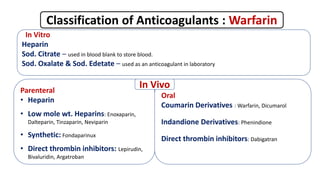
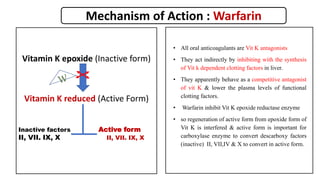
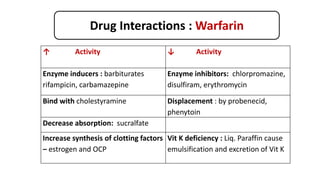
This document discusses anticoagulants, focusing on warfarin. It classifies anticoagulants as in vitro, parenteral, and oral. It describes warfarin's mechanism of action as inhibiting vitamin K epoxide reductase, interfering with the regeneration of vitamin K's active form and the carboxylation of clotting factors. The document outlines warfarin's pharmacokinetics including its oral bioavailability, plasma protein binding, metabolism, and drug interactions. It notes warfarin's therapeutic uses for conditions like deep vein thrombosis and prophylaxis. The document also covers warfarin's adverse drug reactions and contraindications.