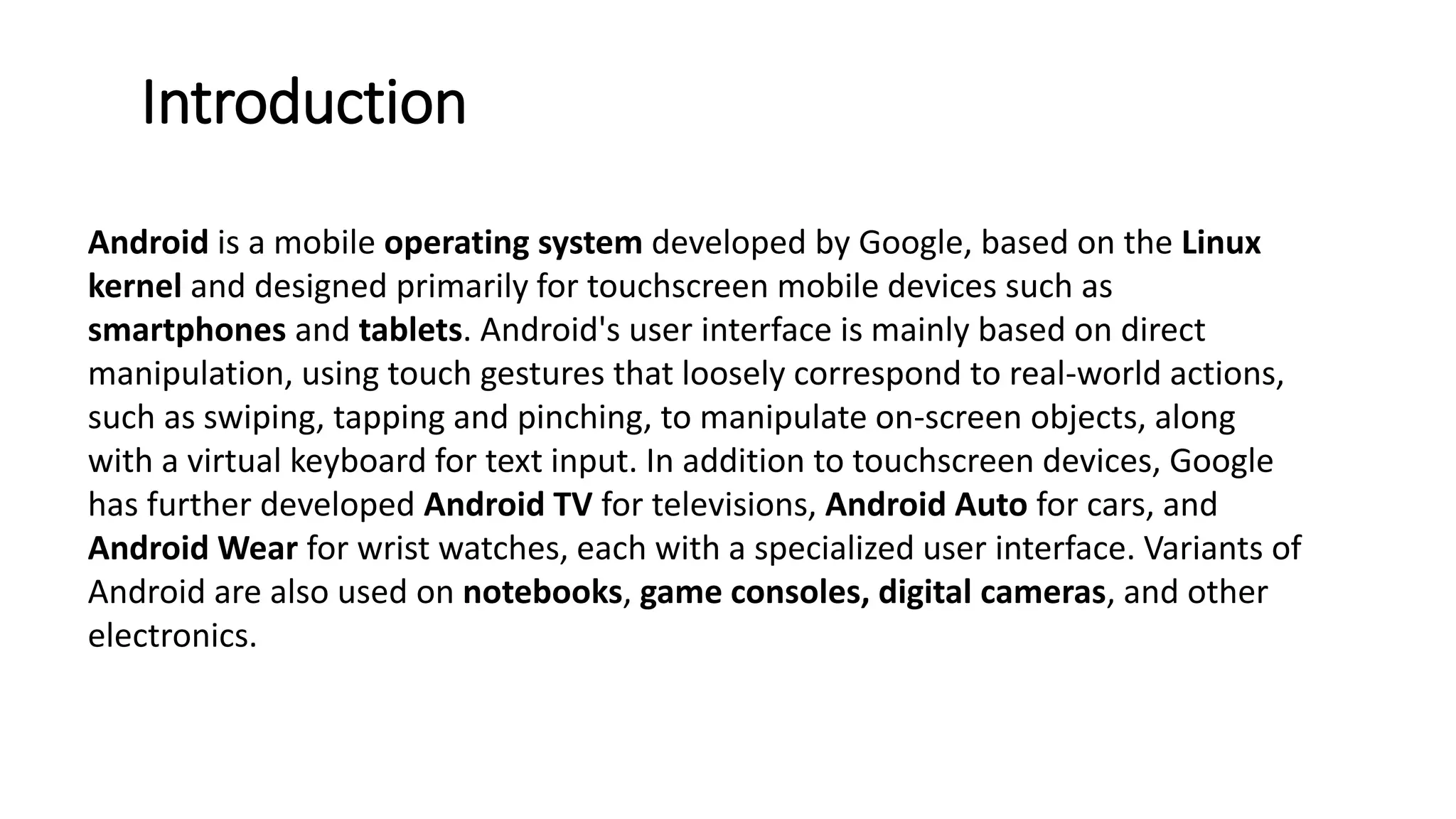
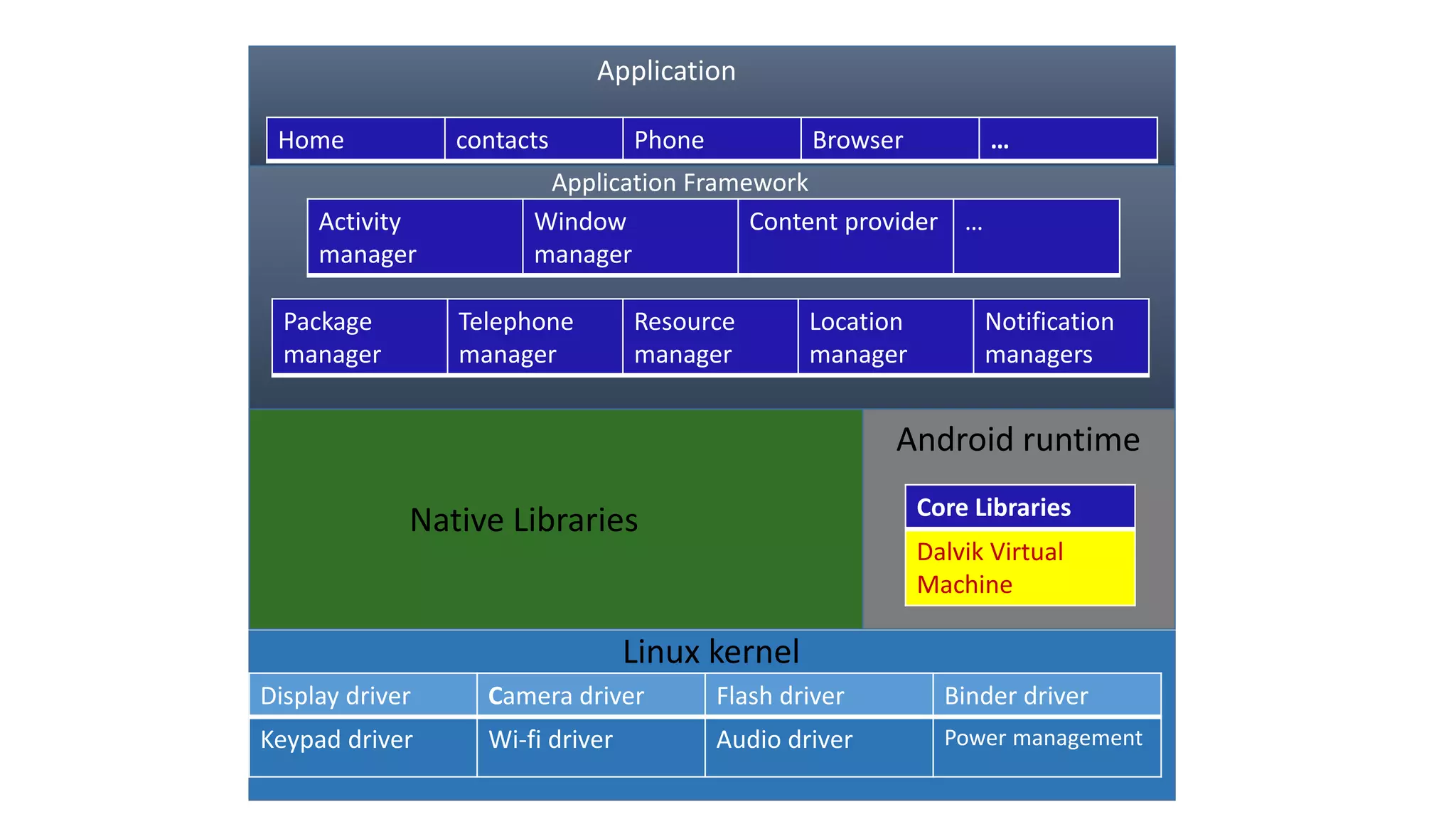
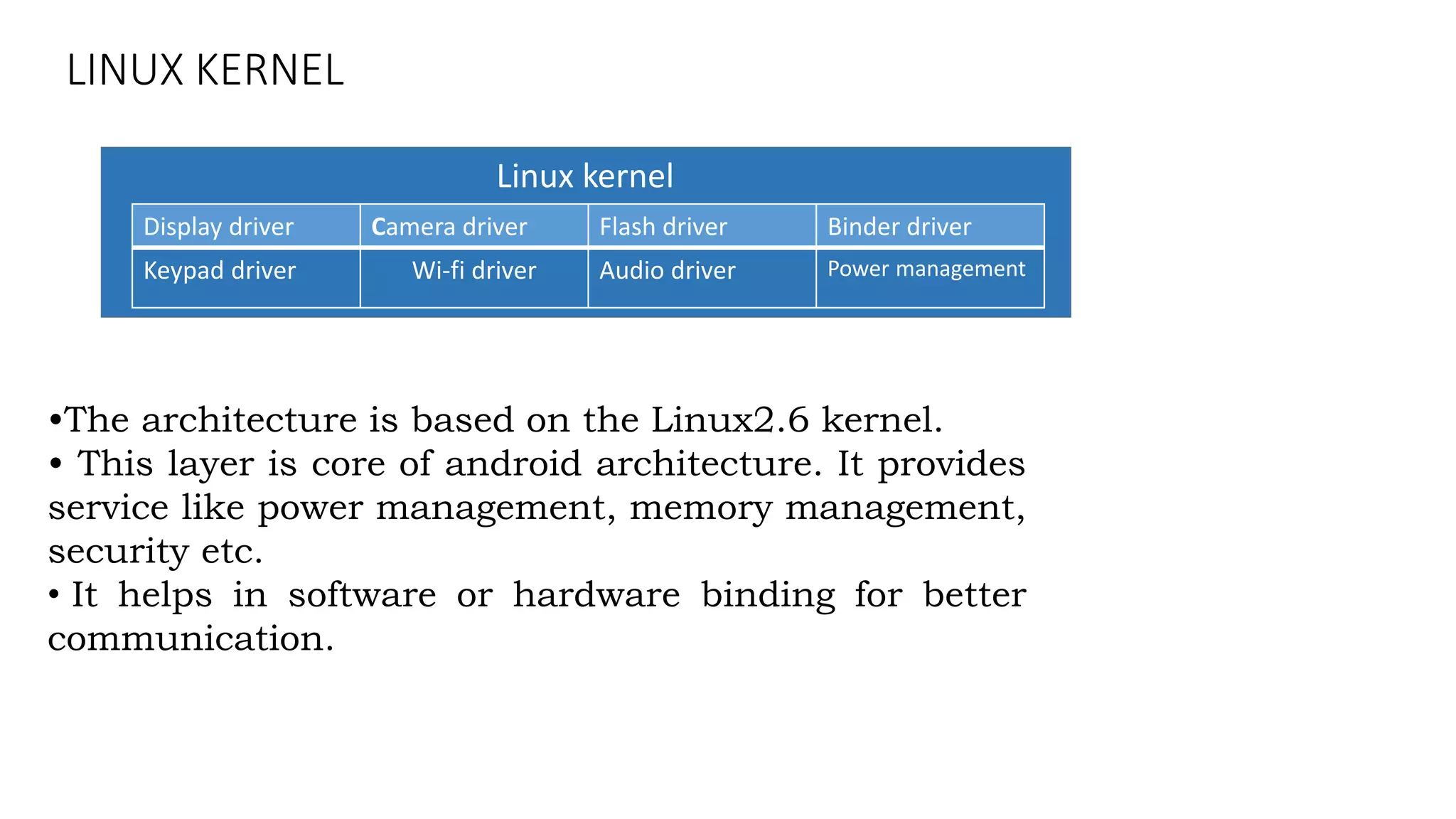
