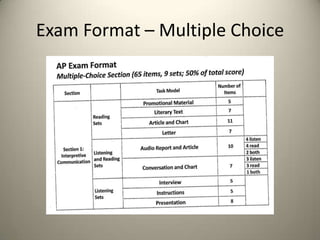
This document provides guidance for teachers on developing students' interpretive communication skills in French. It summarizes key points about the redesigned Advanced Placement French exam, including that students will work with a greater variety of authentic materials from the French-speaking world, both print and audio. It recommends teachers select resources that can differentiate instruction, integrate other communication modes and culture, and vary in type, level, and authenticity. Sample exam questions and timing are outlined, and achievement levels are described to allow more detailed reporting of student performance. Examples of classroom activities integrating various skills and themes are also provided.