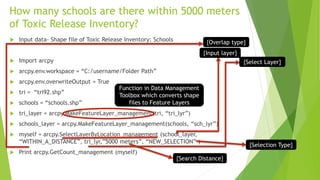
The document provides an overview of the Arcpy package used for geographic data analysis, data management, and map automation with Python, highlighting its structure and functionalities within the mapping module and data management toolbox. It discusses various classes and functions available in Arcpy, including how to create and manipulate map documents, layers, and data frames, as well as perform tasks like copying and merging datasets. Additionally, it includes examples of Python scripts that demonstrate the application of these functionalities for real-world GIS tasks.








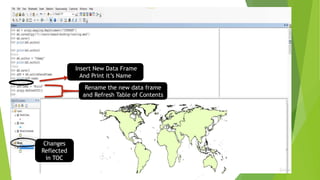



![To show first layer of list indicated by [0] position
Optional Parameters](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticswitharcpypackage-200719102018/85/Analytics-with-arcpy-package-detailing-of-Mapping-Module-Properties-and-Data-management-Tools-13-320.jpg)
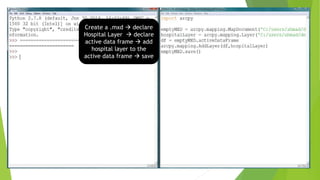

![Merge Management script
Tool used to merge two or more datasets into one.
Arcpy.Merge_management([‘C:/data/parcels1.shp’,’C:/data/parcels2.shp’],’C:/data
/mergedParcels.shp’ )
import arcpy
arcpy.env.workspace = ‘C:/users/name/desktop/sampleData.gdb’
arcpy.env.overwriteOutput = True
arcpy.Merge_management([‘hospitals1’, ‘hospitals2’], ‘allHospitals’)
arcpy.Intersect_analysis([‘allHospitals’,’DC’],’DCHospitals’)
print(“Successfully finished”)
Syntax of Merge Management ;having 2
input shapefiles/layers as list items
and then output shapefile separate.
Fixing environment
variables ; pre-requisite
before running scripts.
Combining two list items
hospitals using merge](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/analyticswitharcpypackage-200719102018/85/Analytics-with-arcpy-package-detailing-of-Mapping-Module-Properties-and-Data-management-Tools-16-320.jpg)