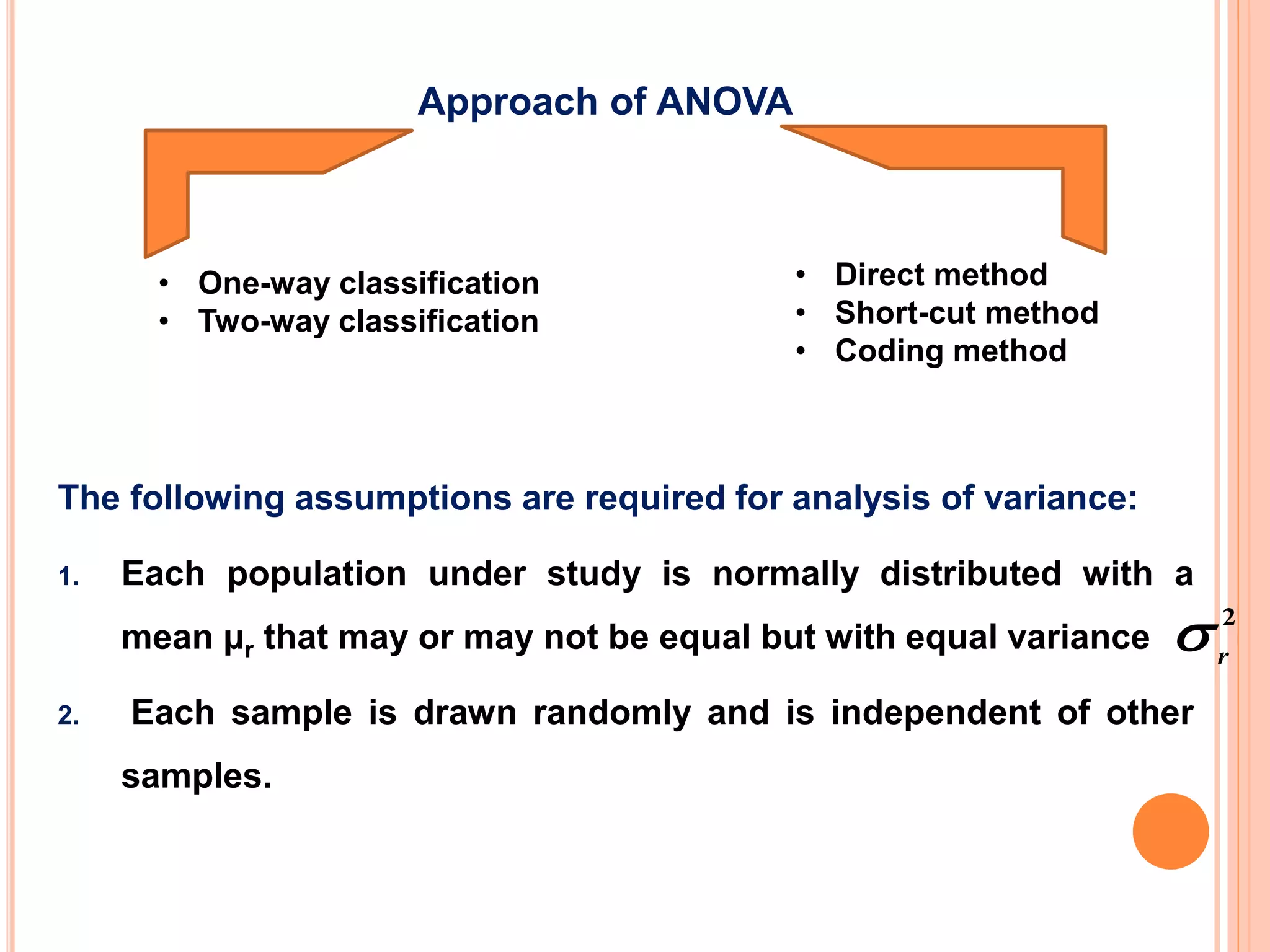
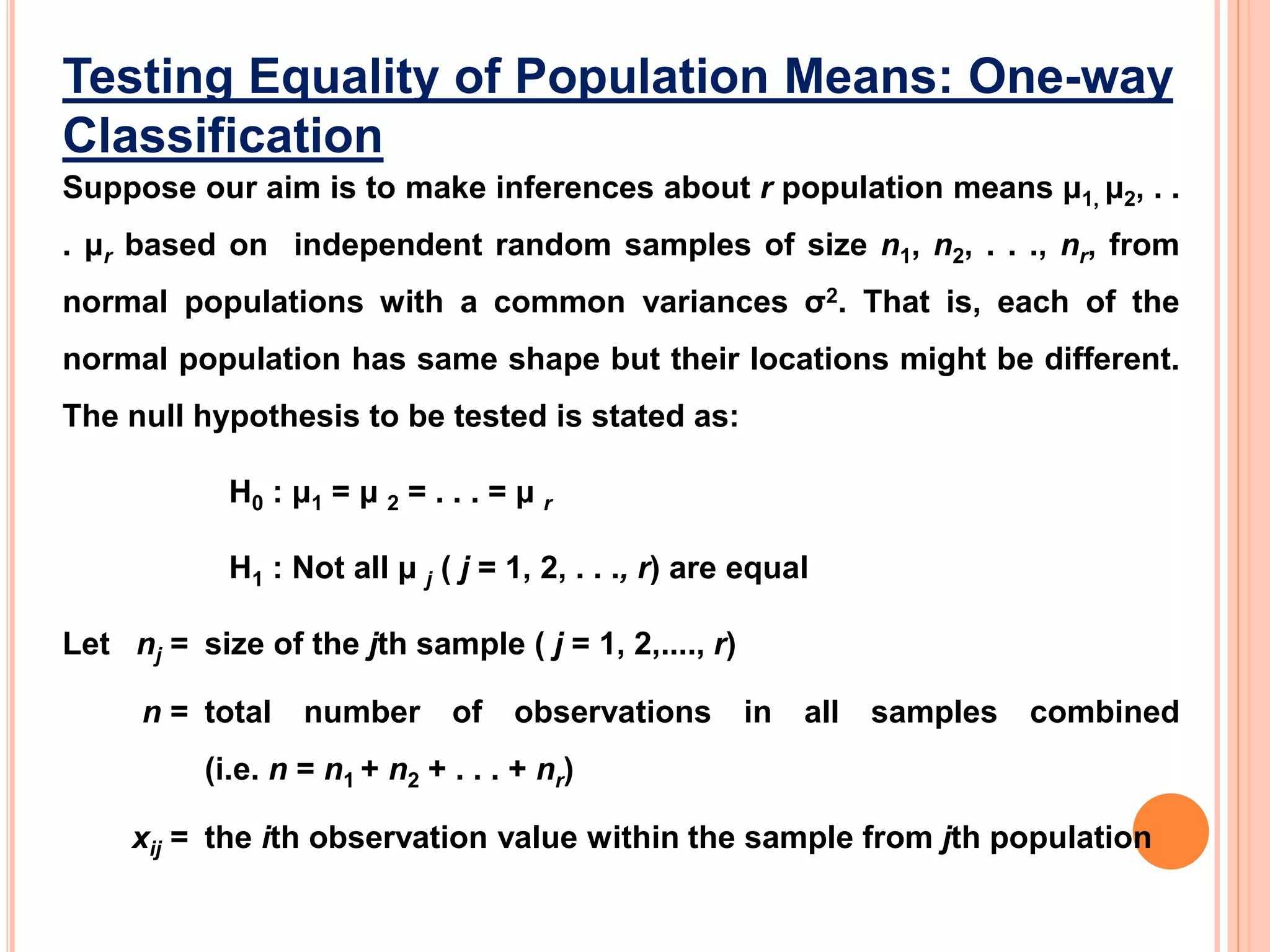
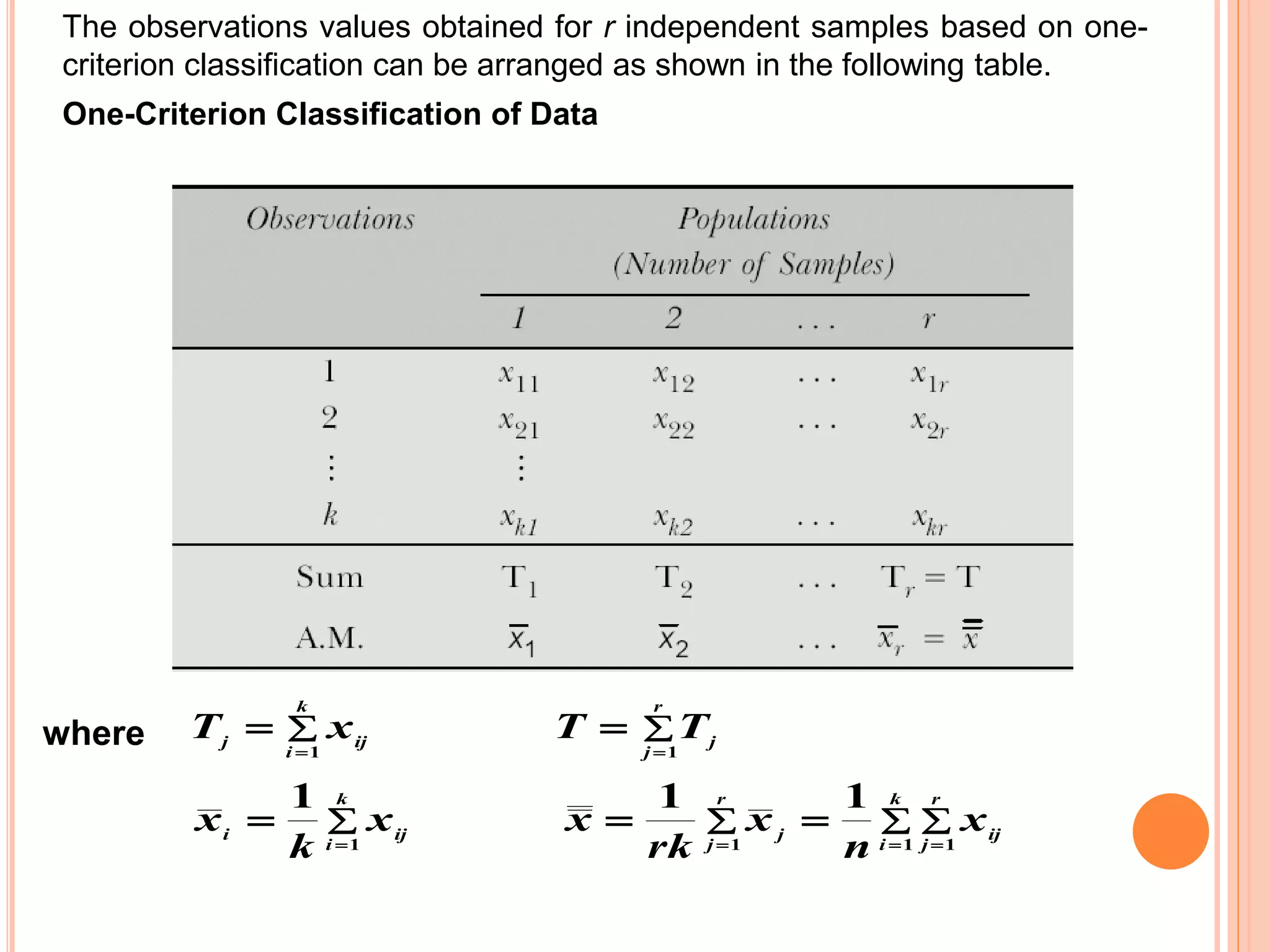
