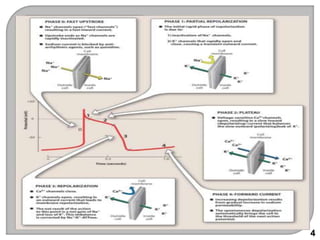
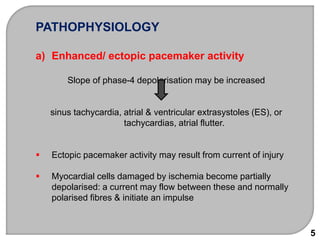
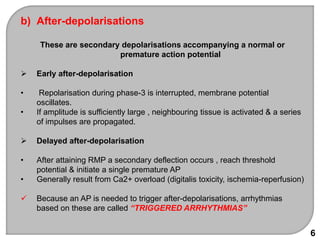
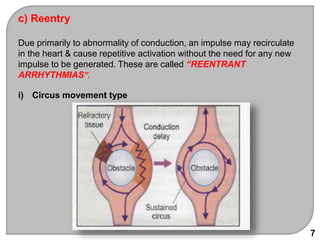
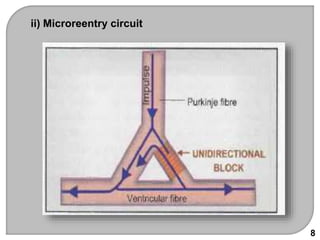
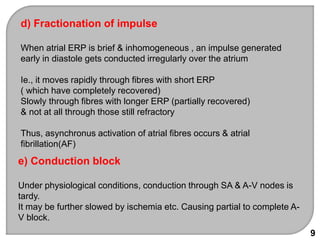
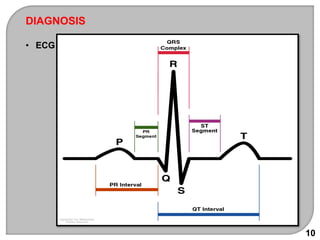
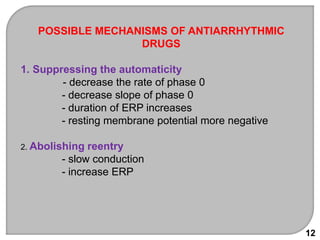
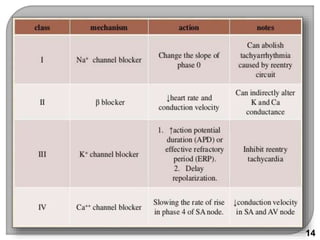
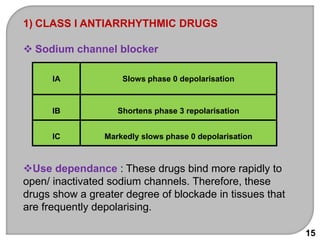
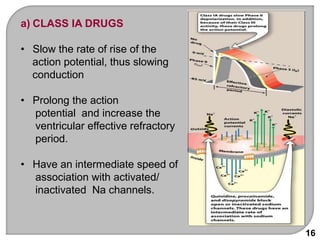
This document discusses antiarrhythmic drugs, which are used to treat and prevent cardiac arrhythmias. It defines arrhythmias and describes their various causes, including abnormal automaticity, impaired conduction, ischemia, electrolyte imbalances, and other factors. The document then explains the mechanisms of different types of arrhythmias such as enhanced pacemaker activity, afterdepolarizations, reentry, fractionated impulses, and conduction block. It proceeds to classify antiarrhythmic drugs into five classes based on their mechanisms of action, such as blocking sodium, potassium, calcium, or beta-adrenergic channels. For each class, specific drugs are discussed along with their indications, mechanisms, effects, interactions and adverse