This document reviews appendicitis in children. It discusses the demographics, natural history, diagnosis, medical and surgical management of both acute and perforated appendicitis. Key points include that appendicitis is most common in adolescents, is caused by luminal obstruction, and diagnosis involves clinical exam and imaging studies like ultrasound or CT scan. Treatment involves antibiotics for uncomplicated cases or appendectomy for acute or perforated cases, which can be performed laparoscopically or openly. Outcomes of laparoscopic appendectomy are generally better with less complications compared to open surgery.

![DemographicsDemographics
Most common acute surgical condition
Life-time risk: 8.7% in boys; 6.7% in girls[1]
Age specific risk: extremely low neonates to
peak 12-18 years
Higher family risk in children under 6 years[2]
Rupture rate significantly increased in poorer
children[3]
1/Addiss D.G., Shaffer N., Fowler B.S., et al:
The epidemiology of appendicitis and appendectomy in the United States. Am J
Epidemiol 1990; 132:910-924. 2/Brender J.D., Marcuse E.K., Weiss N.S., et al:
Is childhood appendicitis familial?. Am J Dis Child 1985; 139:338-340.
3/Jablonski K.A., Guagliardo M.F.:
Pediatric appendicitis rupture rate: A national indicator of disparities in healthcare access. Popul Health
Metr 2005; 3:4.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appendicitisinchildrenvineyard-131003164413-phpapp01/85/Appendicitis-in-children-2-320.jpg)
![Natural HistoryNatural History
Inflammation 2° to luminal obstruction[4]
Fecalith, lymphoid tissue, parasites, foreign
body
Fecaliths related to dietary fiber content[5]
Post obstruction mucous accumulation and
contained bacterial proliferation
Pressure leads to lymphatic, venous & arterial
occlusion. Pressure necrosis and perforation
4/Wangensteen O.H., Dennis C.: Experimental proof of obstructive origin of appendicitis. Ann
Surg 1939; 110:629-647.
5/Jones B.A., Demetriades D., Segal I.: The prevalence of appendiceal fecoliths
in patients with and without appendicitis: A comparative study from Canada and South Africa. Ann
Surg 1985; 202:80-82.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appendicitisinchildrenvineyard-131003164413-phpapp01/85/Appendicitis-in-children-3-320.jpg)
![ Relapsing /chronic appendicitis[6]
Acute inflammation -› perforation -› abscess
Definition of perforation controversial
<5years perforation 82%
<1year perforation +/- 100% [7]
Wide range for perforation in literature
20-76% in 30 paediatric hospitals in the US
6/Mattei P., Sola J.E., Yeo C.J.:
Chronic and recurrent appendicitis are uncommon entities often misdiagnosed. J Am Coll
Surg 1994; 178:385-389.
7/Nance M.L., Adamson W.T., Hedrick H.L.:
Appendicitis in the young child: A continuing diagnostic challenge. Pediatr Emerg Care 2000; 16:160-162](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appendicitisinchildrenvineyard-131003164413-phpapp01/85/Appendicitis-in-children-4-320.jpg)
![DiagnosisDiagnosis
Classic Triad
WBC 11-16000/mm³ significantly higher in
cases of perforation[8]
RBC’s, WBC’s and protein common in urine
No evidence CRP superior to WBC count in
children – unnecessary expence[9]
Normal WBC and CRP doesn’t exclude Dx [10]
8/Guraya S.Y., Al-Tuwaijri T.A., Khairy G.A., et al:
Validity of leukocyte count to predict the severity of acute appendicitis. Saudi Med J 2005; 26:1945-
1947.
9/Rodríguez-Sanjuán J.C., Martín-Parra J.I., Seco I., et al:
C-reactive protein and leukocyte count in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis in children. Dis Colon
Rectum 1999; 42:1325-1329.