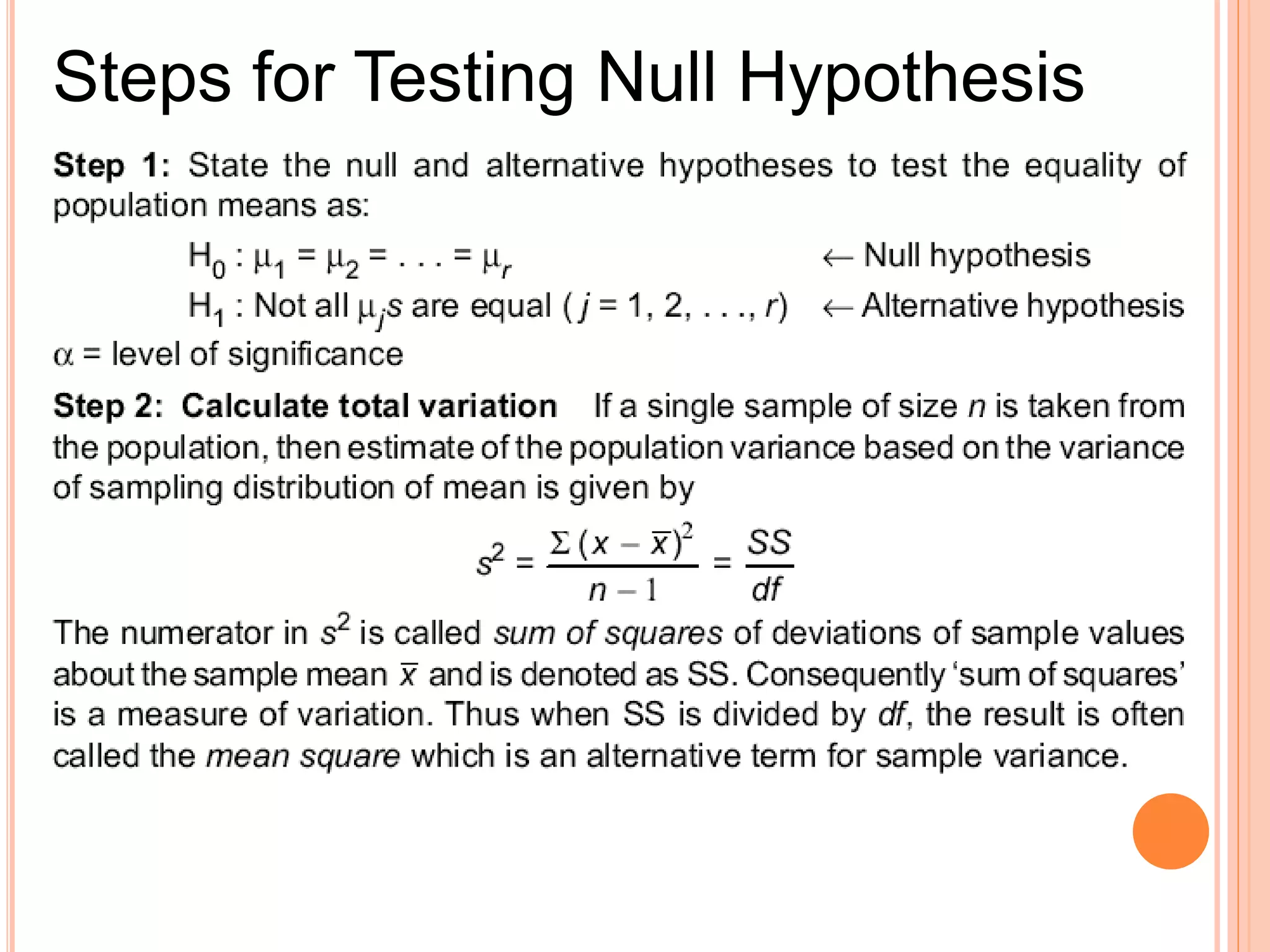
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA) can be used to test if there are significant differences between