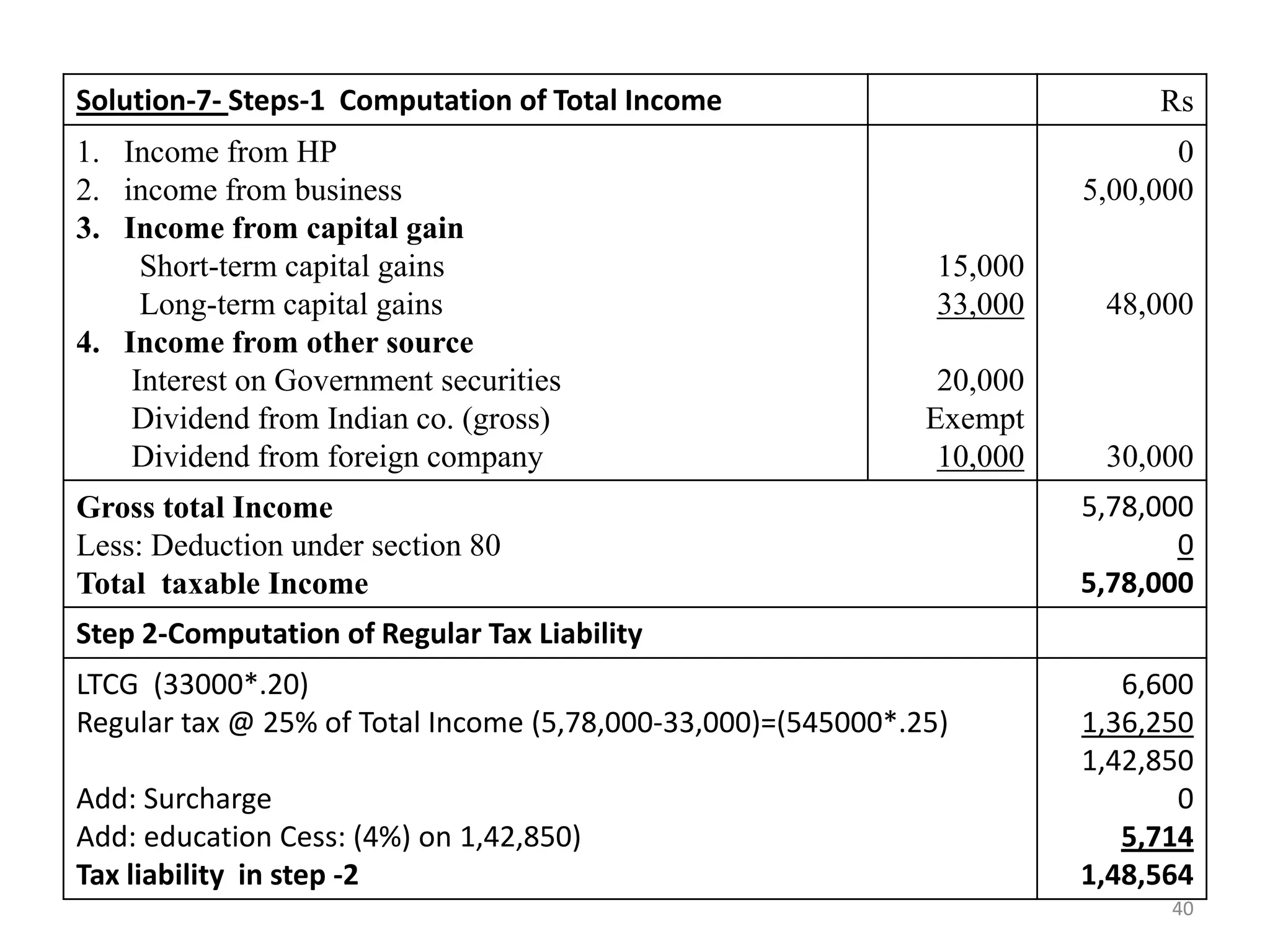
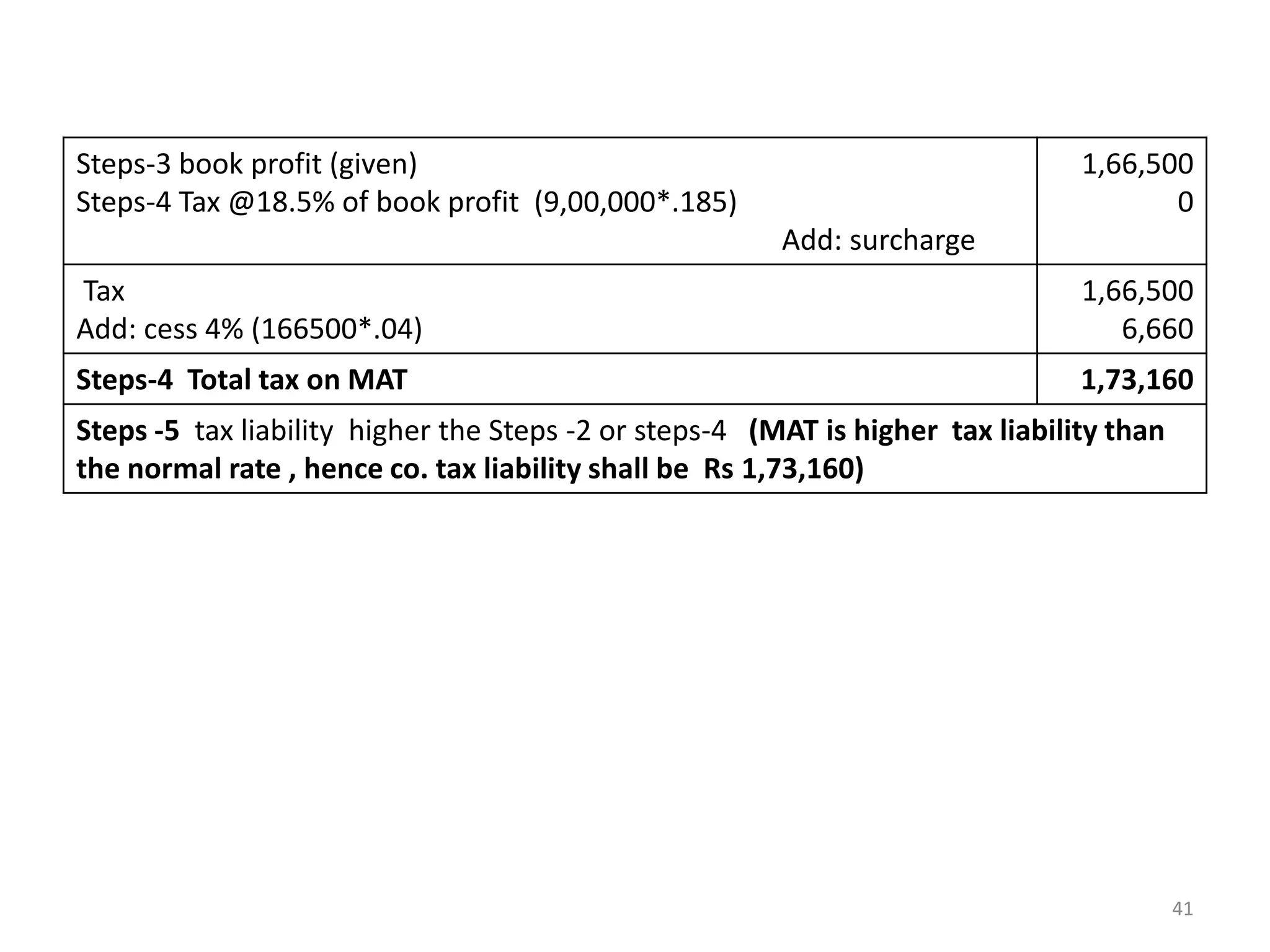
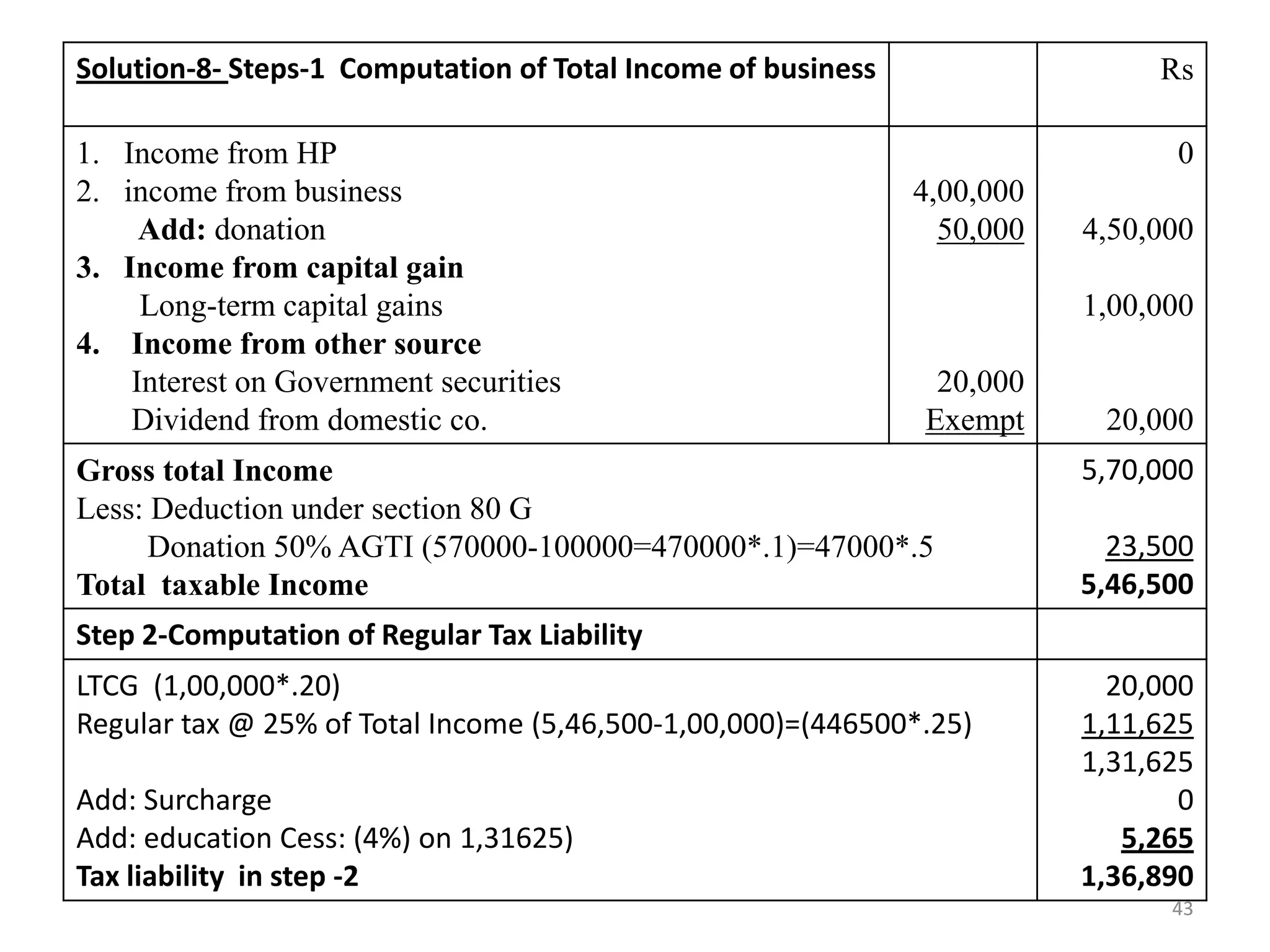
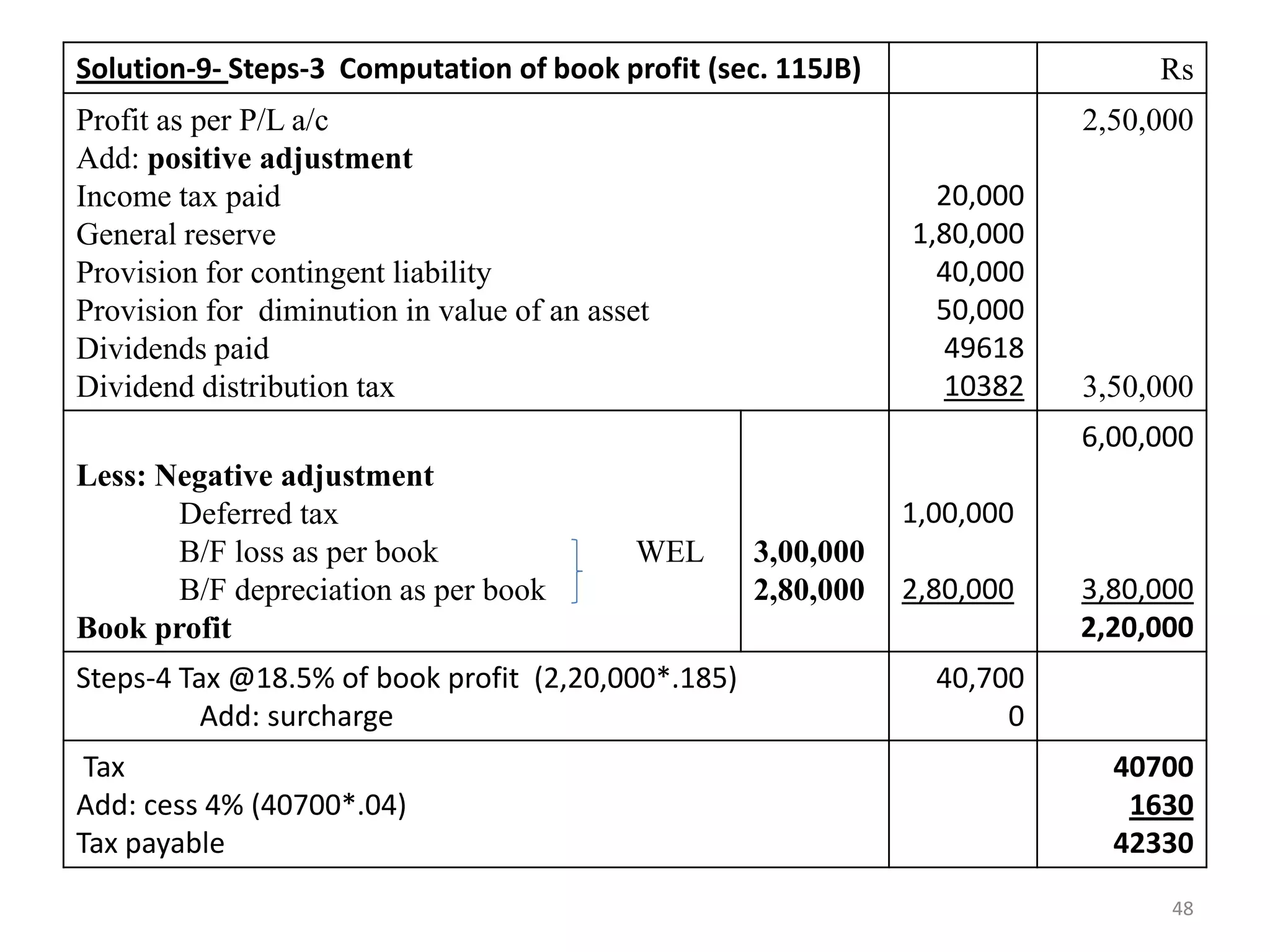
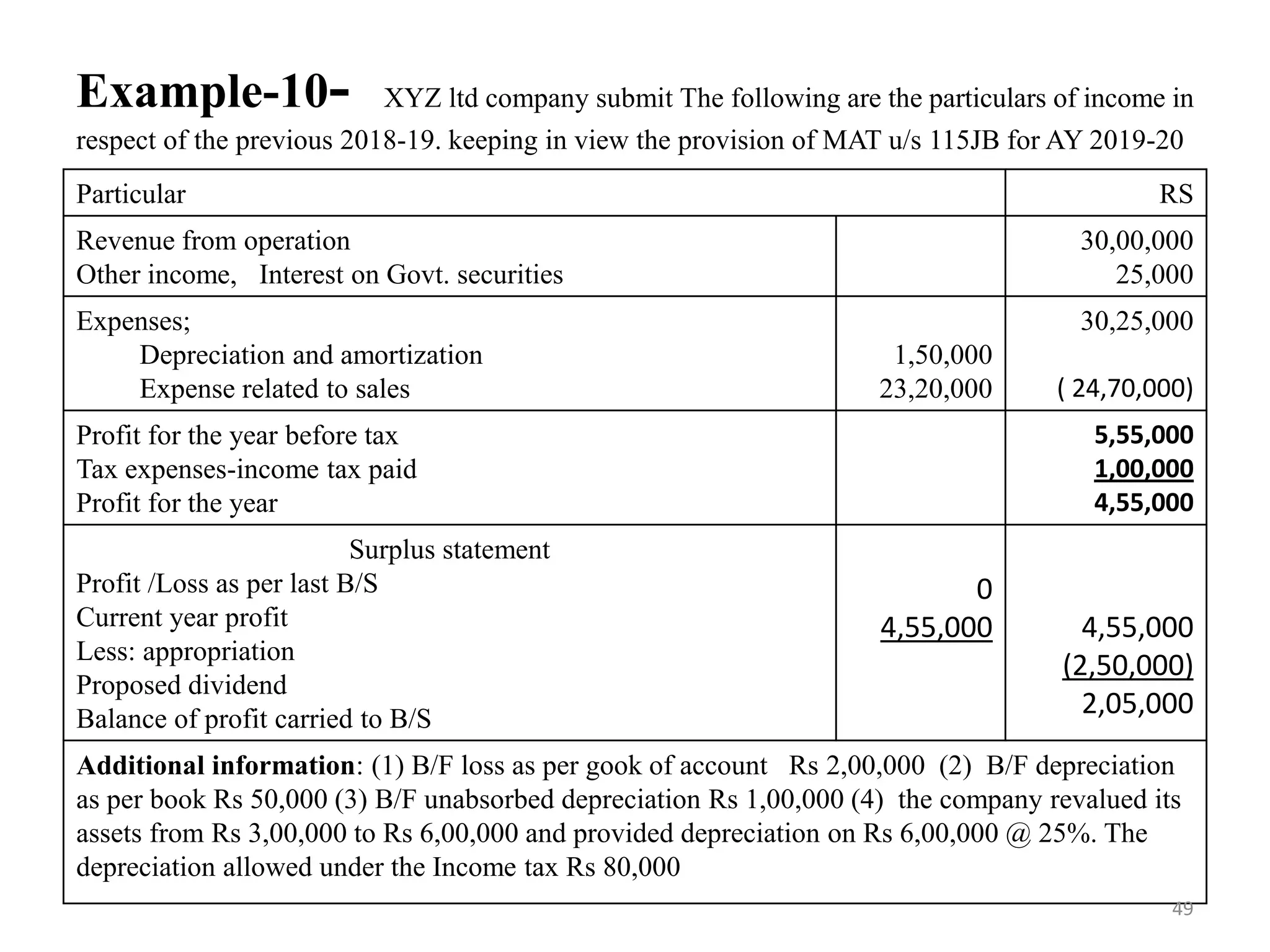
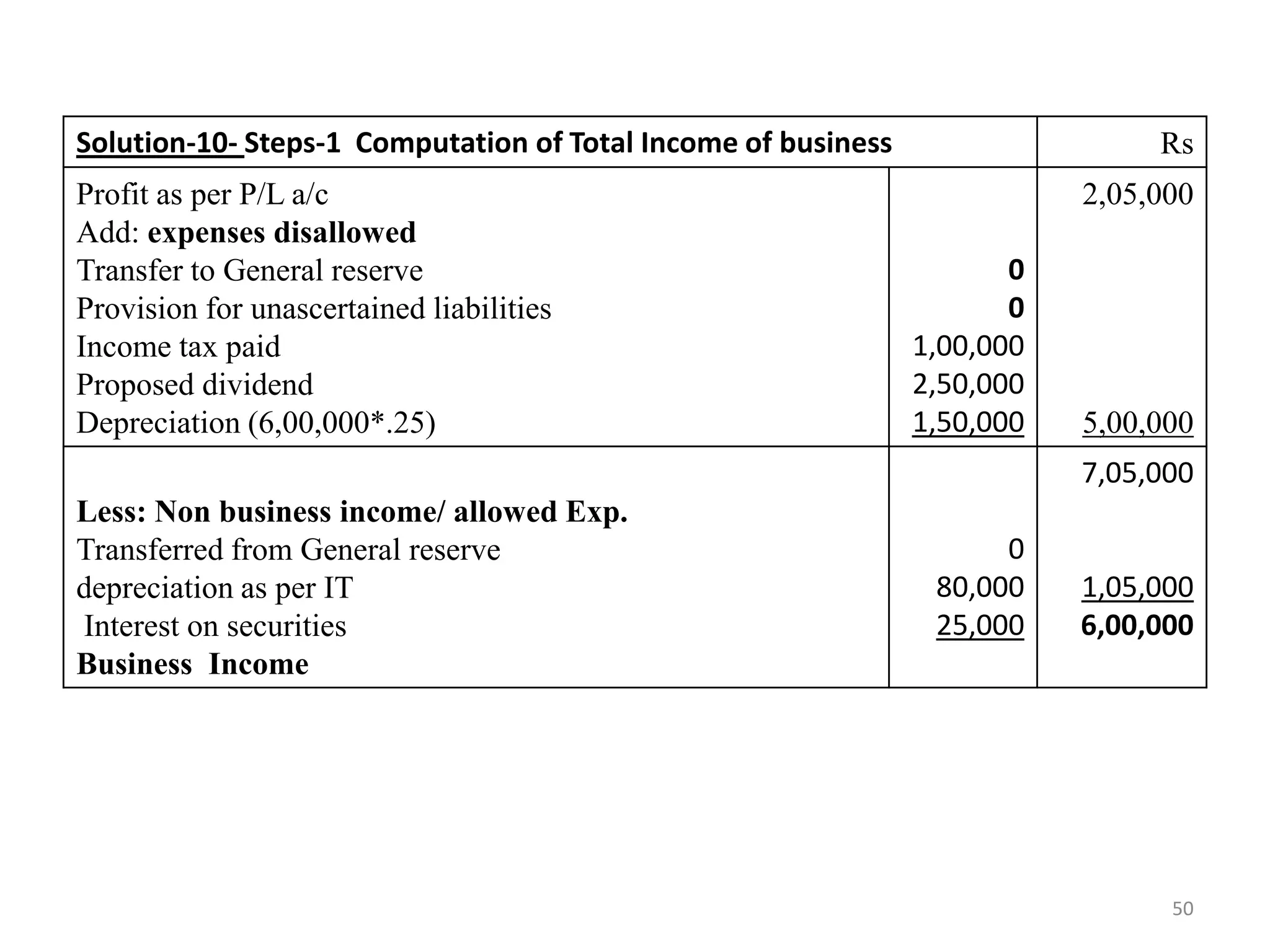
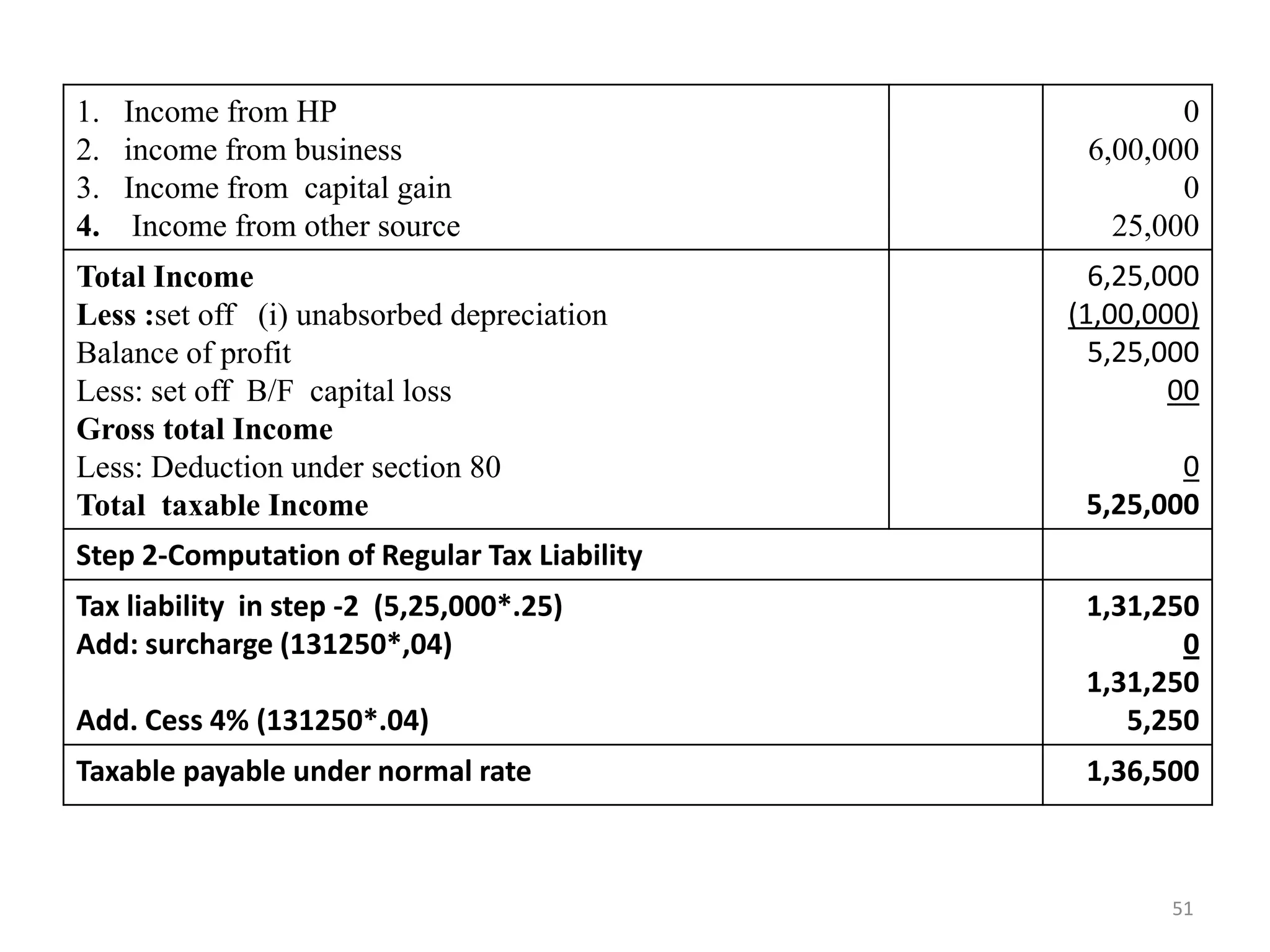
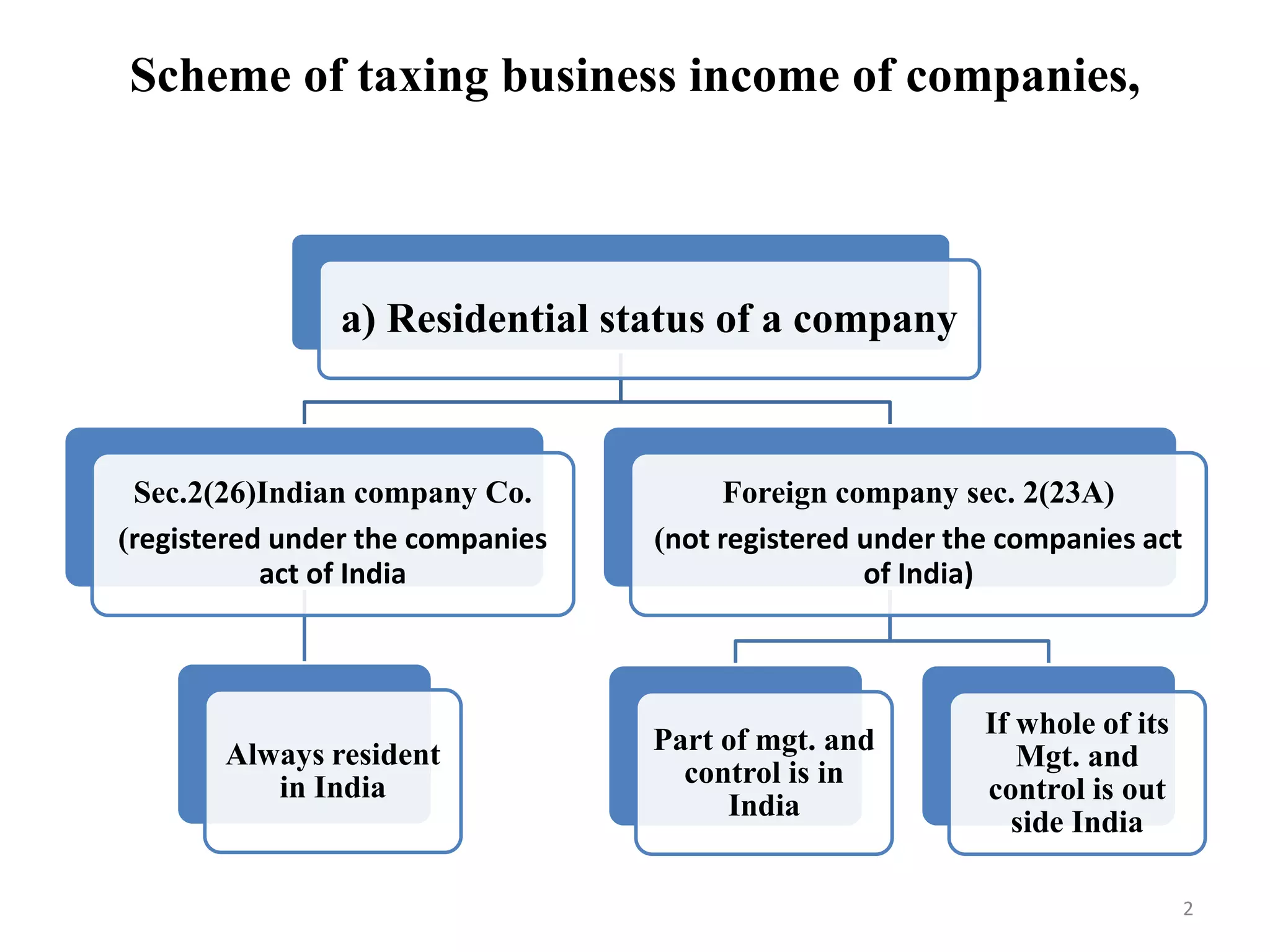
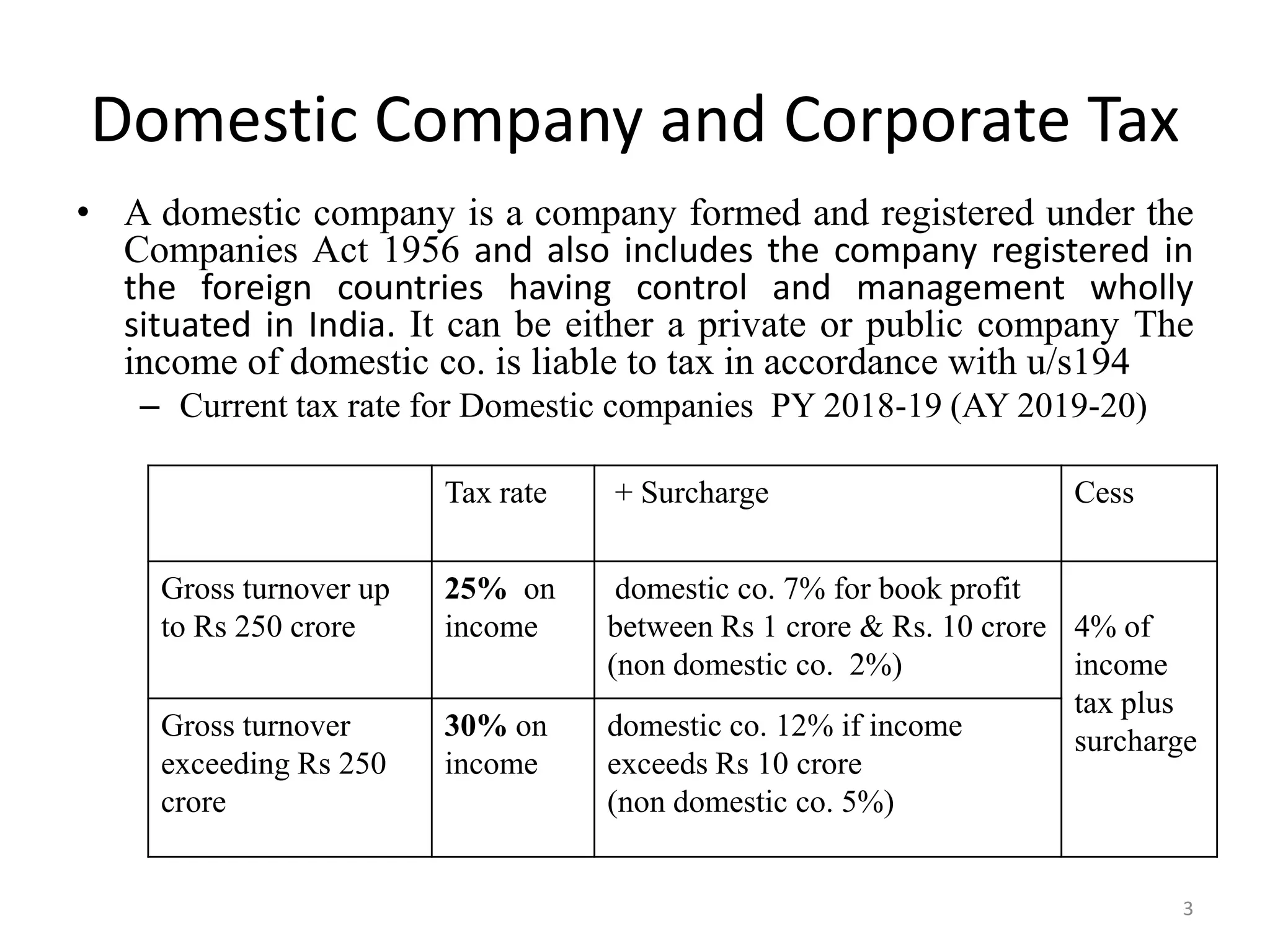
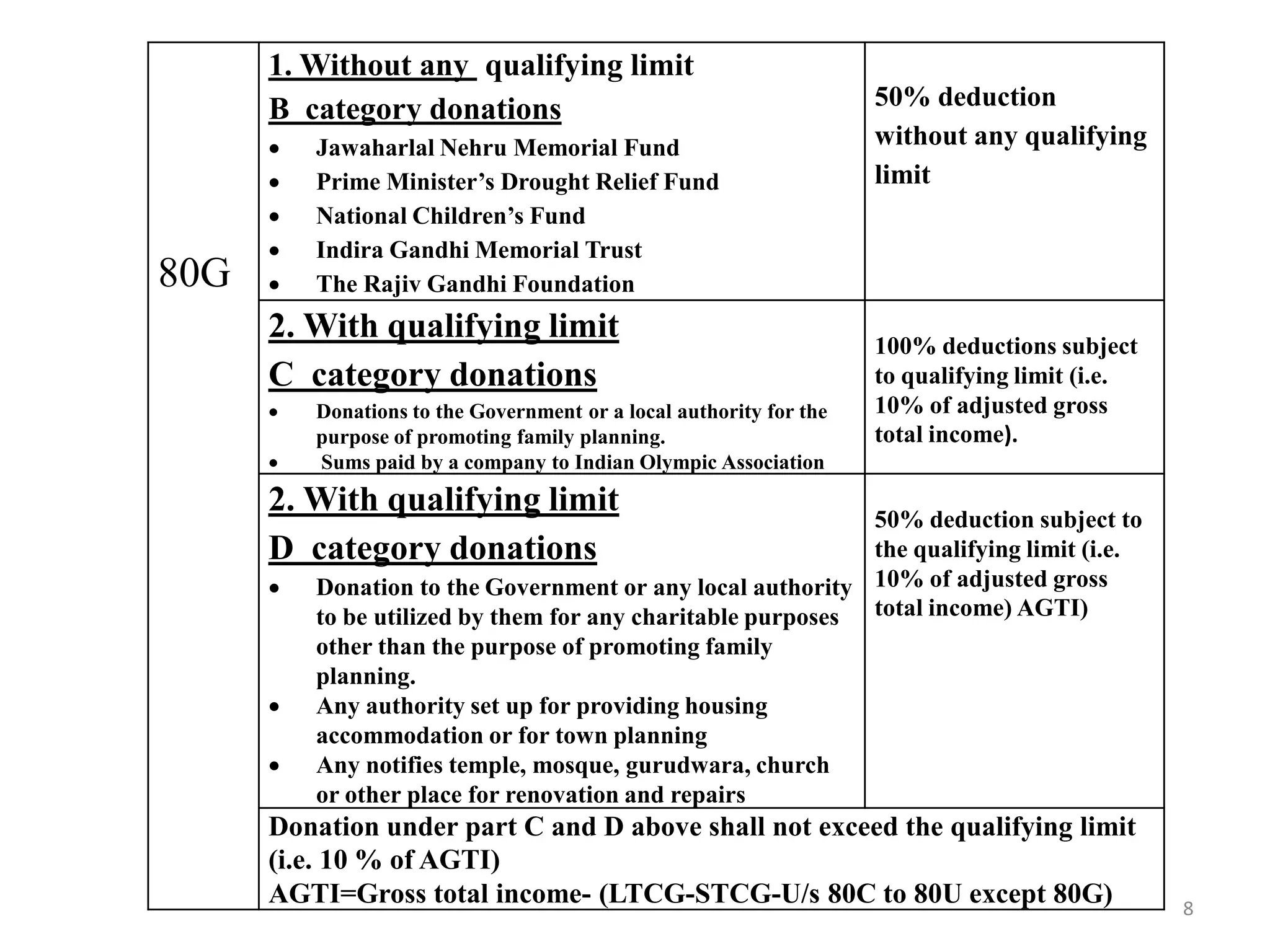
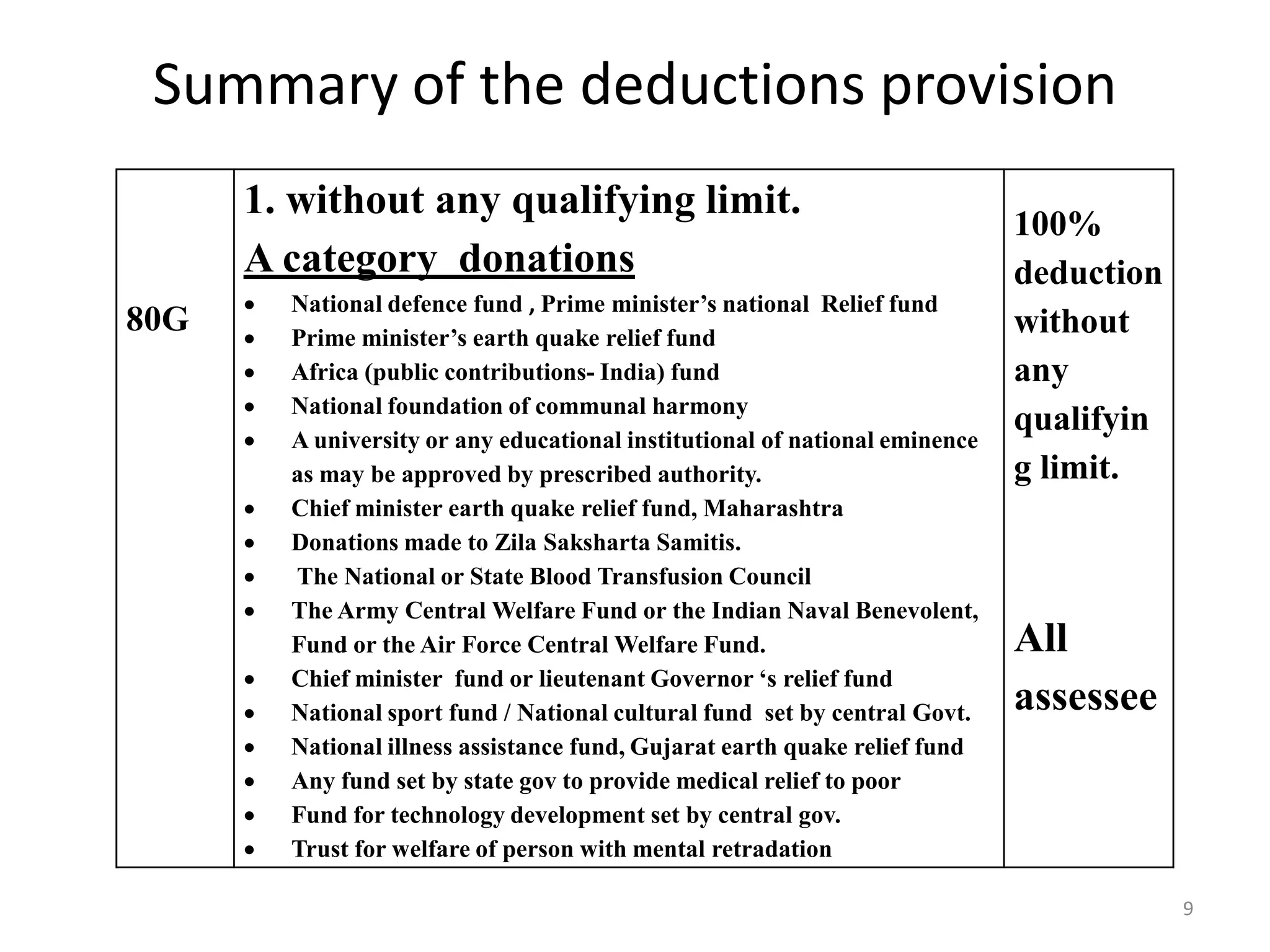
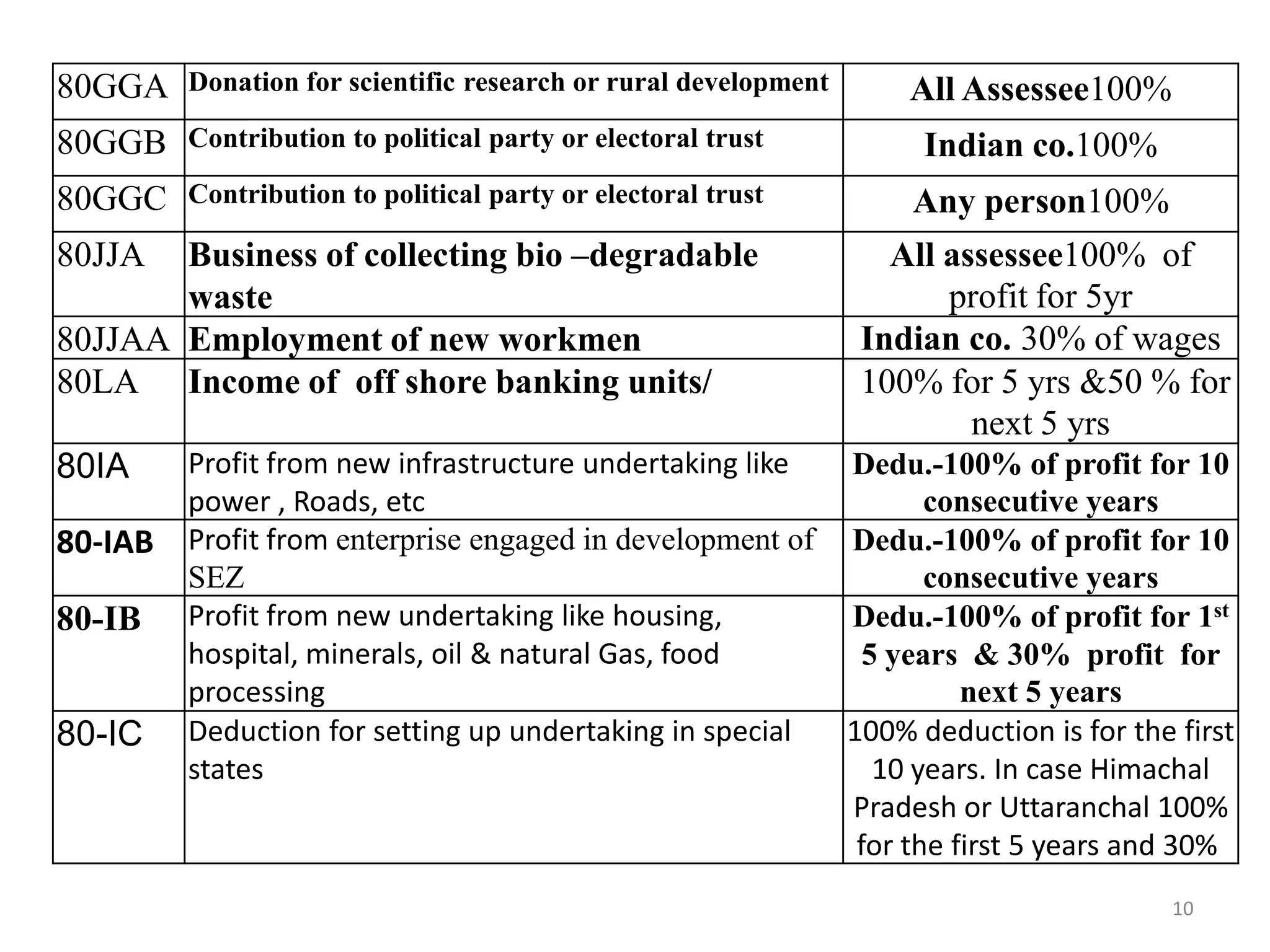
