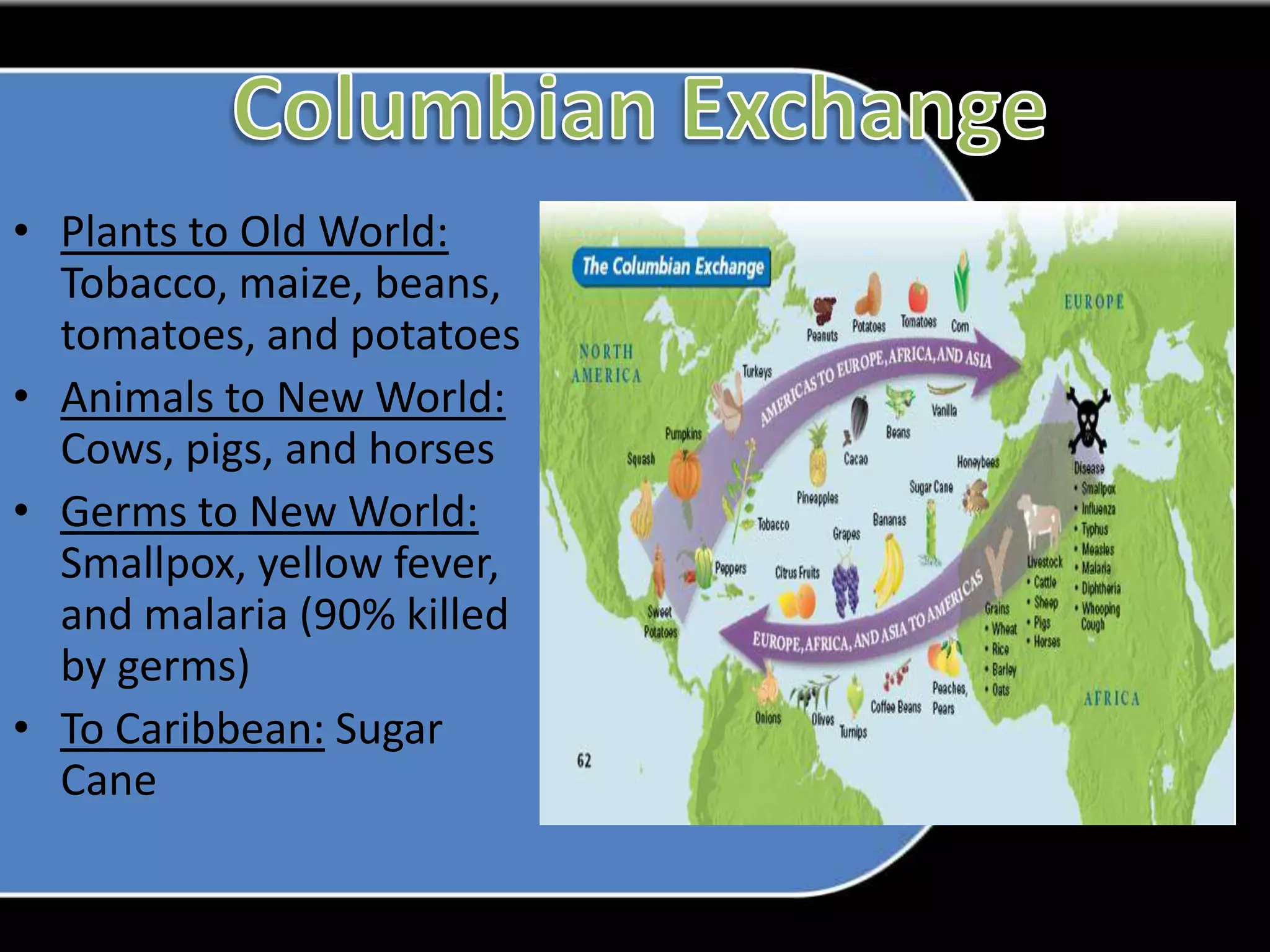
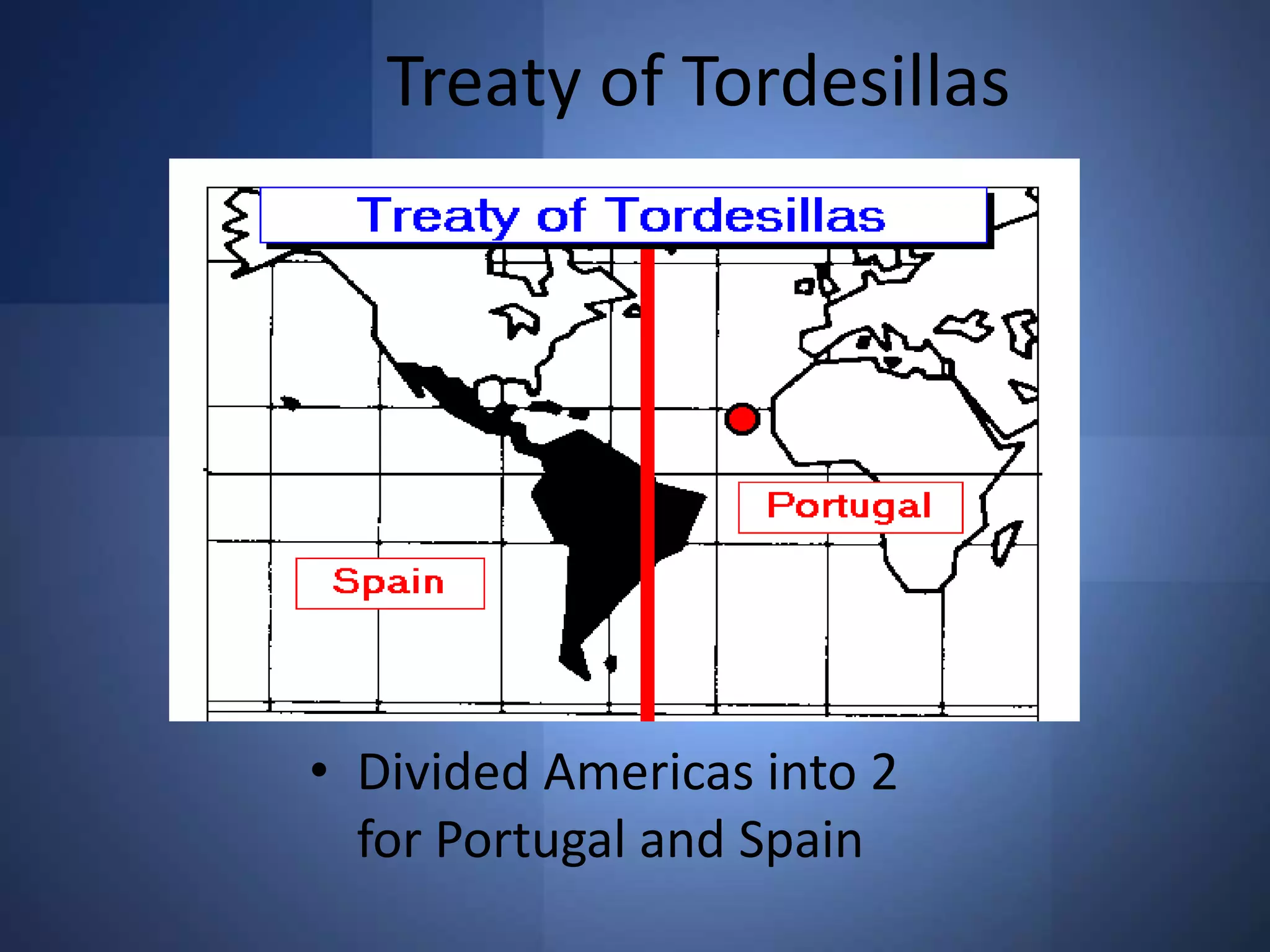
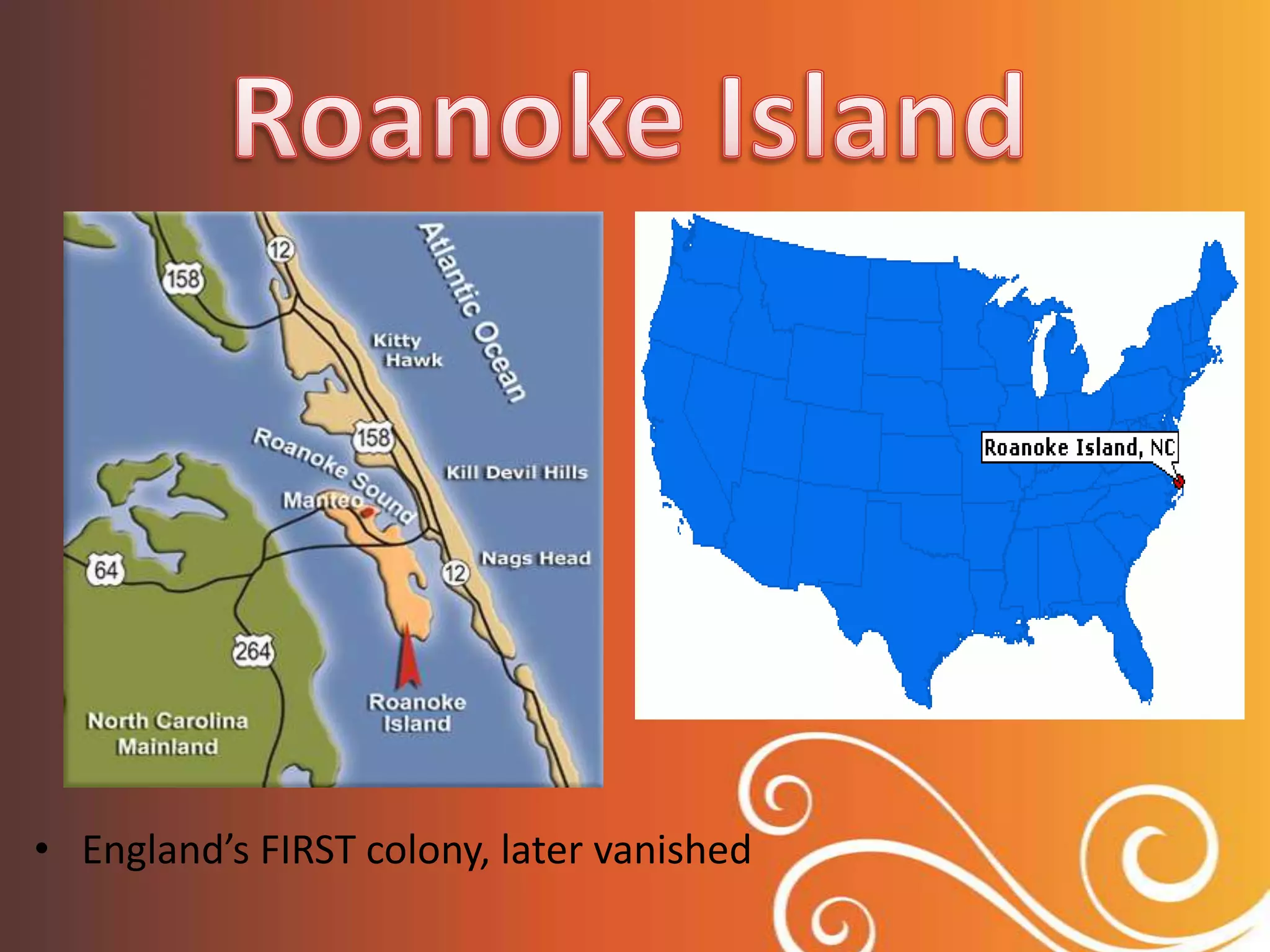