the means of three or more populations. It tests the null hypothesis that all population means are equal.
- Key terms in ANOVA include response variable, factor, treatment, and level. A factor is the independent variable whose levels make up the treatments being compared.
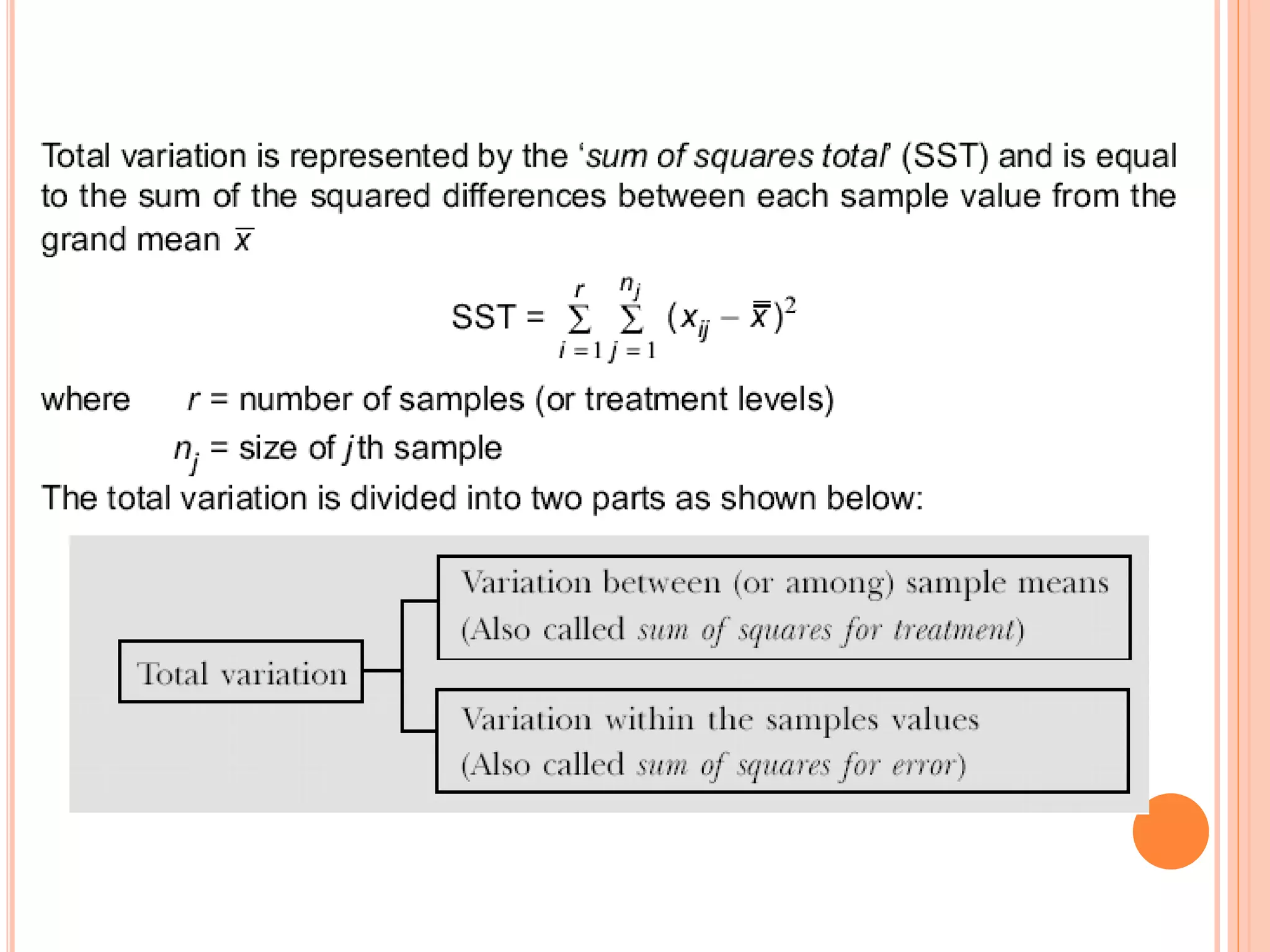
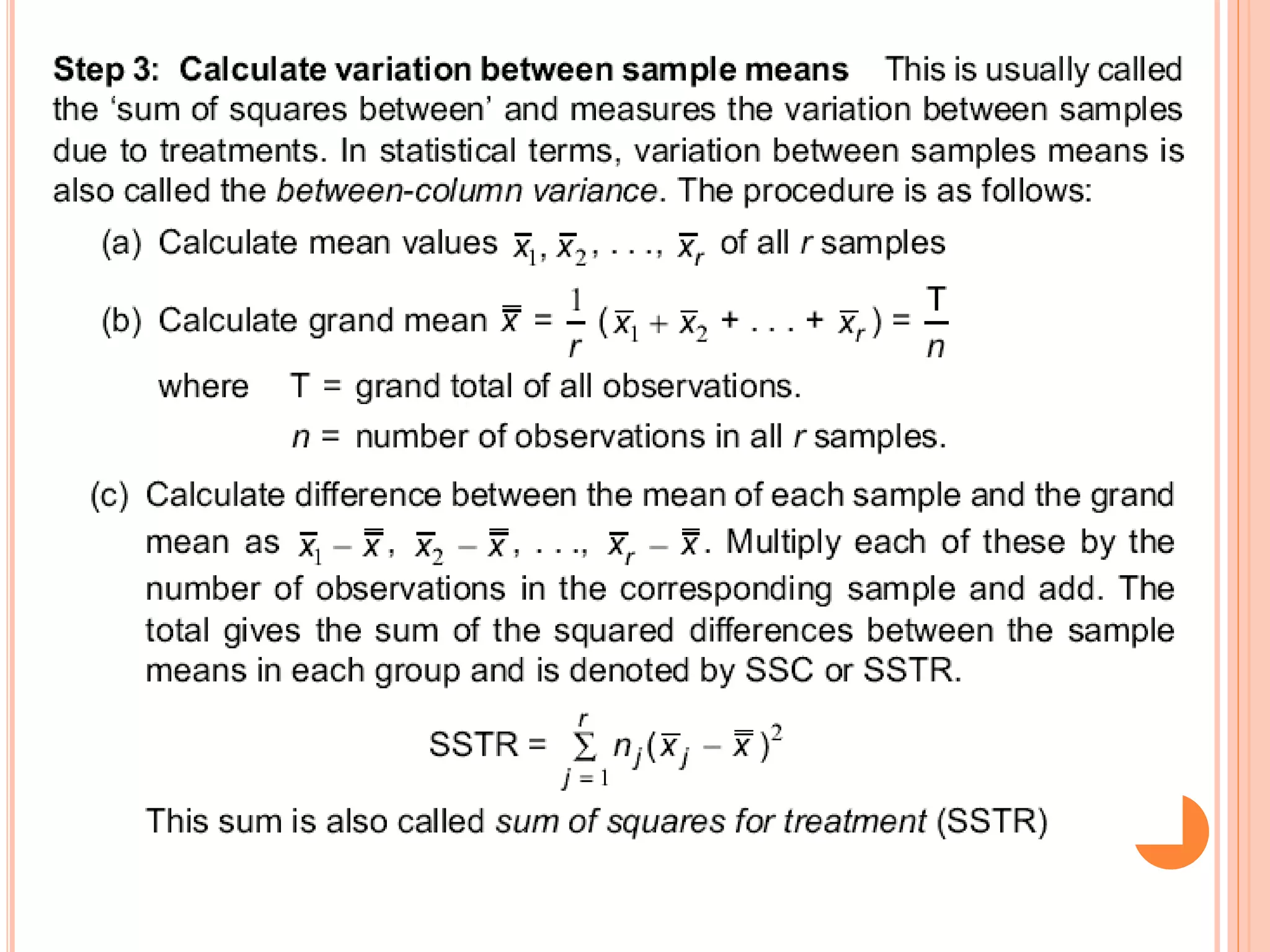
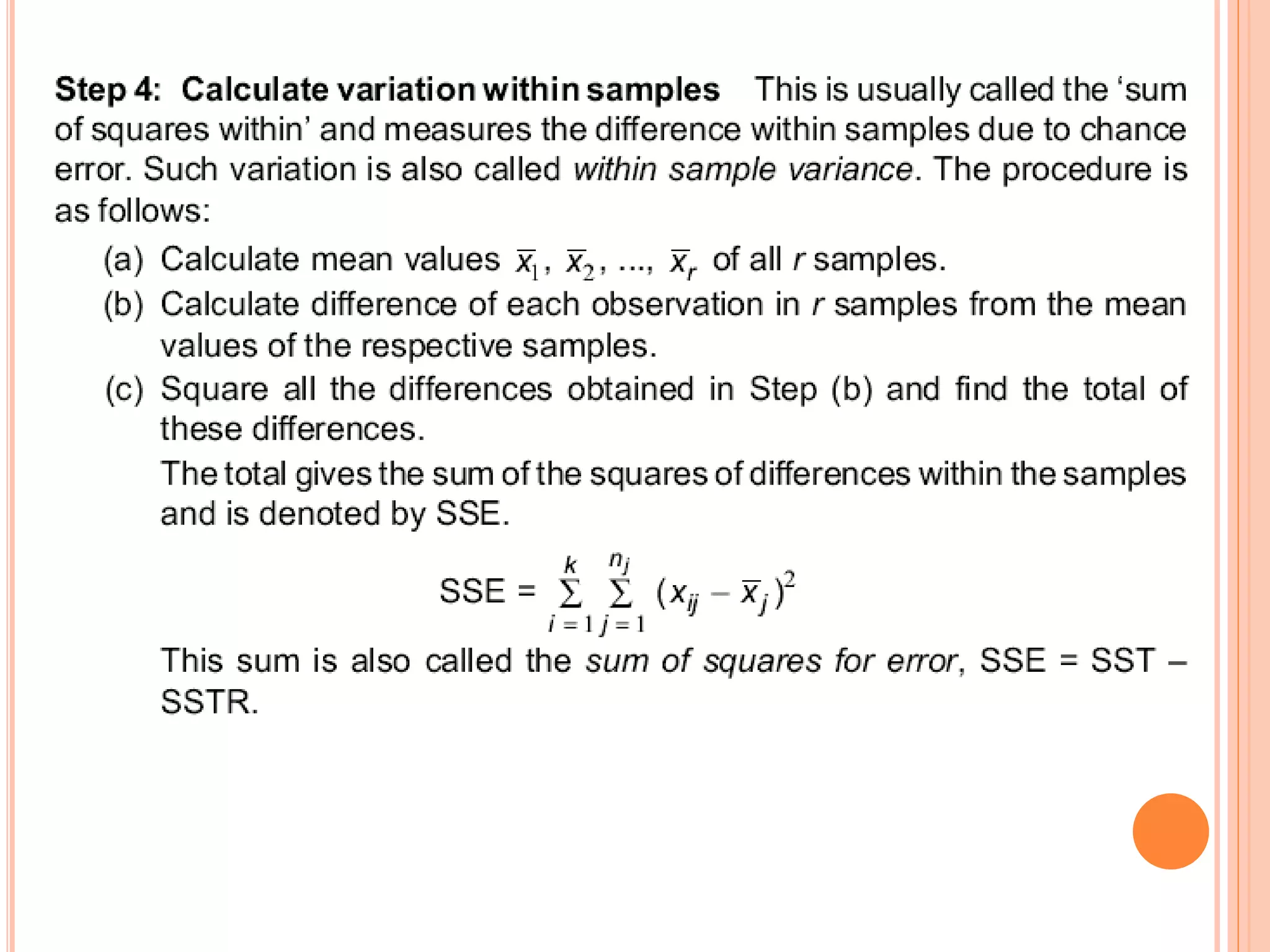
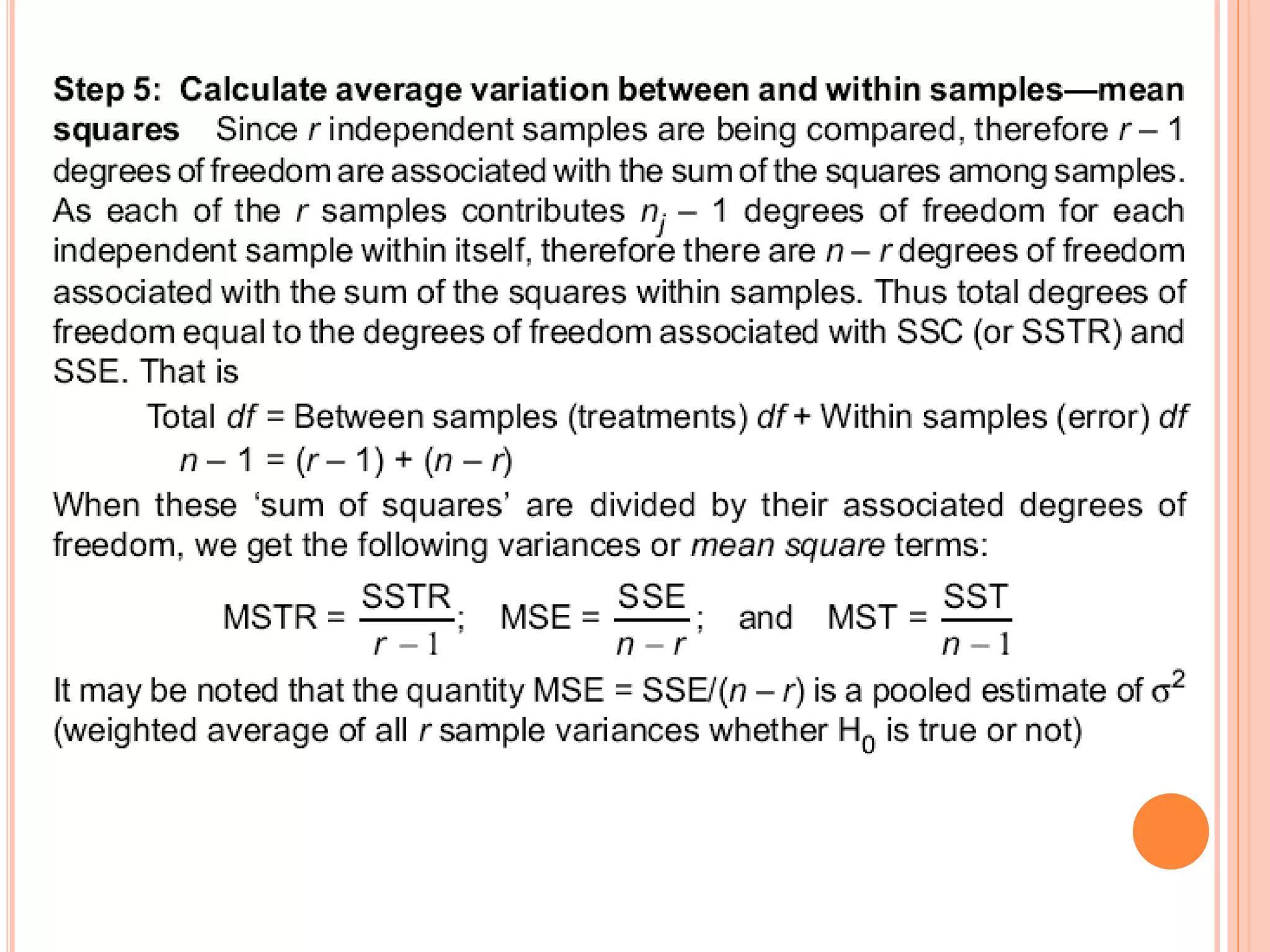
