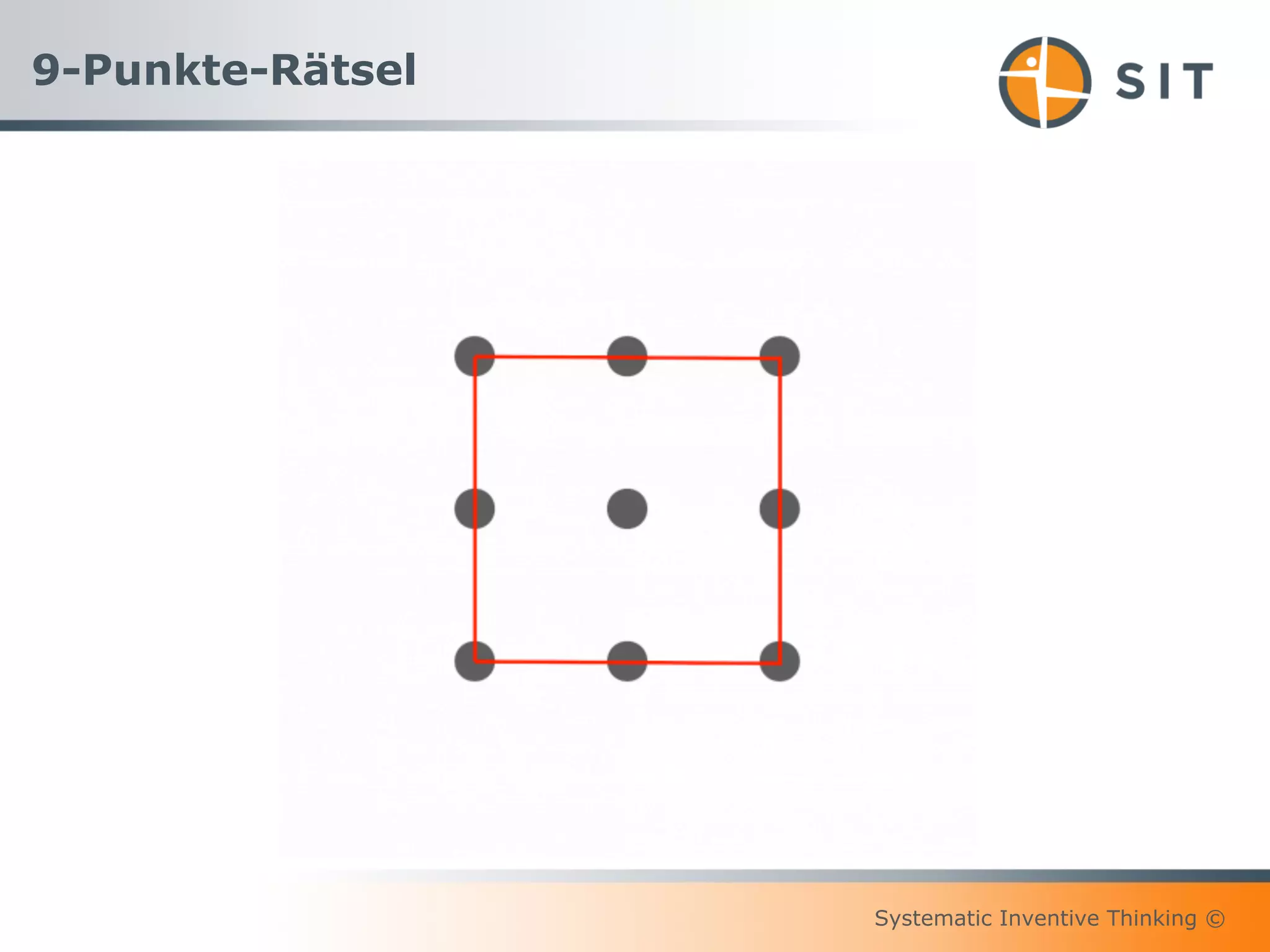