10/Gronroos J.M.:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appendicitisinchildrenvineyard-131003164413-phpapp01/85/Appendicitis-in-children-5-320.jpg)
![ Scoring systems may be of use
Stratify patients into 3 groups
Surgery (high score)
Imaging (intermediate score)
Discharge (low score) [11]
11/McKay R., Shepherd J.:
The use of the clinical scoring system by Alvarado in the decision to perform computed tomography for acute append
Am J Emerg Med 2007; 25:489-493.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appendicitisinchildrenvineyard-131003164413-phpapp01/85/Appendicitis-in-children-6-320.jpg)
![Alvarado ScoreAlvarado Score
Abdominal pain that migrates to the right iliac fossa
Anorexia (loss of appetite) or ketones in the urine
Nausea or vomiting
Pain on pressure in the right iliac fossa
Rebound tenderness
Fever of 37.3 °C or more
Leukocytosis, or more than 10000 white blood cells per
microliter in the serum
Neutrophilia, or an increase in the percentage of neutrophils in
the serum white blood cell count
RIF pain and leucocytosis score 2 points each
0-3: Sensitivity no AA 96% -› Discharge
4-6: Sensitivity of AA 36% -› Imaging
>7: Sensitivity of AA 78% -› +/- theatre [11]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appendicitisinchildrenvineyard-131003164413-phpapp01/85/Appendicitis-in-children-7-320.jpg)
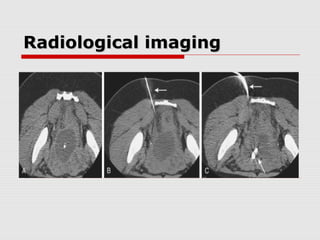
![Radiological imagingRadiological imaging
Abdominal X-ray, no benefit except in setting
of bowel obstruction and young patients
Ultrasound, safe, non-invasive, radiation and
contrast free, but operator dependent
Review of multiple paediatric series (N=5000+)
Sensitivity 78-94% Specificity 89-98%[13]
CT Scan Sensitivity and Specificity 95%[14]
MRI extremely accurate (no radiation) [15]
13/Vignault F., Filiatrault D., Brandt M.L., et al: Acute appendicitis in children: Evaluation with US.
Radiology 1990; 176:501-504.
14/Horton M.D., Counter S.F., Florence M.G., et al: A prospective trial of computed tomography and ultrasonography
for diagnosing appendicitis in the atypical patient. Am J Surg 2000; 179:379-381.
15/Horman M., Paya K., Eibenberger K., et al: MR imaging in children with nonperforated
acute appendicitis: Value of unenhanced MR imaging in sonographically selected cases. AJR Am J
Roentgenol 1998; 171:467-470.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appendicitisinchildrenvineyard-131003164413-phpapp01/85/Appendicitis-in-children-8-320.jpg)
![Medical ManagementMedical Management
Treatment starts with IV fluid and antibiotics
Uncomplicated appendicitis: current evidence
suggests single pre-op dose sufficient[16]
Post-op antibiotics indicated in perforation
Duration of treatment determined by resolution
of symptoms
CDC guidelines for peritonitis 7-10 days
16/Mui L.M., Ng C.S., Wong S.K., et al:
Optimum duration of prophylactic antibiotics in acute non-perforated appendicitis. Aust NZ J
Surg 2005; 75:425-428.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appendicitisinchildrenvineyard-131003164413-phpapp01/85/Appendicitis-in-children-9-320.jpg)
![Antibiotic regimensAntibiotic regimens
Triple therapy
(ampicillin,gentamycin,metronidazole)
Piptaz as effective as triples[17]
Ceftriaxone and metronidazole daily as
effective as triples (cost and time benefit)[18]
Early transition to oral antibiotics as effective
as prolonged IV’s [19]
17/Nadler E.P., Reblock K.K., Ford H.R., et al: Monotherapy
versus multi-drug therapy for the treatment of perforated appendicitis in children. Surg Infect (Larchmt) 2003; 4:327-
333.
18/St Peter S.D., Little D.C., Calkins C.M., et al:
A simple and more cost-effective antibiotic regimen for perforated appendicitis. J Pediatr Surg 2006; 41:1020-1024.
19/Adibe O.O., Barnaby K., Dobies J., et al:
Postoperative antibiotic therapy for children with perforated appendicitis: Long course of intravenous antibiotics versus early conver](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appendicitisinchildrenvineyard-131003164413-phpapp01/85/Appendicitis-in-children-10-320.jpg)
![Surgical ManagementSurgical Management
Acute Appendicitis
Acute appendicitis cured with surgery
Prompt appendicectomy treatment of choice
Appendicitis can be treated with antibiotics
alone[20]
Antibiotics change from emergency to elective
Appendicectomy in the middle of the night not
justified[21]
20/ Styrud J., Eriksson S., Nilsson I., et al:
Appendectomy versus antibiotic treatment in acute appendicitis: A prospective multicenter randomized controlled trial.
