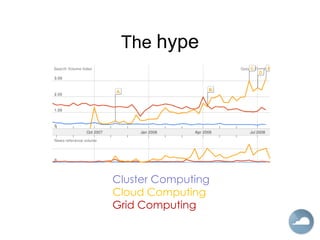
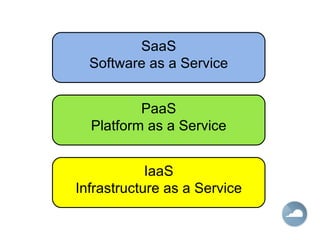
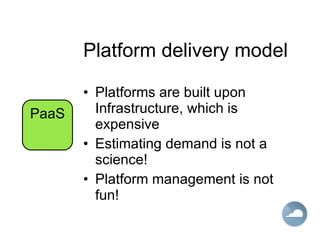
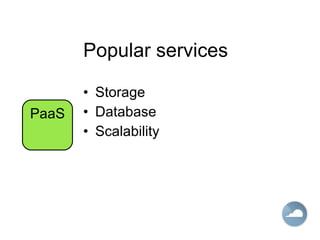
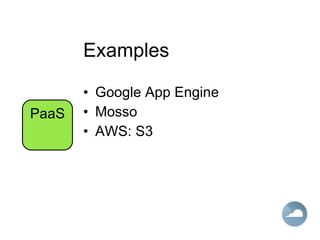
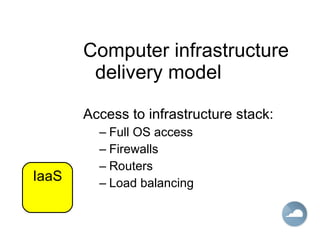
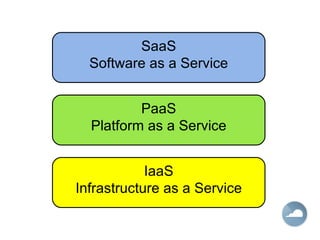
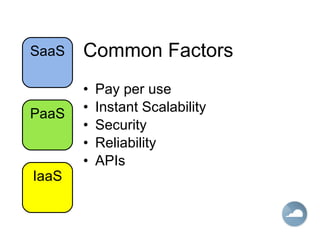
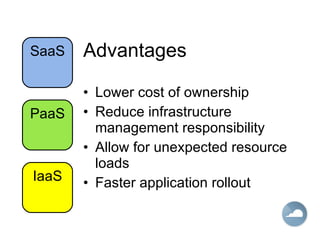
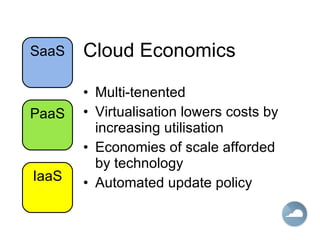
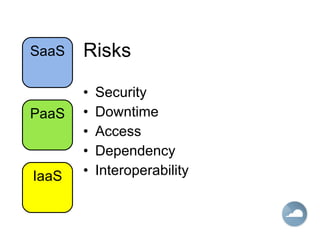
The document discusses cloud computing and different cloud service models including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). IaaS refers to accessing computer infrastructure resources like servers and storage. PaaS allows accessing platforms and development tools without installing them locally. SaaS delivers software applications through a web browser without installing or managing the software. The cloud offers advantages like scalability, pay-per-use pricing, and reduced maintenance costs compared to locally hosted infrastructure and applications.