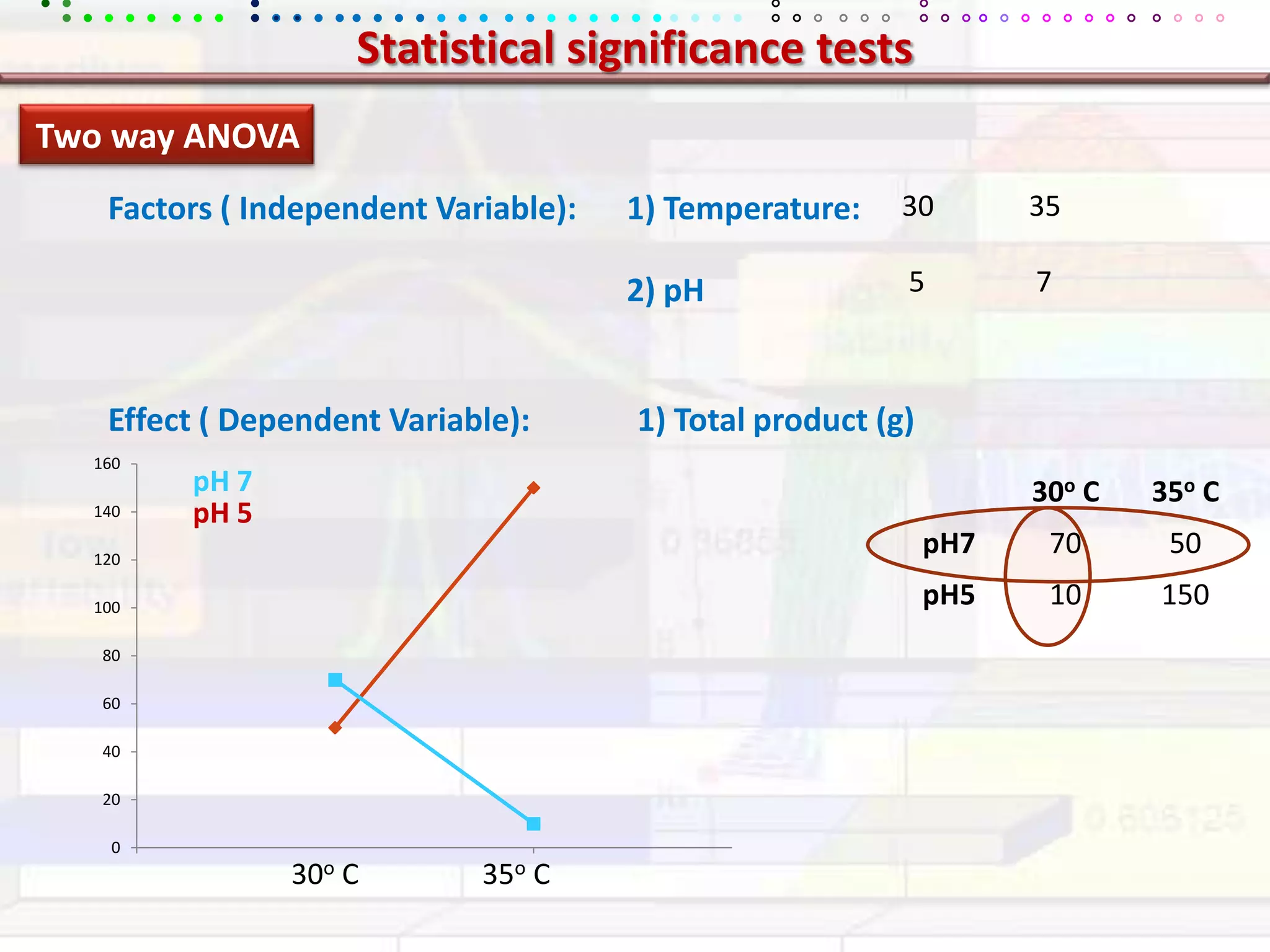
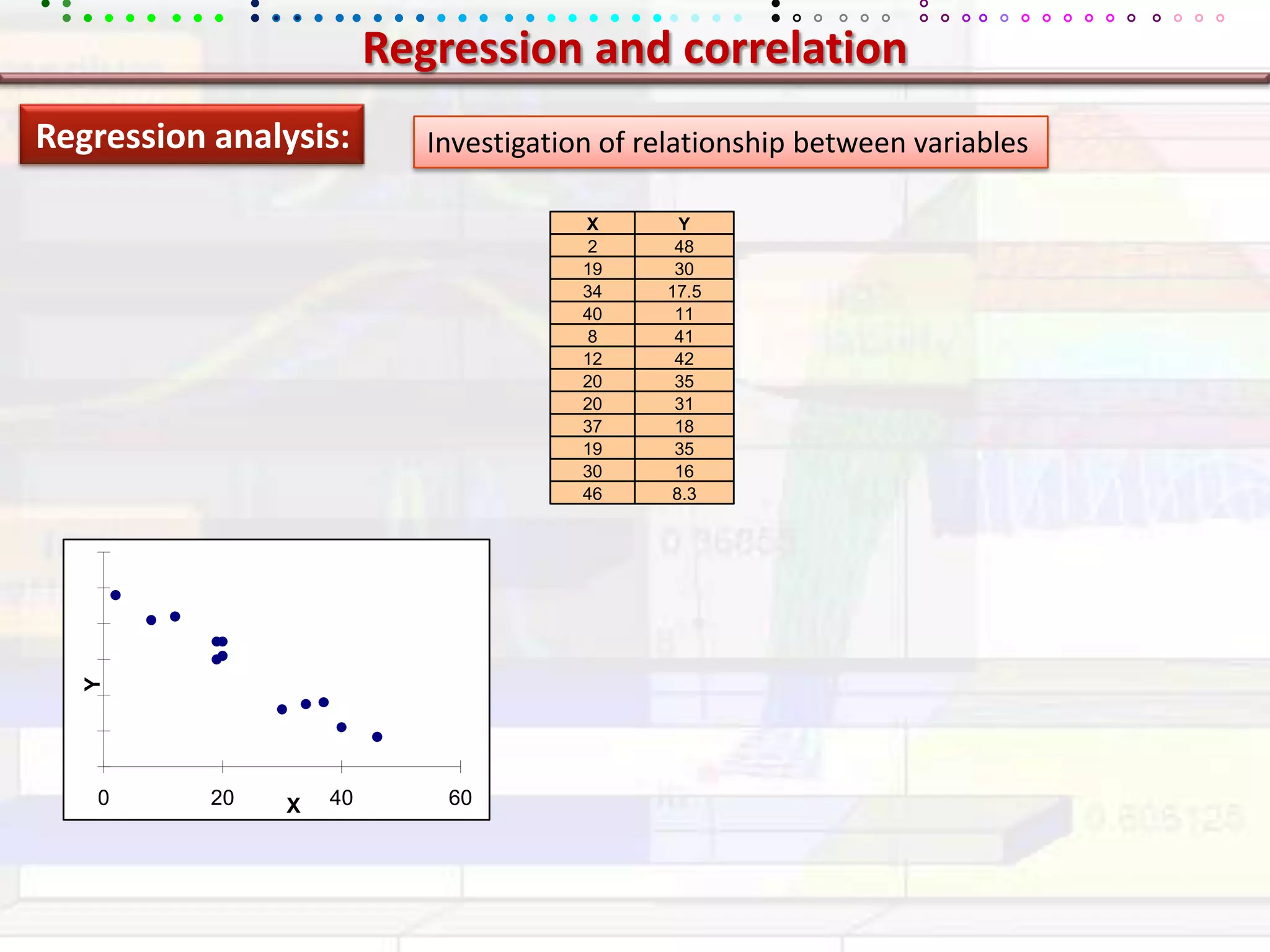
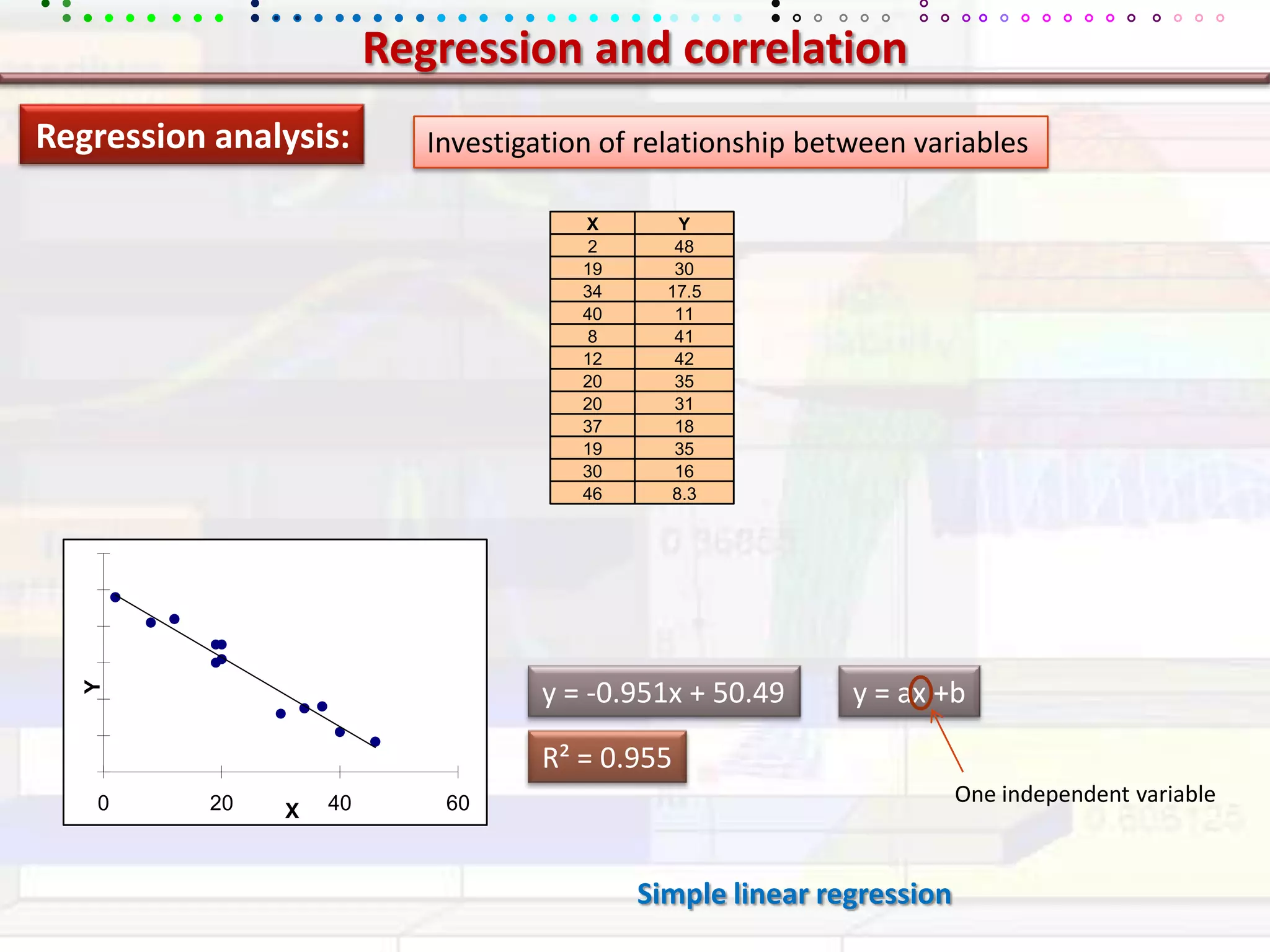
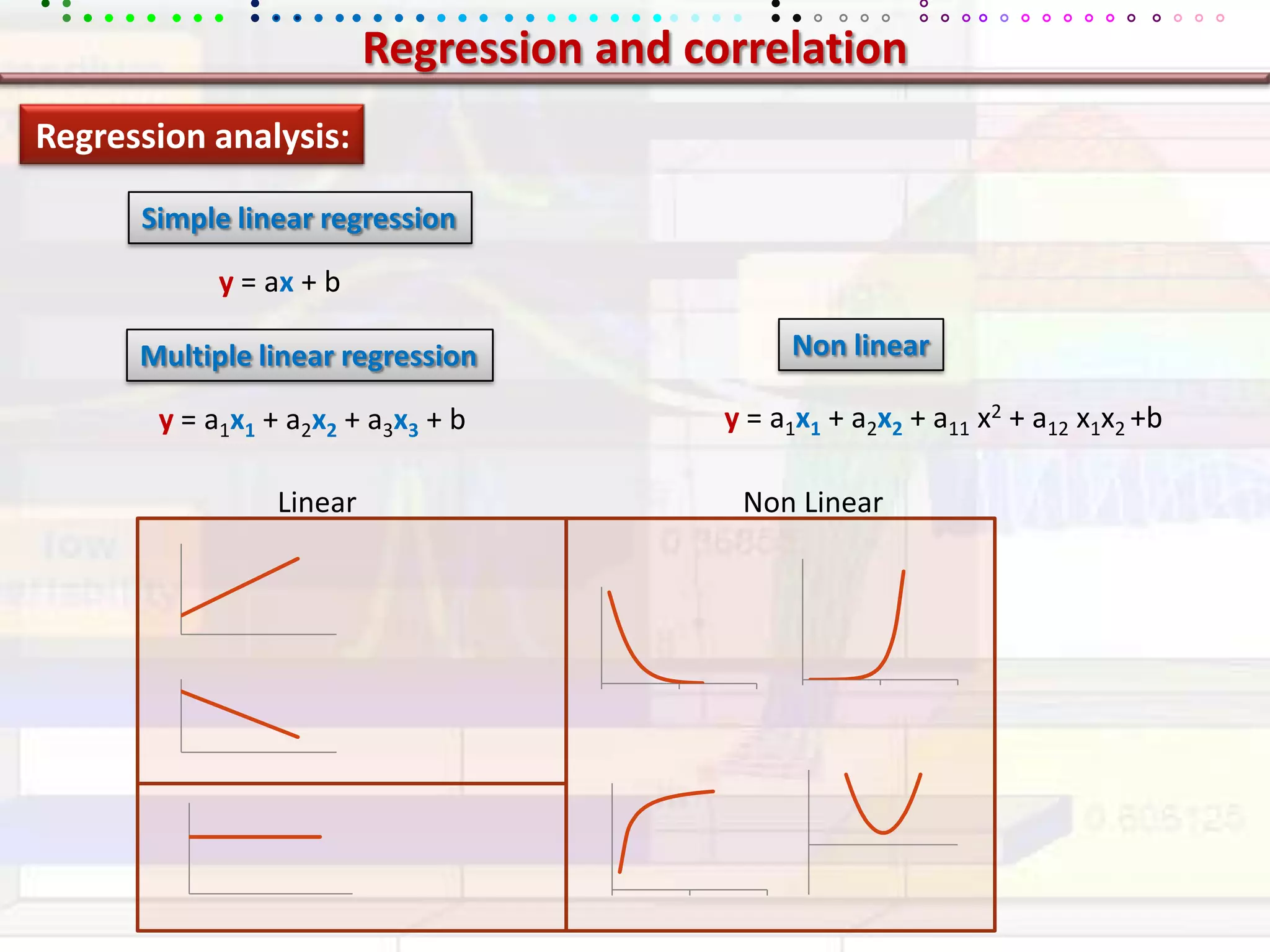