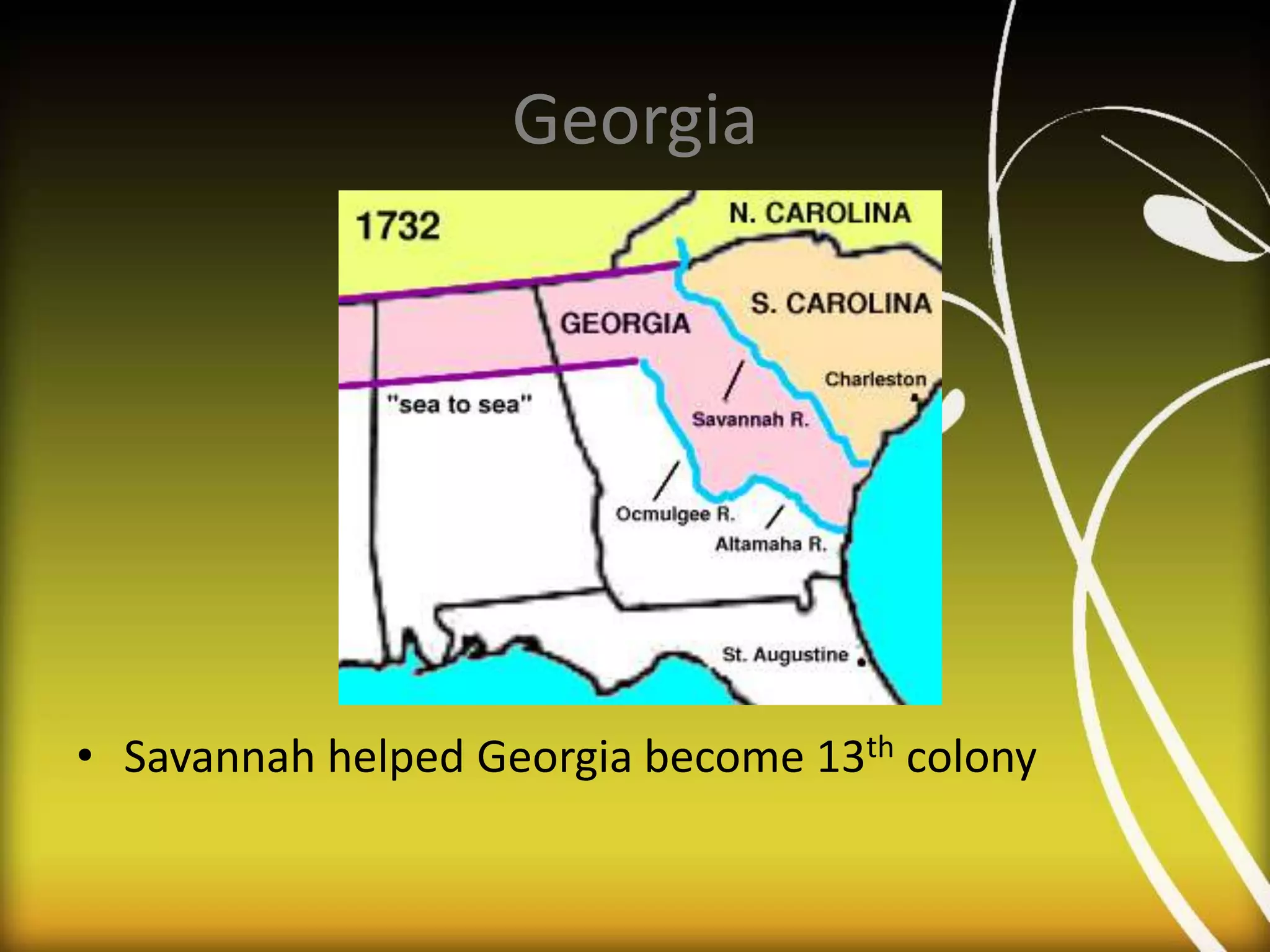
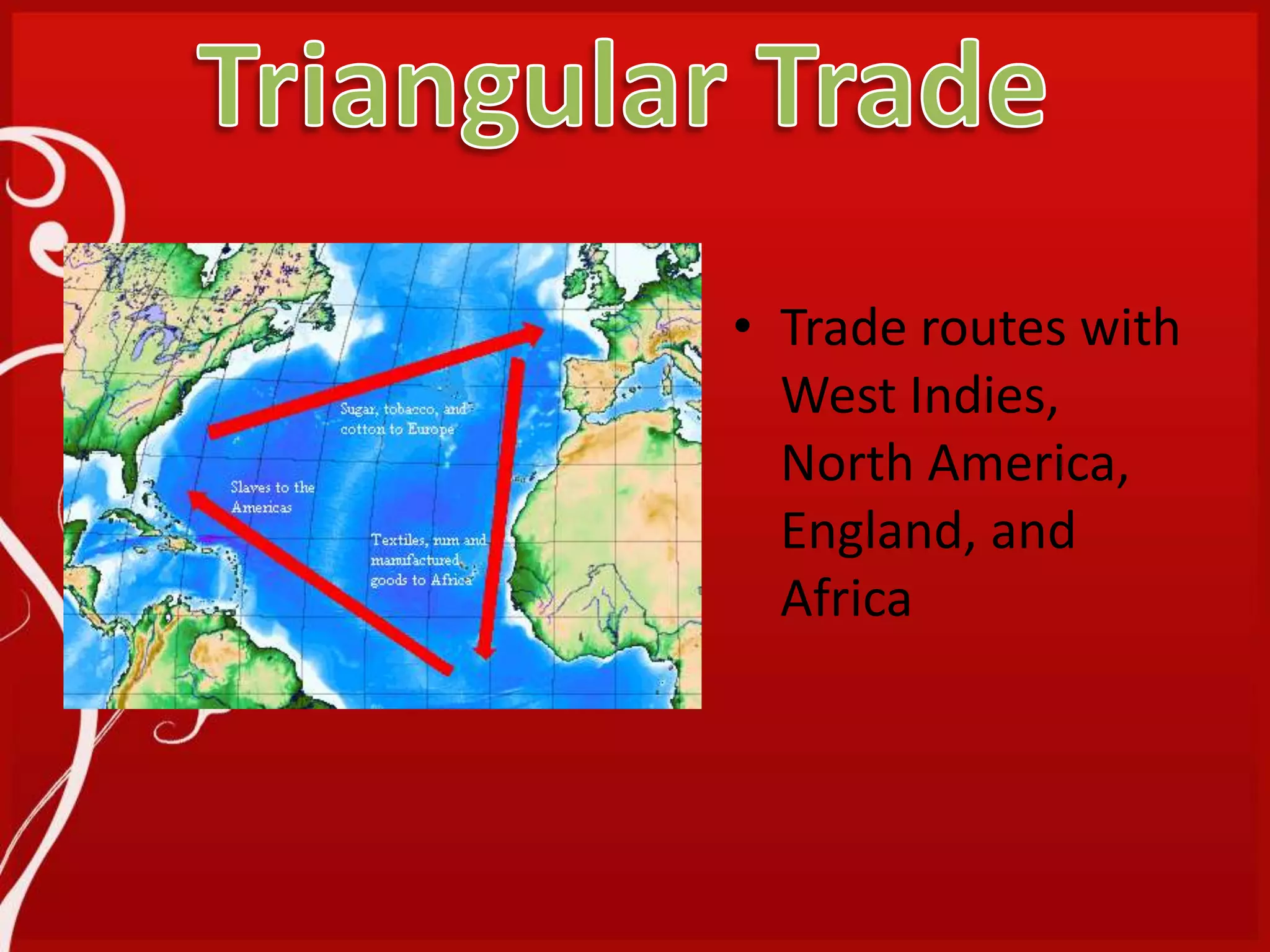
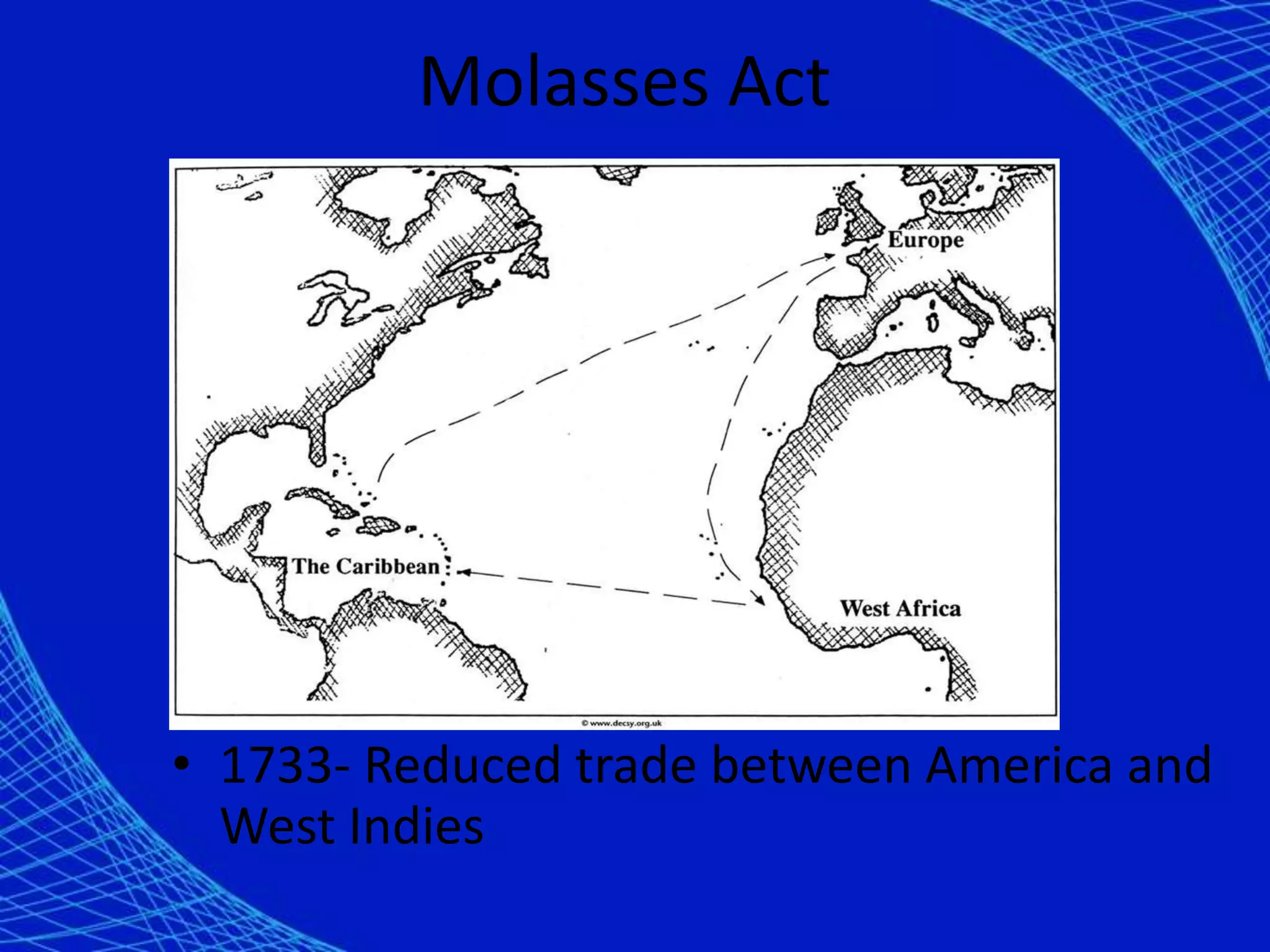
