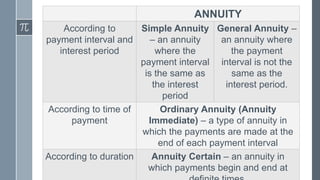
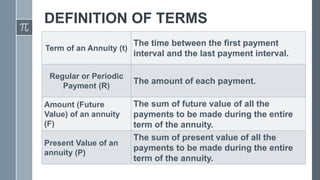
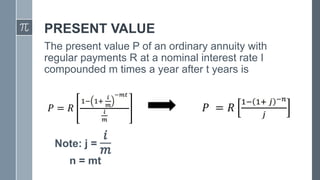
This document defines and provides examples of different types of annuities. It discusses simple and general annuities, ordinary and annuity certain annuities, and defines key terms like term, periodic payment, future value, and present value. Examples are provided to demonstrate calculating the future and present value of annuities given periodic payments, interest rates, and time periods.