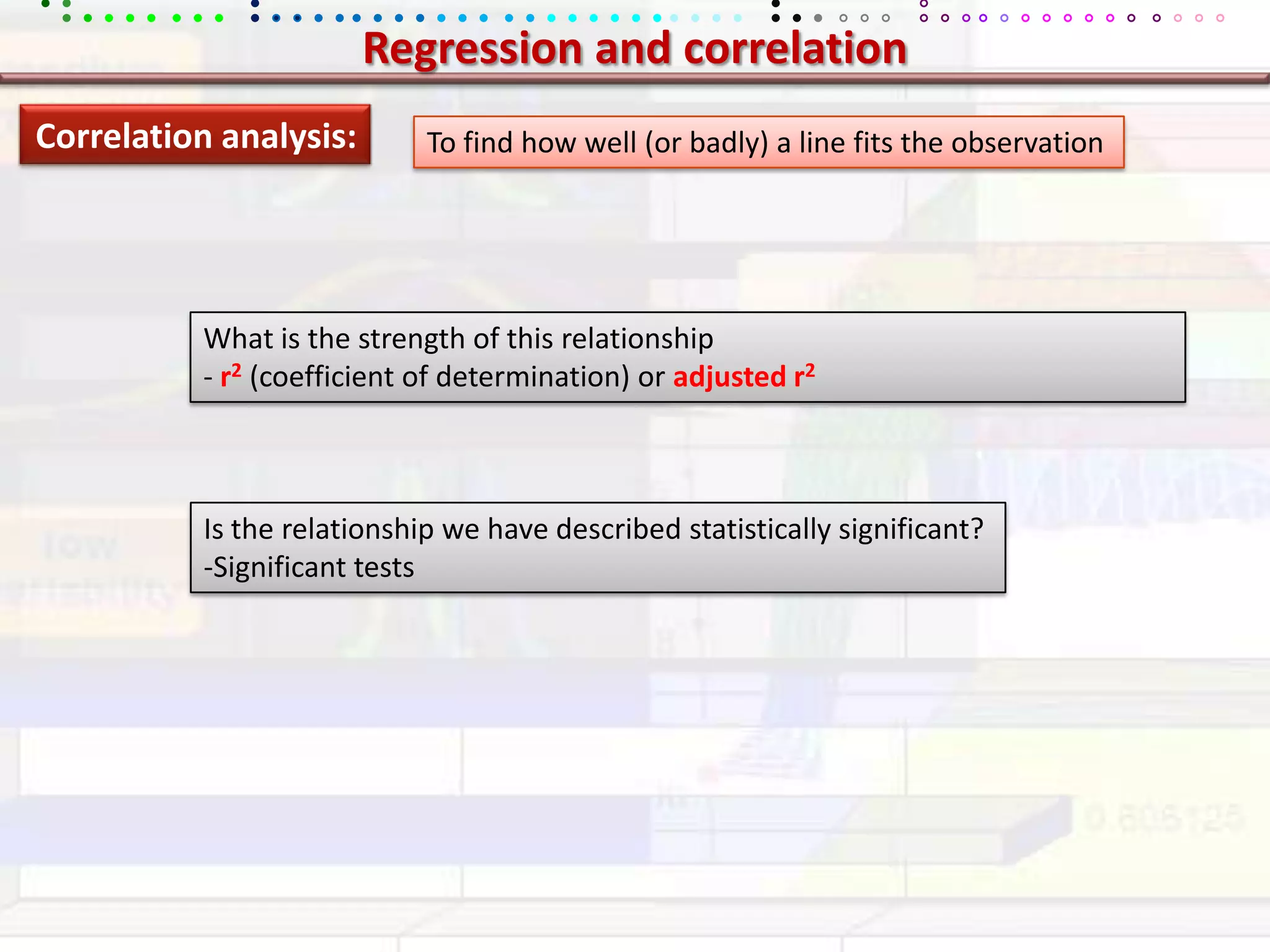
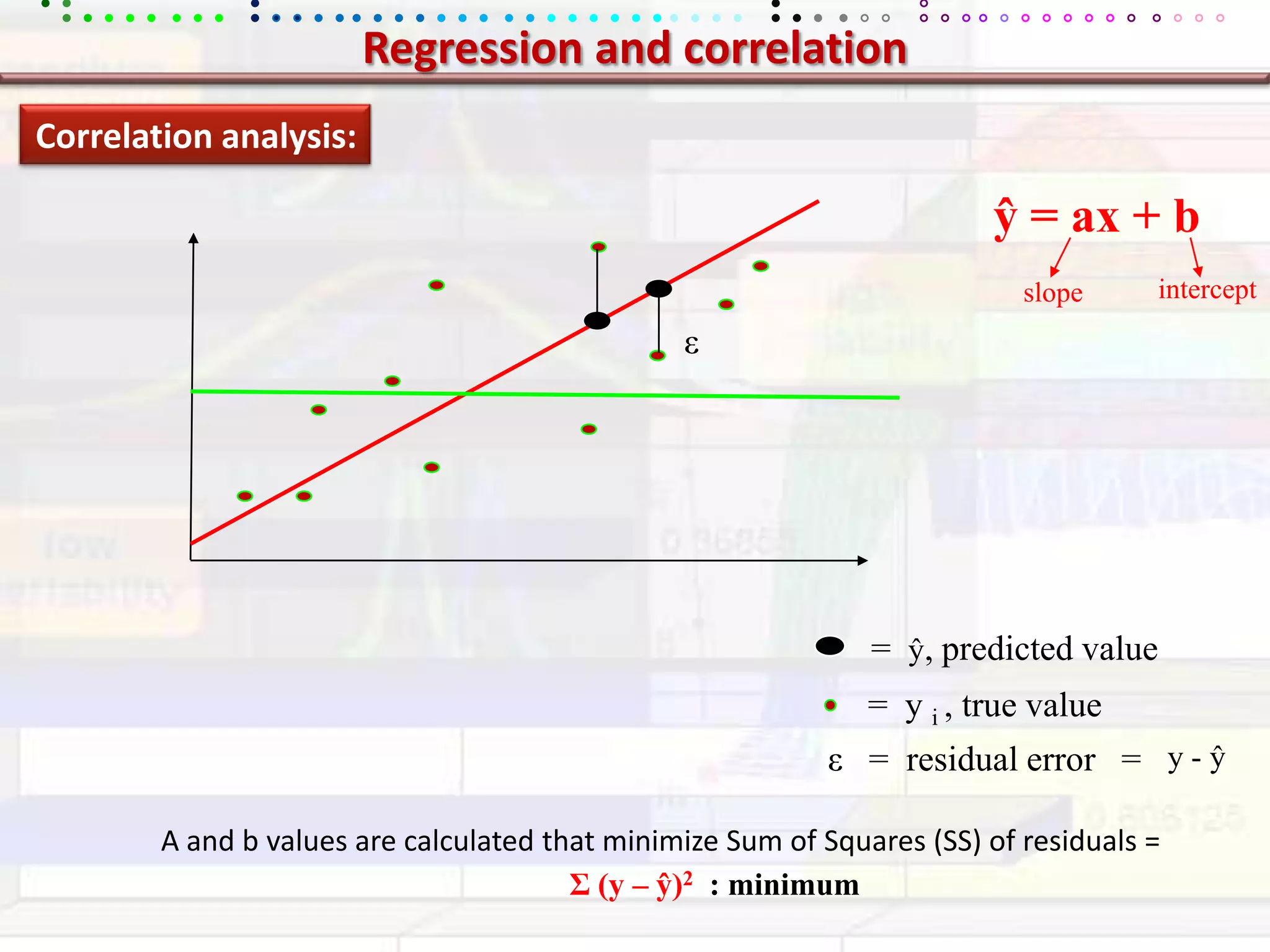
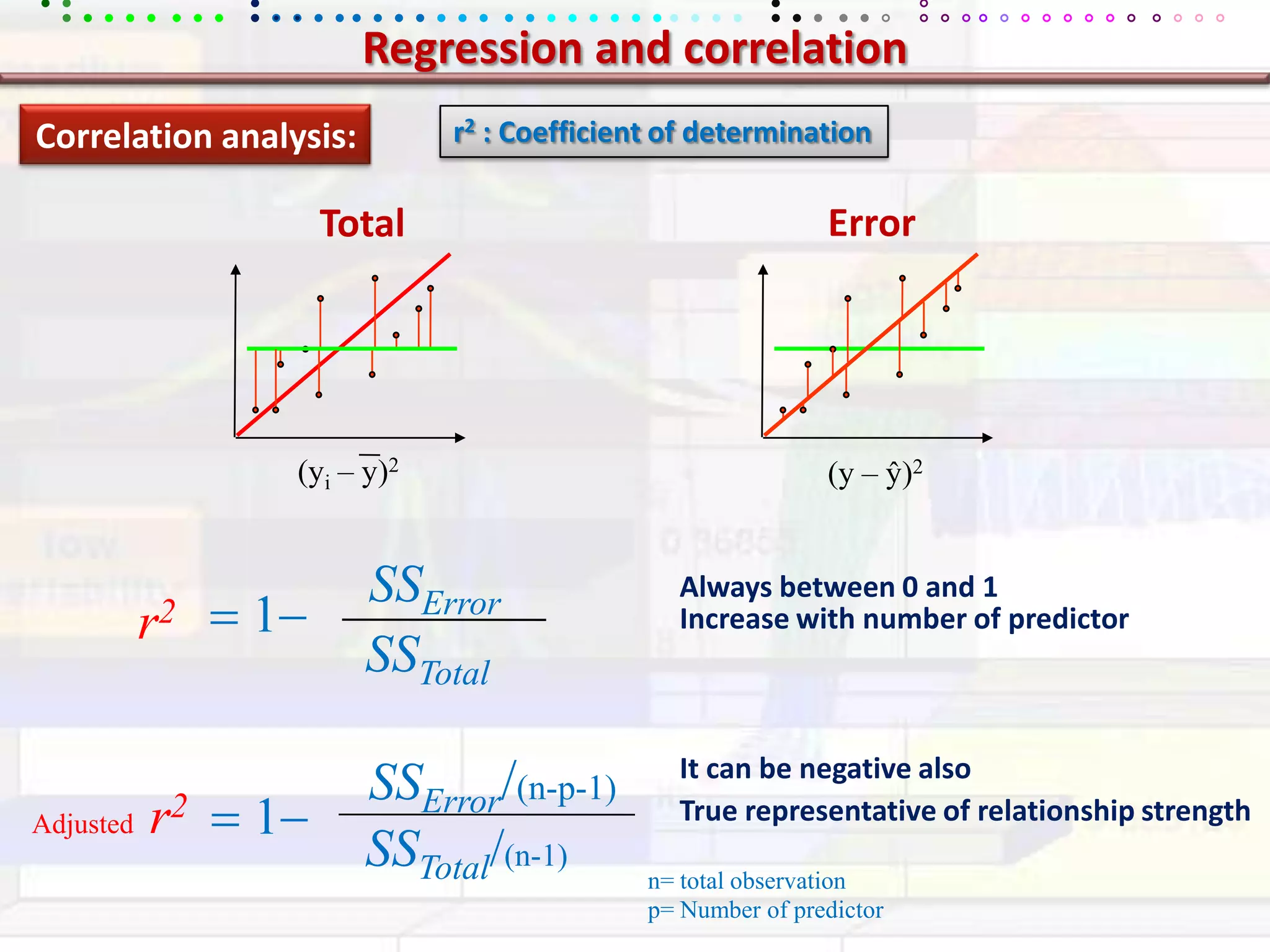
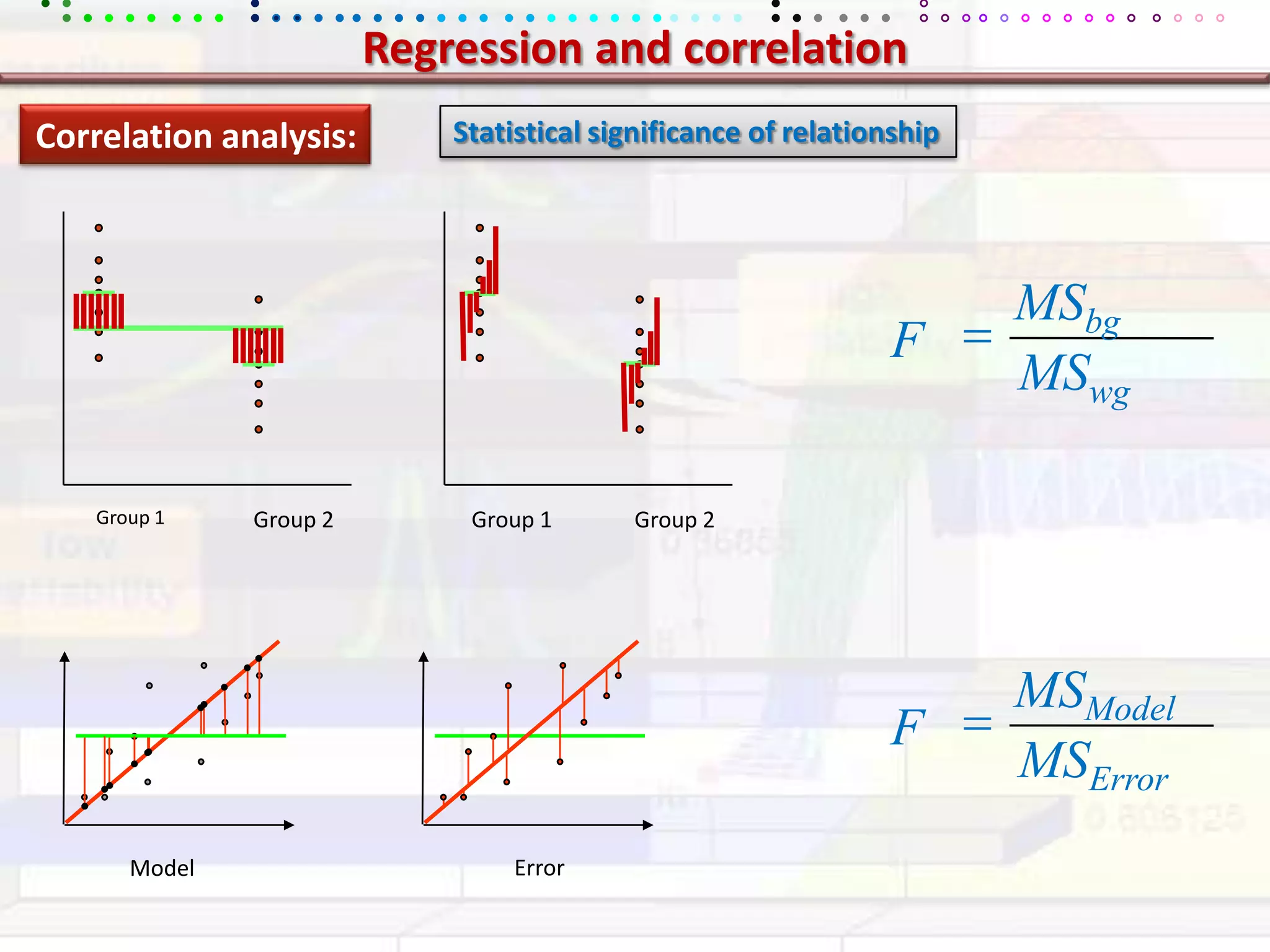
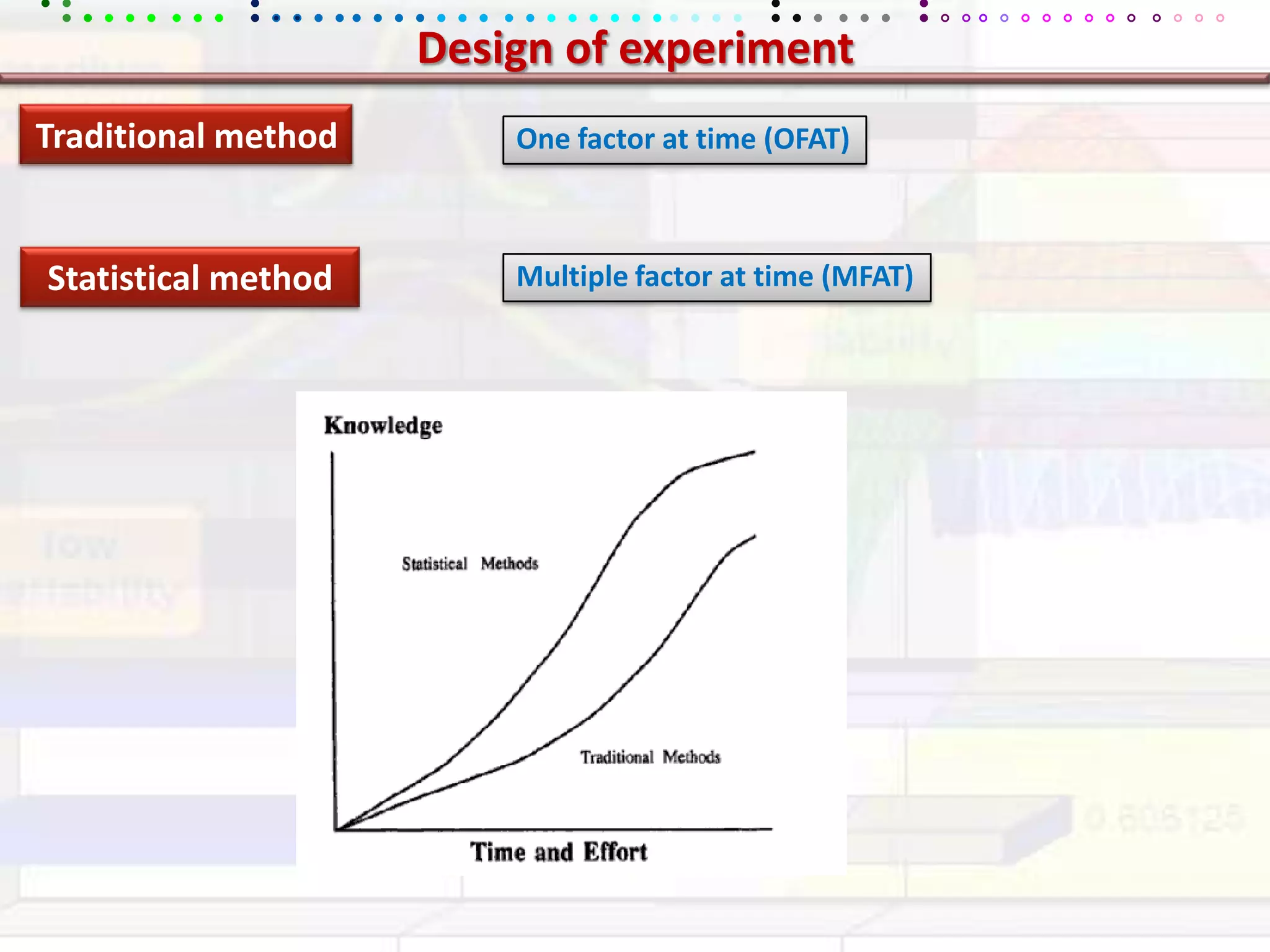