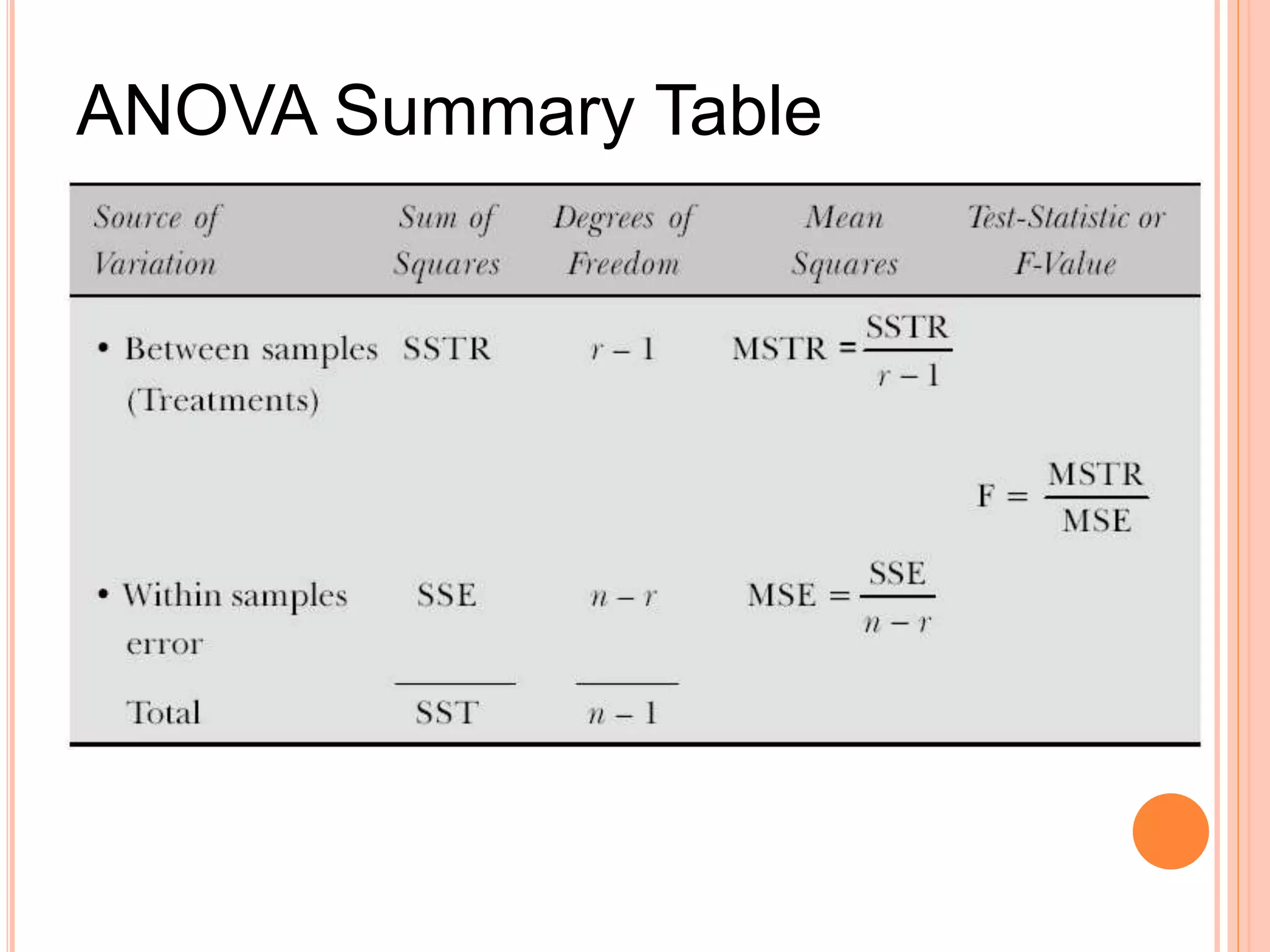
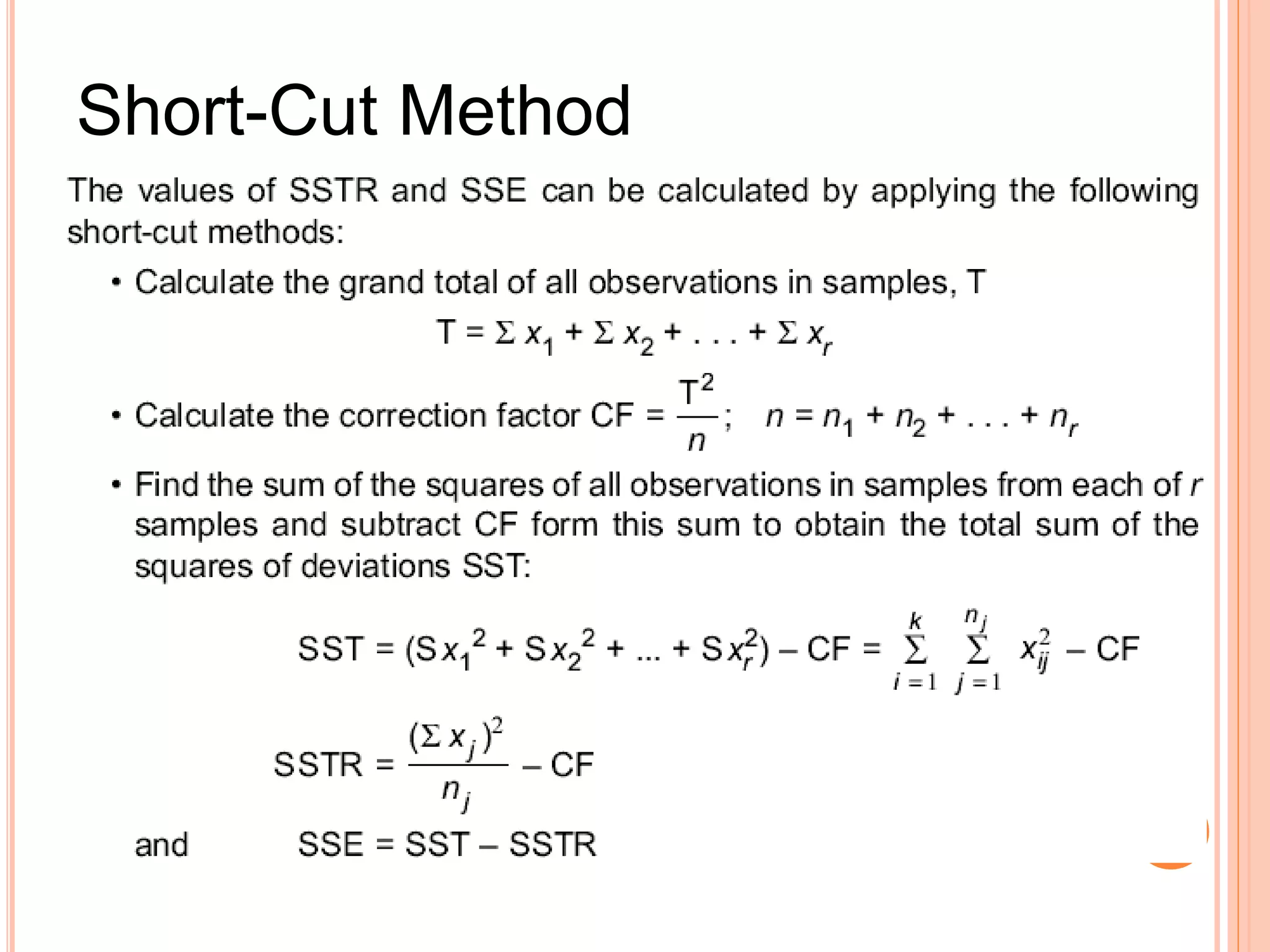
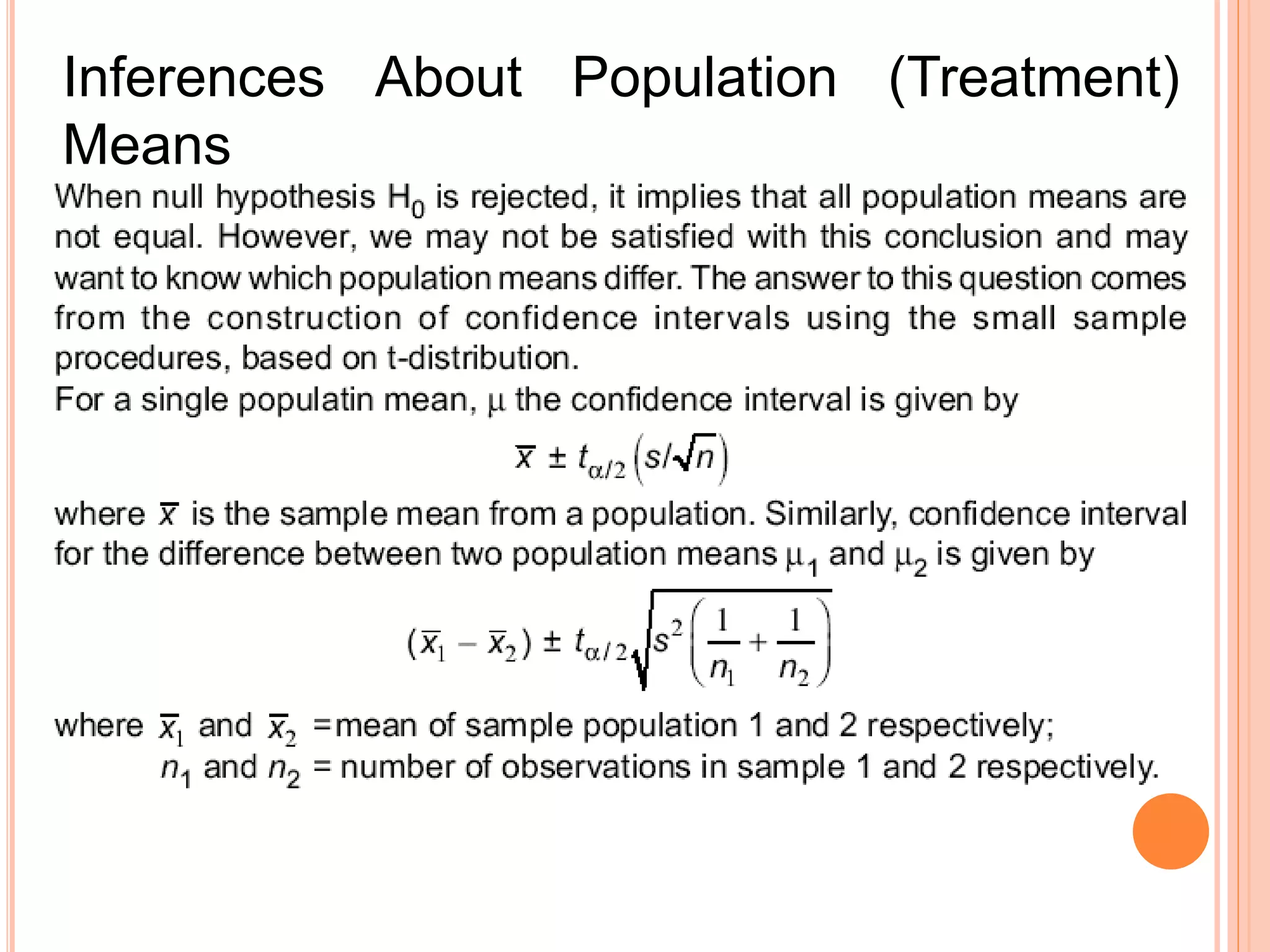