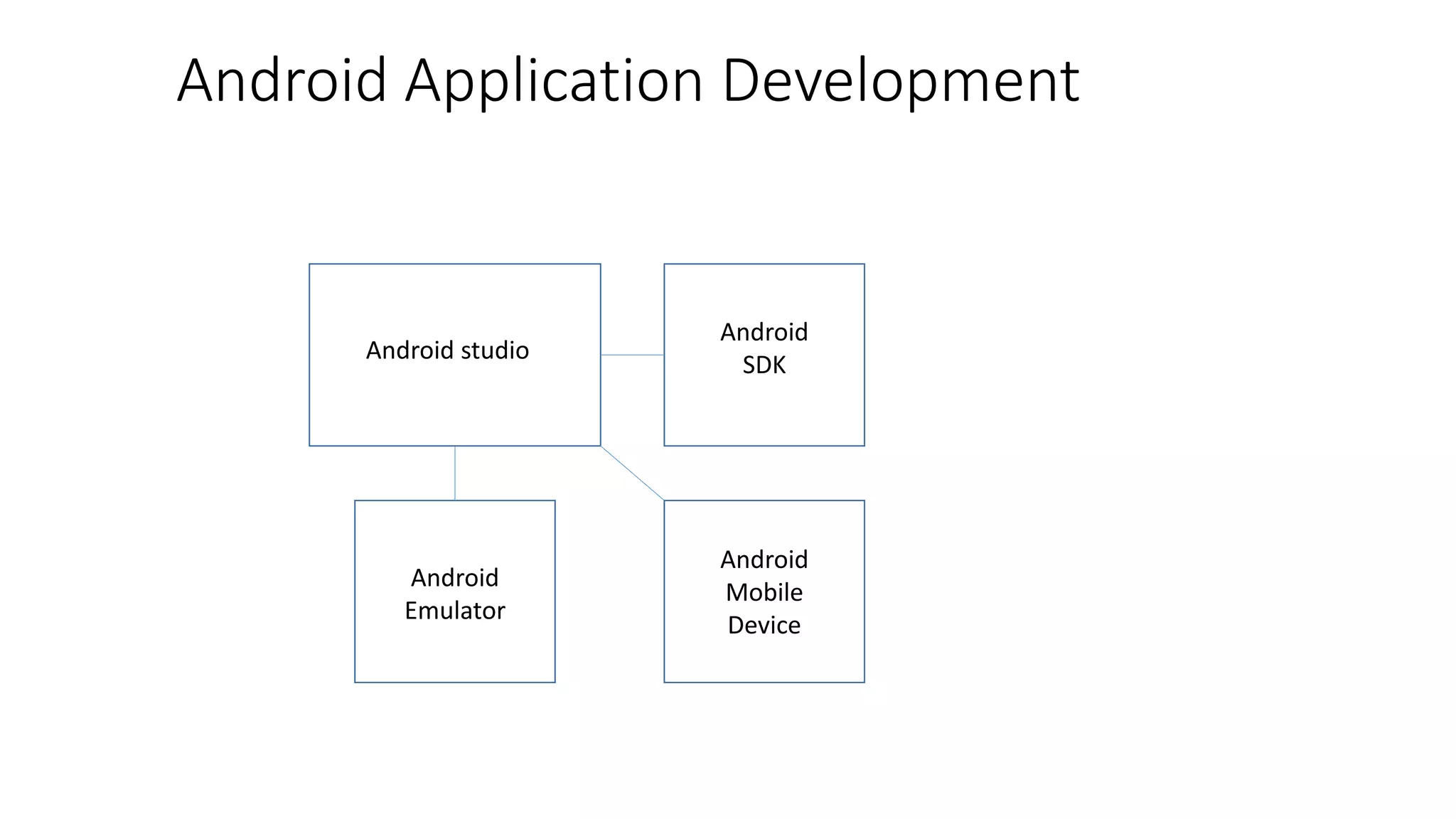
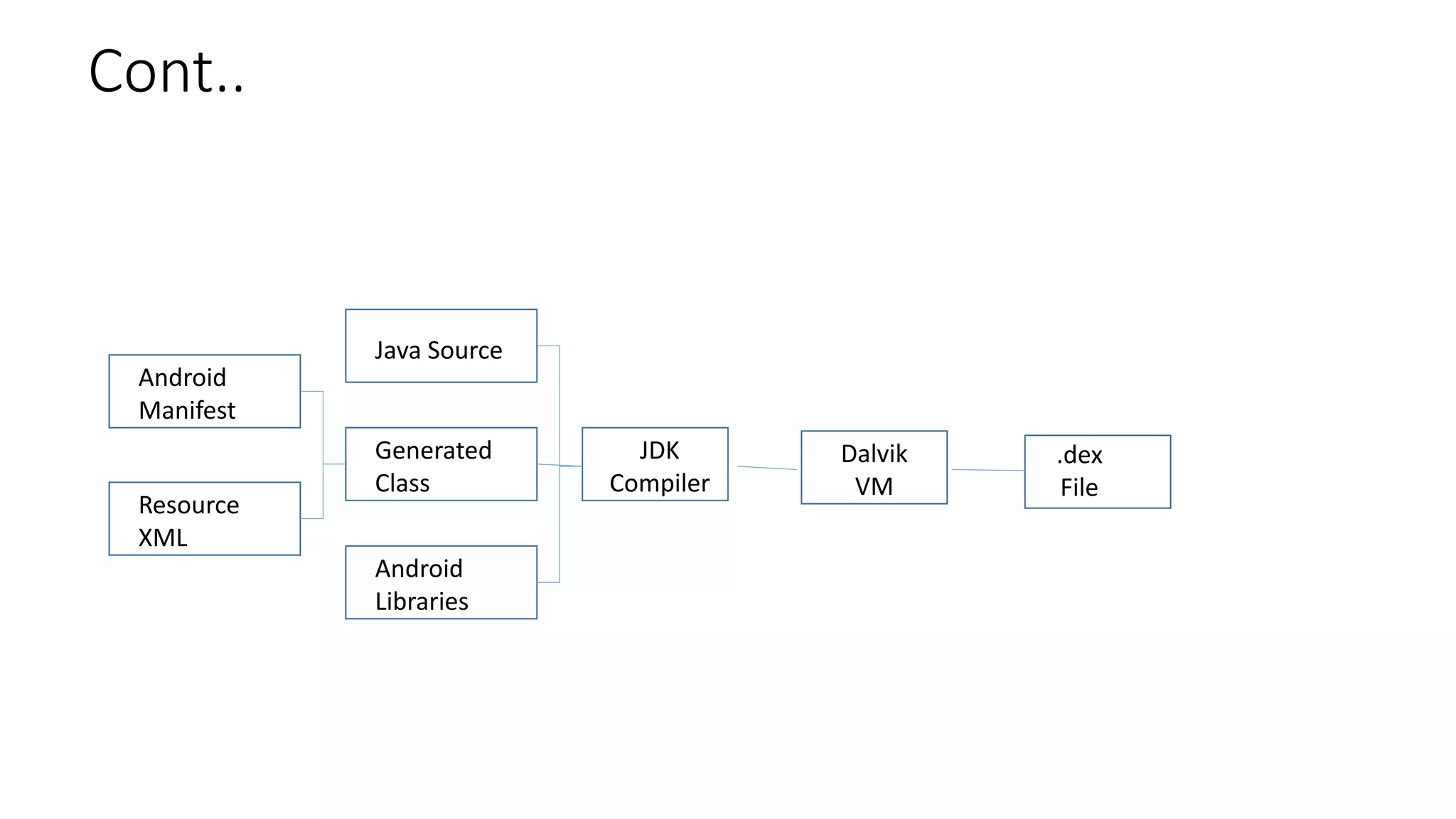
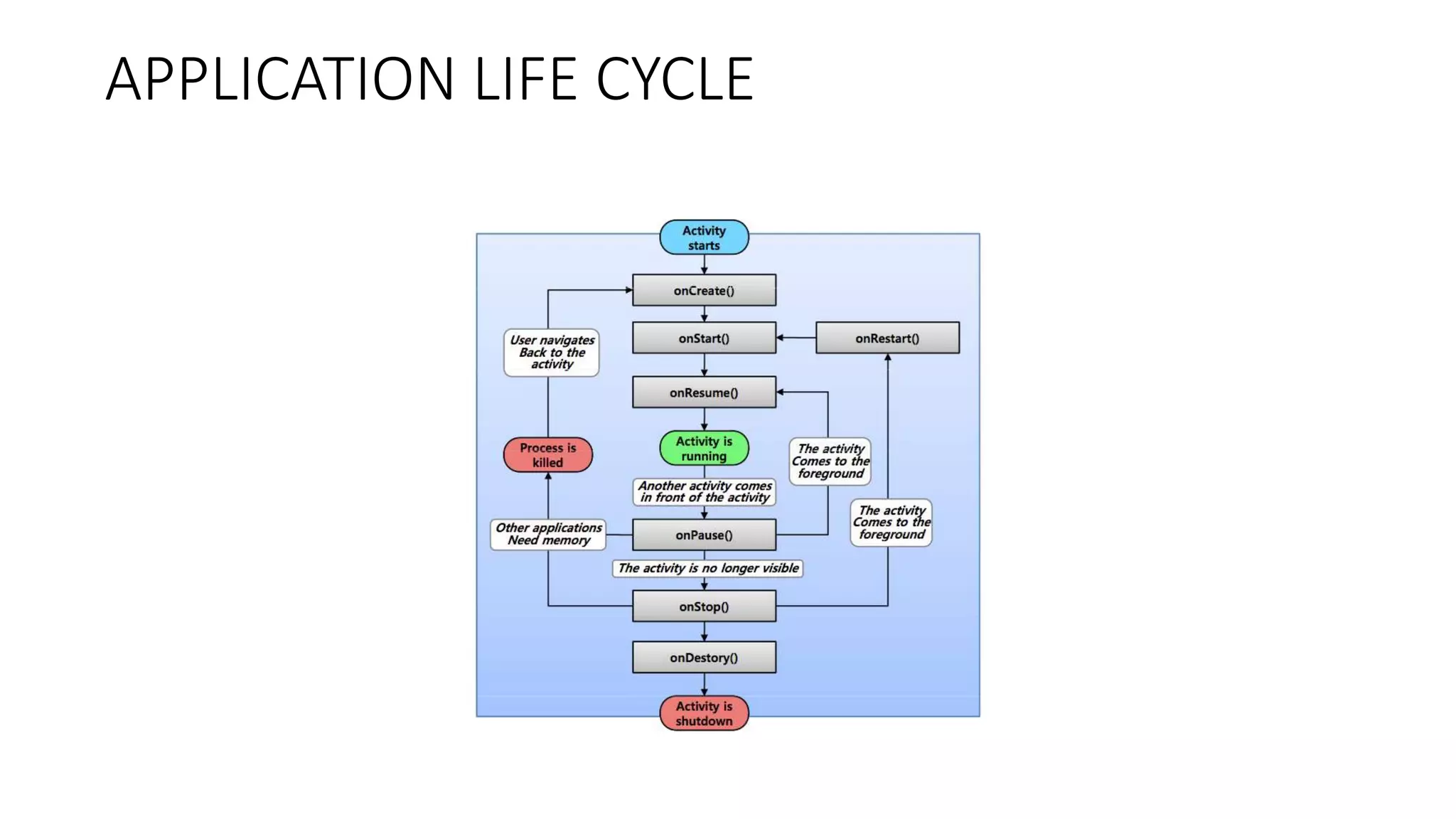