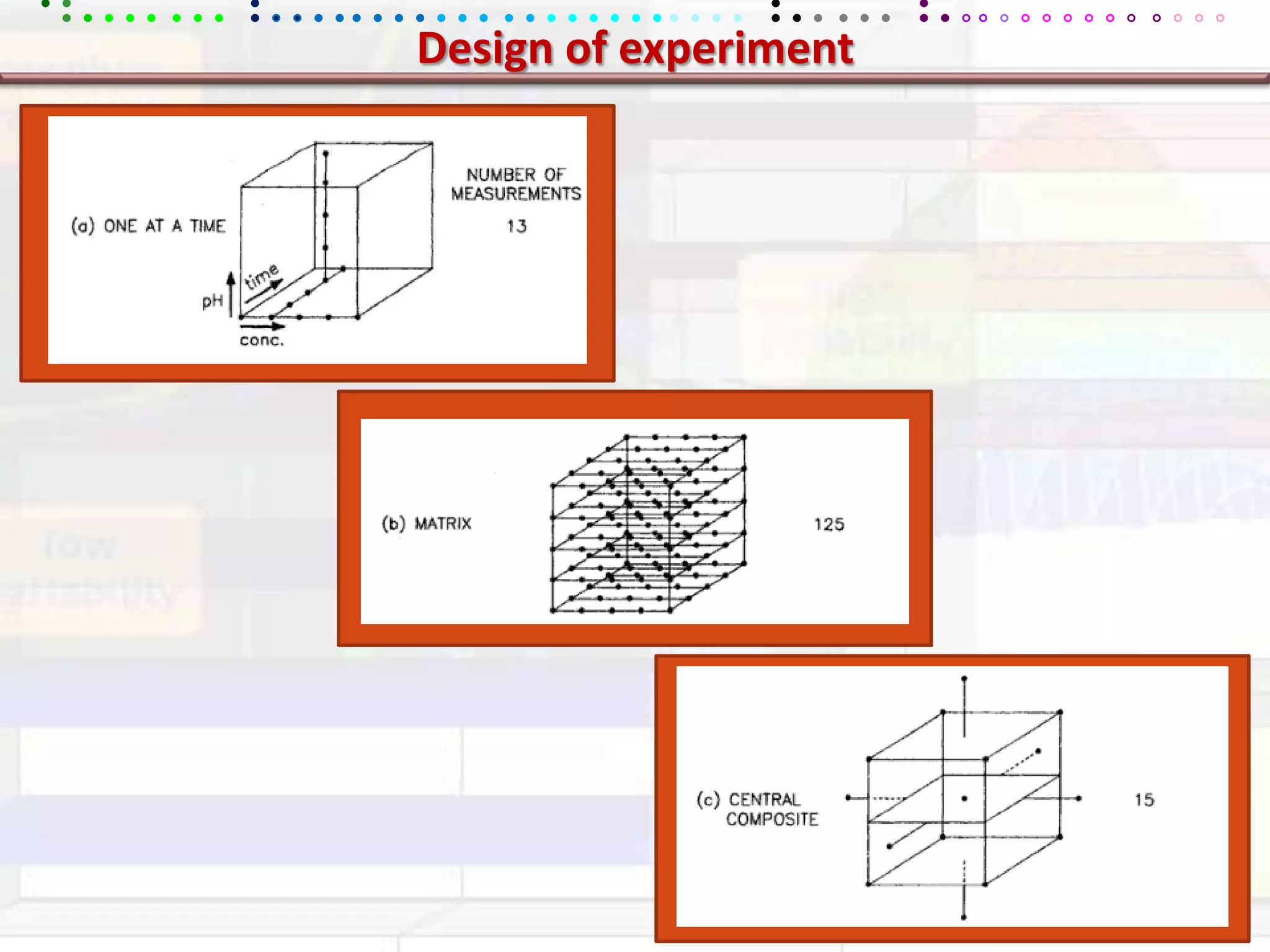
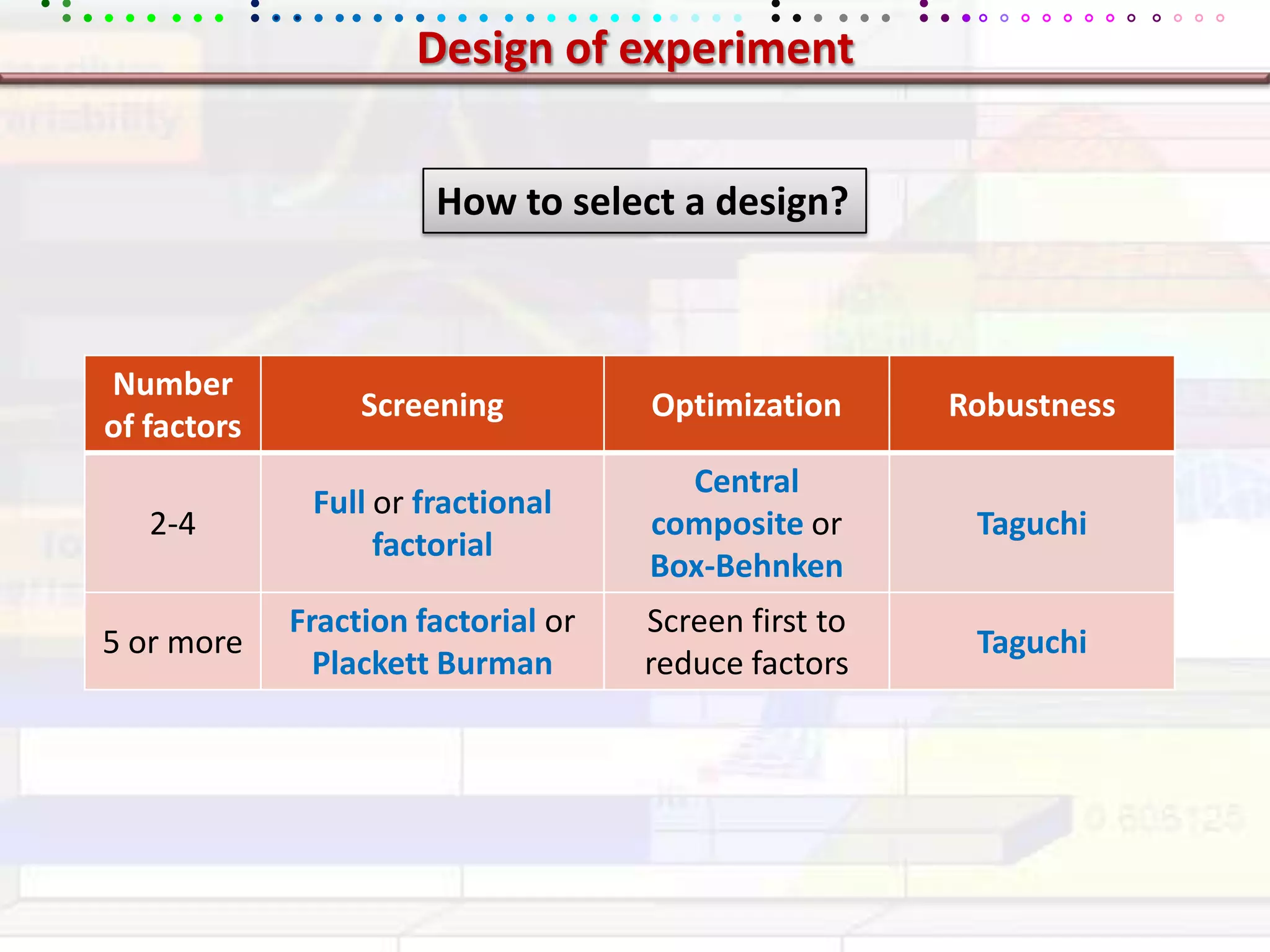
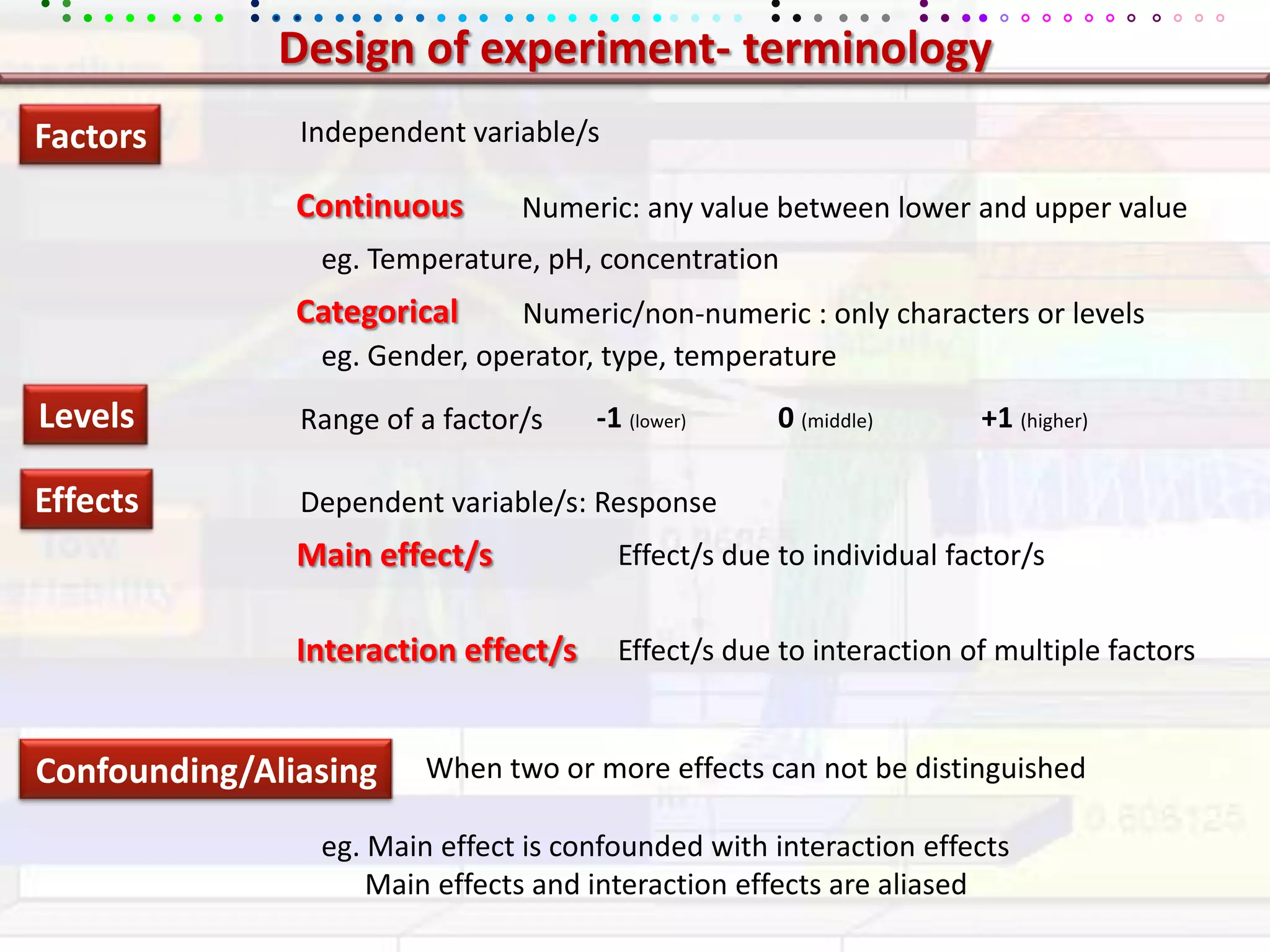
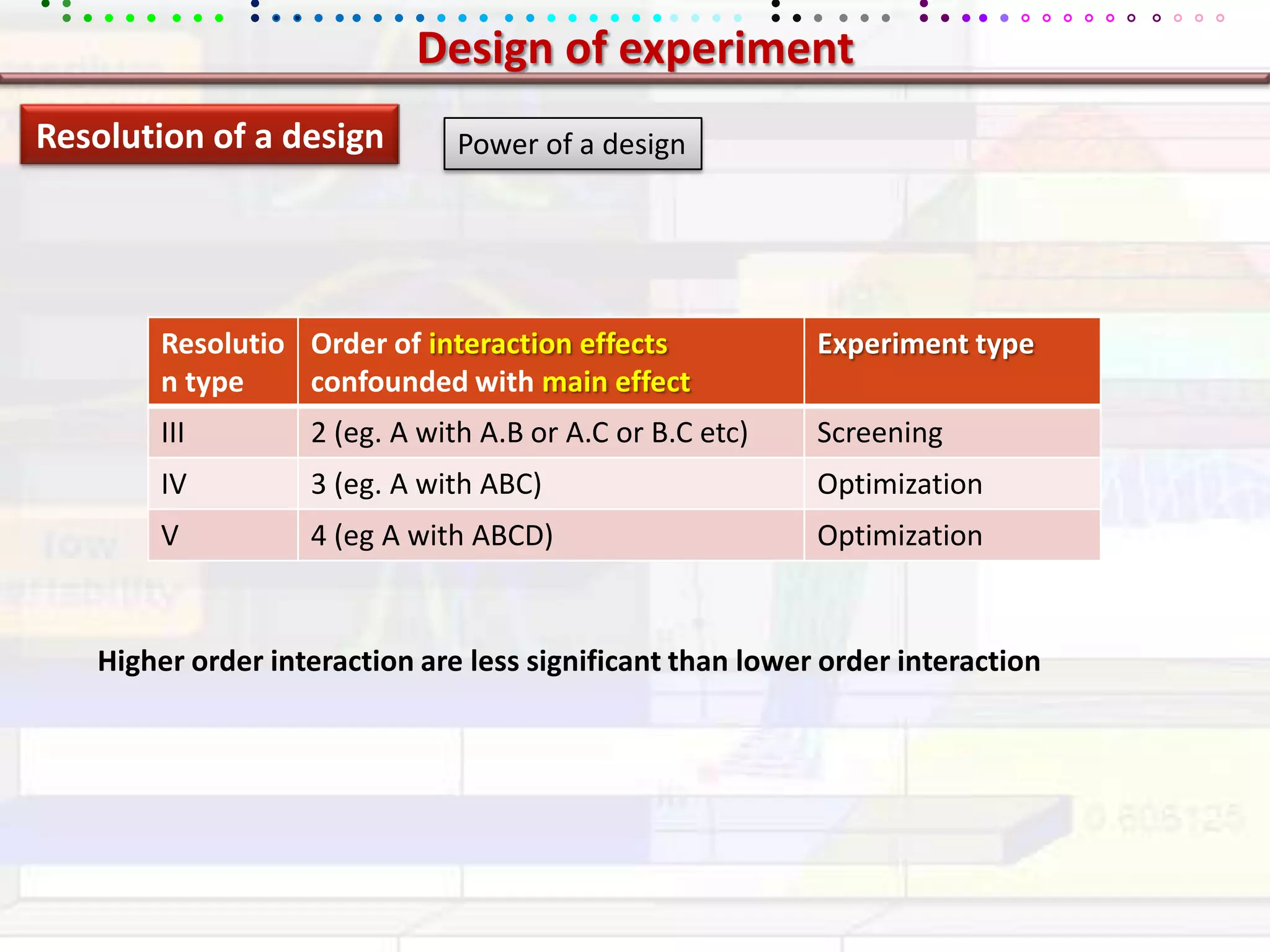
