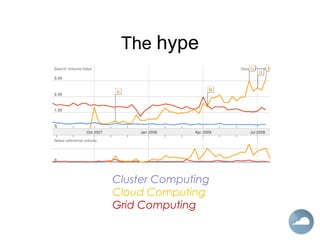
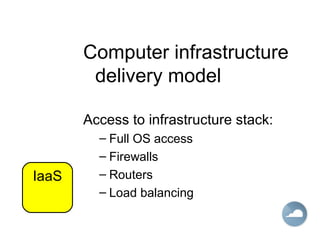
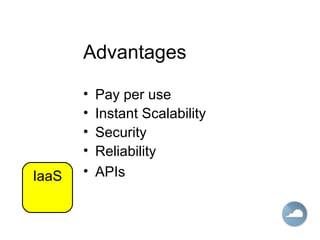
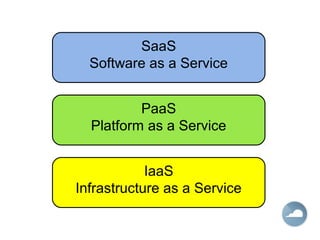
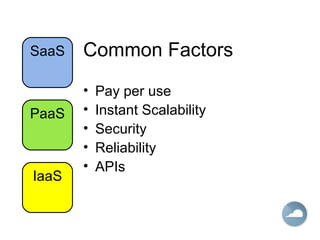
This document provides an introduction to Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) cloud computing models. It defines cloud computing as providing on-demand access to IT resources and applications from the internet without requiring technical knowledge of the underlying infrastructure. The three main cloud service models - SaaS, PaaS, and IaaS - are described along with their advantages of pay-per-use pricing, instant scalability, security, reliability and APIs. Popular commercial examples for each service model are also listed.