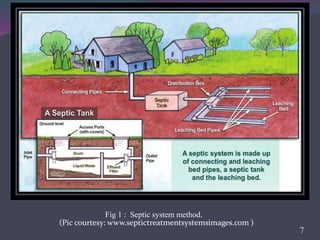
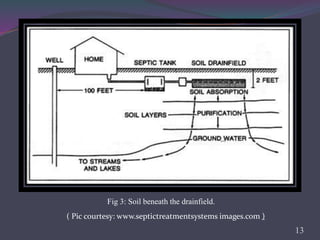
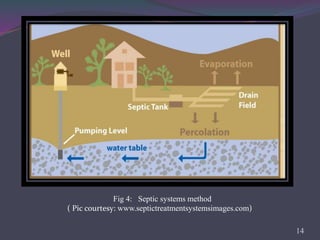
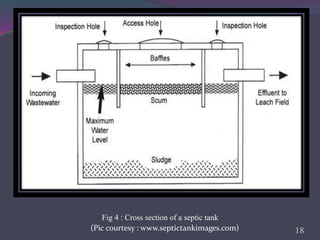
This document provides an overview of subsurface sewage treatment systems (SSTS), also known as septic systems. It discusses the key components of septic systems including septic tanks, drainfields, and the soil beneath. It describes the physical, chemical, and biological treatment processes involved. Requirements for SSTS include proper site and soil conditions. Design considerations include sizing of tanks and drainfields. Proper operation and maintenance, such as periodic pumping, is also outlined. Advantages include low cost and returning nutrients to soil, while disadvantages can include odor and potential pollution.