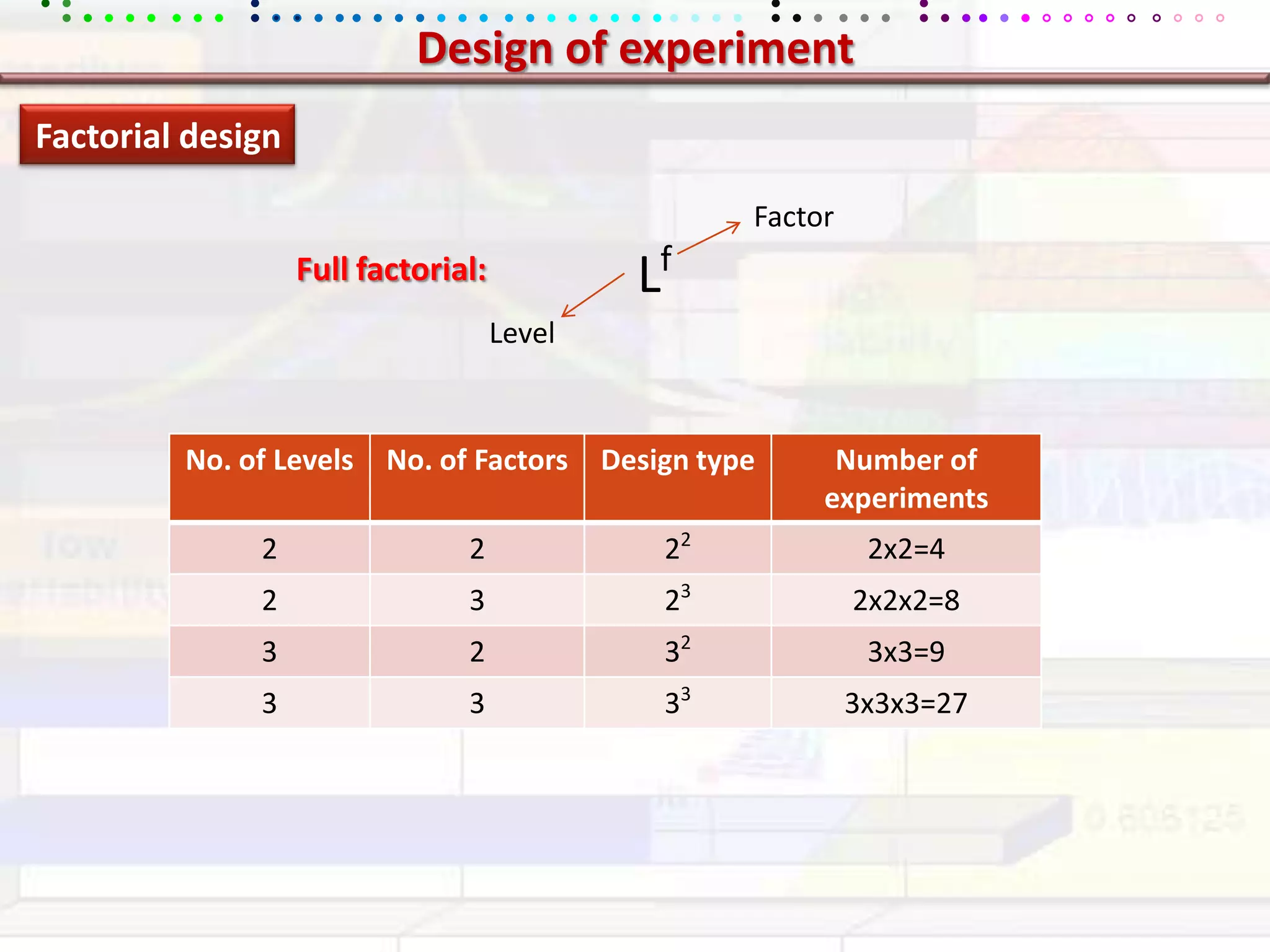
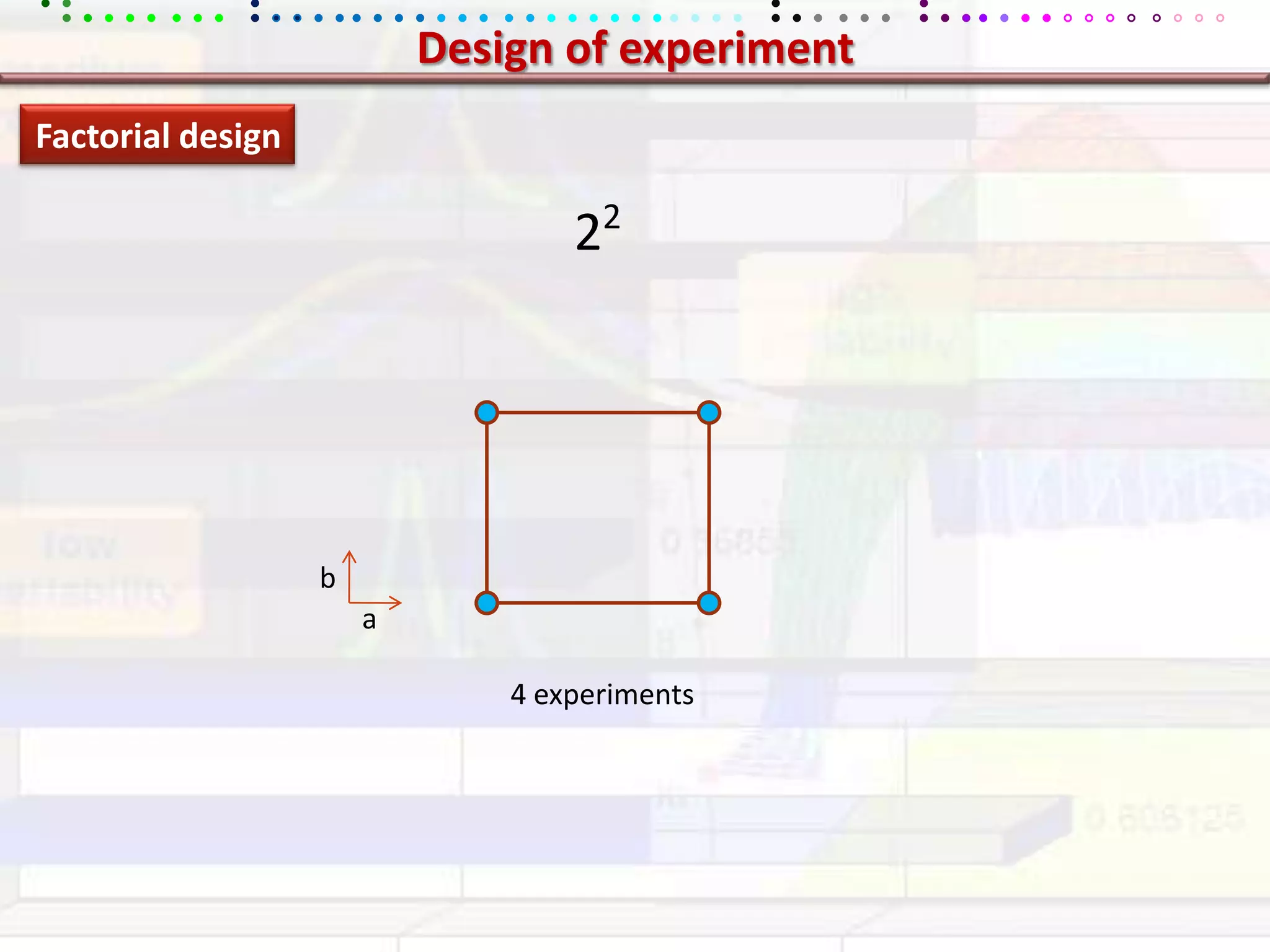
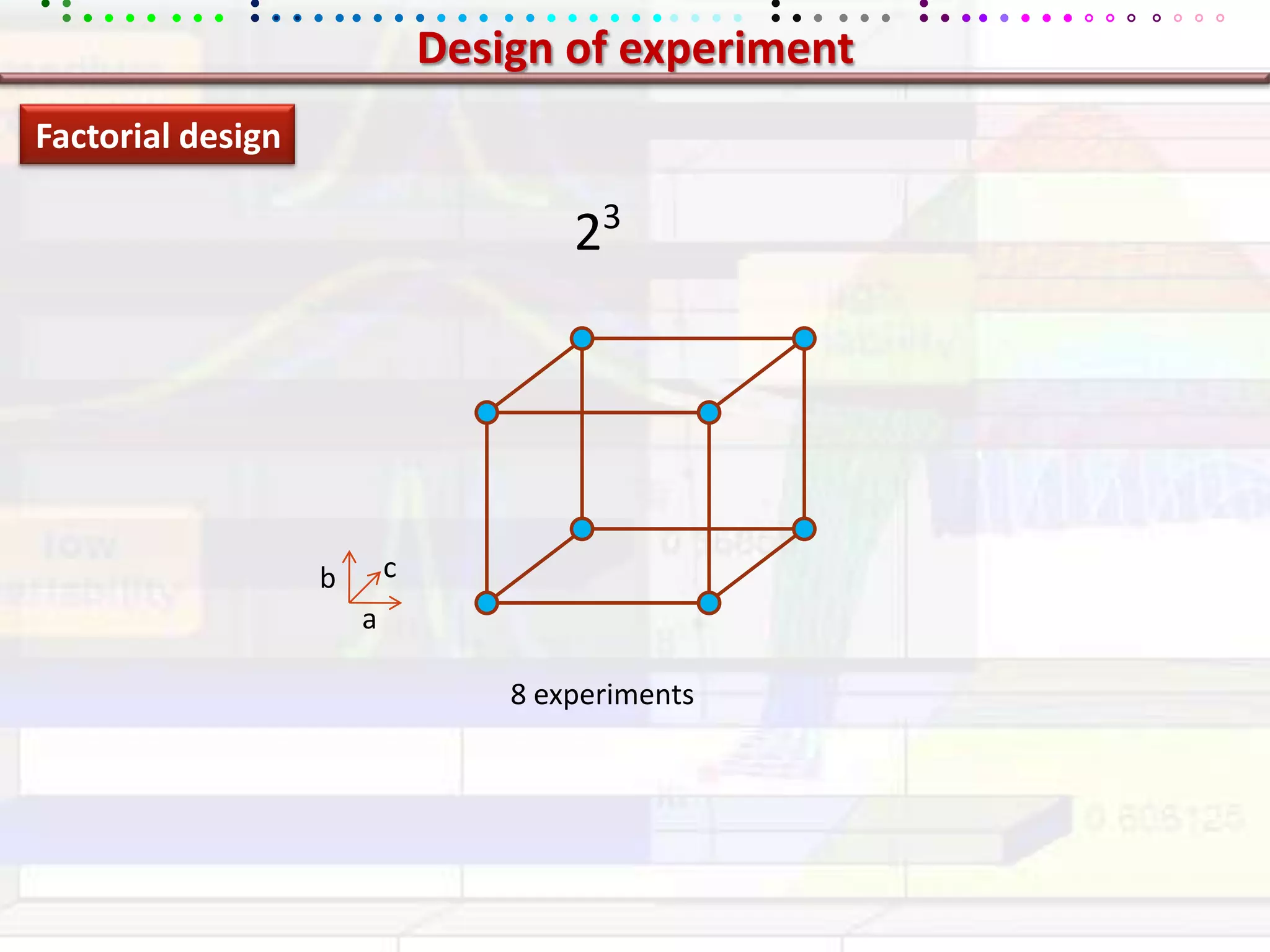
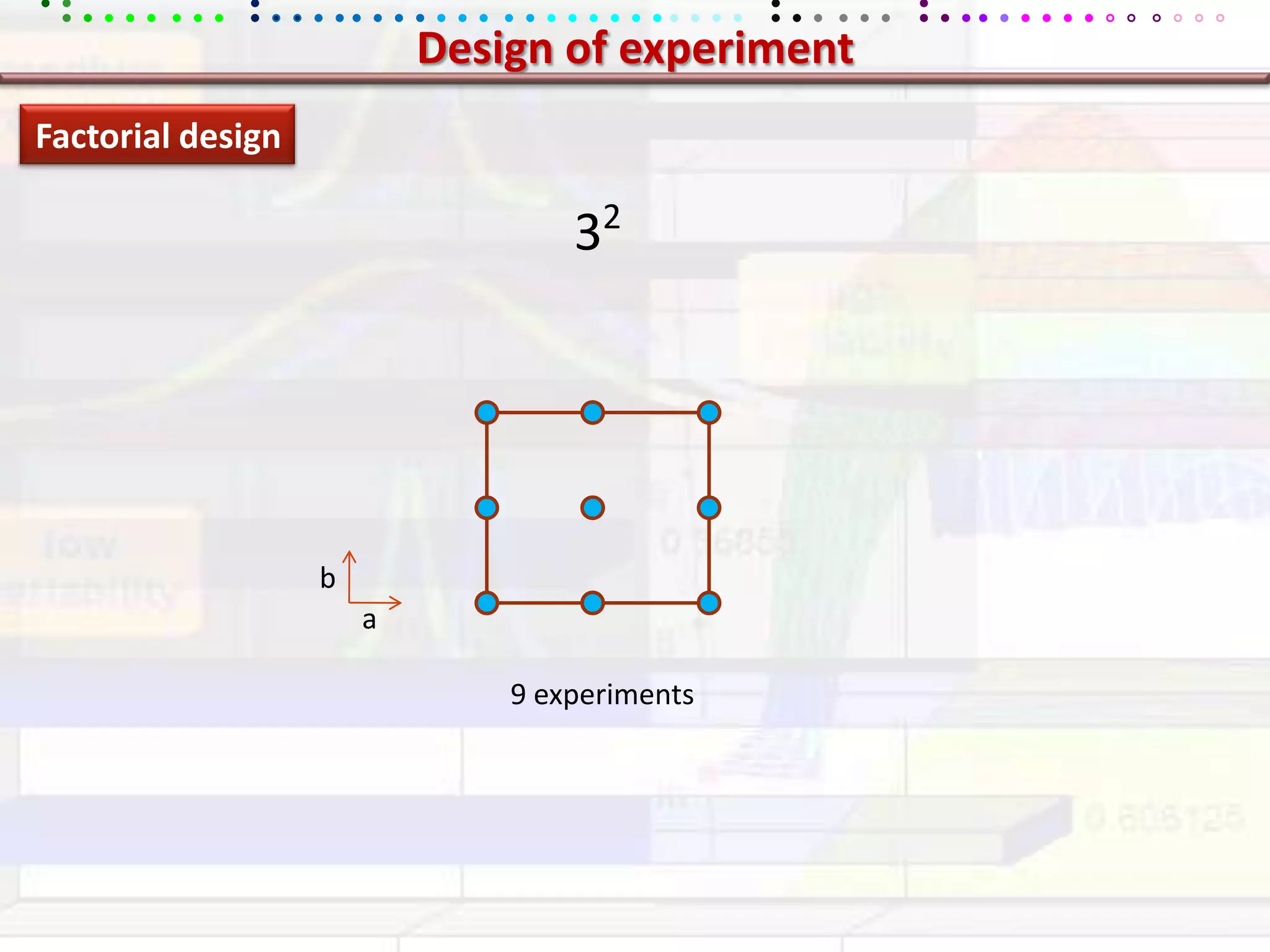
