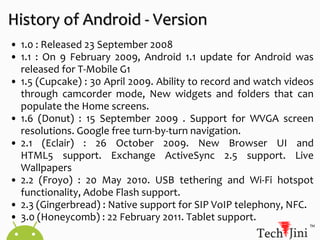
Android was founded in 2003 and acquired by Google in 2005. It has grown significantly, becoming the second largest operating system after Windows. The document then discusses Android's history and versions, architecture, application fundamentals including components, and tools for development. It provides an overview of creating a basic "Hello World" Android application.











![Android - What is Android?“Android is a [open source] software stack for mobile devices that includes an operating system, middleware and key applications. The Android SDK provides the tools and APIs necessary to begin developing applications on the Android platform using the Java programming language.”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/android-110416121536-phpapp01/85/Android-16-320.jpg)
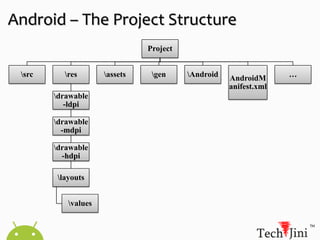
![Android – Sourcesource.android.com/source/download.html [bit.ly/SrcAnd]License : Apache 2.0 & GPL v2Git repositories.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/android-110416121536-phpapp01/85/Android-18-320.jpg)




