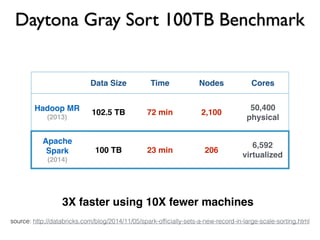
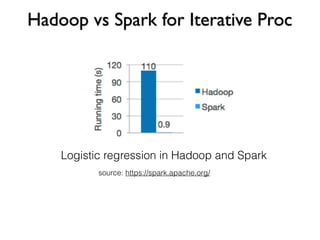
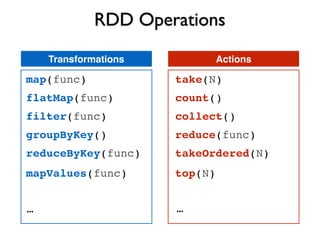
Apache Spark is a fast, general engine for large-scale data processing. It supports batch, interactive, and stream processing using a unified API. Spark uses resilient distributed datasets (RDDs), which are immutable distributed collections of objects that can be operated on in parallel. RDDs support transformations like map, filter, and reduce and actions that return final results to the driver program. Spark provides high-level APIs in Scala, Java, Python, and R and an optimized engine that supports general computation graphs for data analysis.








![Spark API
val spark = new SparkContext()
val lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://docs/”) // RDD[String]
val nonEmpty = lines.filter(l => l.nonEmpty()) // RDD[String]
val count = nonEmpty.count
Scala
SparkContext spark = new SparkContext();
JavaRDD<String> lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://docs/”)
JavaRDD<String> nonEmpty = lines.filter(l -> l.length() > 0);
long count = nonEmpty.count();
Java8Python
spark = SparkContext()
lines = spark.textFile(“hdfs://docs/”)
nonEmpty = lines.filter(lambda line: len(line) > 0)
count = nonEmpty.count()](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachespark-141115145614-conversion-gate01/85/Apache-Spark-with-Scala-19-320.jpg)

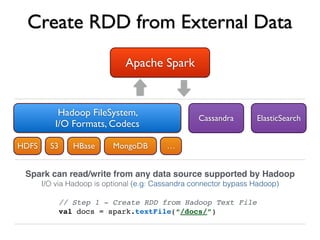
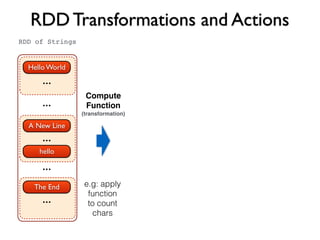
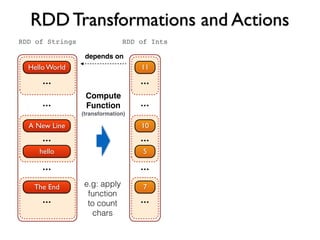
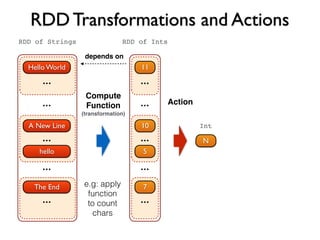
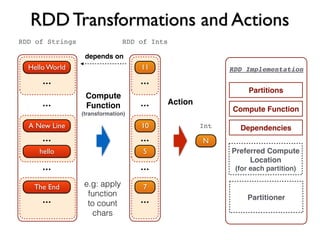
![Function map
Hello World
A New Line
hello
...