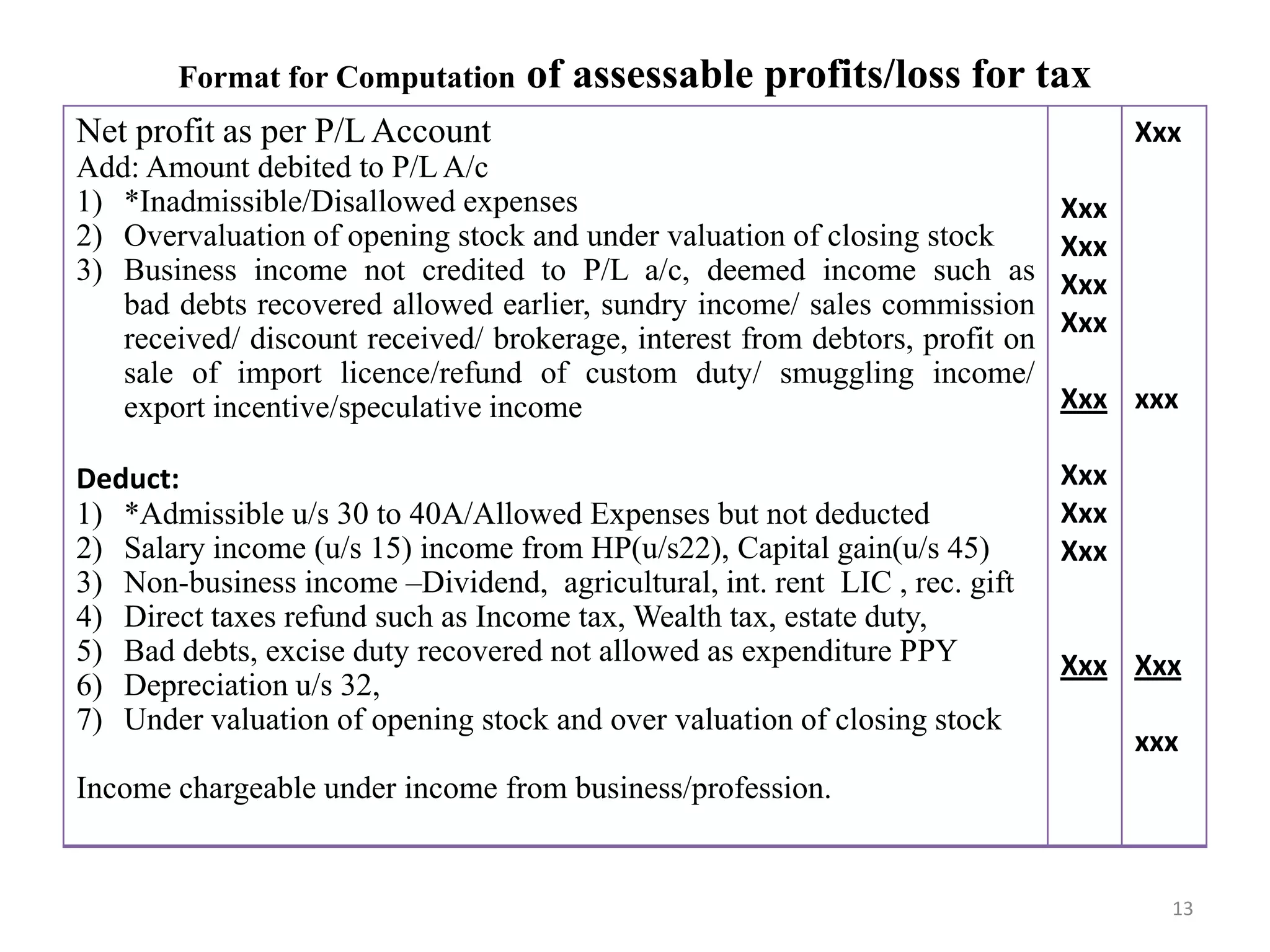
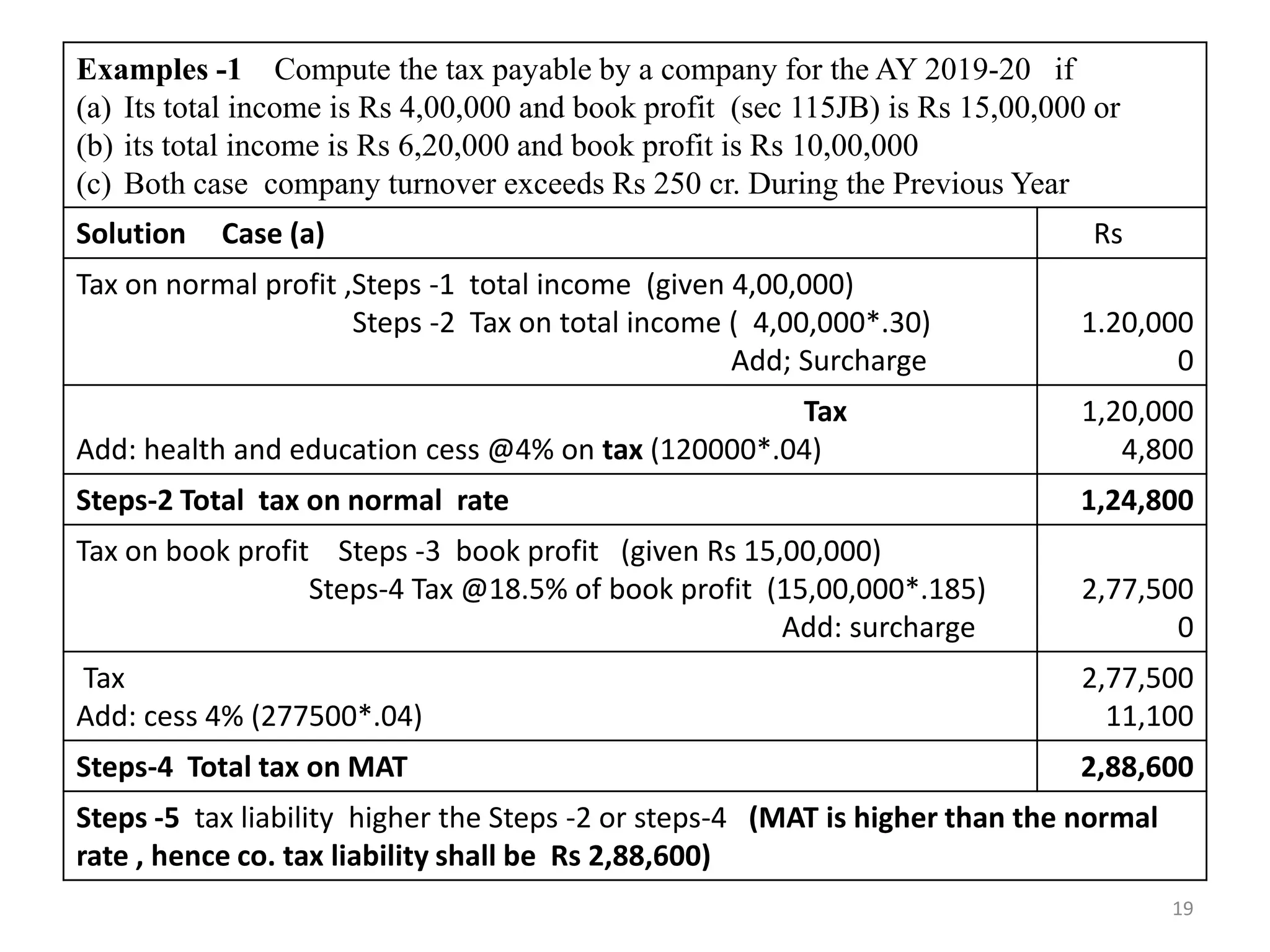
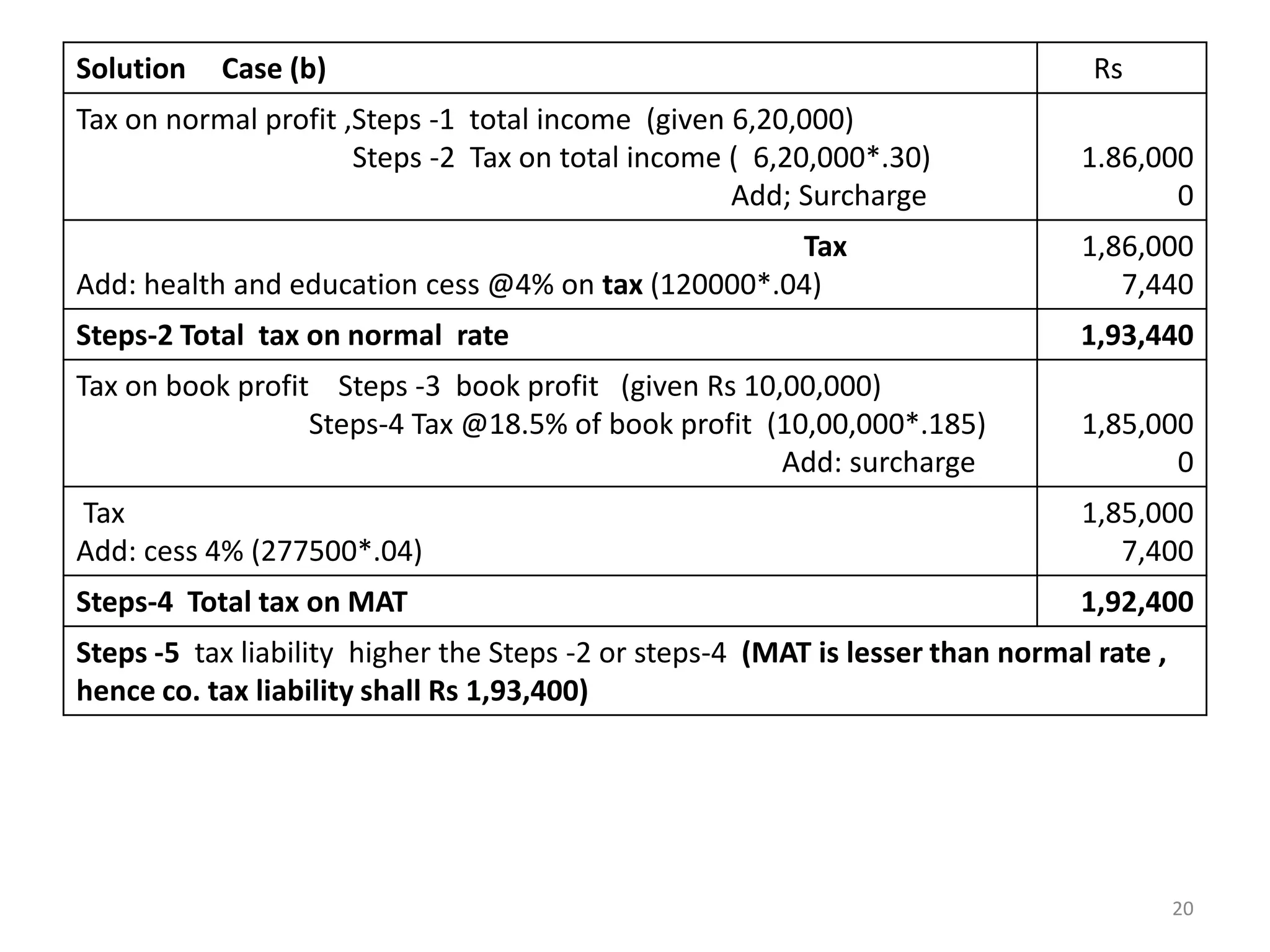
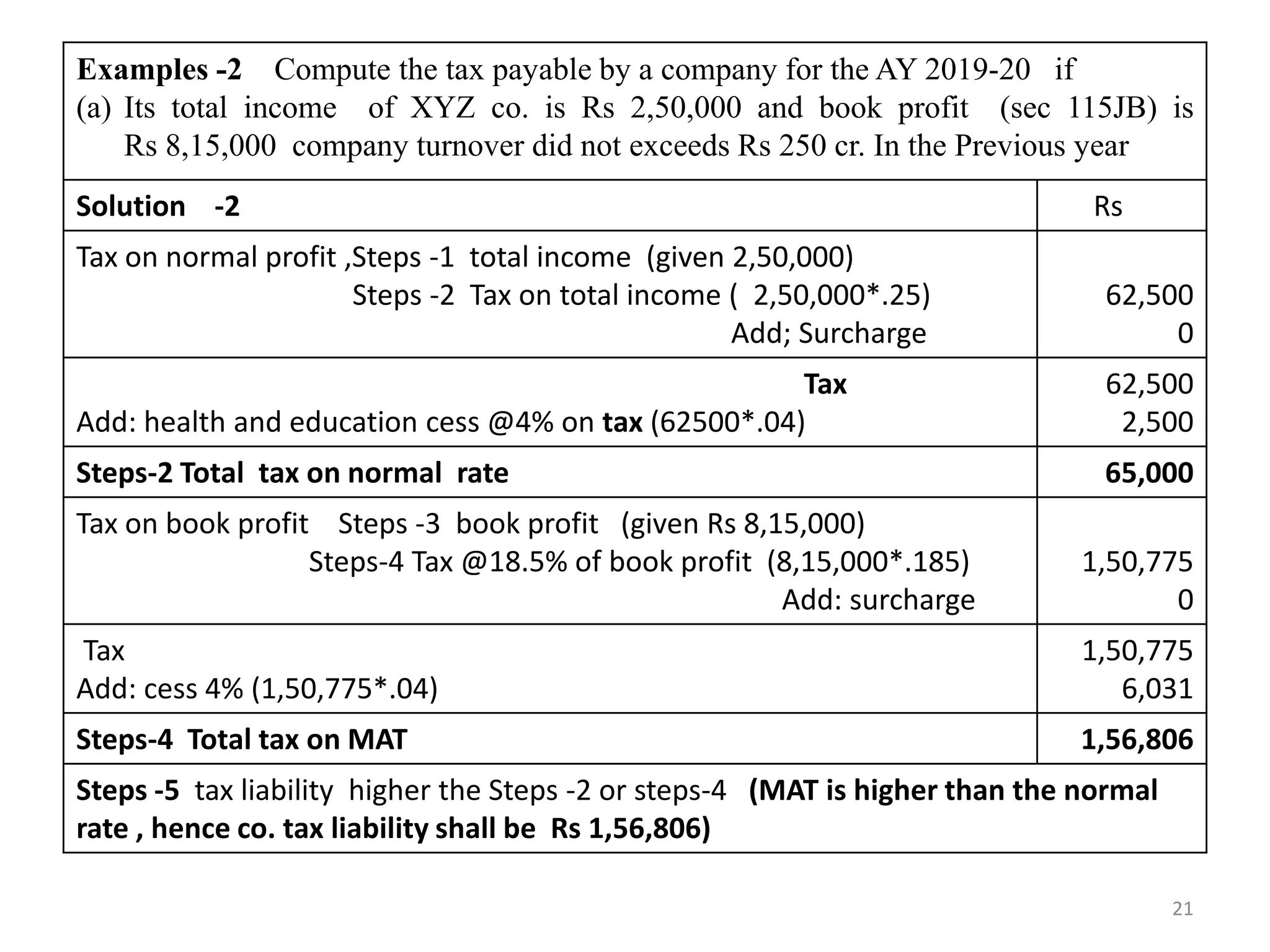
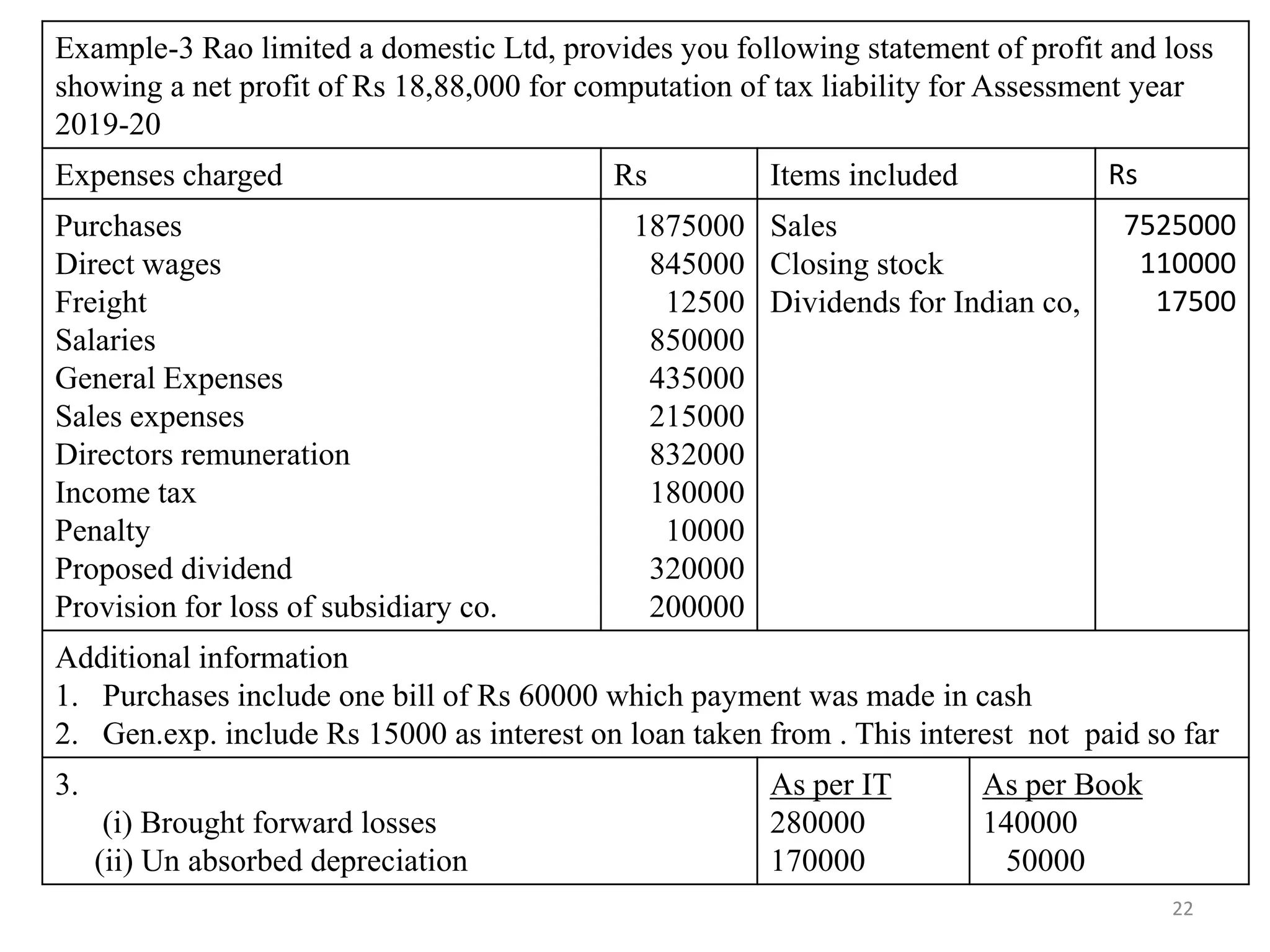
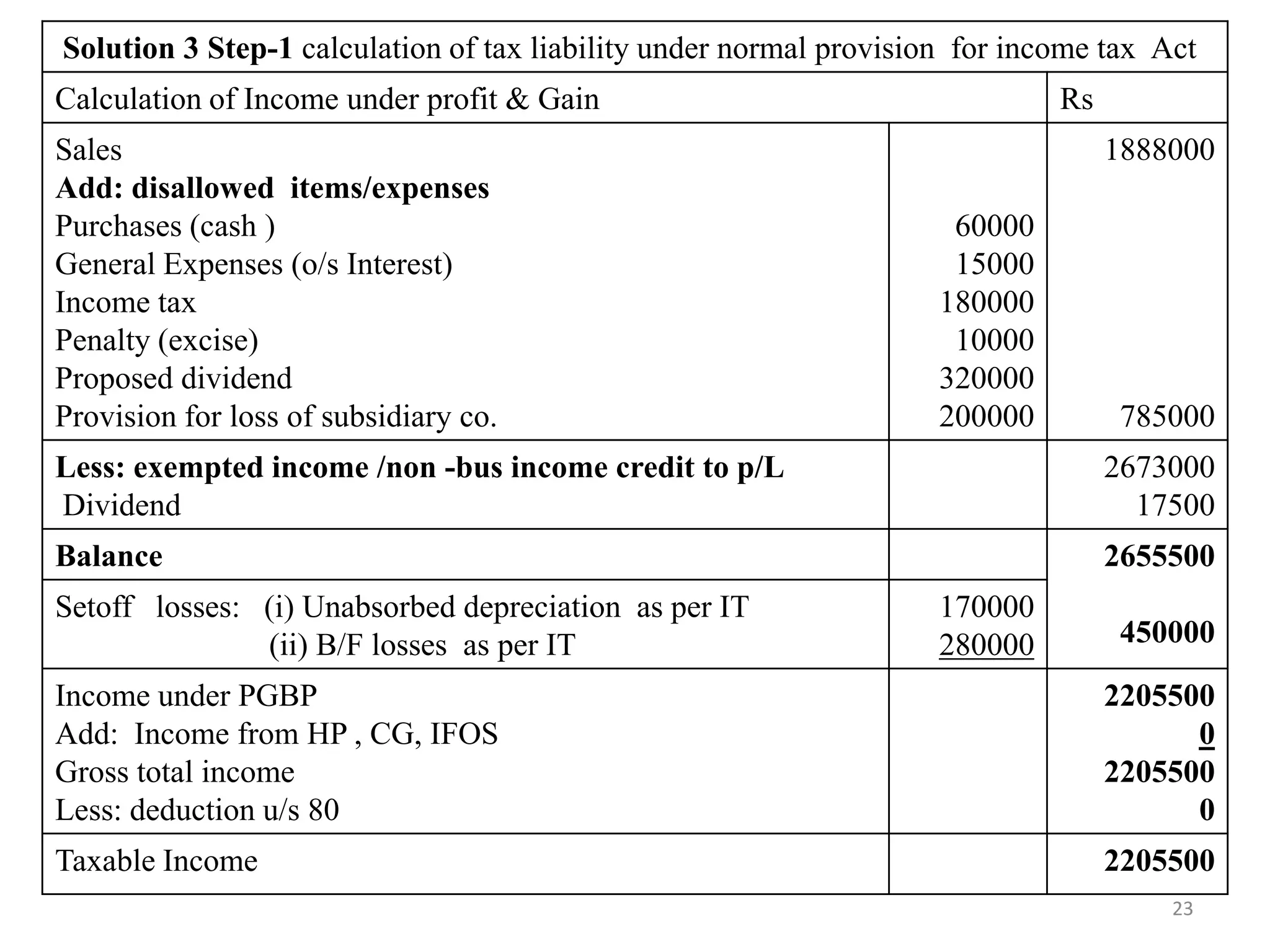
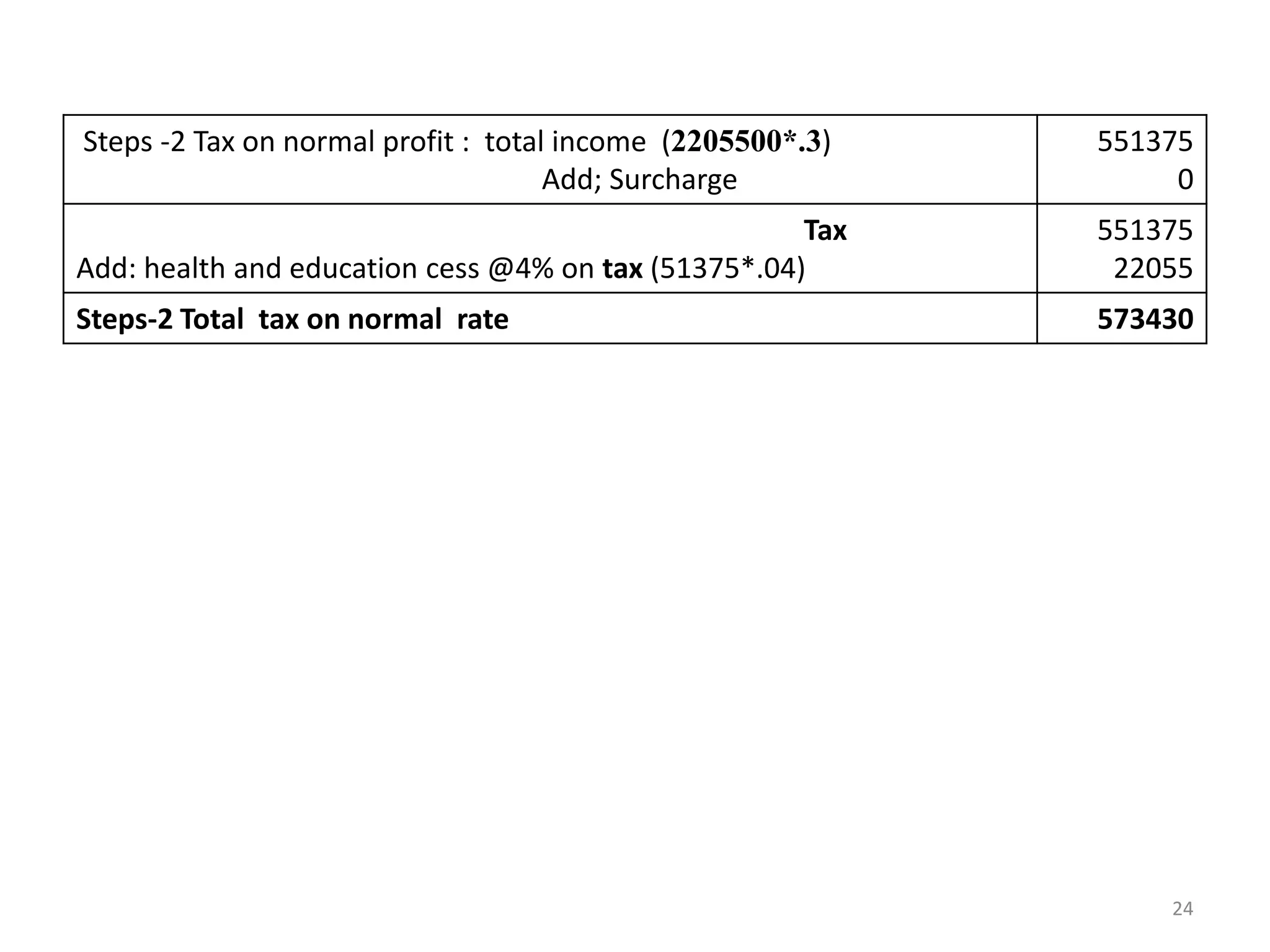
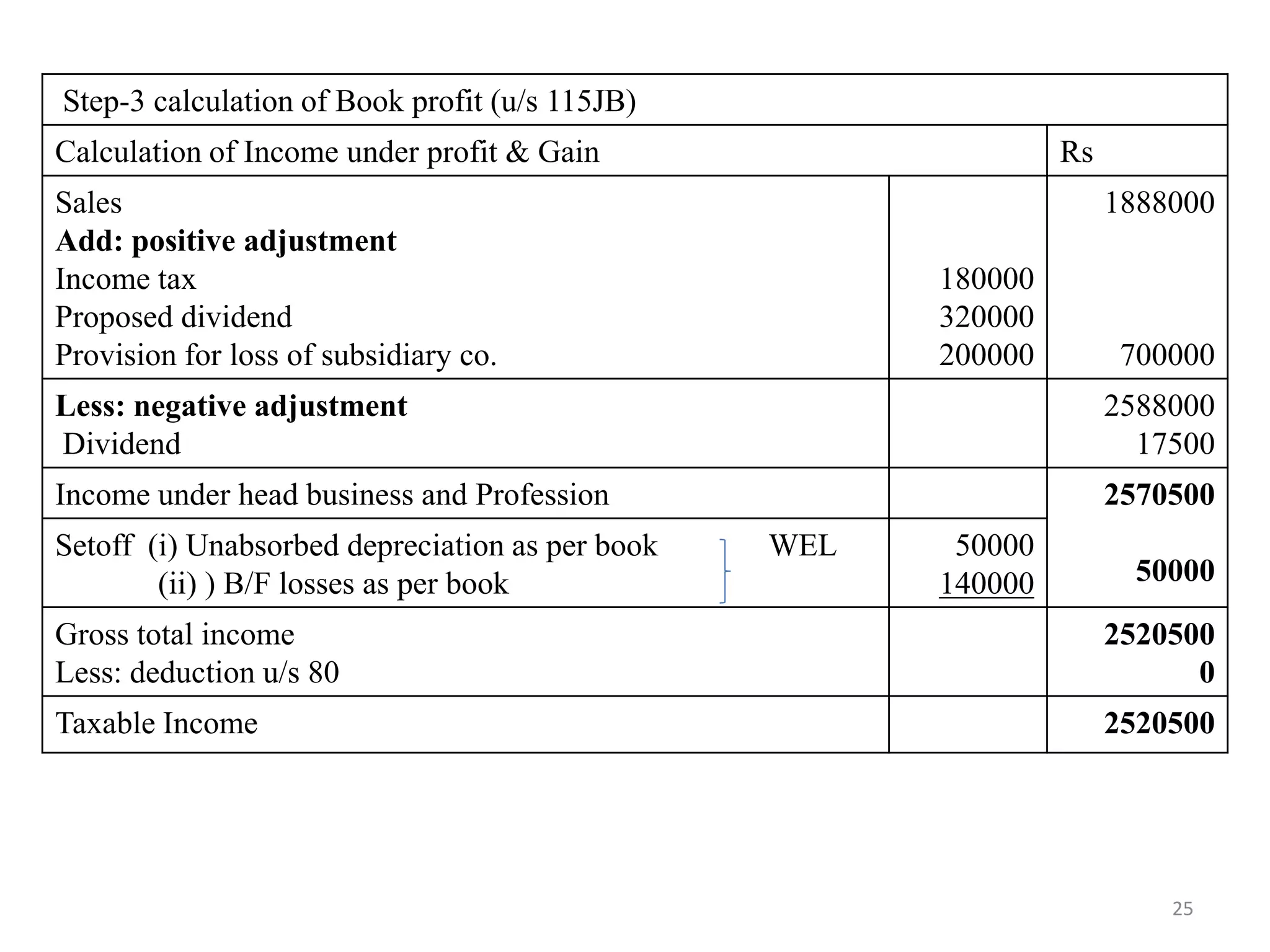
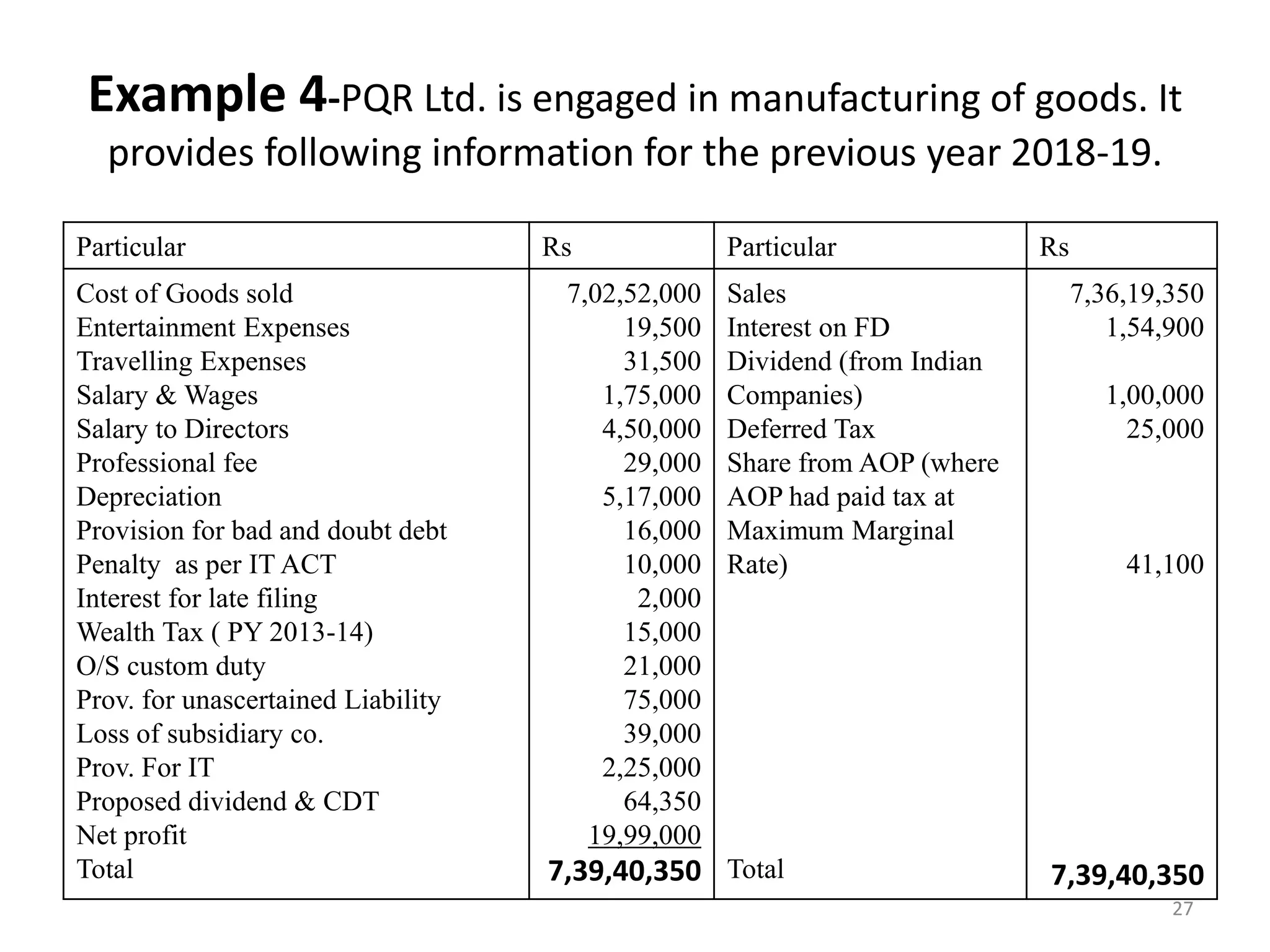
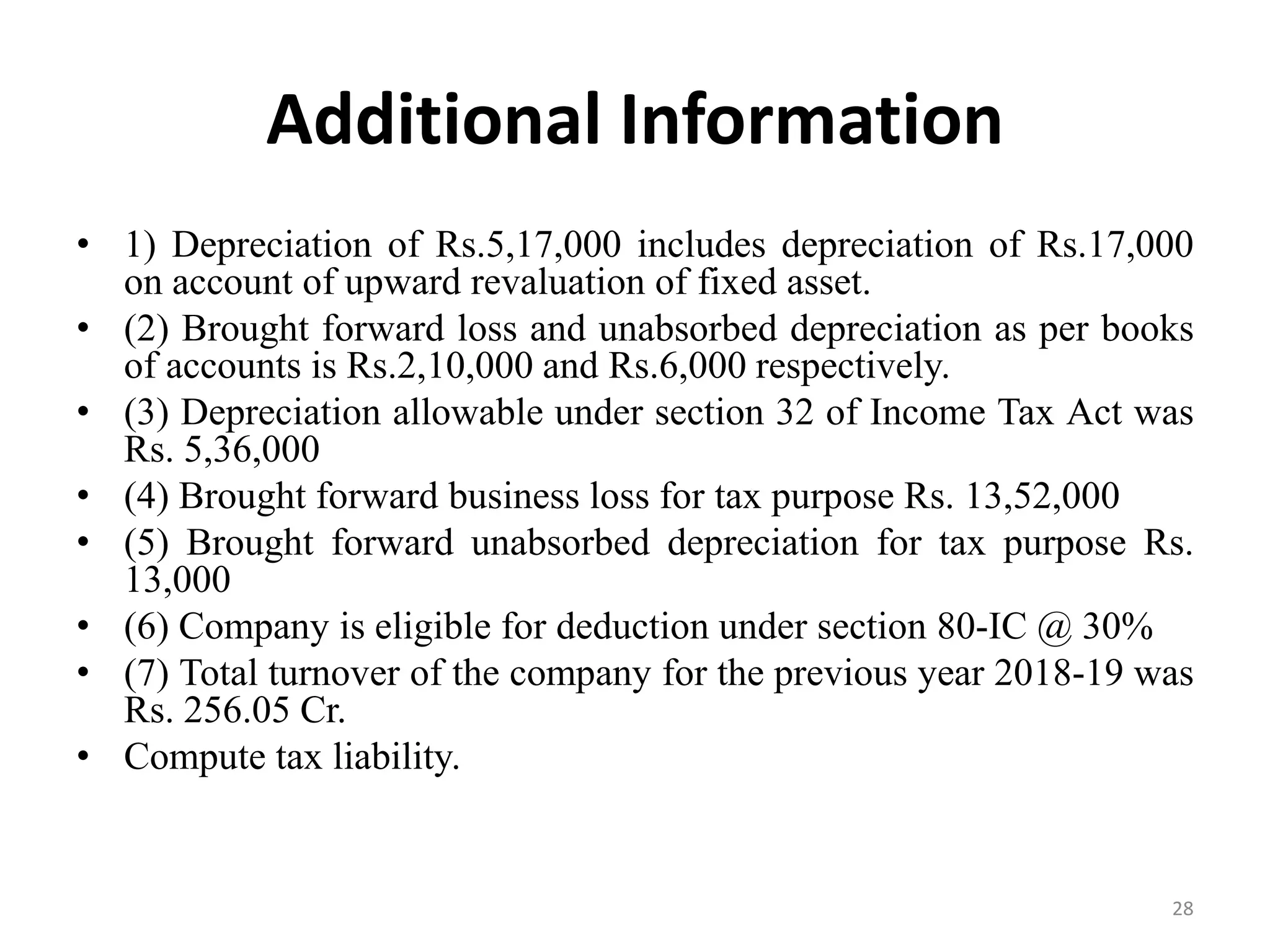
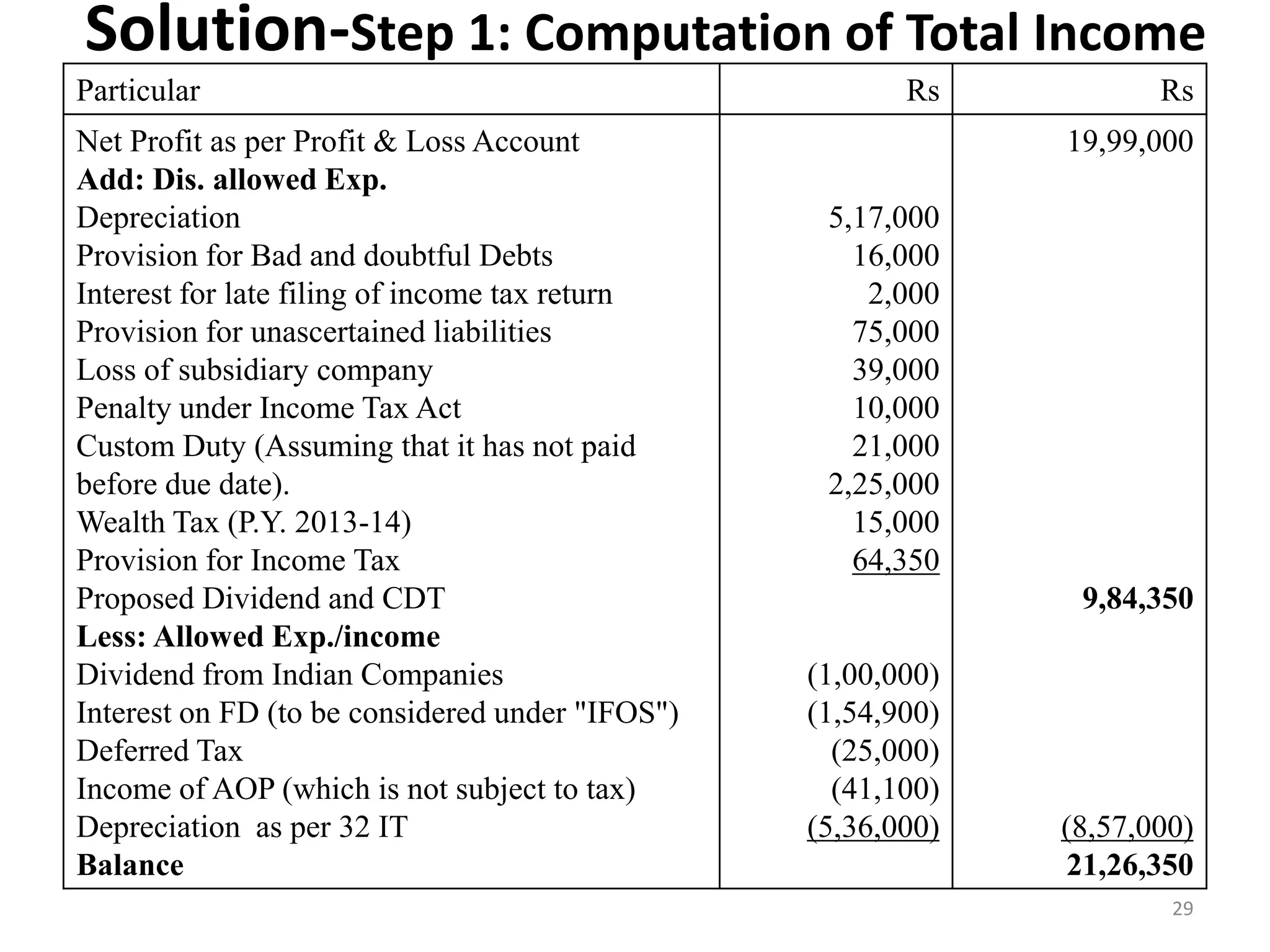
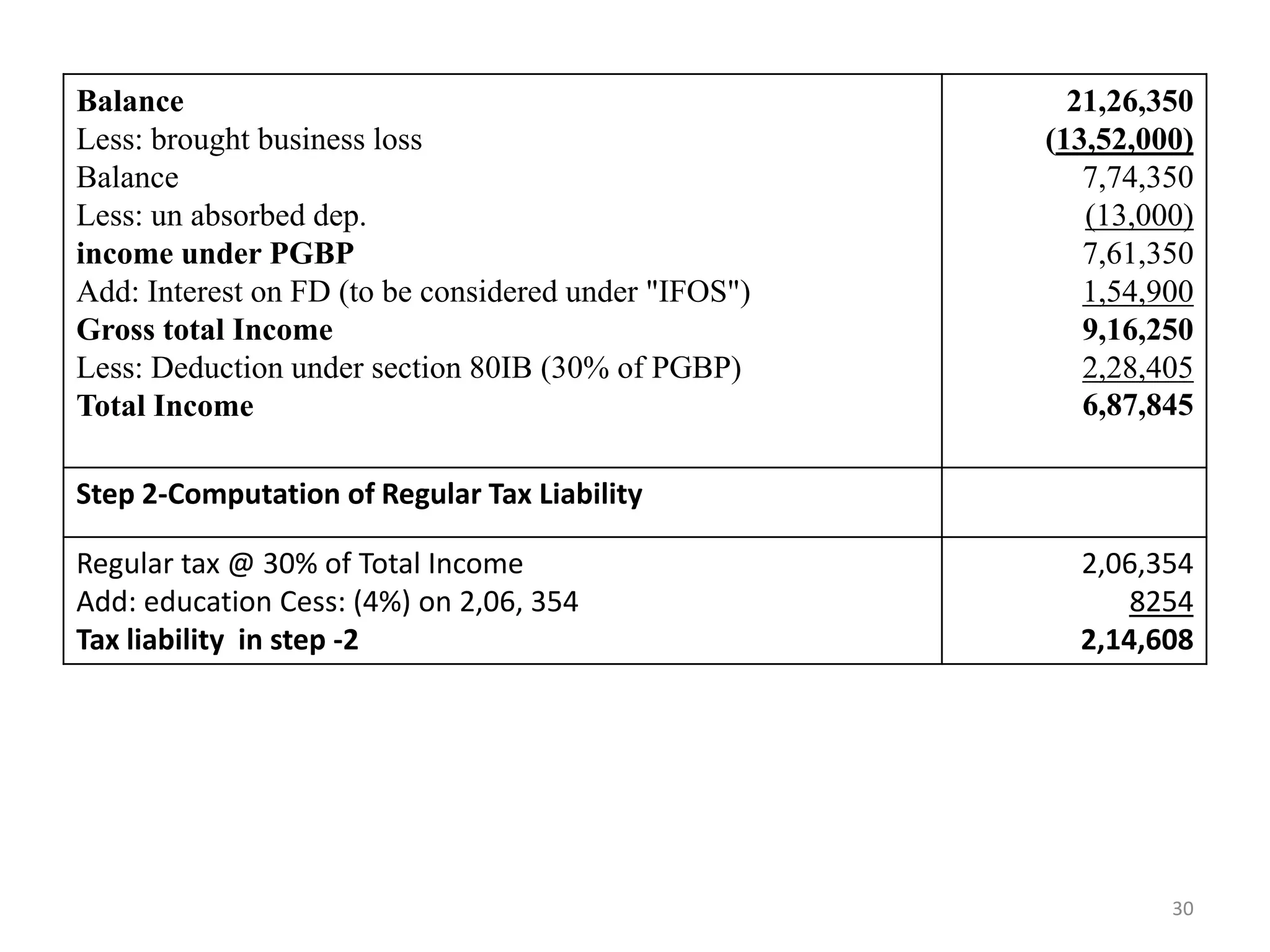
