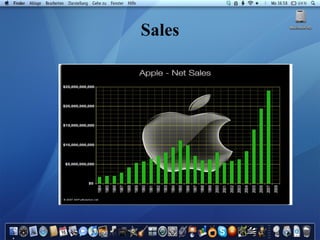
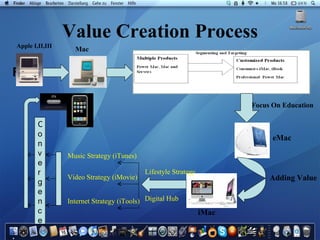
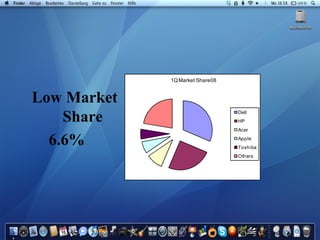
Apple Inc. was founded in 1976 by Steve Jobs and Steve Wozniak. It grew rapidly in the 1980s by selling the Apple II computer but faced decline in the 1990s as Microsoft gained dominance in the PC market with its Windows operating system. Jobs was ousted from Apple in 1985 but returned as an advisor in 1996 and became interim CEO in 1997, helping turn the company around with products like the iMac and iTunes store that established Apple as a leader in personal technology and digital media.