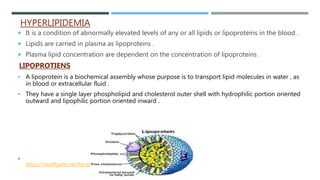
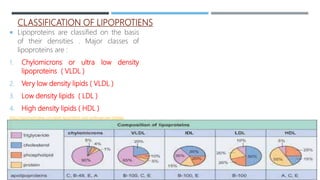
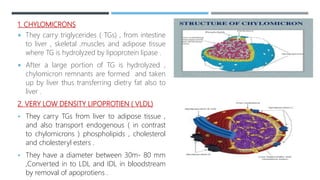
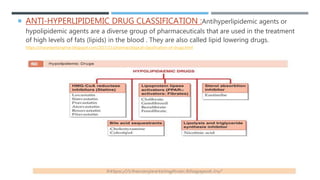
This document describes preclinical screening models used to evaluate antihyperlipidemic drugs. It discusses in vivo models like triton-induced hyperlipidemia in rats and cholesterol-diet induced atherosclerosis in rabbits. It also discusses in vitro models like inhibition of the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase and ACAT inhibitory activity assays. The purpose of these preclinical models is to test potential lipid-lowering drugs for their ability to reduce elevated lipid levels or inhibit key enzymes prior to clinical trials.















![IN – VITRO ACAT INHIBITORY ACTIVITY .
PURPOSE AND RATIONALE : IN-vitro ACAT inhibitory activity can be determined in
microsomal preparations from liver or intestine of rabbits .
PROCEDURE :
Hepatic or intestinal microsomes are prepared from rabbits . Prior to sacrifice , the animals
receive chow supplemented with 2% cholesterol and 10% safflower oil for 6 weeks.
Each assay contain 0.2 mg of microsomal protein and fatty acid-poor bovine serum albumin
in KH2PO4 buffer , PH 7.4 , containing KCL , EDTA and sucrose .
Drug dilutions are made in DMSO ( 5 ul DMSO/200ul total incubation volume ) . The
reaction is started by the addition of oleyl CoA .
After 3 min the reaction is stopped by the addition of chloroform – methanol 2:1 [3H] ,
cholesteryl oleate is used as internal standard .
Lipid extract are dissolved in chloroform , spotted on TCL plates (silica gel G) and developed
in hexane – petroleum ether –acetic acid 80:20:1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hyperlipidemic-220202075636/85/ANTIHYPERLIPIDEMIC-screening-models-20-320.jpg)