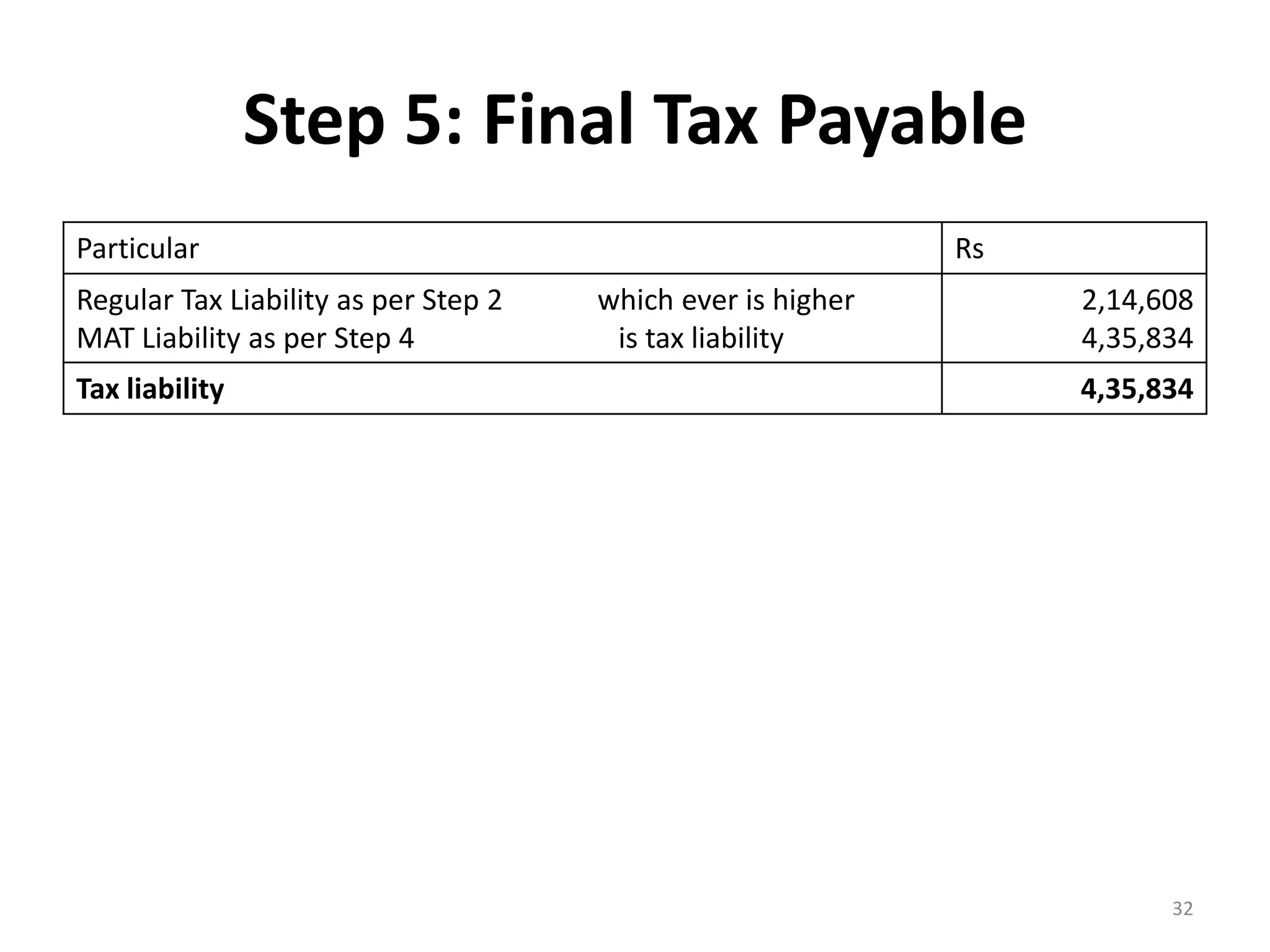
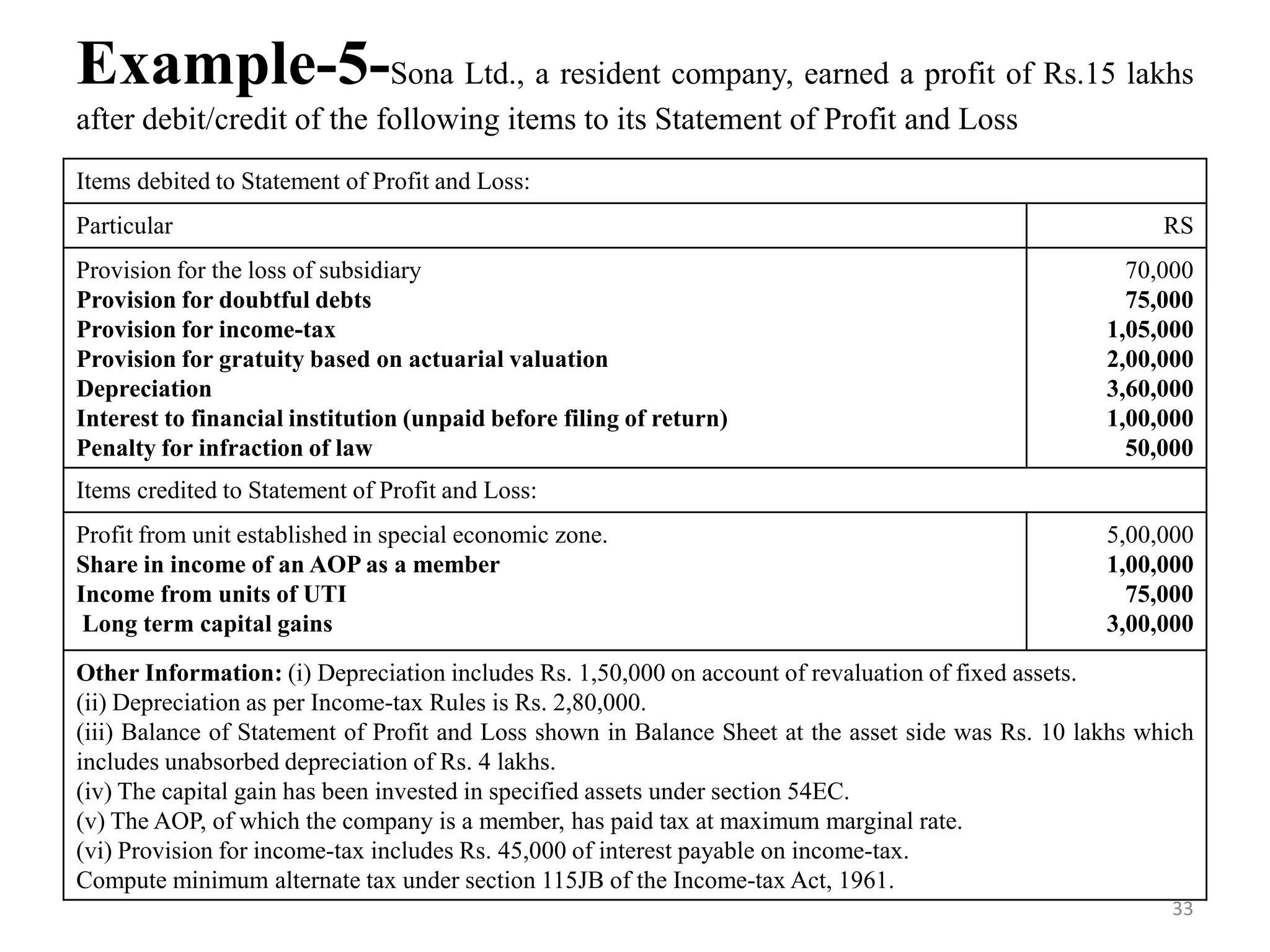
The document discusses the taxation scheme for business income of companies in India, detailing the residential status of companies, corporate tax rates for domestic and foreign companies, and the computation of gross total income. It covers provisions for set-off and carry forward of losses, deductions under section 80G, and minimum alternate tax for companies with book profits. Additionally, the