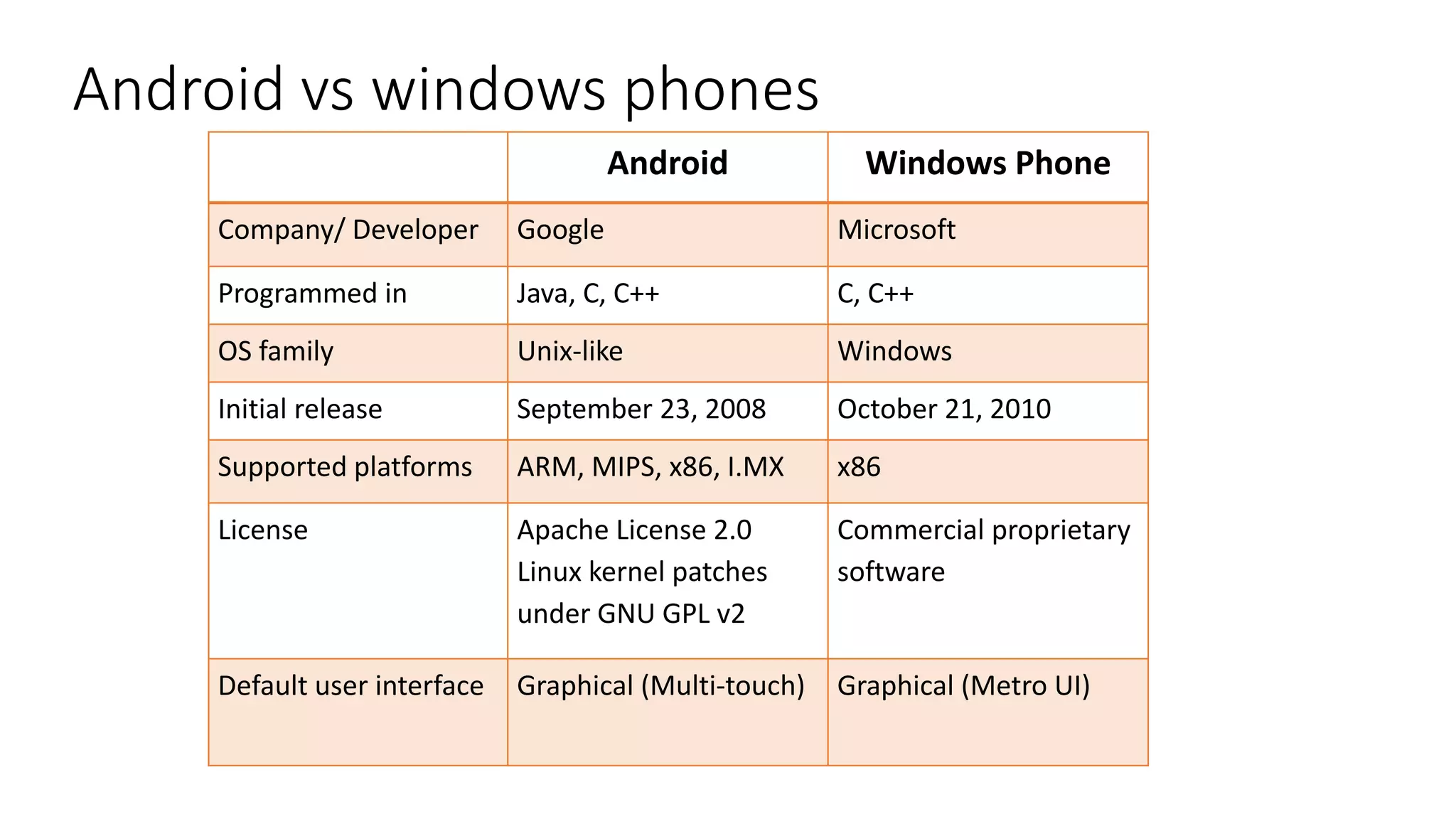
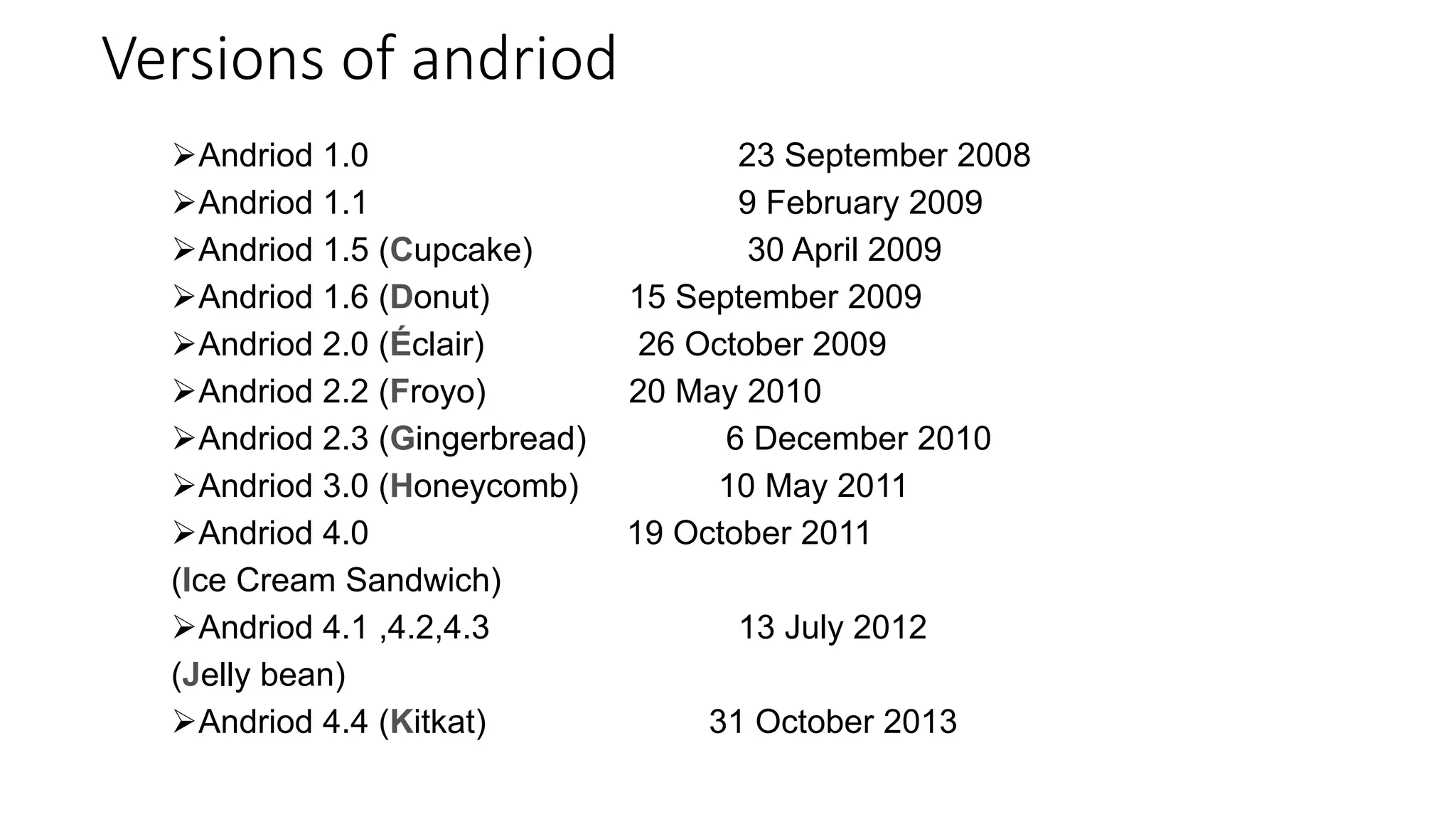
The document provides an overview of the Android operating system. It describes Android's architecture as having four layers - the application layer, application framework, native libraries and runtime, and the Linux kernel. The application framework provides common services like activity management, resource management, and notifications. Android uses a multi-process model with user and group IDs for security between applications. Features of Android include background location, developer tools, optimization for mobile, component reuse/replacement, and support for media, touch, cameras and more. The document also discusses Android versions and compares Android to other operating systems.