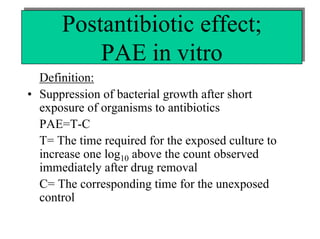
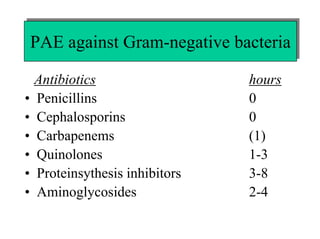
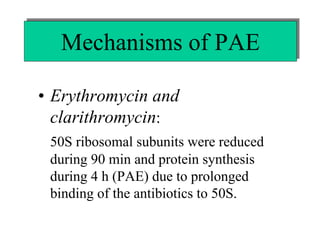
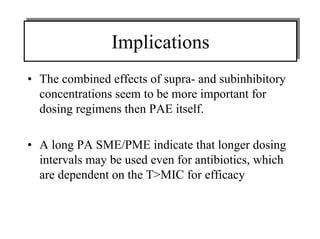
The document discusses postantibiotic effects (PAE) and sub-minimum inhibitory concentration (sub-MIC) effects of antibiotics in vitro and in vivo. It defines PAE as the suppression of bacterial growth after brief antibiotic exposure. PAE depends on antibiotic type, bacteria, concentration, and exposure duration. It is longer for Gram-positives than Gram-negatives. Sub-MICs can prolong PAE and cause sub-MIC effects, suppressing bacterial growth. Prolonged PAE and sub-MIC effects indicate antibiotics may be effective at lower doses or longer intervals than expected based solely on in vitro MICs.