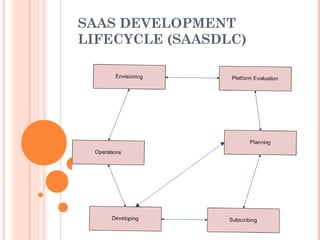
SaaS (Software as a Service) is software owned and managed remotely by providers and delivered via the cloud. It is commonly used for HR, CRM, collaboration tools, and procurement. Benefits include lower costs than on-premise software, reduced development time, pay-as-you-go pricing, and vendor handling of upgrades, security, and uptime. The SaaS development lifecycle includes envisioning, platform evaluation, planning, subscribing, developing, operations, patching, and upgrades, with upgrades typically done during scheduled downtime through automated processes. SaaS spending is projected to continue rising as it becomes a preferred model for both large enterprises and SMBs.