The end
.map(line => line.toLowerCase)
RDD[String] RDD[String]
hello world
a new line
hello
...
the end
.map(_.toLowerCase)
// Step 2 - Convert lines to lower case
val lower = docs.map(line => line.toLowerCase)
=](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachespark-141115145614-conversion-gate01/85/Apache-Spark-with-Scala-23-320.jpg)
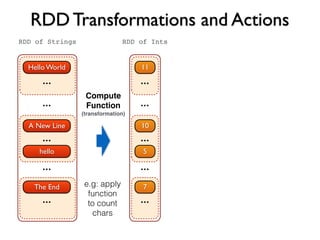
![Functions map and flatMap
hello world
a new line
hello
...
the end
RDD[String]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachespark-141115145614-conversion-gate01/85/Apache-Spark-with-Scala-24-320.jpg)
![Functions map and flatMap
hello world
a new line
hello
...
the end
RDD[String]
.map( … )
_.split(“s+”)
a
hello
hello
...
the
world
new line
end
RDD[Array[String]]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachespark-141115145614-conversion-gate01/85/Apache-Spark-with-Scala-25-320.jpg)
![Functions map and flatMap
hello world
a new line
hello
...
the end
RDD[String]
.map( … )
_.split(“s+”)
a
hello
hello
...
the
world
new line
end
RDD[Array[String]]
.flatten
hello
a
...
world
new
line
RDD[String]
*](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachespark-141115145614-conversion-gate01/85/Apache-Spark-with-Scala-26-320.jpg)
![Functions map and flatMap
hello world
a new line
hello
...
the end
.flatMap(line => line.split(“s+“))
RDD[String]
.map( … )
_.split(“s+”)
a
hello
hello
...
the
world
new line
end
RDD[Array[String]]
.flatten
hello
a
...
world
new
line
RDD[String]
*](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachespark-141115145614-conversion-gate01/85/Apache-Spark-with-Scala-27-320.jpg)
![Functions map and flatMap
hello world
a new line
hello
...
the end
.flatMap(line => line.split(“s+“))
Note: flatten() not available in spark, only flatMap
RDD[String]
.map( … )
_.split(“s+”)
a
hello
hello
...
the
world
new line
end
RDD[Array[String]]
// Step 3 - Split lines into words
val words = lower.flatMap(line => line.split(“s+“))
.flatten
hello
a
...
world
new
line
RDD[String]
*](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachespark-141115145614-conversion-gate01/85/Apache-Spark-with-Scala-28-320.jpg)
![Key-Value Pairs
hello
a
...
world
new
line
hello
hello
a
...
world
new
line
hello
.map(word => Tuple2(word, 1))
1
1
1
1
1
1
.map(word => (word, 1))
RDD[String] RDD[(String, Int)]
// Step 4 - Split lines into words
val counts = words.map(word => (word, 1))
=
RDD[Tuple2[String, Int]]
Pair RDD](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachespark-141115145614-conversion-gate01/85/Apache-Spark-with-Scala-29-320.jpg)
![Shuffling
hello
a
world
new
line
hello
1
1
1
1
1
1
RDD[(String, Int)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachespark-141115145614-conversion-gate01/85/Apache-Spark-with-Scala-30-320.jpg)
![Shuffling
hello
a
world
new
line
hello
1
1
1
1
1
1
world
a
1
1
new 1
line
hello
1
1
.groupByKey
RDD[(String, Iterator[Int])]
1
RDD[(String, Int)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachespark-141115145614-conversion-gate01/85/Apache-Spark-with-Scala-31-320.jpg)
![Shuffling
hello
a
world
new
line
hello
1
1
1
1
1
1
world
a
1
1
new 1
line
hello
1
1
.groupByKey
RDD[(String, Iterator[Int])]
1
RDD[(String, Int)]
world
a
1
1
new 1
line
hello
1
2
.mapValues
_.reduce(…)
(a,b) => a+b
RDD[(String, Int)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachespark-141115145614-conversion-gate01/85/Apache-Spark-with-Scala-32-320.jpg)
![Shuffling
hello
a
world