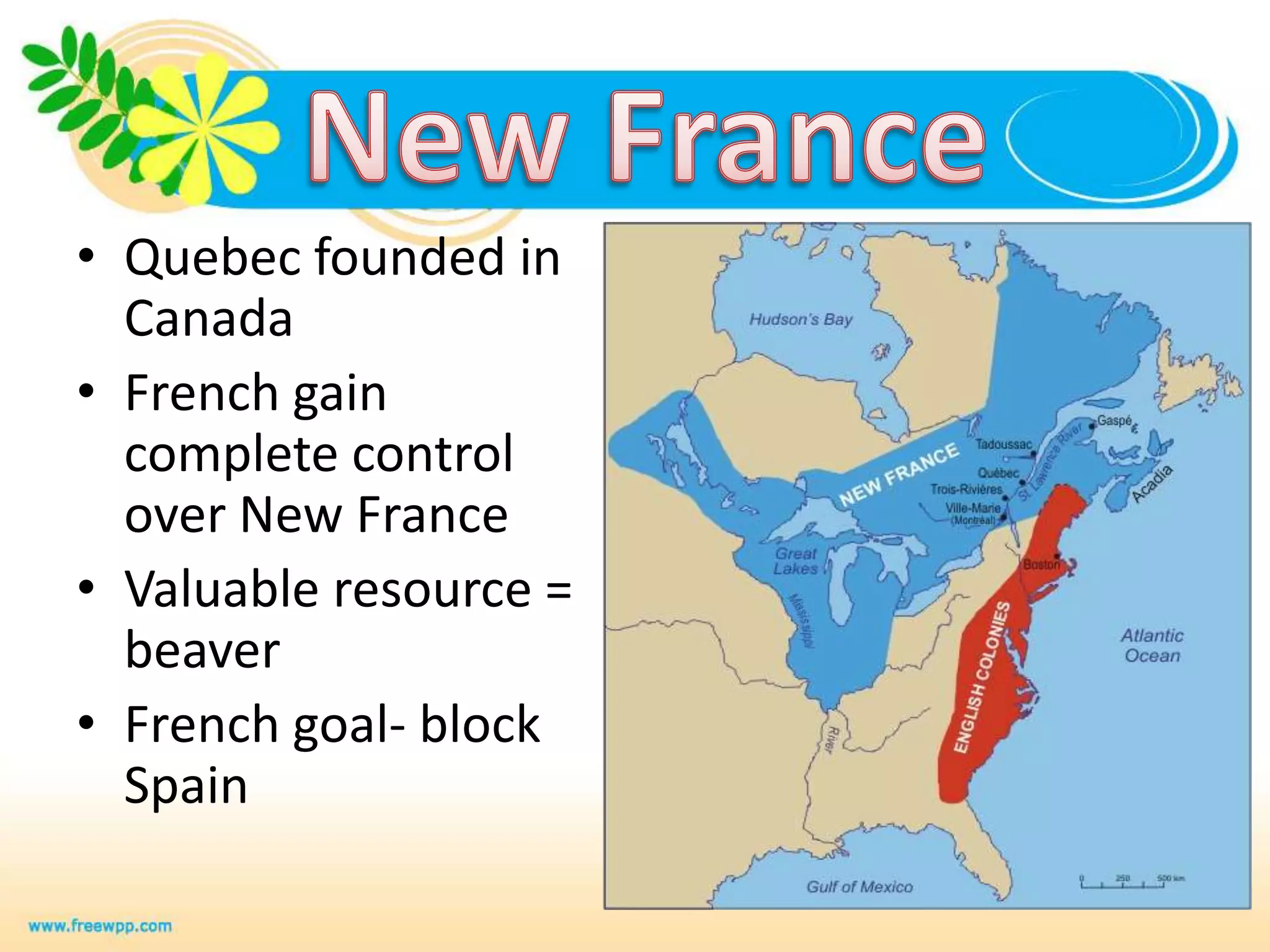
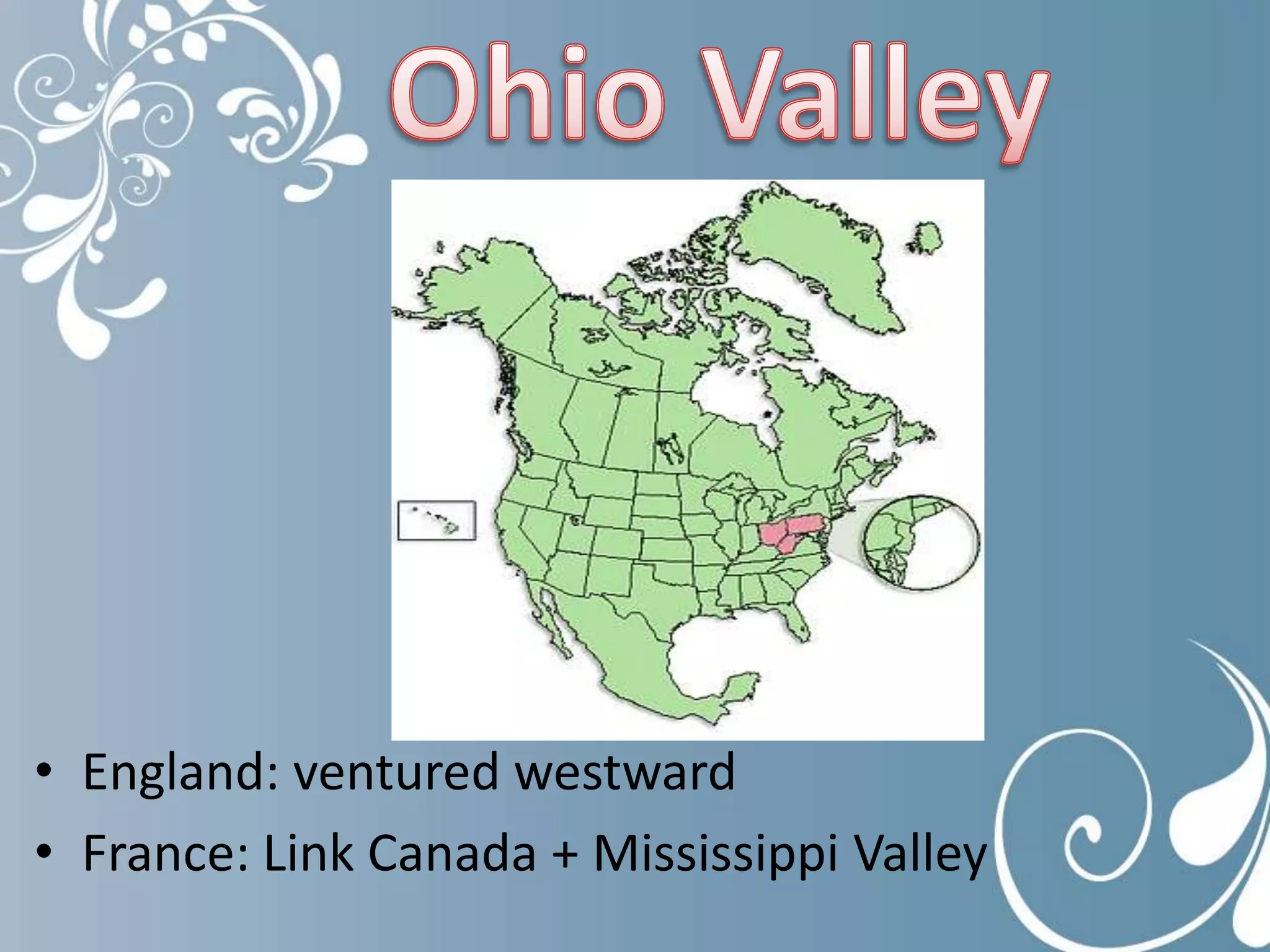
1. The study guide covers 10 chapters on American history