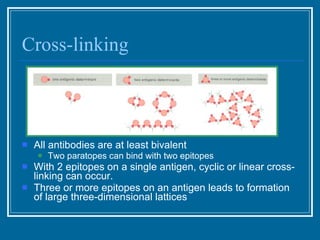
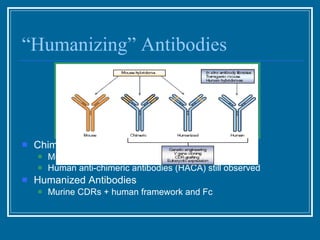
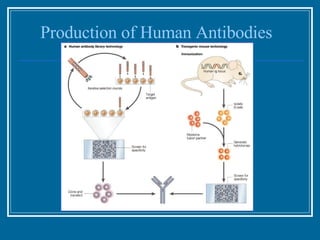
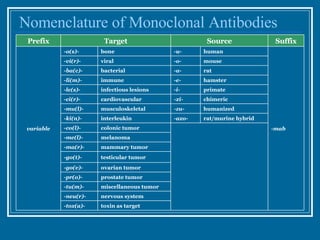
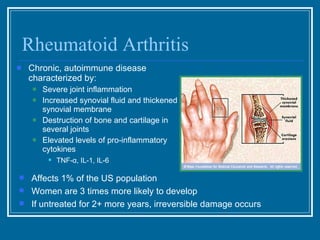
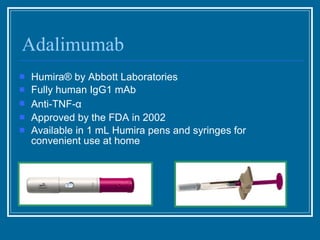
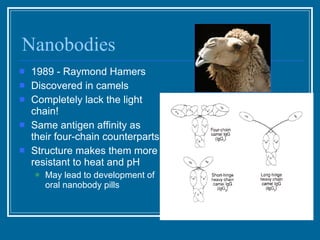
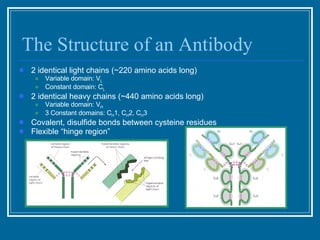
Antibodies have emerged as a promising class of therapeutic drugs due to their high specificity and ability to activate the immune system. Major breakthroughs included the development of serum therapy in the early 1900s and the discovery of monoclonal antibodies in the 1970s-80s. Today, over 20 antibody drugs are approved to treat various diseases including rheumatoid arthritis, with hundreds more in development. Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease characterized by joint inflammation and damage, and antibody drugs that target cytokines like TNF-α have proven effective in slowing its progression.







![Antibody Pharmokinetics Antigen binding is reversible Antigen (Ag) + Antibody (Ab) ↔ AntigenAntibody (AgAb) [bound] K affinity = [AgAb] [Ag][Ab] For some therapeutic mAbs, the affinity must be balanced so that effective antigen binding occurs while tissue penetration is allowed](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1395404/85/Antibodies-as-Drugs-12-320.jpg)