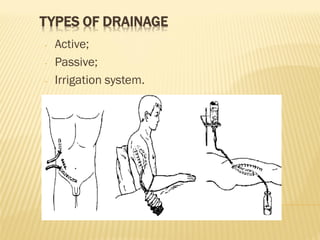
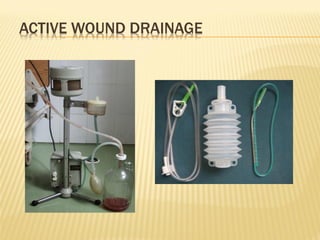
Antisepsis refers to the control of infection in wounds and tissues through mechanical, physical, chemical, and biological methods. The key types of antisepsis include mechanical removal of debris from wounds, use of antiseptic solutions and dressings, drainage of wounds, and application of factors like ultrasound, laser, or antibiotics to eliminate microorganisms. Effective antisepsis requires initial cleaning and debridement of the wound, followed by continued drainage and prevention of further contamination. A variety of antiseptic chemicals like iodine, metals, alcohols, and acids can be applied based on the situation.