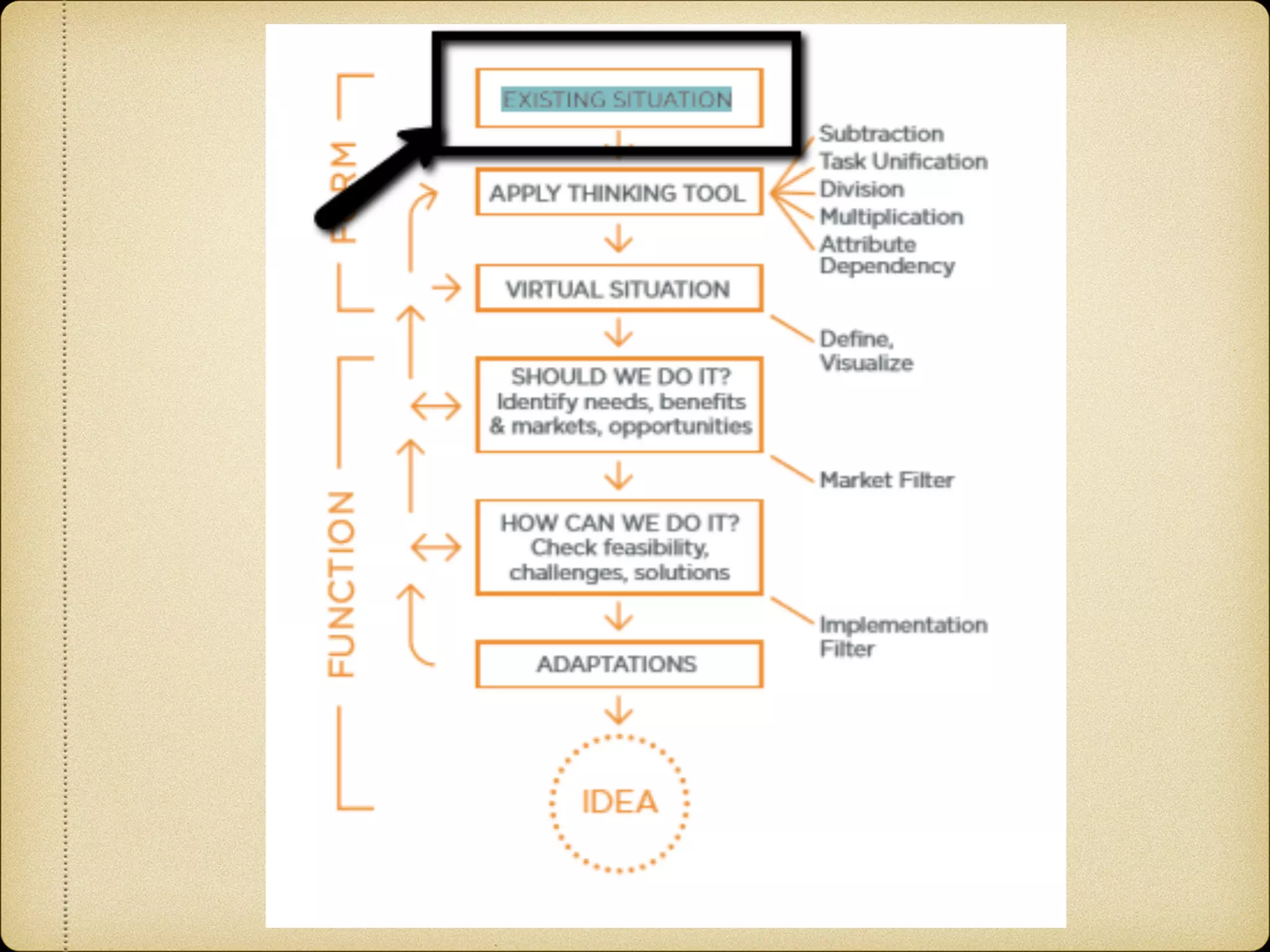
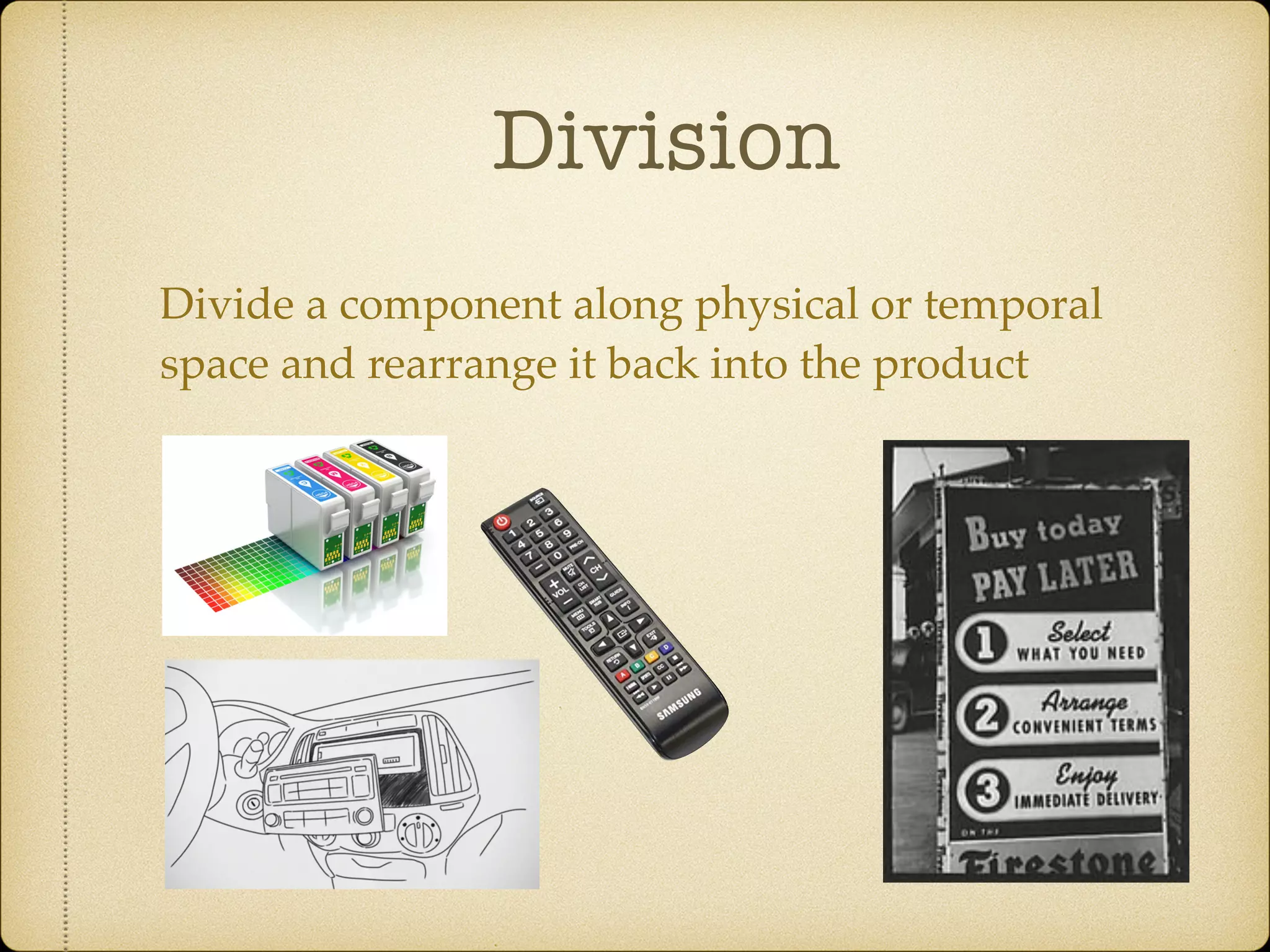
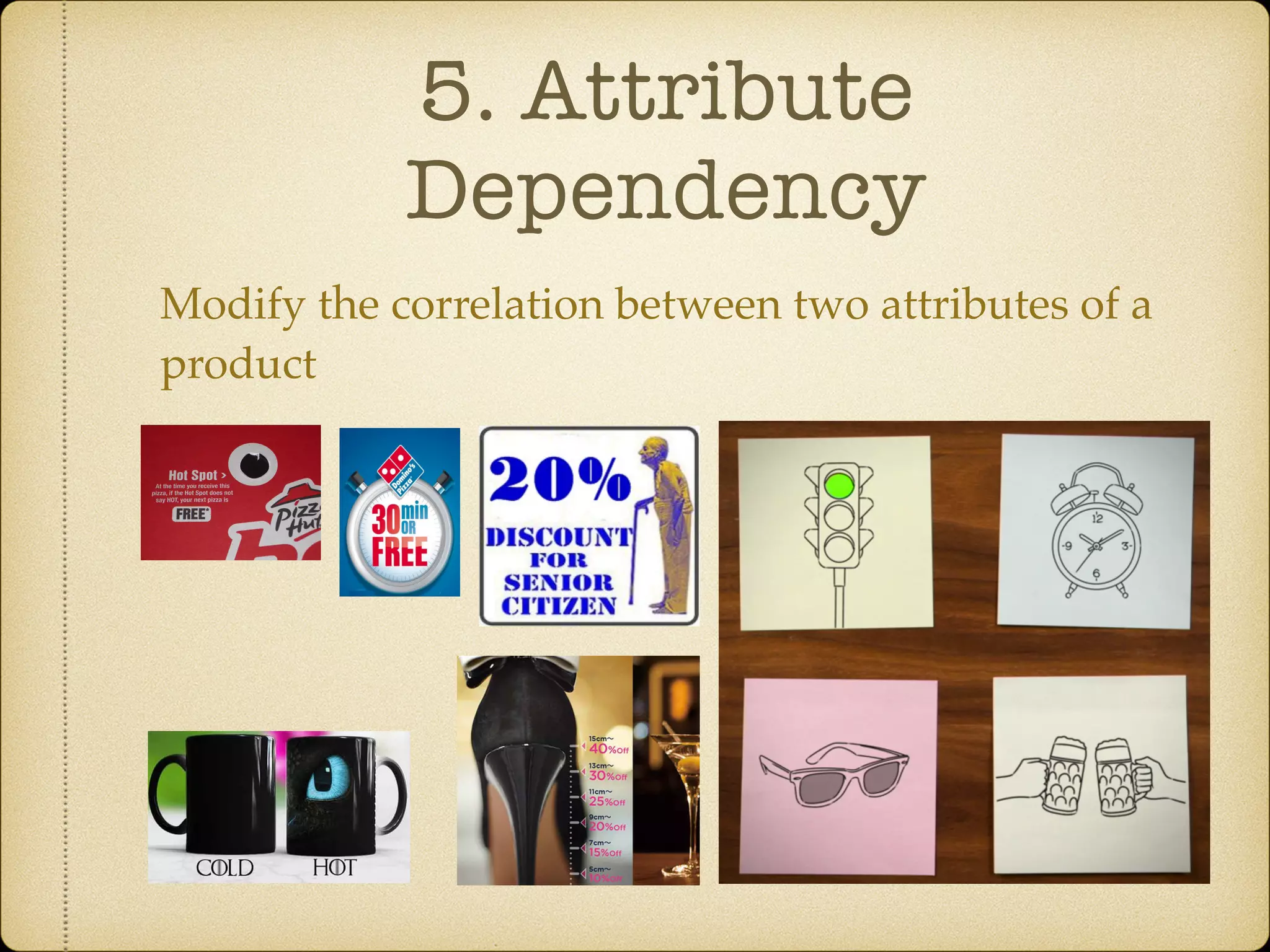
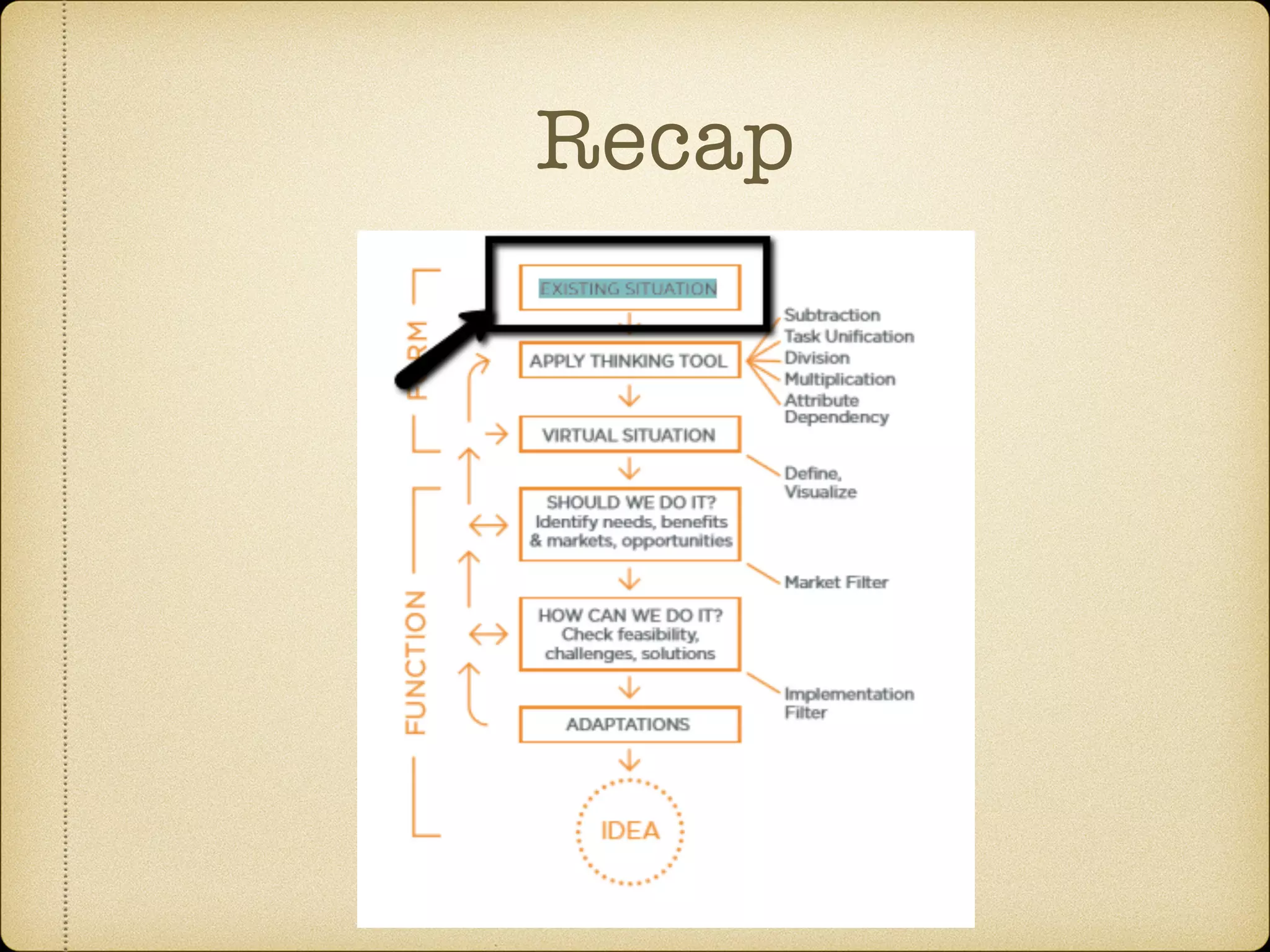
The Systematic Inventive Thinking (SIT) method identifies five patterns that have historically driven innovation, emphasizing the importance of overcoming cognitive fixedness and utilizing existing resources in creative processes. Key principles include the Path of Most Resistance, which encourages unconventional thinking, and the Closed World principle that focuses on generating ideas within established boundaries. Additionally, the Function Follows Form approach suggests creating virtual products by defining existing situations clearly before applying SIT tools for more efficient innovation.