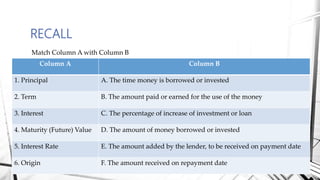
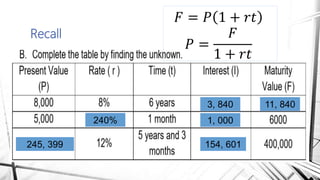
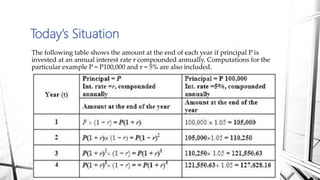
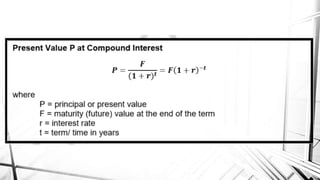
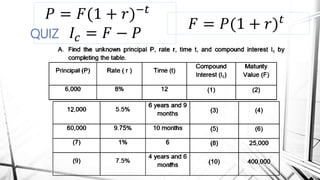
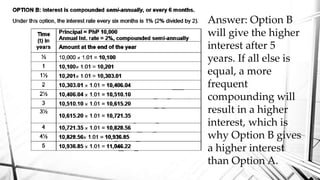
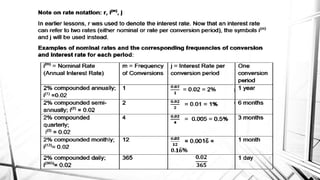
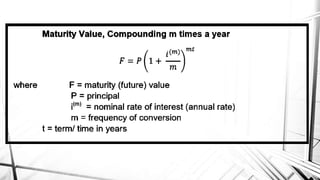
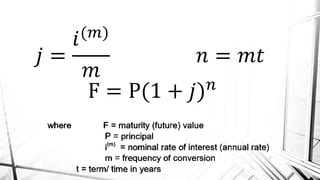
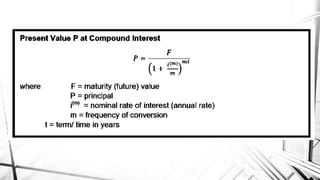
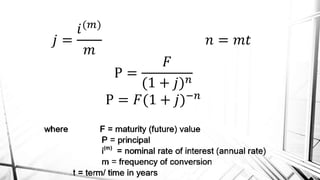
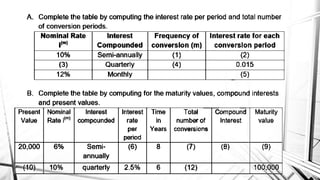
Compound interest is interest calculated on the initial principal and also on the accumulated interest from previous periods of time. More frequent compounding results in higher total interest earned over time. For example, compounding interest semi-annually instead of annually means interest is earned twice as often, leading to greater overall growth of the principal amount. The document provides examples of compound interest calculations using common formulas and variables like principal, interest rate, time period, and future/maturity value.