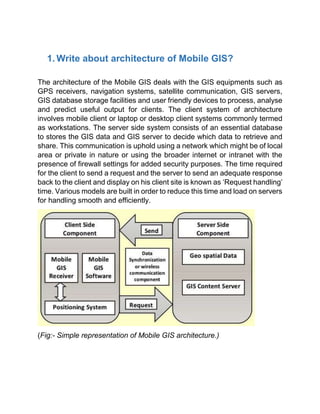
Mobile GIS architecture involves GPS receivers, navigation systems, satellite communication, GIS servers, databases, and mobile/desktop clients. The client sends requests to the server, which retrieves data from its database and sends a response. This communication occurs over a local or private network or the internet.
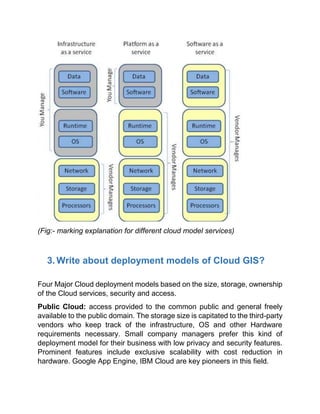
Cloud GIS has three service models: Software as a Service (SAAS) provides applications via thin clients; Platform as a Service (PAAS) deploys applications using data platforms; Infrastructure as a Service (IAAS) involves configuring all hardware and software.
There are four cloud deployment models: Public cloud for general public access; Private cloud for a single organization; Community cloud for groups agreeing on access; Hybrid cloud