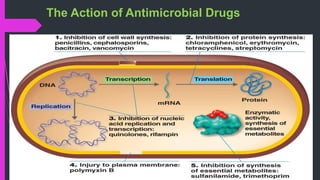
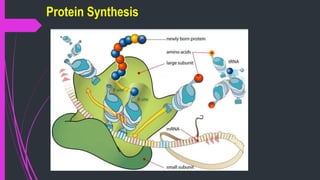
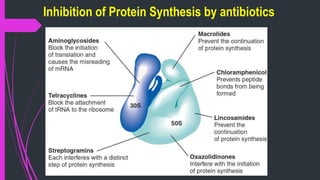
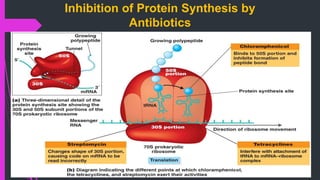
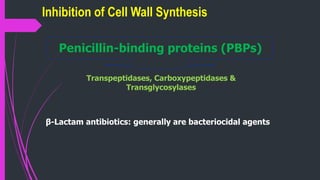
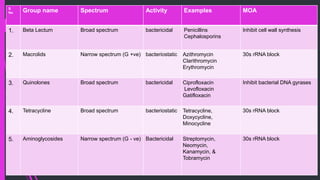
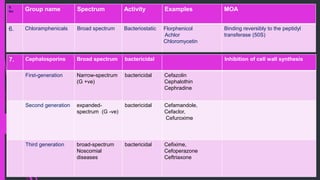
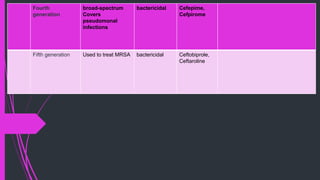
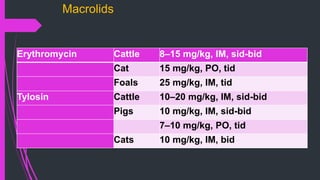
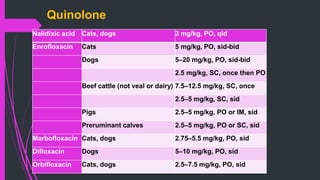
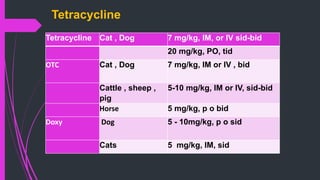
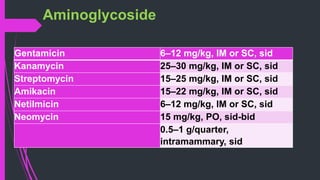
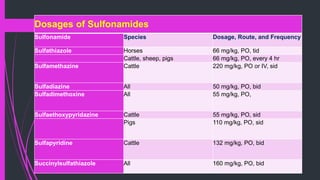
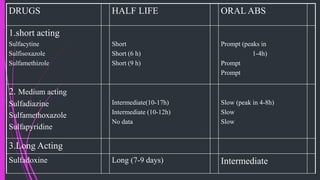
The document discusses various classes of antibiotics including their spectrum of activity, mechanisms of action, and examples. It describes narrow and broad-spectrum antibiotics, and whether they are bacteriostatic or bactericidal. The main classes covered are beta-lactams like penicillins and cephalosporins, macrolides, quinolones, tetracyclines, aminoglycosides, chloramphenicol, and sulfonamides. It provides details on their mechanisms of inhibiting cell wall synthesis, protein synthesis, or nucleic acid synthesis. Examples of commonly used antibiotics in different species are given along with typical dosage ranges.