from early civilizations like the Aztecs to the early administrations under Washington.
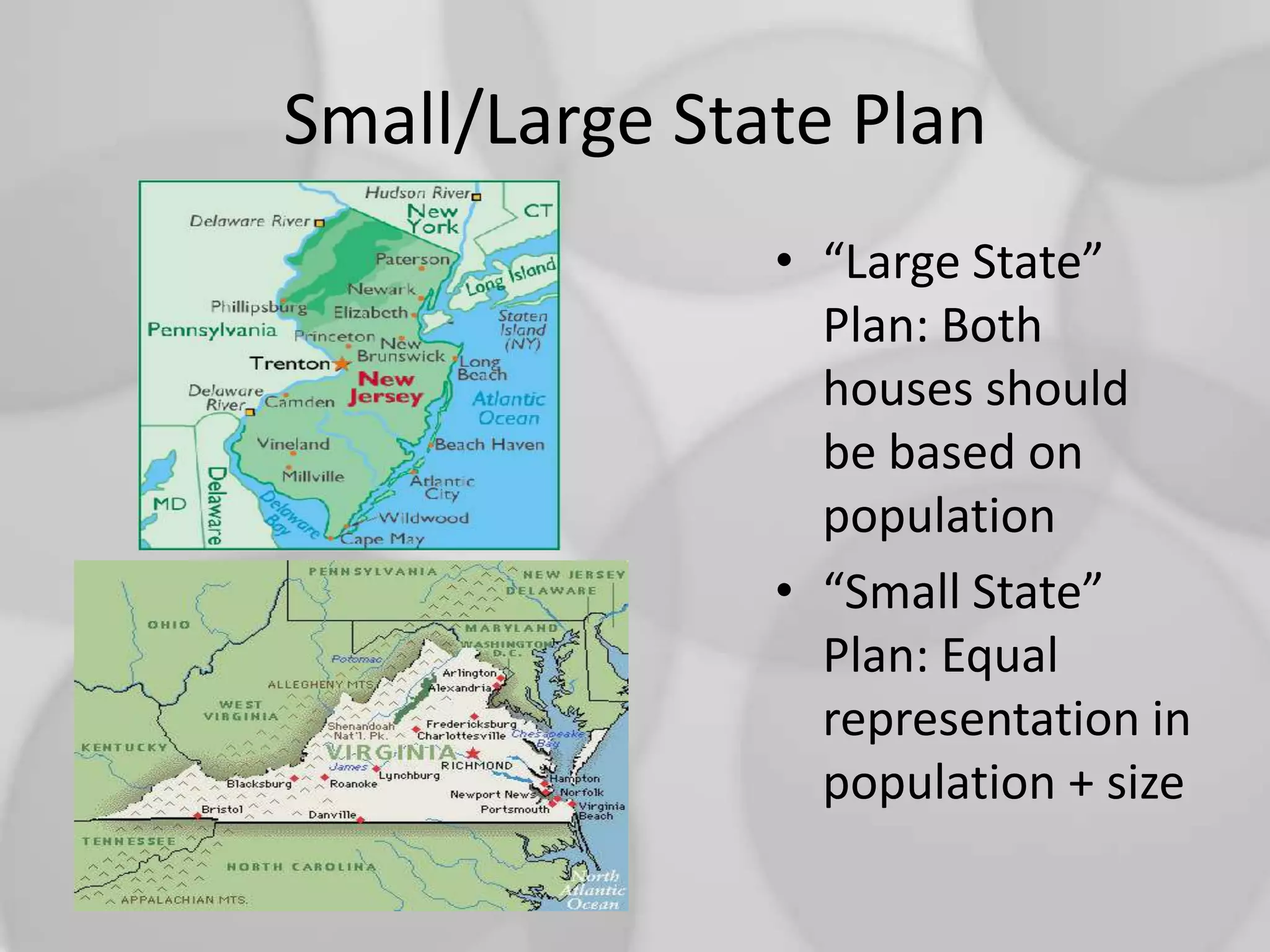
2. Key topics include European exploration and colonization, the development of distinct regional colonies, conflicts with Native Americans, the causes and events of the American Revolution, and the creation of the US governmental system under the Constitution.
