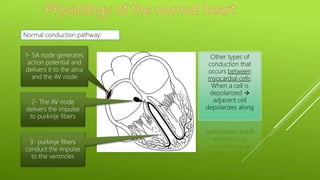
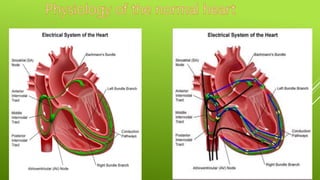
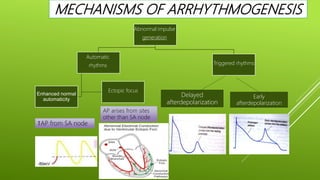
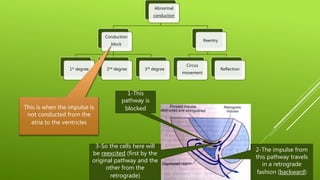
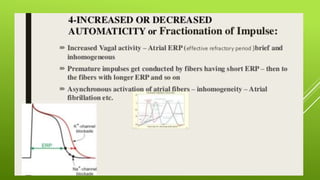
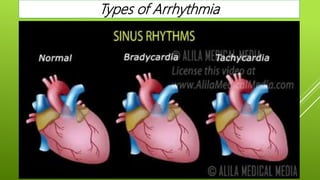
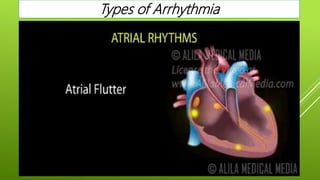
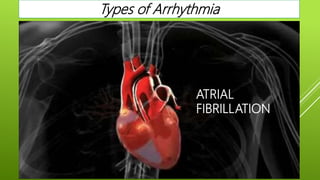
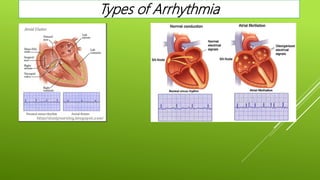
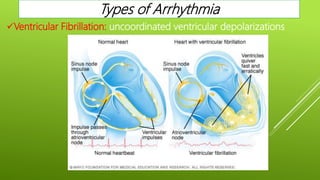
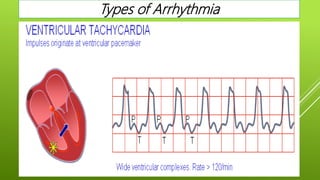
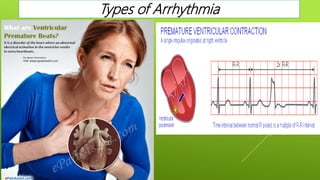
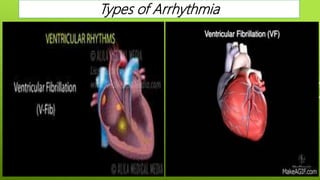
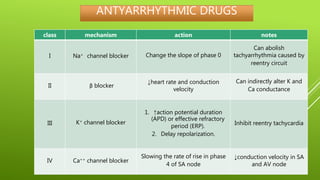
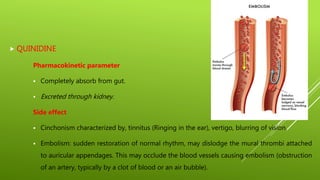
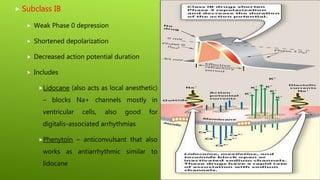
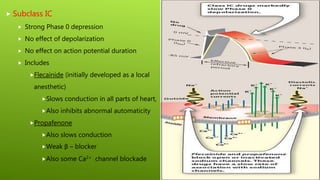
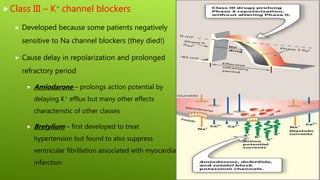
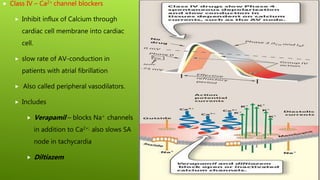
This document discusses antiarrhythmic agents and their mechanisms and classifications. It begins by describing the normal cardiac conduction pathway and different types of arrhythmias including their causes. Antiarrhythmic drugs are classified into four classes based on their effects on the cardiac action potential and ion channels. Class I drugs block fast sodium channels, class II are beta blockers, class III block potassium channels, and class IV block calcium channels. Examples from each class like quinidine, propranolol, amiodarone, and verapamil are described in more detail regarding their mechanisms and uses.