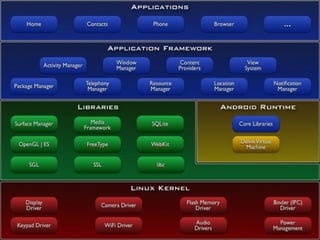
This document provides an overview of the Android operating system, including its history and development. It describes Android's origins at Google and the Open Handset Alliance in 2007. It outlines the major versions of Android from 1.0 to the present and discusses Android's open source architecture, including its Linux kernel base, native C/C++ libraries, Java-based framework and application layer. The document also briefly touches on Android's advantages in customization and applications, as well as some of its limitations, such as requirements for Java and SDK use.