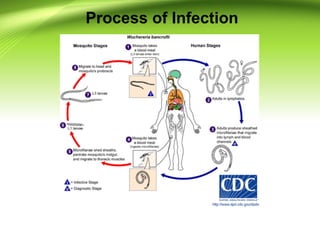
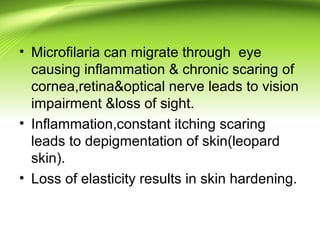
1) Filariasis is caused by parasitic roundworms transmitted through mosquito bites. It affects lymphatic vessels and can cause elephantiasis.
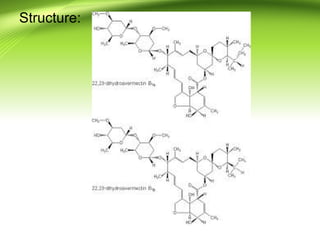
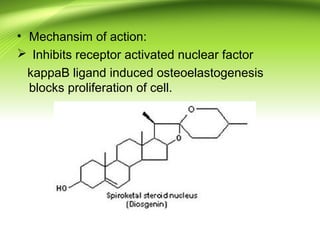
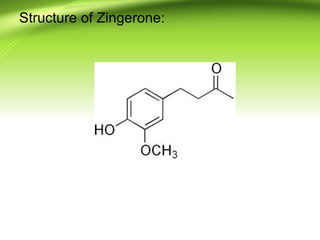
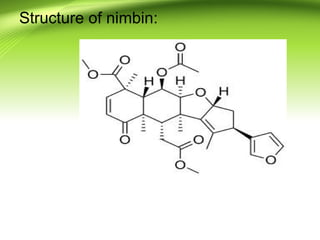
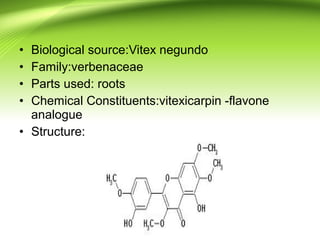
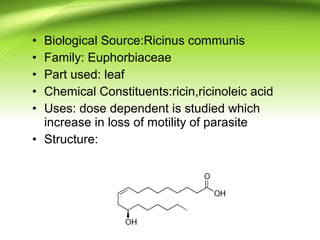
2) There are several antifilarial herbs and drugs used to treat filariasis including diethylcarbamazine citrate, ivermectin, Vitex negundo, Zingiber officinale, and Melia azadirachta.
3) Diagnosis involves tests to detect filarial antigens or microfilariae in blood samples. Treatment requires multiple doses of antifilarial drugs over time to eliminate microfilariae and prevent further infection.