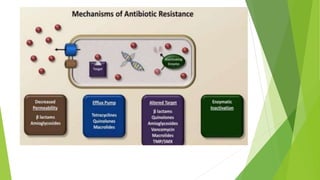
This document discusses antibiotics, including their definitions, classifications, mechanisms of action, and resistance. Antibiotics are substances produced by microorganisms that kill or inhibit the growth of other microorganisms. They are classified based on their mechanism of action (such as inhibiting cell wall synthesis or protein synthesis), spectrum of activity (narrow or broad), and mode of action (bacteriostatic or bactericidal). Antibiotic resistance can occur through several mechanisms such as bacteria producing enzymes to inactivate antibiotics or reducing permeability to drugs. Combining antibiotics can result in synergistic effects against certain organisms.