document includes steps for computing tax liability and examples illustrating the calculation of payable tax.






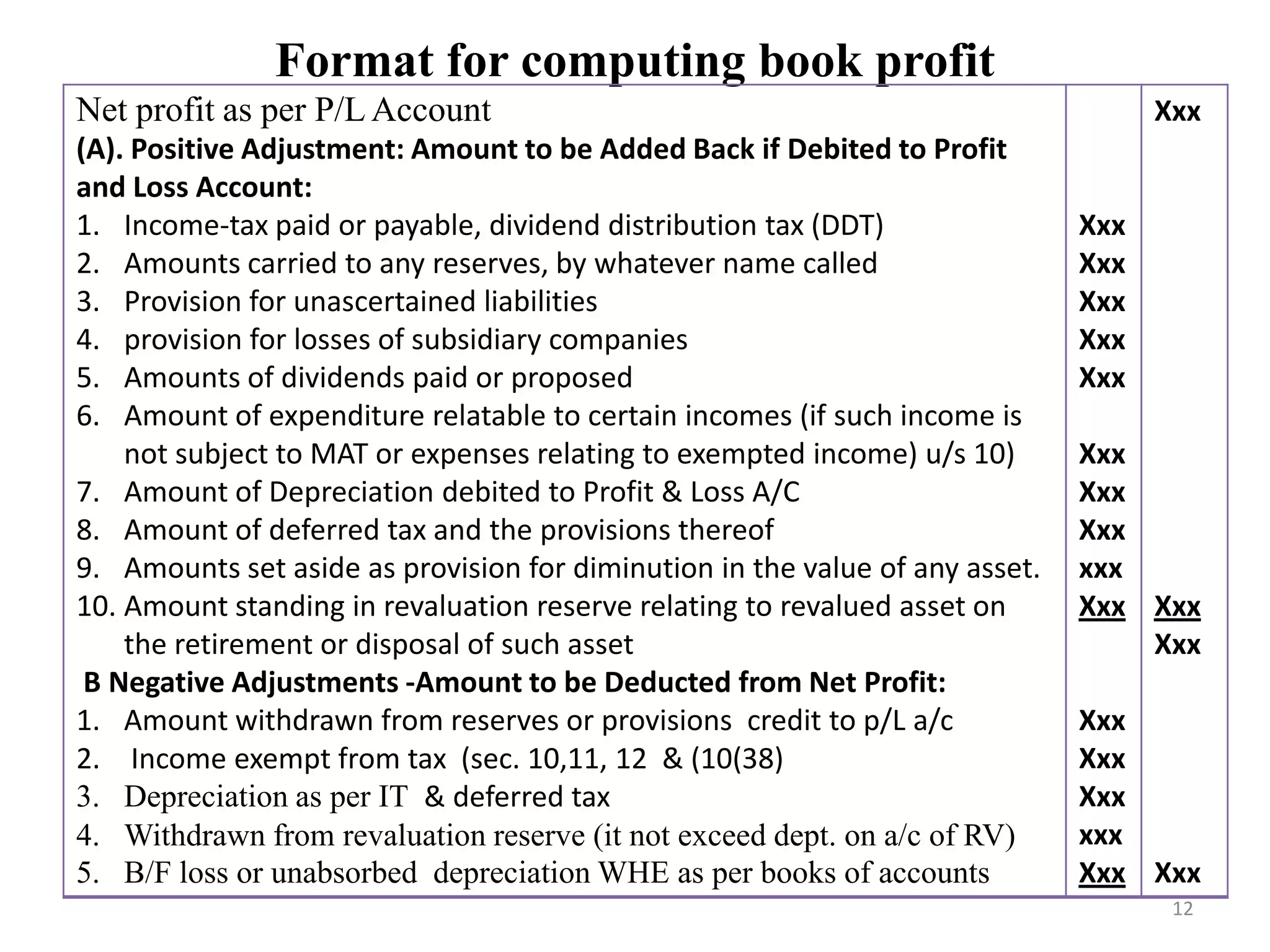





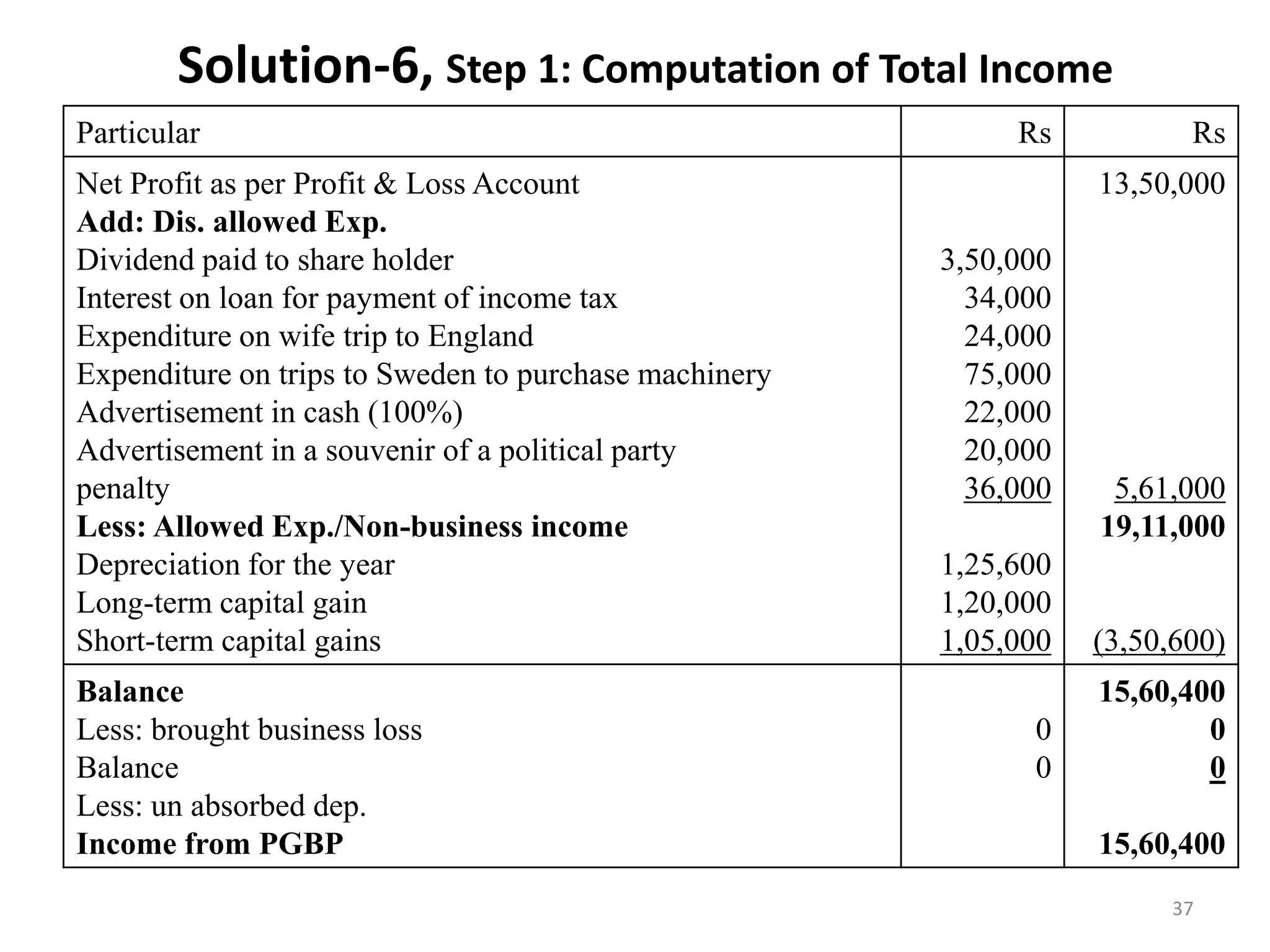
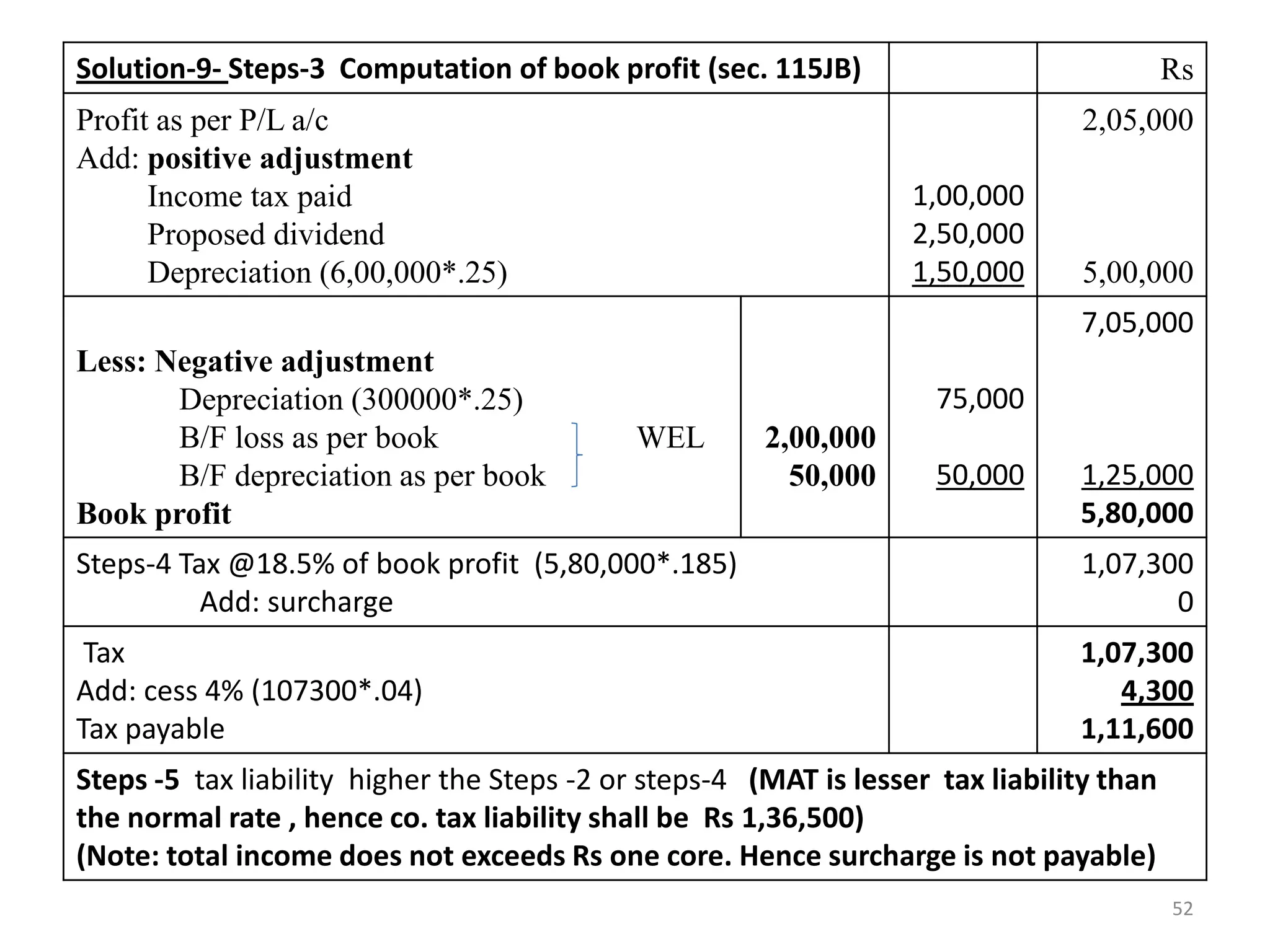
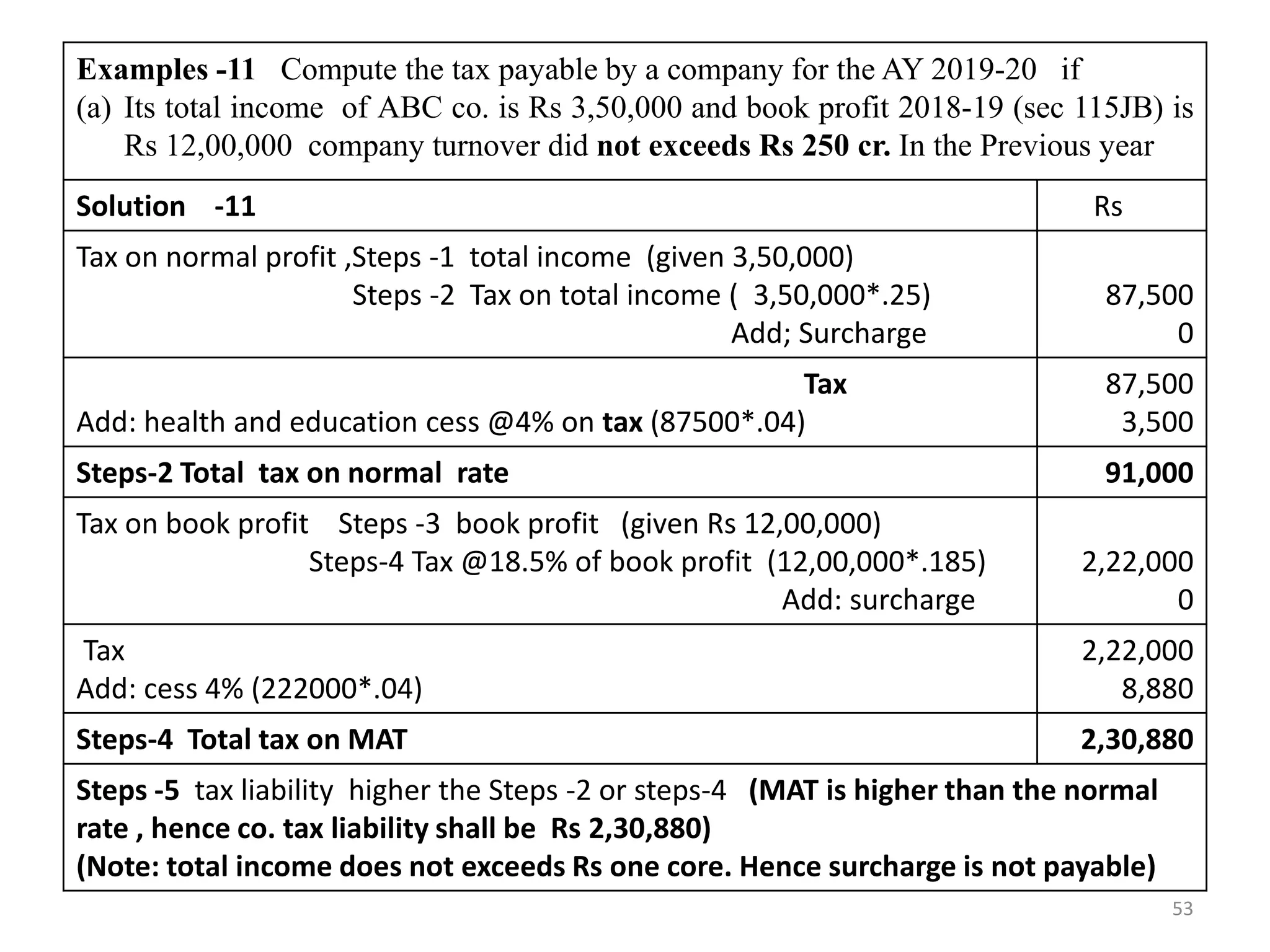
![Solution-Step 3: Computation of Book Profit
Particular Rs Rs
Net Profit as per Profit & Loss Account
Add: Positive Adjustments/statutory additions
Depreciation
Provision for Bad and doubtful Debts
