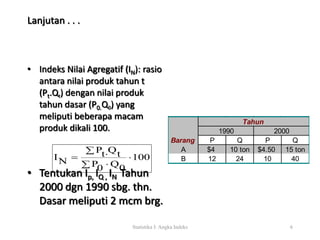
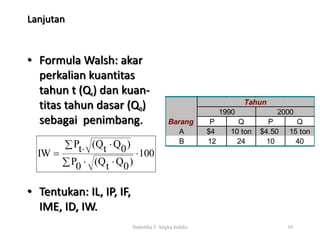
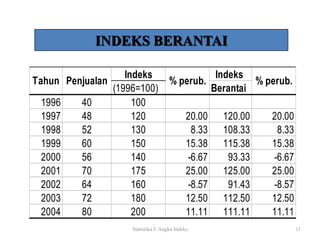
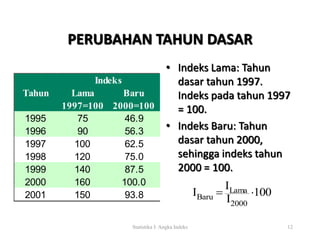
Dokumen ini menjelaskan tentang angka indeks, termasuk definisi, klasifikasi, dan berbagai tipe indeks seperti indeks sederhana, agregatif, dan agregatif tertimbang. Disebutkan juga cara menghitung masing-masing indeks dengan contoh tahun 1990 dan 2000 serta metode penimbang yang berbeda dalam indeks agregatif. Selain itu, terdapat informasi mengenai perubahan tahun dasar untuk indeks lama dan baru.