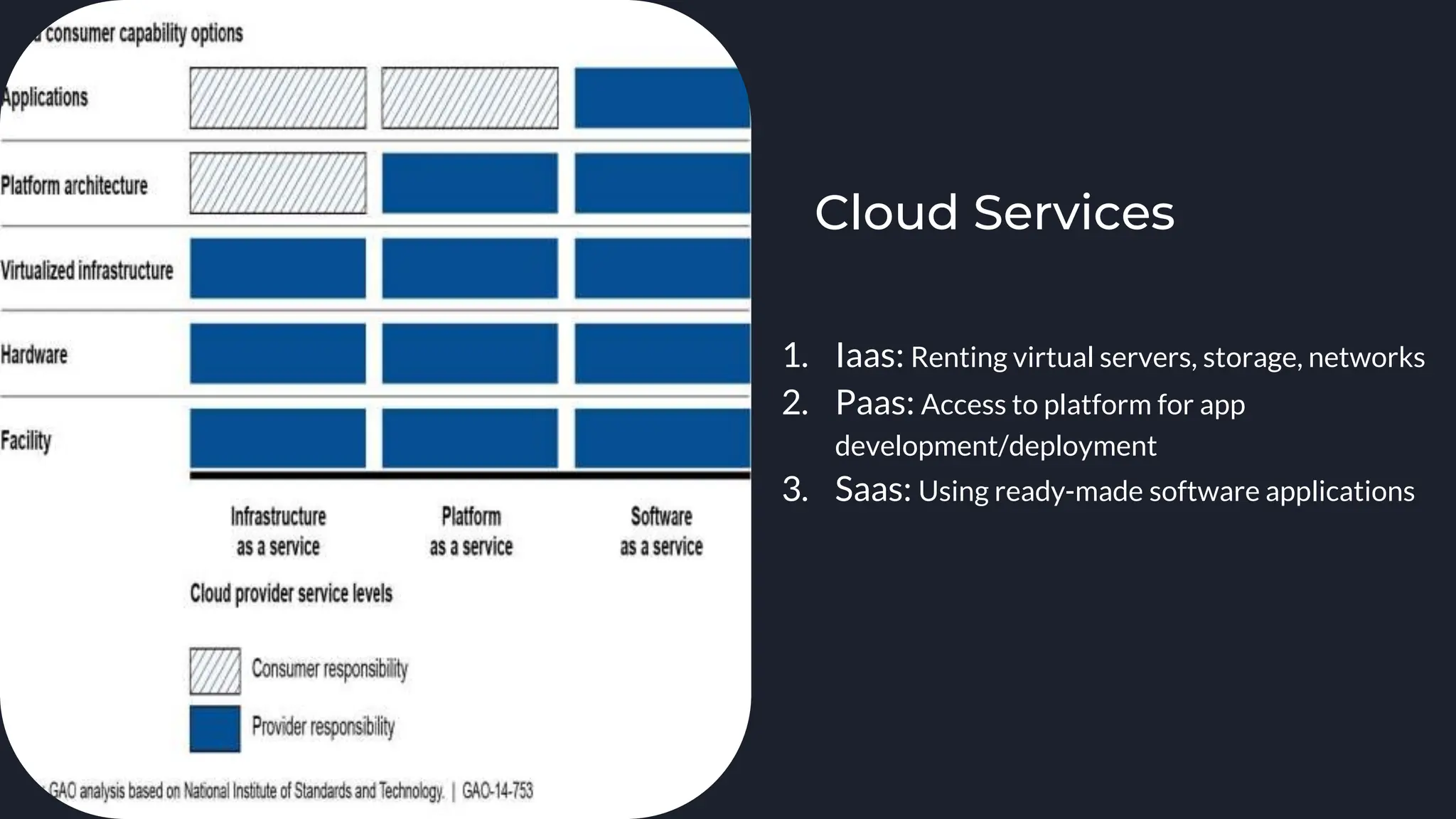
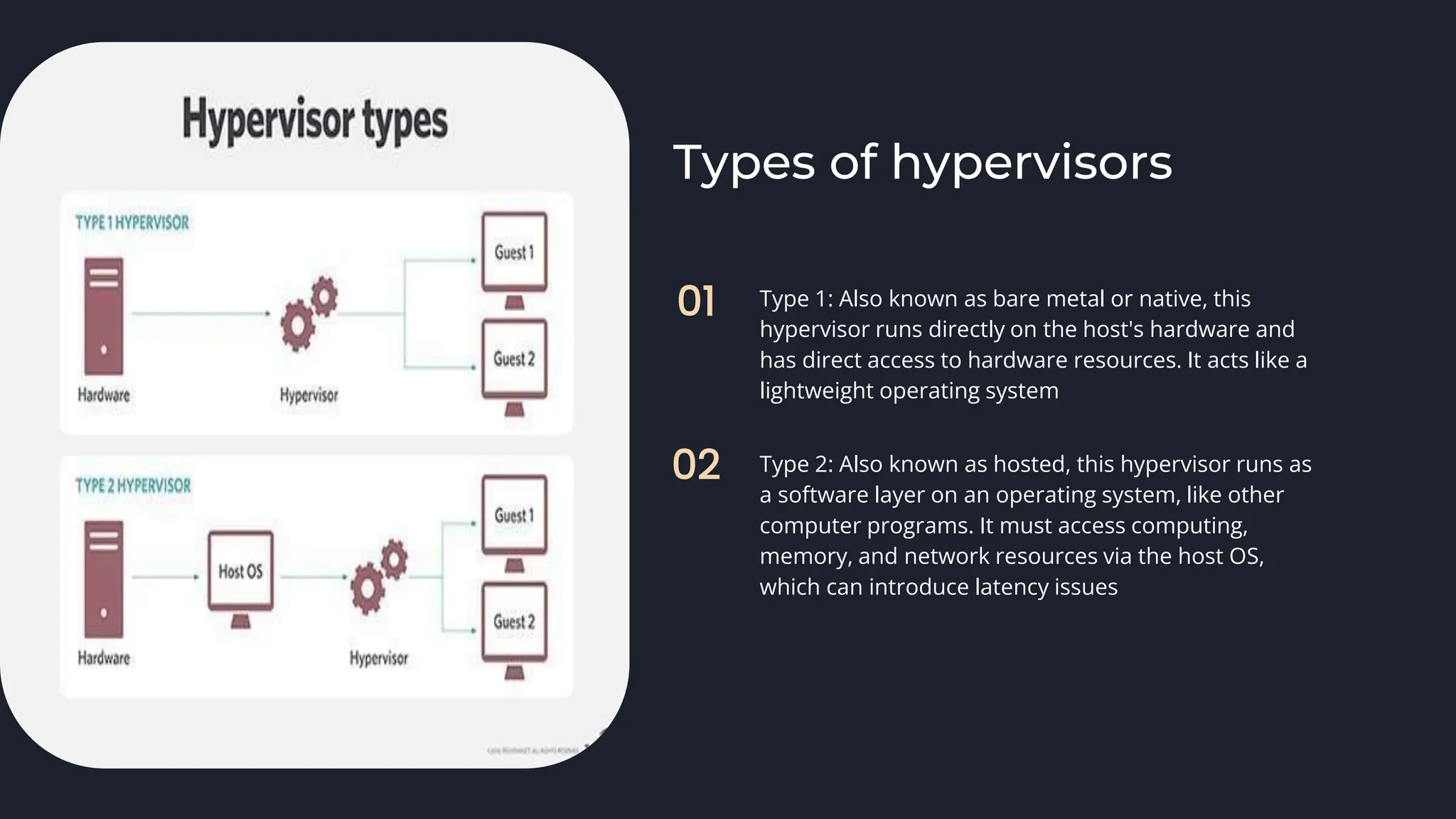
The document provides an introduction to cloud computing, defining it as the on-demand delivery of IT resources over the internet with various pricing models. It explains the three main services: IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service), and SaaS (Software as a Service), detailing their functions and benefits. Additionally, it discusses deployment models, virtualization technologies, and emerging job roles within the cloud computing market, which is projected to grow significantly in the coming years.