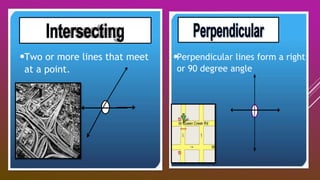
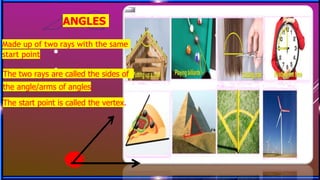
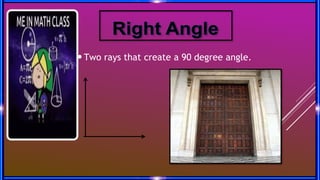
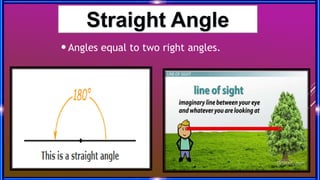
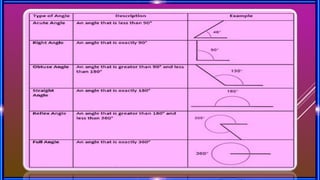
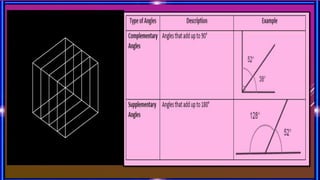
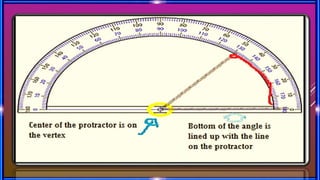
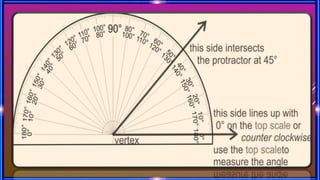
This document provides an overview of geometry concepts to be covered in a 5th grade mathematics class. It will discuss basic geometry symbols, how angles are formed, types of angles including acute, obtuse, right, straight and complementary/supplementary angles. It will also cover using a protractor to measure and draw angles.