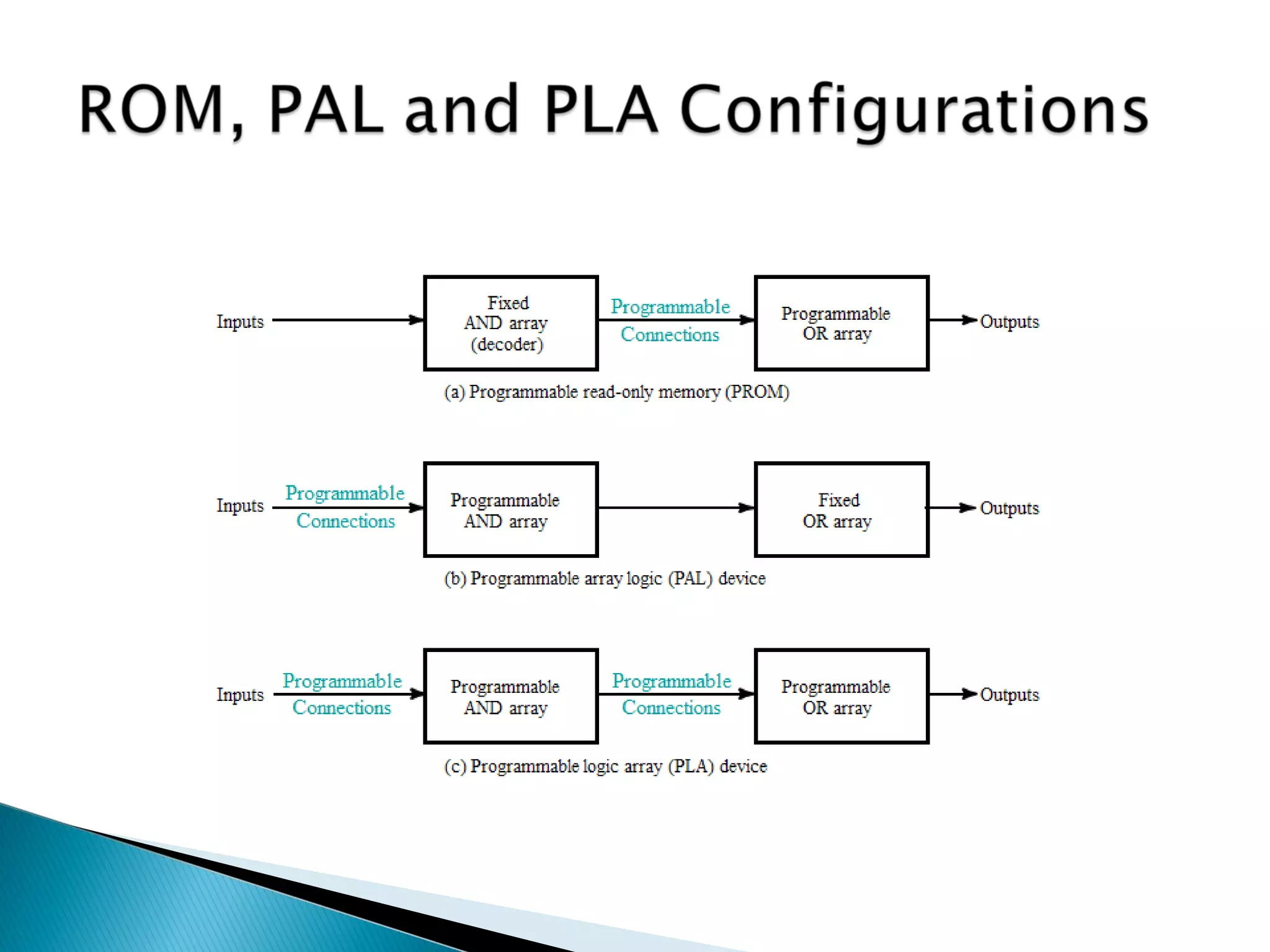
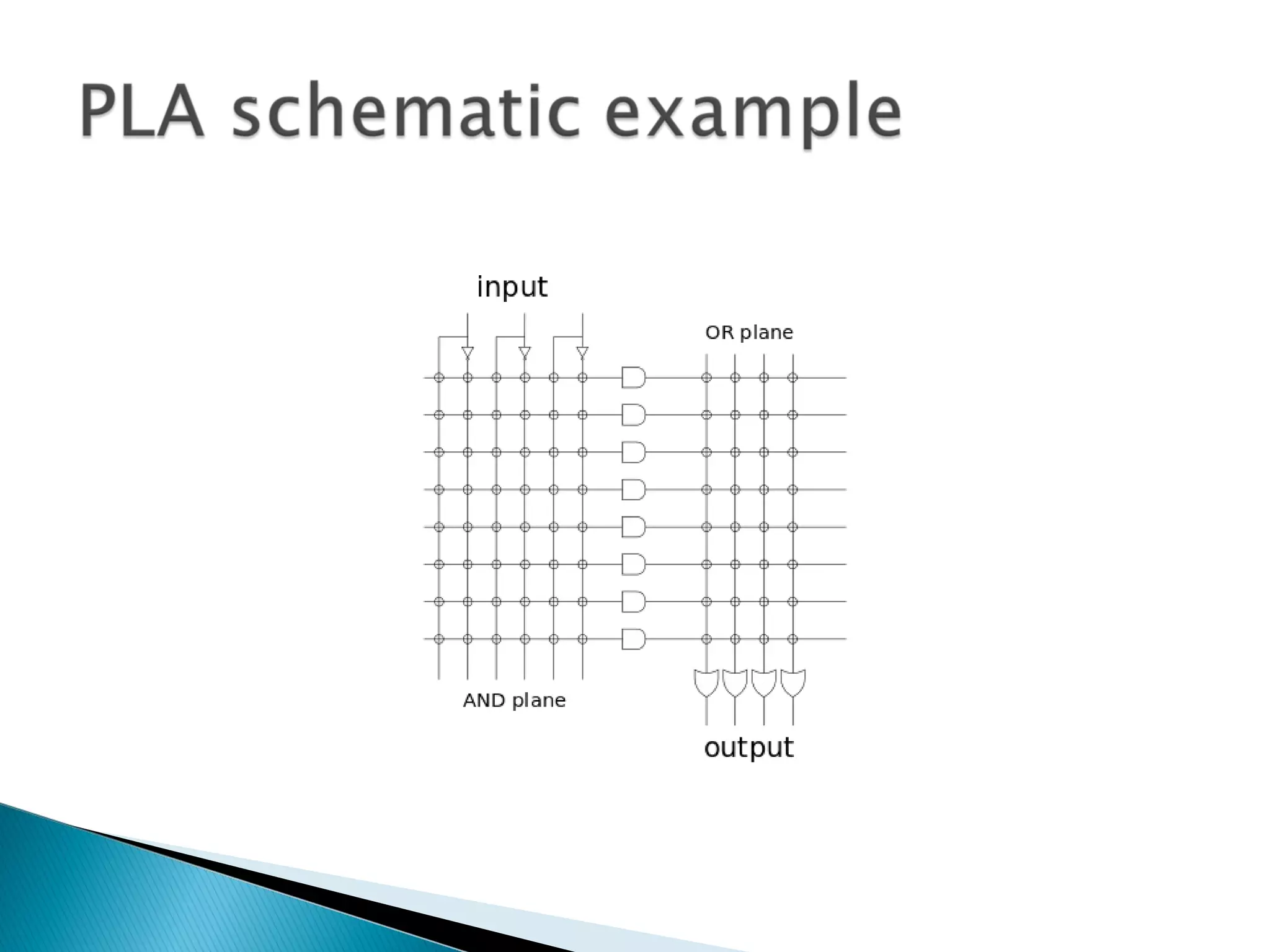
This document discusses programmable logic devices and how they can be used to implement integrated circuit designs that are required in small volumes but need to be produced in large volumes. It describes how programmable logic devices like PLDs, PALs, PLAs, CPLDs and FPGAs can be manufactured at large scale and then programmed to implement different designs. These programmable devices use technologies like lookup tables, transistor switching control and non-volatile memory to allow designs to be programmed after manufacturing.