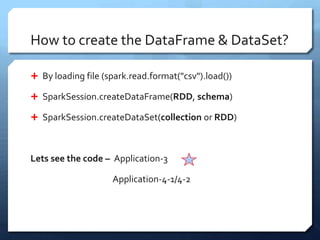
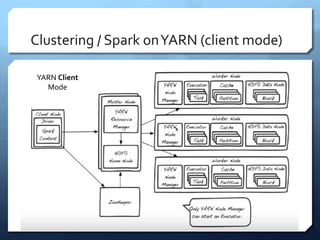
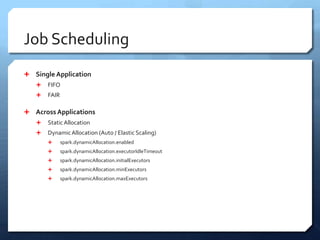
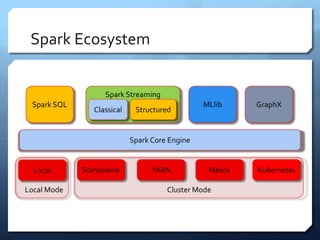
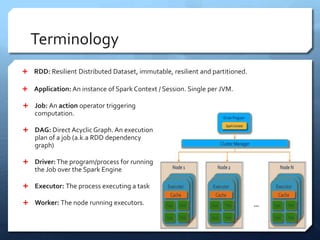
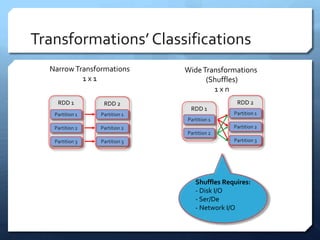
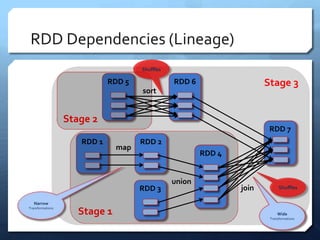
Apache Spark is a distributed computing engine that originated in 2009 at UC Berkeley, becoming an Apache project in 2013 with significant community contributions. It provides functionalities like RDDs, transformations, and actions for data processing, alongside newer abstractions such as DataFrames and Datasets. The training covers Spark's architecture, lifecycle, various operations, and job scheduling techniques.





![Transformations
map(func)
flatMap(func)
filter(func)
union(dataset)
join(dataset, usingColumns: Seq[String])
intersect(dataset)
coalesce(numPartitions)
repartition(numPartitions)
Full List:
https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/rdd-programming-
guide.html#transformations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachesparktraining-180510110903/85/Apache-Spark-Fundamentals-Training-9-320.jpg)

![ExecutionTiers
=>The main program is executed on Spark Driver
=>Transformations are executed on SparkWorker
=> Action returns the results from workers to driver
val wordCountTuples: Array[(String, Int)] = sparkSession.sparkContext
.textFile("src/main/resources/vivaldi_life.txt")
.flatMap(_.split(" "))
.map(word => (word, 1))
.reduceByKey(_ + _)
.collect()
wordCountTuples.foreach(println)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachesparktraining-180510110903/85/Apache-Spark-Fundamentals-Training-14-320.jpg)
![RDD Evolution
RDD
V1.0
(2011)
DataFrame
V1.3
(2013)
DataSet
V1.6
(2015)
Untyped API
Schema based -Tabular
Java Objects
Low level data-structure
To work with
Unstructured Data
Typed API: [T]
Tabular
SQL Support
To work with
Semi-Structured (csv, json) / Structured Data (jdbc)
Catalyst Optimizer
Cost Optimizer
ProjectTungsten
Three tier
optimizations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachesparktraining-180510110903/85/Apache-Spark-Fundamentals-Training-15-320.jpg)