Interest for late filing of income tax return
Provision for unascertained liabilities
Loss of subsidiary company
Provision for Income Tax
Proposed Dividend and CDT
Less: Negative Adjustments/ Statutory deductions
Dividend from Indian Companies (exempt)
Deferred Tax
Income of AOP (which is not subject to tax)
Depreciation (excl.dep. on a/c of revaluation)
Brought forward loss or unabsorbed dep. whichever is
lower [as per books of accounts]
Book Profit
5,17,000
16,000
2,000
75,000
39,000
2,25,000
64,350
(1,00,000)
(25,000)
(41,100)
(5,00,000)
(6,000)
19,99,000
9,38,350
(6,72,100)
22,65,250
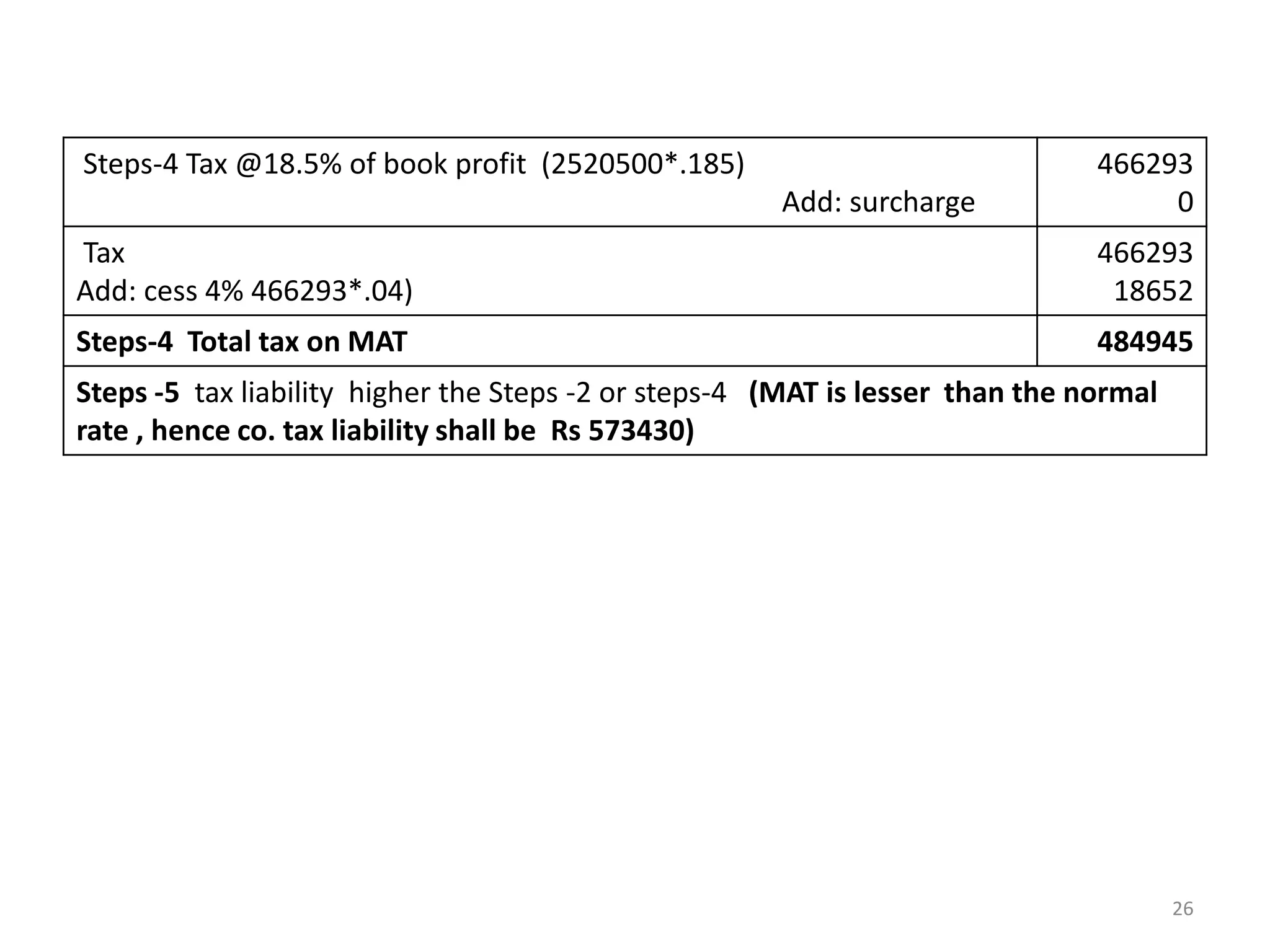
Step 4-MAT Liability= MAT @18.5% of Book Profit Rs. 22,65,250
Educ.Cess 4% on 4,19,071
Mat liability
4,19,071
16,763
4,35,834](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aoc-221210134720-130c5d50/75/aoc-pdf-31-2048.jpg)
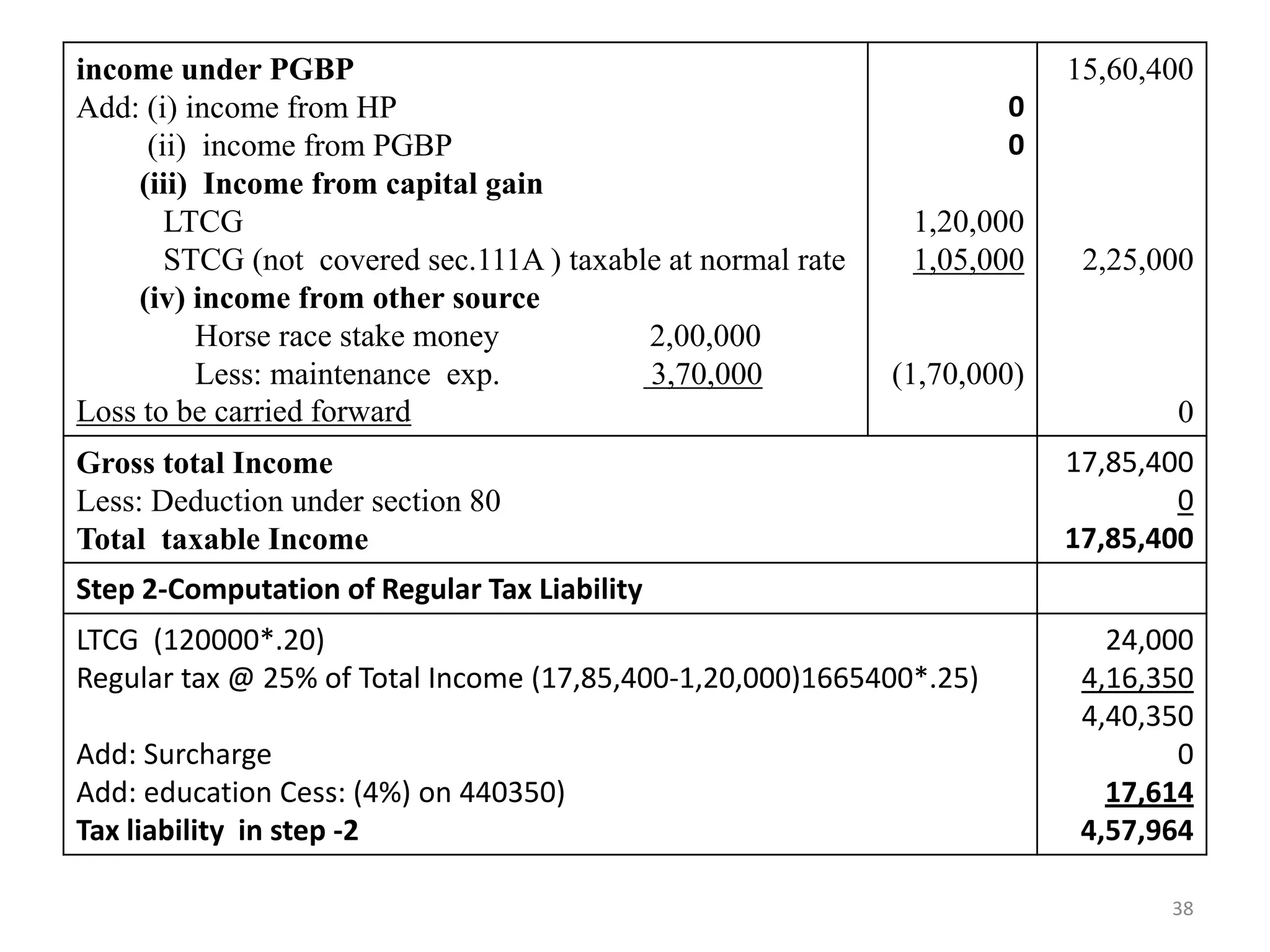
![Solution -5 Computation of Book Profit
Particulars RS
Net Profit as per profit and loss account
Positive Adjustments/statutory additions
Provision for the loss of subsidiary
Provision for doubtful debts,
Provision for income-tax
Depreciation
Negative Adjustments/statutory deductions
Share in income of an AOP as a member
Income from units in UTI [Income from units in UTI shall be reduced while
computing the book profits, since the same is exempt under section 10(35)]
Depreciation other than dep. on revaluation of assets(Rs.3,60,000–Rs.1,50,000)
Unabsorbed dep. or b/f business loss, whichever is less, as per the books of
account.[Here, unabsorbed dep. is Rs.4,00,000 while b/f business loss Rs 6,00,000
15,00,00
70,000
75,000
1,05,000
3,60,000
(1,00,000)
(75,000)
(2,10,000)
(4,00,000)
Book Profit 13,25,000
MAT @18.5% of Book Profit (Rs. 13,25,000)
Add: education Cess: (4%)
2,45,125
9,805
MAT Liability
2,54,930
34](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aoc-221210134720-130c5d50/75/aoc-pdf-34-2048.jpg)