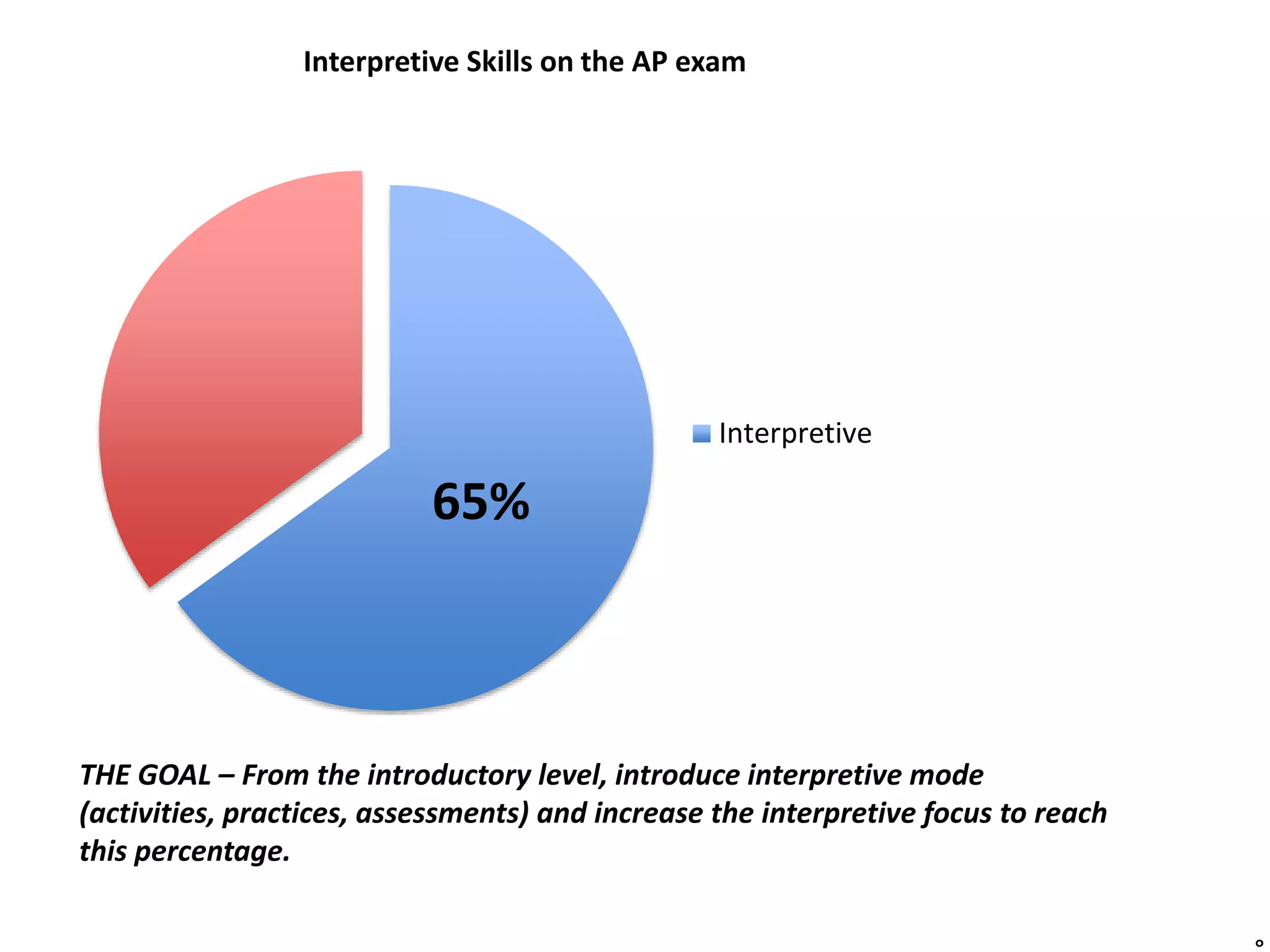
The document provides an overview of a presentation on communication and the interpretive mode in language learning. It discusses the importance of interpretive communication as assessed on the Advanced Placement exam. The presentation agenda includes defining interpretive communication, its importance in the curriculum, materials to use, and teaching strategies. Key aspects of interpretive communication emphasized are using authentic materials from the target culture and scaffolding tasks by language proficiency level. Listening and reading are discussed, highlighting challenges and resources to support comprehension at different levels.