new
line
hello
1
1
1
1
1
1
.reduceByKey((a, b) => a + b)
world
a
1
1
new 1
line
hello
1
1
.groupByKey
RDD[(String, Iterator[Int])]
1
RDD[(String, Int)]
world
a
1
1
new 1
line
hello
1
2
.mapValues
_.reduce(…)
(a,b) => a+b
RDD[(String, Int)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachespark-141115145614-conversion-gate01/85/Apache-Spark-with-Scala-33-320.jpg)
![Shuffling
hello
a
world
new
line
hello
1
1
1
1
1
1
.reduceByKey((a, b) => a + b)
// Step 5 - Count all words
val freq = counts.reduceByKey(_ + _)
world
a
1
1
new 1
line
hello
1
1
.groupByKey
RDD[(String, Iterator[Int])]
1
RDD[(String, Int)]
world
a
1
1
new 1
line
hello
1
2
.mapValues
_.reduce(…)
(a,b) => a+b
RDD[(String, Int)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachespark-141115145614-conversion-gate01/85/Apache-Spark-with-Scala-34-320.jpg)
![Top N (Prepare data)
world
a
1
1
new 1
line
hello
1
2
// Step 6 - Swap tuples (partial code)
freq.map(_.swap)
.map(_.swap)
world
a
1
1
new1
line
hello
1
2
RDD[(String, Int)] RDD[(Int, String)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachespark-141115145614-conversion-gate01/85/Apache-Spark-with-Scala-35-320.jpg)
![Top N (First Attempt)
world
a
1
1
new1
line
hello
1
2
RDD[(Int, String)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachespark-141115145614-conversion-gate01/85/Apache-Spark-with-Scala-36-320.jpg)
![Top N (First Attempt)
world
a
1
1
new1
line
hello
1
2
RDD[(Int, String)]
.sortByKey
RDD[(Int, String)]
hello
world
2
1
a1
new
line
1
1
(sortByKey(false) for descending)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachespark-141115145614-conversion-gate01/85/Apache-Spark-with-Scala-37-320.jpg)
![Top N (First Attempt)
world
a
1
1
new1
line
hello
1
2
RDD[(Int, String)] Array[(Int, String)]
hello
world
2
1
.take(N).sortByKey
RDD[(Int, String)]
hello
world
2
1
a1
new
line
1
1
(sortByKey(false) for descending)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachespark-141115145614-conversion-gate01/85/Apache-Spark-with-Scala-38-320.jpg)
![Top N
Array[(Int, String)]
world
a
1
1
new1
line
hello
1
2
RDD[(Int, String)]
world
a
1
1
.top(N)
hello
line
2
1
hello
line
2
1
local top N *
local top N *
reduction
// Step 6 - Swap tuples (complete code)
val top = freq.map(_.swap).top(N)
* local top N implemented by bounded priority queues](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachespark-141115145614-conversion-gate01/85/Apache-Spark-with-Scala-39-320.jpg)

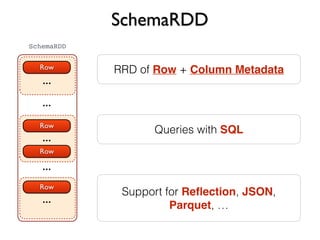
![SchemaRDD
Row
...
...
...
...
Row
Row
Row
...
topWords
case class Word(text: String, n: Int)
val wordsFreq = freq.map {
case (text, count) => Word(text, count)
} // RDD[Word]
wordsFreq.registerTempTable("wordsFreq")
val topWords = sql("select text, n
from wordsFreq
order by n desc
limit 20”) // RDD[Row]
topWords.collect().foreach(println)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachespark-141115145614-conversion-gate01/85/Apache-Spark-with-Scala-43-320.jpg)
![nums = words.filter(_.matches(“[0-9]+”))
RDD Lineage
HadoopRDDwords = sc.textFile(“hdfs://large/file/”)
.map(_.toLowerCase)
alpha.count()
MappedRDD
alpha = words.filter(_.matches(“[a-z]+”))
FlatMappedRDD.flatMap(_.split(“ “))
FilteredRDD
Lineage
(built on the driver
by the transformations)
FilteredRDD
Action (run job on the cluster)
RDD Transformations](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/apachespark-141115145614-conversion-gate01/85/Apache-Spark-with-Scala-44-320.jpg)