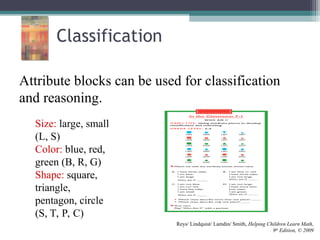
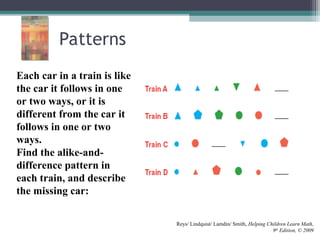
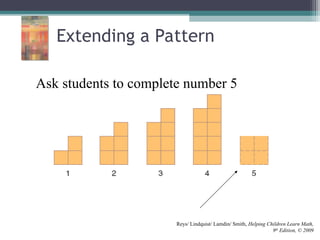
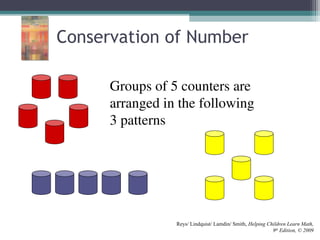
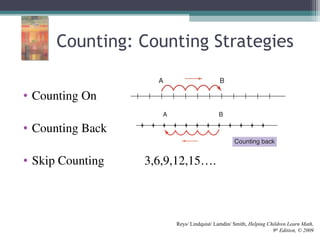
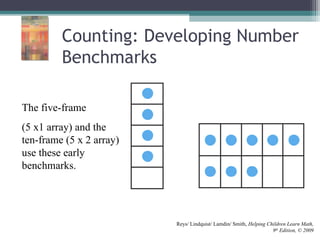
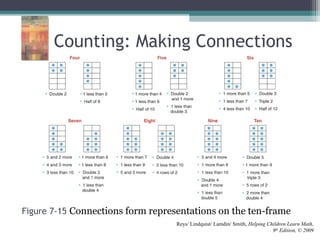
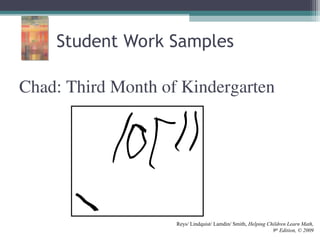
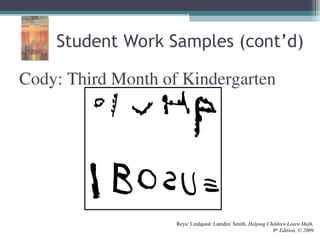
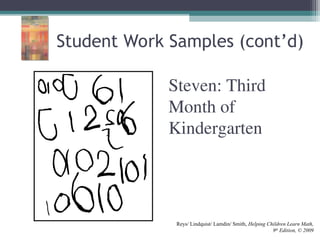
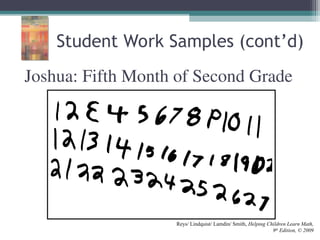
This document discusses the importance of counting and number sense in early childhood and primary education, highlighting stages of development from prenumber concepts to early number skills. It emphasizes the significance of subitizing, classification, patterns, and various counting strategies, including the use of calculators to aid learning. Furthermore, it outlines the principles of counting and provides examples of student work to illustrate these concepts.