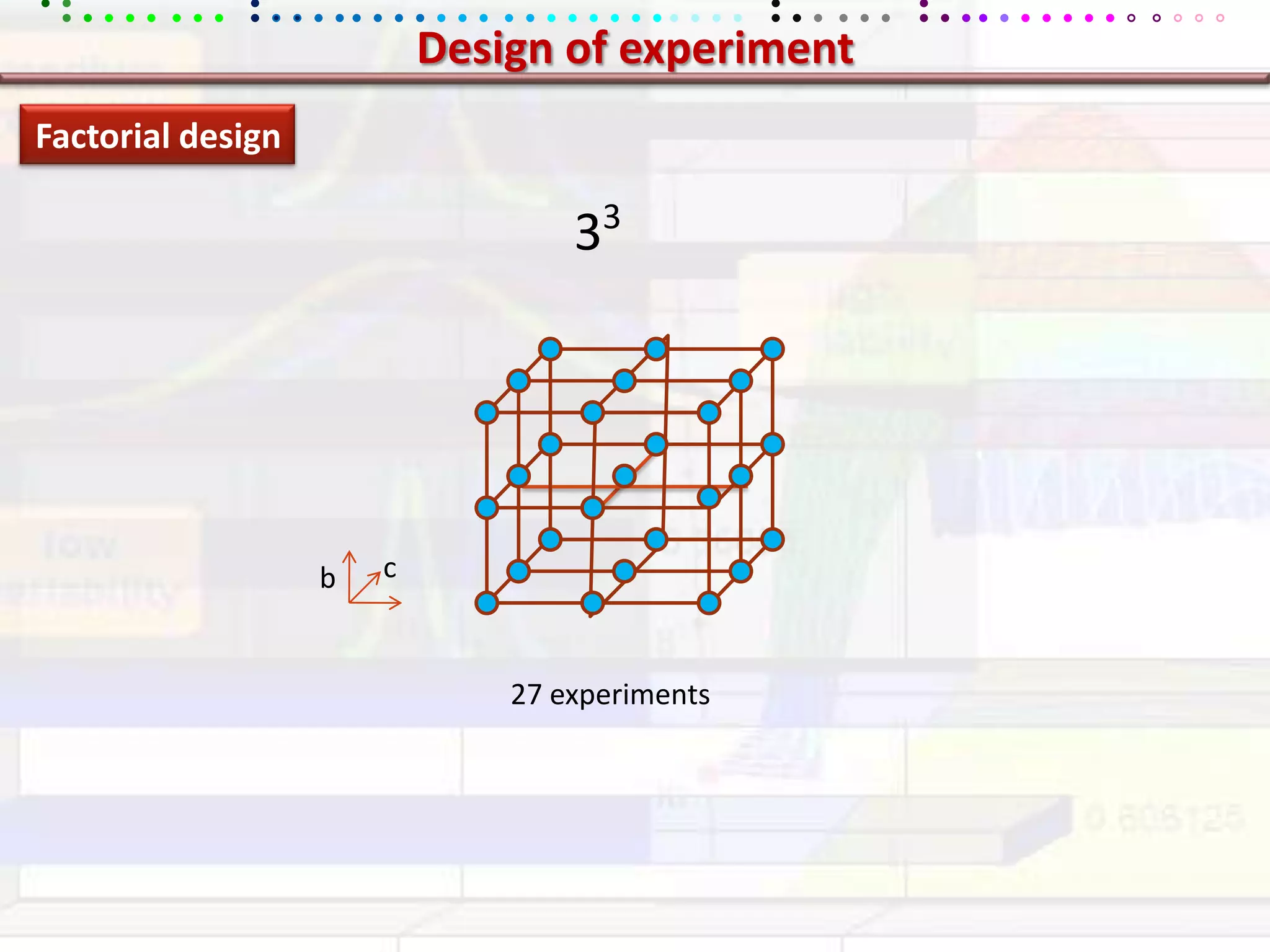
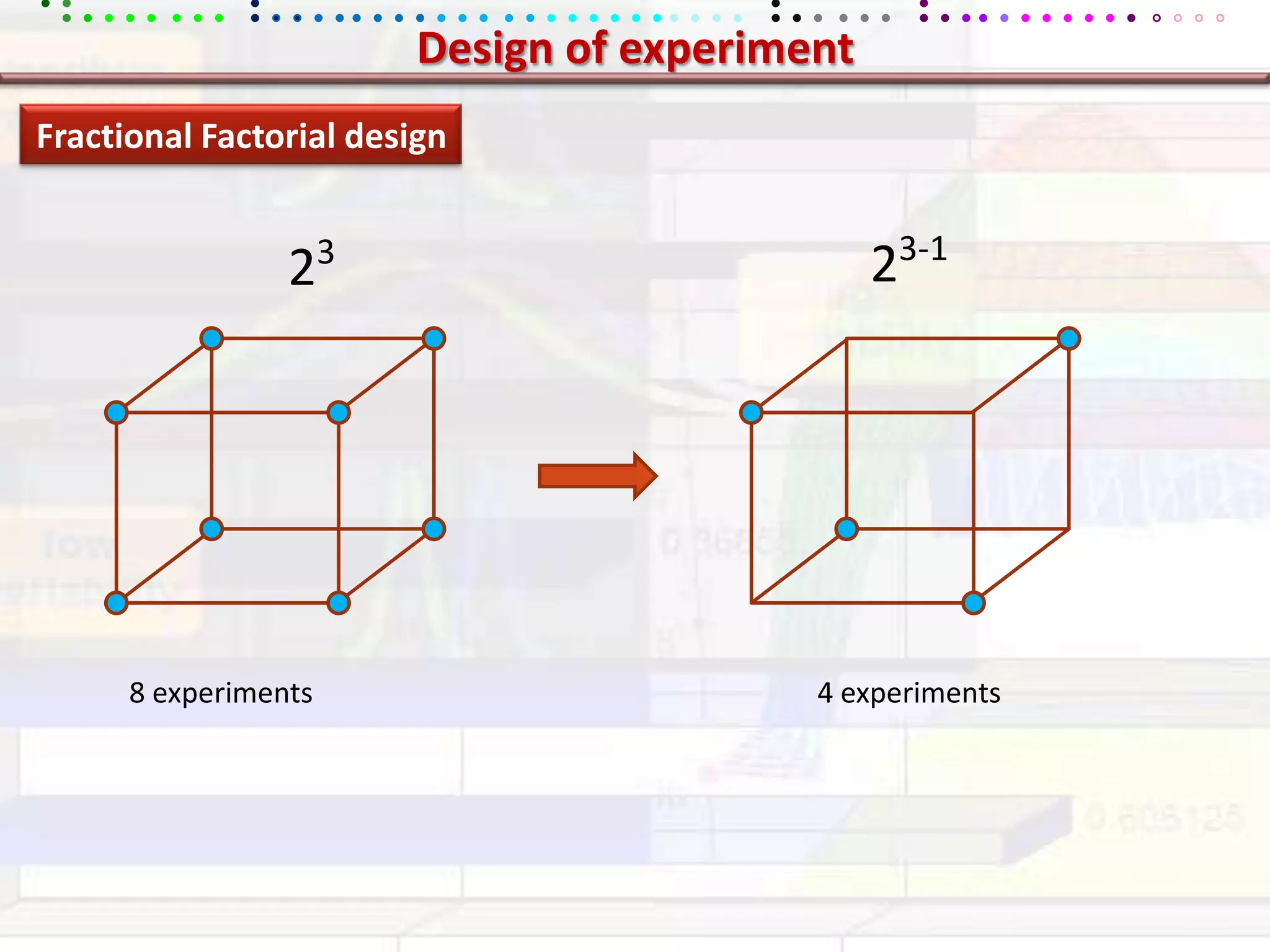
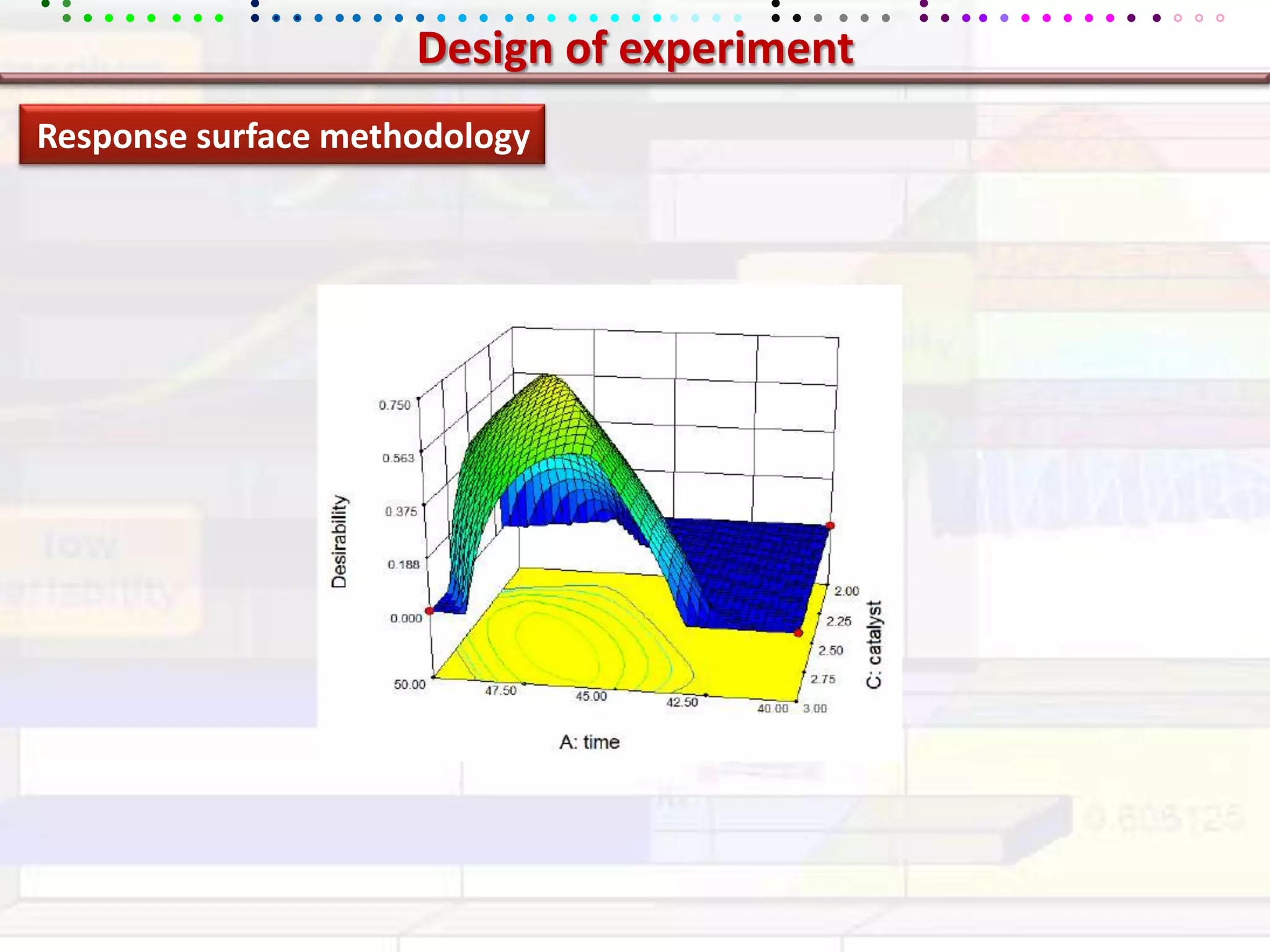
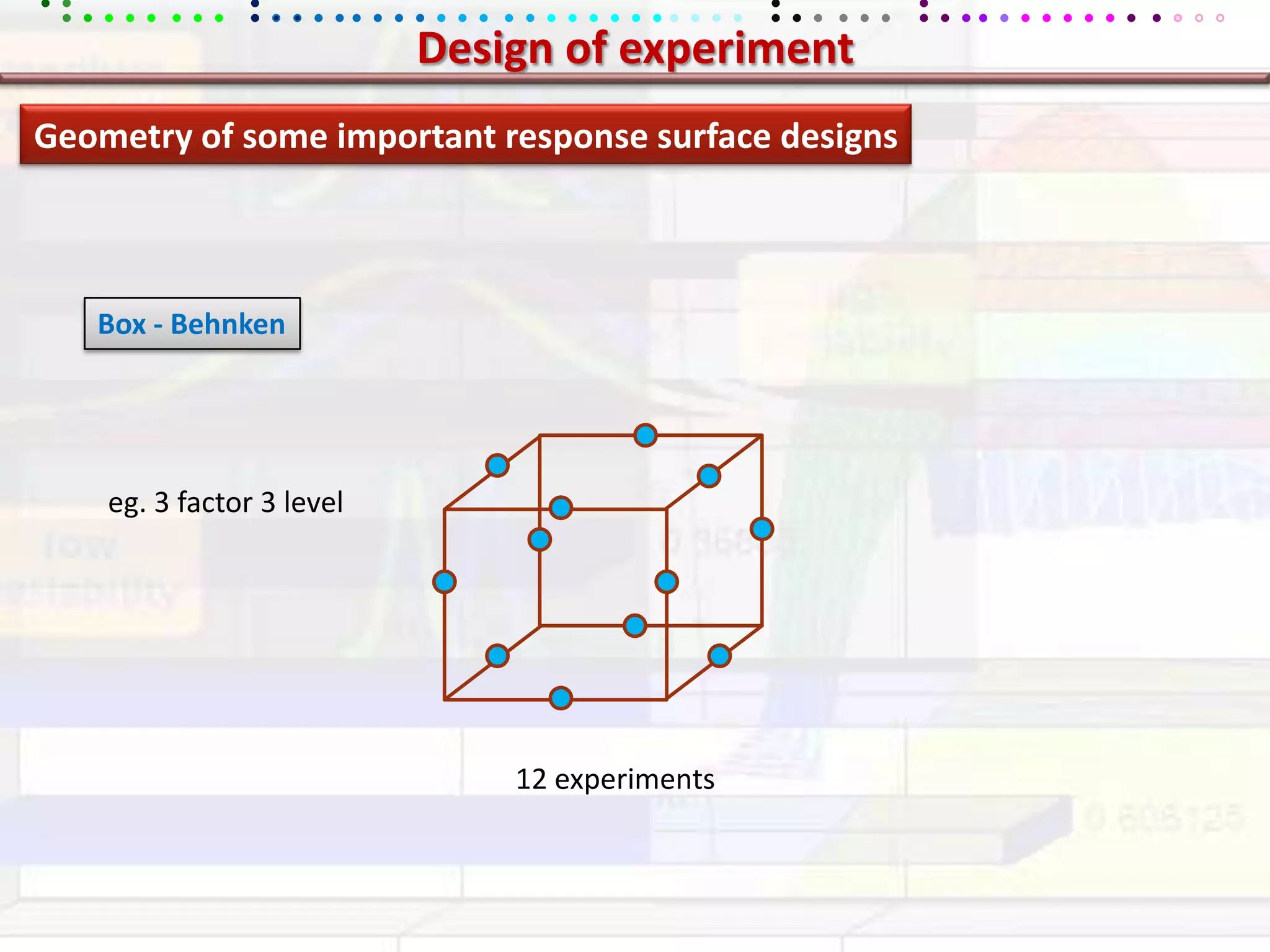
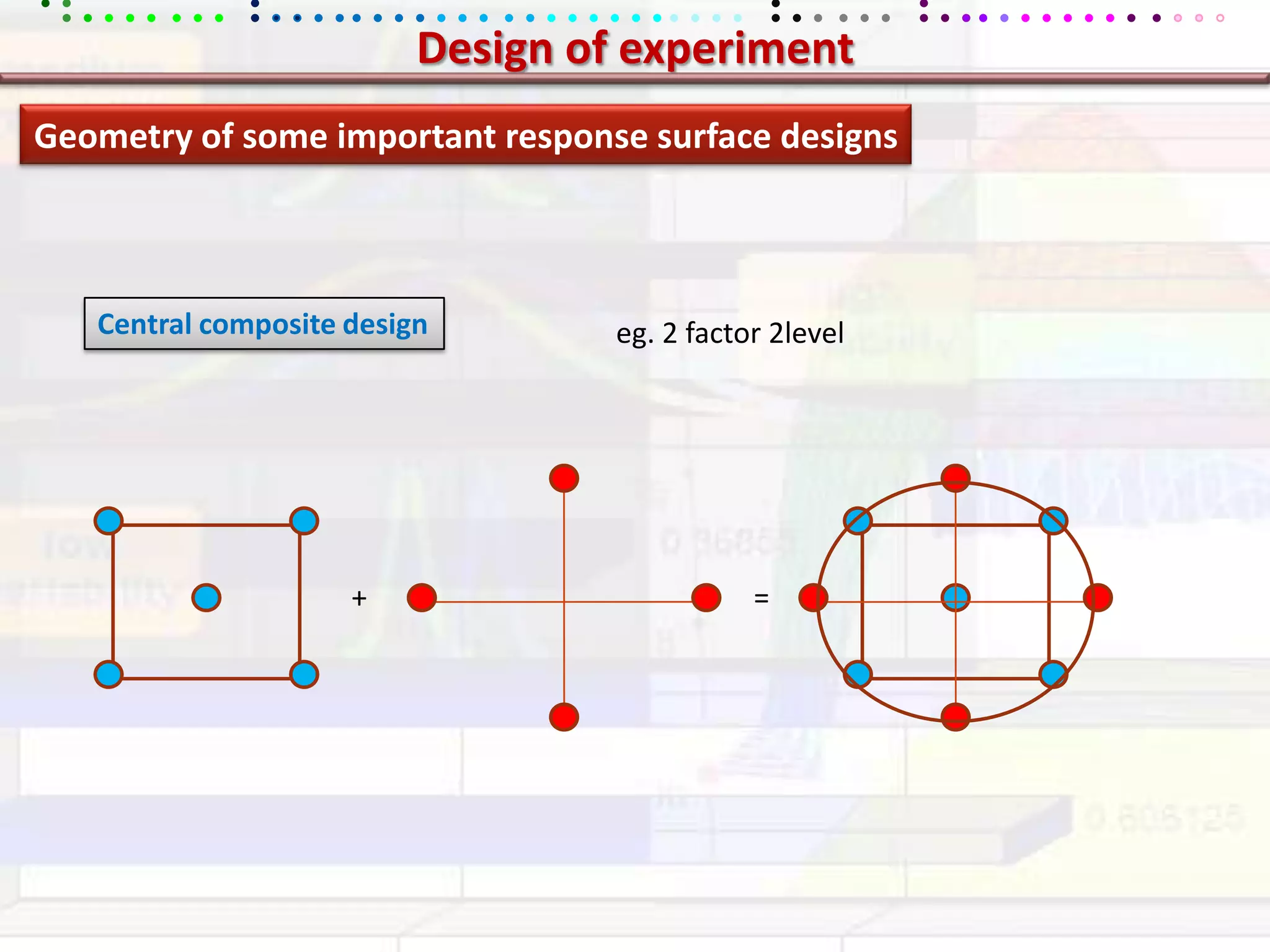
