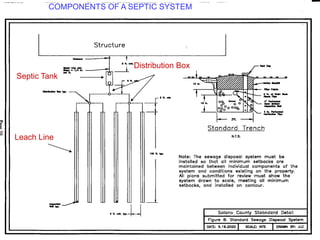
This document describes various sewage treatment processes including septic tanks, Imhoff tanks, ponds, lagoons and ditches. It provides details on the process, components and design of septic tanks. Septic tanks use sedimentation and anaerobic digestion to treat sewage. The design criteria includes detention time, tank dimensions, sludge storage volume and absorption field sizing based on percolation rates. An example problem demonstrates how to design a septic tank and absorption field for a hostel.