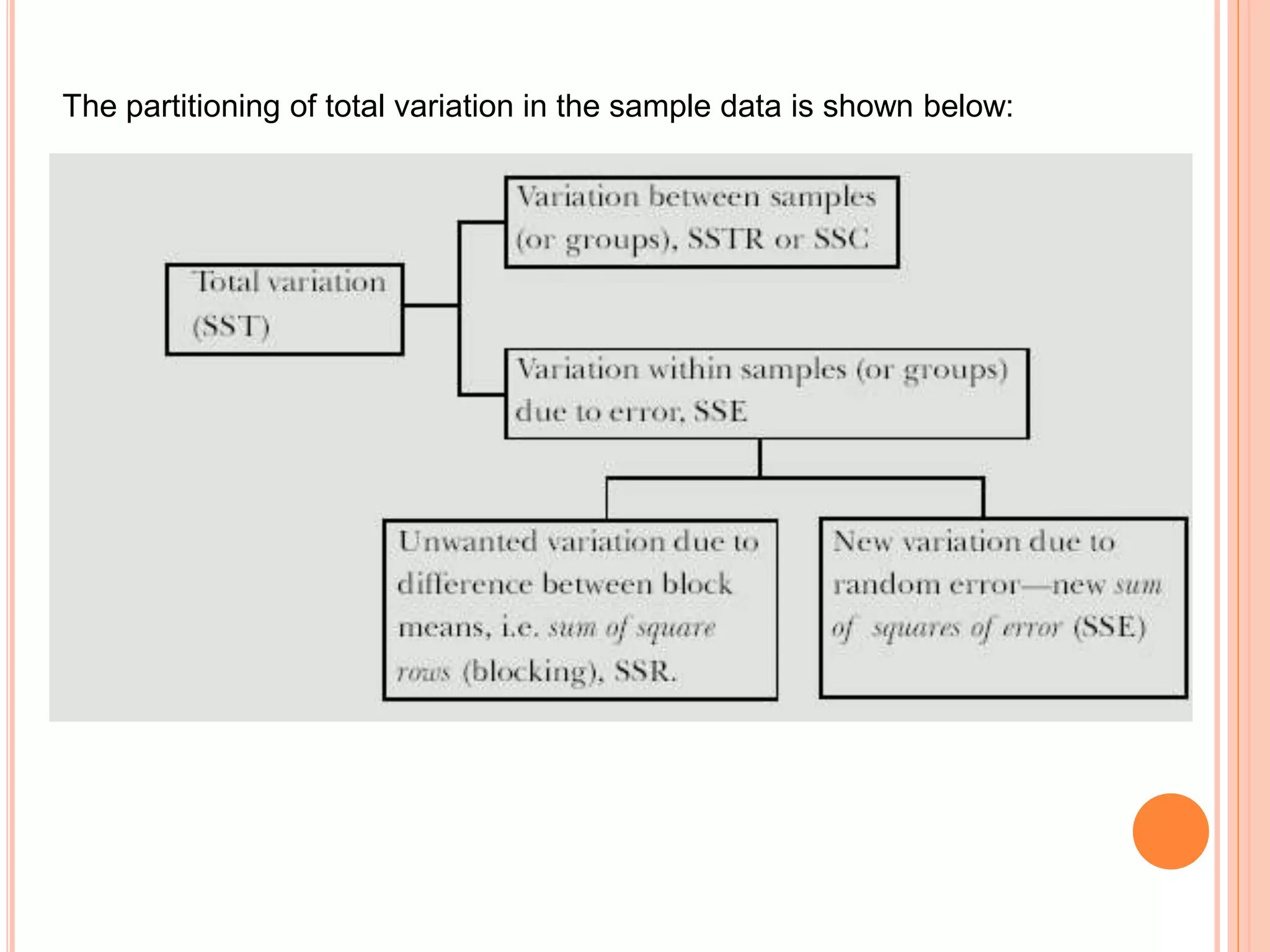
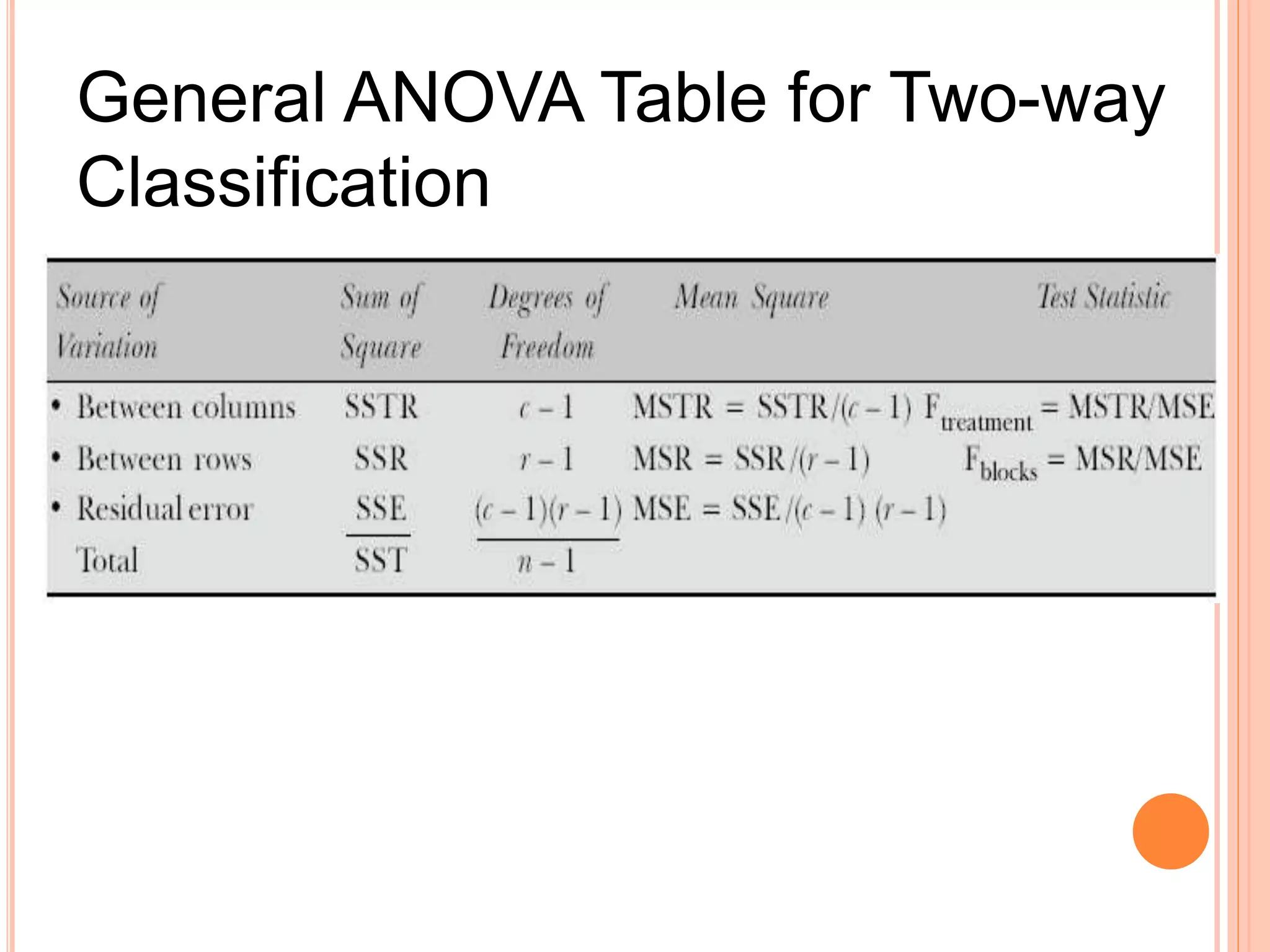
- ANOVA partitions total variation in data into variations due to treatments and random error. If the treatment variation is large compared to error variation, the null hypothesis of equal means is rejected.