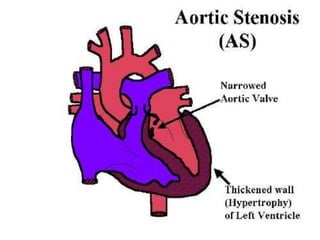
1. Aortic stenosis can be caused by rheumatic heart disease, congenital abnormalities of the aortic valve, or age-related degeneration and calcification of the valve.
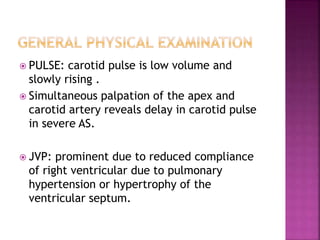
2. Obstructed left ventricular outflow due to aortic stenosis leads to increased pressure and compensatory hypertrophy of the left ventricle. While cardiac output is maintained at rest, it often fails to rise normally during exertion in severe aortic stenosis.
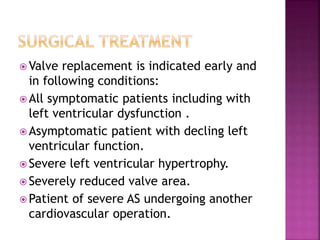
3. Symptoms of aortic stenosis include angina, syncope, exertional dyspnea, and heart failure, which typically appear when the aortic orifice is reduced to one third of its normal size. Valve replacement surgery is