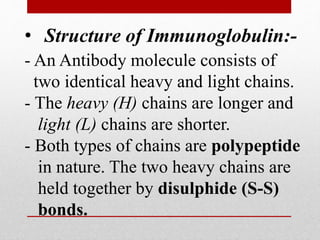
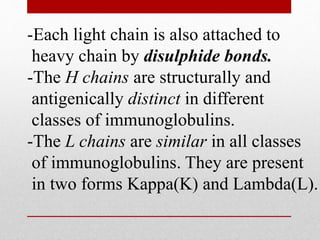
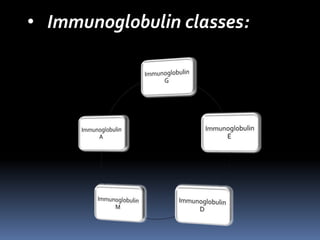
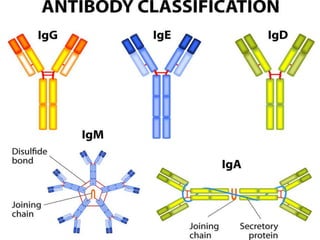
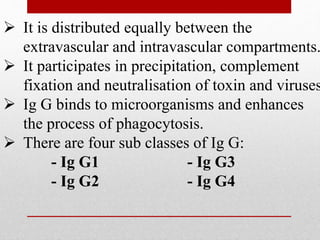
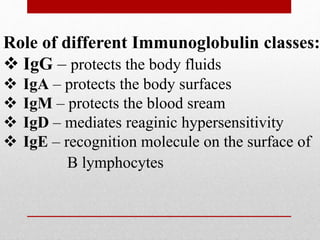
The document details the characteristics and functions of various classes of antibodies, known as immunoglobulins, which are proteins formed in response to antigens. It describes the chemical nature of antibodies, their structure, and the specific roles of different immunoglobulin classes such as IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD, and IgE. Each class has distinct properties, concentrations, half-lives, and functions, such as providing immunity, protecting mucous membranes, and mediating hypersensitivity reactions.