World J Surg 2006; 30:1033-1037.
21/Surana R., Quinn F., Puri P.:
Is it necessary to perform appendectomy in the middle of the night in children?. BMJ 1993; 306:1168.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appendicitisinchildrenvineyard-131003164413-phpapp01/85/Appendicitis-in-children-11-320.jpg)
![Surgical ManagementSurgical Management
Perforated Appendicitis
Appendicectomy in the presence of known
perforation is controversial
Antibiotics alone; Antibiotics and interval
appendicectomy; Appendicectomy at
presentation
Recurrent appendicitis(8-14%) short term [22]
APSA 86% responders perform interval
appendicectomy[23]
22/ Puapong D., Lee S.L., Haigh P.I., et al: Routine interval appendectomy in children is not indicated. J Pediatr
Surg 2007; 42:1500-1503.
23/ Chen C., Botelho C., Cooper A., et al:
Current practice patterns in the treatment of perforated appendicitis in children. J Am Coll Surg 2003; 196:212-
221.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appendicitisinchildrenvineyard-131003164413-phpapp01/85/Appendicitis-in-children-12-320.jpg)
![Surgical ManagementSurgical Management
Perforated Appendicitis
Causes of failure of nonoperative management
1. Band count >15% at presentation[24]
2. Appendicolith present on imaging[25]
3. Contamination beyond RIF on imaging[26]
Experienced surgeon should be able to deal
with situation at presentation
APSA survey: Senior surgeons base practice
on personal preference
24/Kogut K.A., Blakely M.L., Schropp K.P., et al:
The association of elevated percent bands on admission with failure and complications of interval appendectomy.
J Pediatr Surg 2001; 36:165-168.
25/Aprahamian C.J., Barnhart D.C., Bledsoe S.E., et al: Failure in the nonoperative
management of pediatric ruptured appendicitis: Predictors and consequences. J Pediatr Surg 2007; 42:934-938.
26/Levin T., Whyte C., Borzykowski R., et al: Nonoperative](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appendicitisinchildrenvineyard-131003164413-phpapp01/85/Appendicitis-in-children-13-320.jpg)
![Surgical ManagementSurgical Management
Abscess at presentation
Open surgery high morbidity
Percutaneous drainage and interval
appendicectomy[27]
Long course of treatment, cost burden[28]
Prospective trial currently in progress
comparing early laparoscopic surgery with
percutaneous drain and delayed surgery[29]
27/Chen C., Botelho C., Cooper A., et al: Current practice patterns in the treatment of perforated appendicitis in children. J
Am Coll Surg 2003; 196:212-221.
28/Keckler S.J., St Peter S.D., Tsao K., et al: Resource utilization and outcomes from percutaneous
drainage and interval appendectomy for perforated appendicitis. J Pediatr Surg 2008; 43:977-980.
29/ National Institutes of Health: Early versus delayed operation for perforated appendicitis. Available at
www.clinicaltrials.gov—NCT# 00414375](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appendicitisinchildrenvineyard-131003164413-phpapp01/85/Appendicitis-in-children-14-320.jpg)
![Surgical ManagementSurgical Management
Abscess at presentation
Regardless of route of drainage cultures not of
benefit[30]
One study showed that changing according to
cultures had a worse outcome (N=308)[31]
Lavage with saline or antibiotic solution not
shown to be of benefit[32]
Post-op intra-peritoneal AB’s may benefit (48h)
Drains only useful in walled off collections[33]
30/Bilik R., Burnweit C., Shandling B.: Is abdominal cavity culture of any value in appendicitis?. Am J Surg 1998; 175:267-270.
31/Kokoska E.R., Silen M.L., Tracy T.F., et al: The impact of intraoperative
culture on treatment and outcome in children with perforated appendicitis. J Pediatr Surg 1999; 34:749-753.
32/Sherman J.O., Luck S.R., Borger J.A.: Irrigation of the peritoneal cavity for appendicitis in children: A double blind study. J Pediatr
Surg 1976; 11:371-374.
33/Kokoska E.R., Silen M.L., Tracy T.F., et al: Perforated appendicitis in children: Risk factors for the development of complications.
