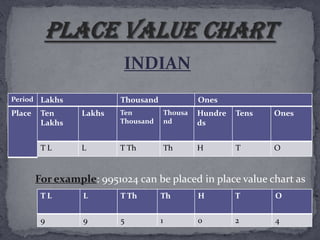
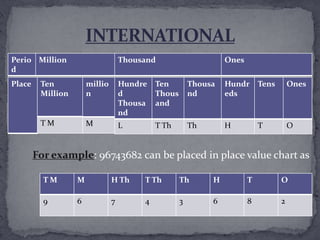
Numbers help us count objects and represent quantities through numerals. They also help communicate quantities and compare the size of collections by arranging them in order. Place value systems like the Indian and modern systems organize numbers by placing values (ones, tens, hundreds, etc.) in columns to easily represent and compare numbers. Rounding is the process of approximating a number to a desired place value like the nearest ten, hundred or thousand by following set rules. Roman numerals also represented an early system of writing numbers using symbols that corresponded to values.