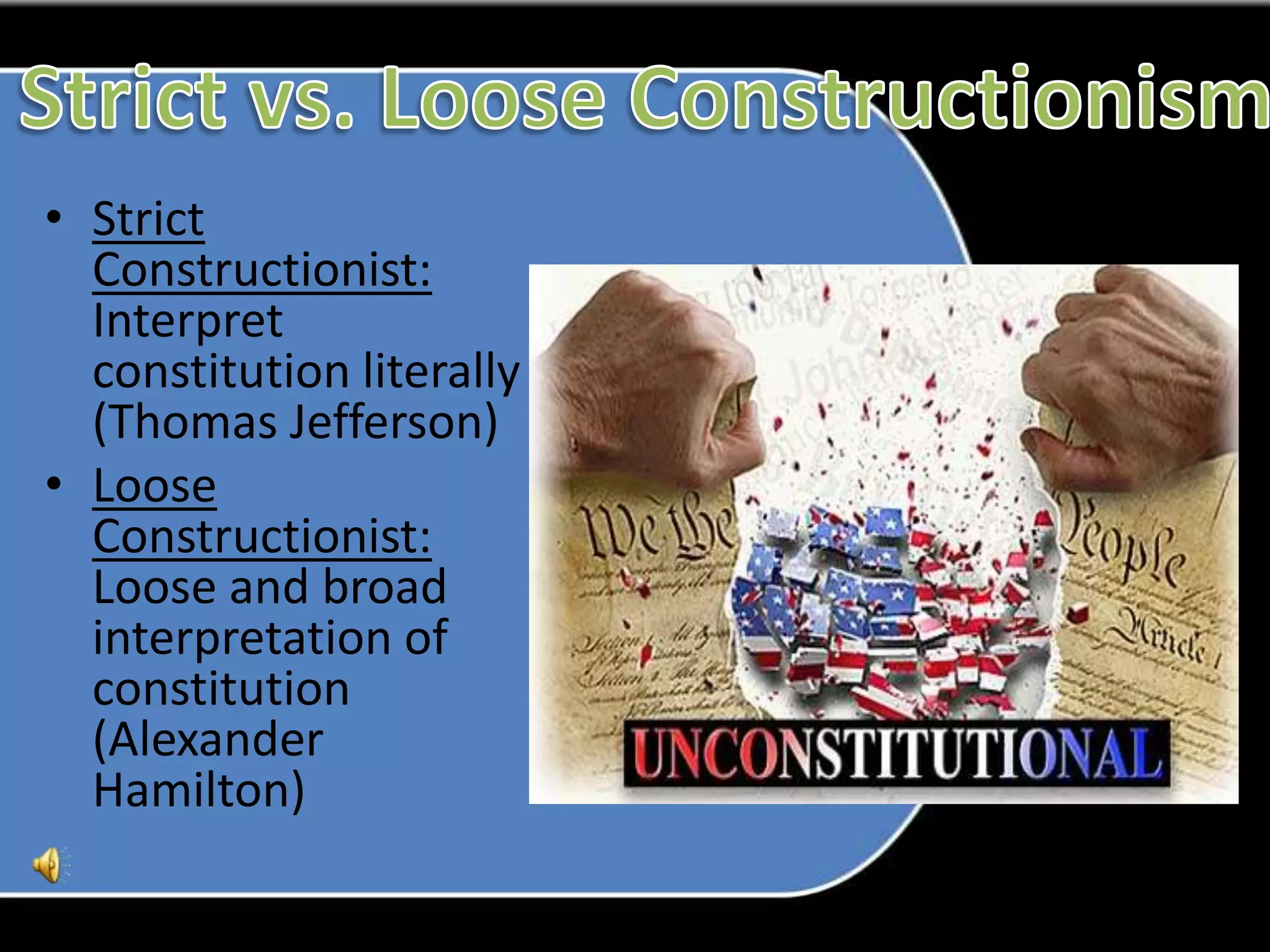
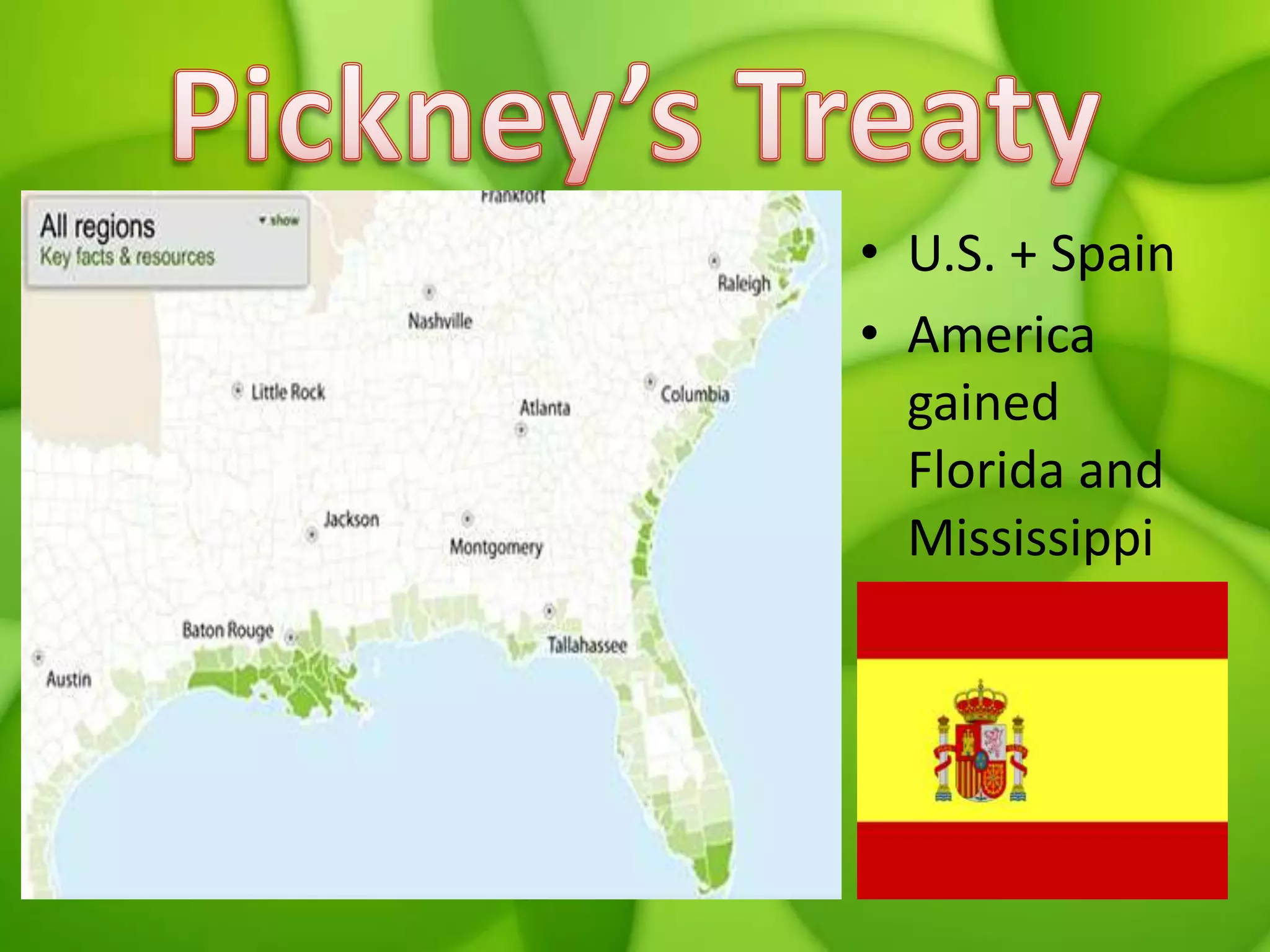
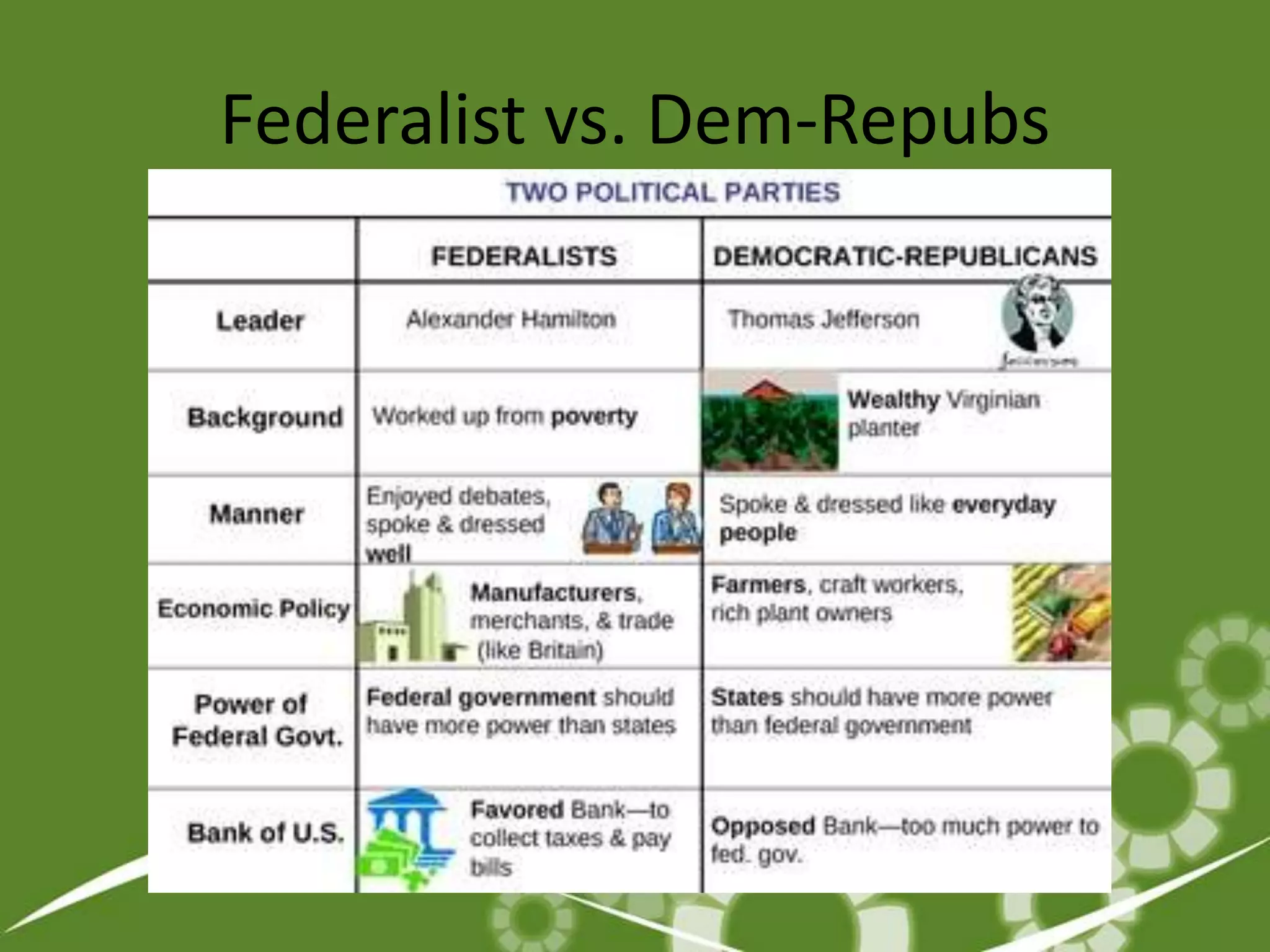
3. Challenges in the early decades included developing a national economy, tensions between Federalists and Democratic-Republicans over the scope of federal power, and maintaining neutrality in European conflicts.