Surgery 1998; 124:619-625.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appendicitisinchildrenvineyard-131003164413-phpapp01/85/Appendicitis-in-children-15-320.jpg)
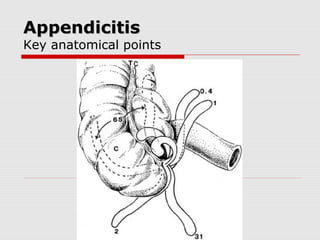
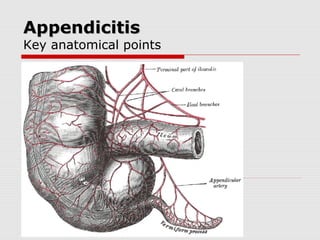
![Laparoscopic AppendicectomyLaparoscopic Appendicectomy
Umbilical port and two working ports (open)
Initial data, longer operative time and more
intra-abdominal complications in LA[34]
Newer evidence suggests no difference in
operative time and IAA in the 2 groups[35]
Risk of abscess formation justification for
continued use of open surgery
Substantially lower risk of wound infection[36]
34/Horwitz J.R., Custer M.D., May B.H., et al:
Should laparoscopic appendectomy be avoided for complicated appendicitis in children?. J Pediatr
Surg 1997; 32:1601-1603.
35/Aziz O., Athanasiou T., Tekkis P.P., et al:
Laparoscopic versus open appendectomy in children: A meta-analysis. Ann Surg 2006; 243:17-27.
36/Sauerland S., Lefering R., Neugebauer E.A.: Laparoscopic versus open surgery for suspected appendicitis.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2004; 18:CD001546](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appendicitisinchildrenvineyard-131003164413-phpapp01/85/Appendicitis-in-children-17-320.jpg)
![Laparoscopic AppendicectomyLaparoscopic Appendicectomy
Substantially lower complication rate in obese
patients[37]
Shorter duration of hospital stay[36]
Earlier return to work and normal activity[36]
Prospective RCT quality of life, GIT
complication and overall complications lower
for laparoscopy (N=43757)[38]
Recent Cochrane review: LA 1° operation[36]
36/Sauerland S., Lefering R., Neugebauer E.A.: Laparoscopic versus open surgery for suspected appendicitis.
Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2004; 18:CD001546
37/Corneille M.G., Steigelman M.B., Myers J.G., et al:
Laparoscopic appendectomy is superior to open appendectomy in obese patients. Am J Surg 2007; 194:877-
880.
38/Guller U., Hervey S., Purves H., et al:
Laparoscopic versus open appendectomy: Outcomes comparison based on a large administrative database.
Ann Surg 2004; 239:43-52.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appendicitisinchildrenvineyard-131003164413-phpapp01/85/Appendicitis-in-children-18-320.jpg)
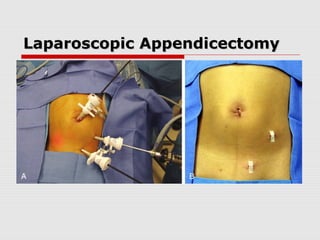
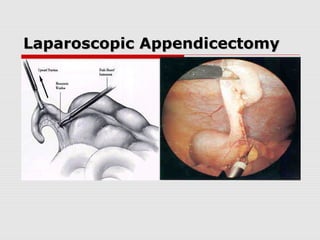
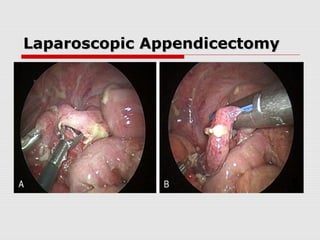
![Laparoscopic AppendicectomyLaparoscopic Appendicectomy
Most recent prospective RCT had a mean
operation time of 44min in laparoscopic
perforated appendicectomy[39]
Evidence heavily in favour of LA
39/St Peter S.D., Tsao K., Spilde T.L., et al: Single daily dosing ceftriaxone and metronidazole
vs. standard triple antibiotic regimen for perforated appendicitis in children: A prospective randomized trial.
J Pediatr Surg 2008; 43:981-985.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/appendicitisinchildrenvineyard-131003164413-phpapp01/85/Appendicitis-in-children-24-320.jpg)