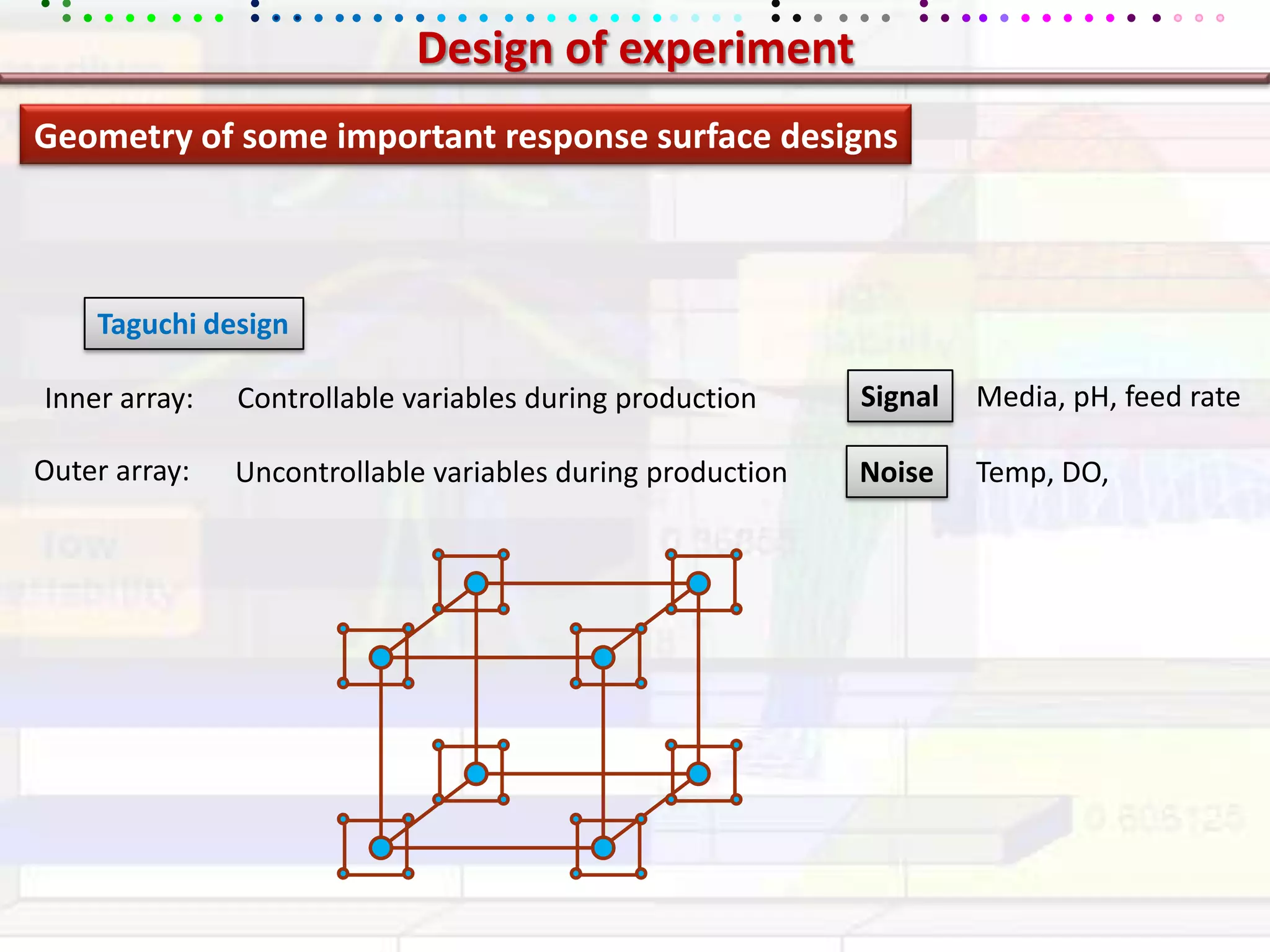
This document provides an overview of key concepts in applied statistics and design of experiments (DOE). It defines common measures of central tendency (mean, median, mode) and dispersion (variance, standard deviation, coefficient of variation). It also describes hypothesis testing using z-tests, t-tests, F-tests and ANOVA. Key concepts in regression, correlation and different experimental designs like factorial, fractional factorial and response surface methodology are summarized.