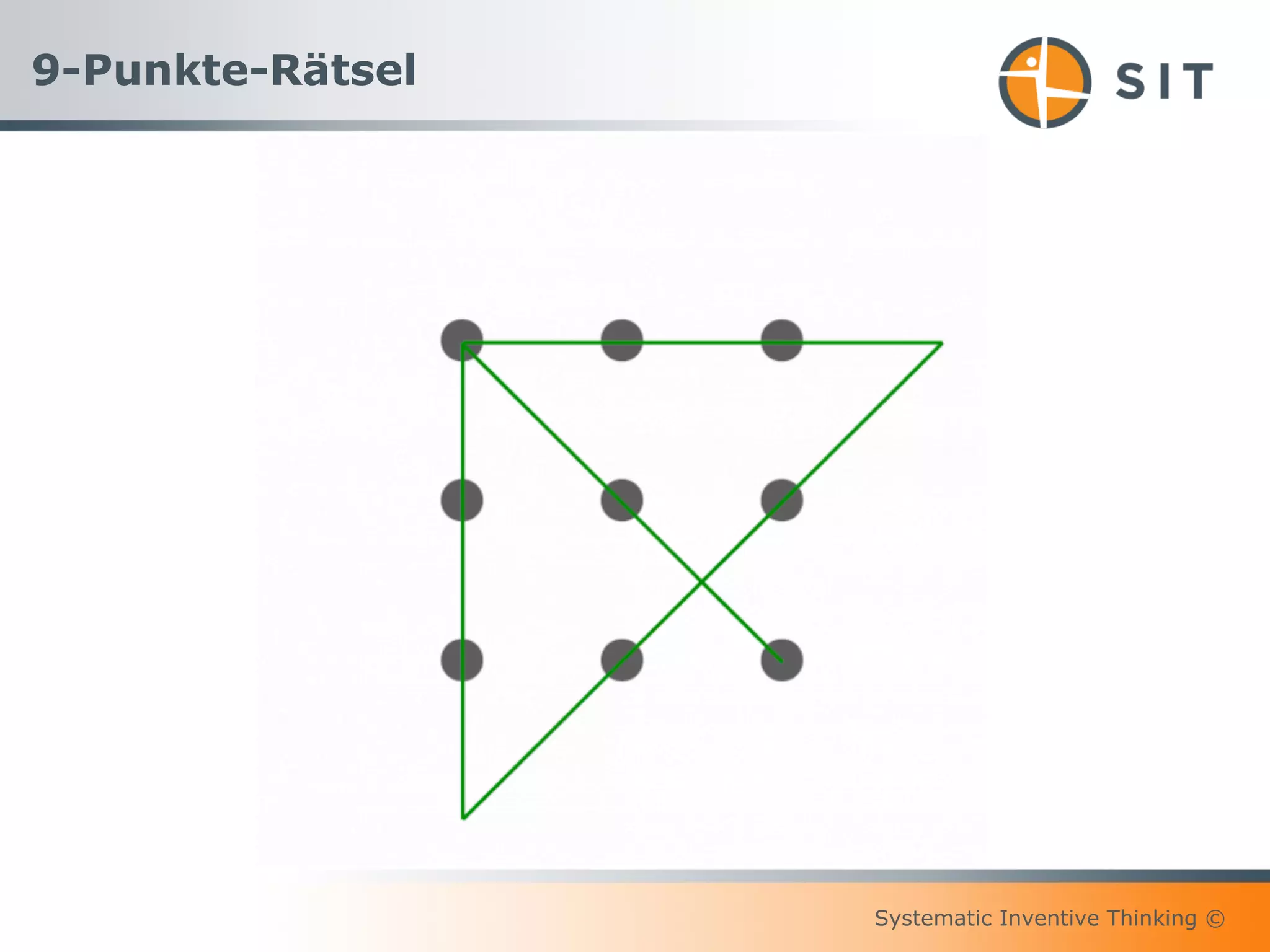
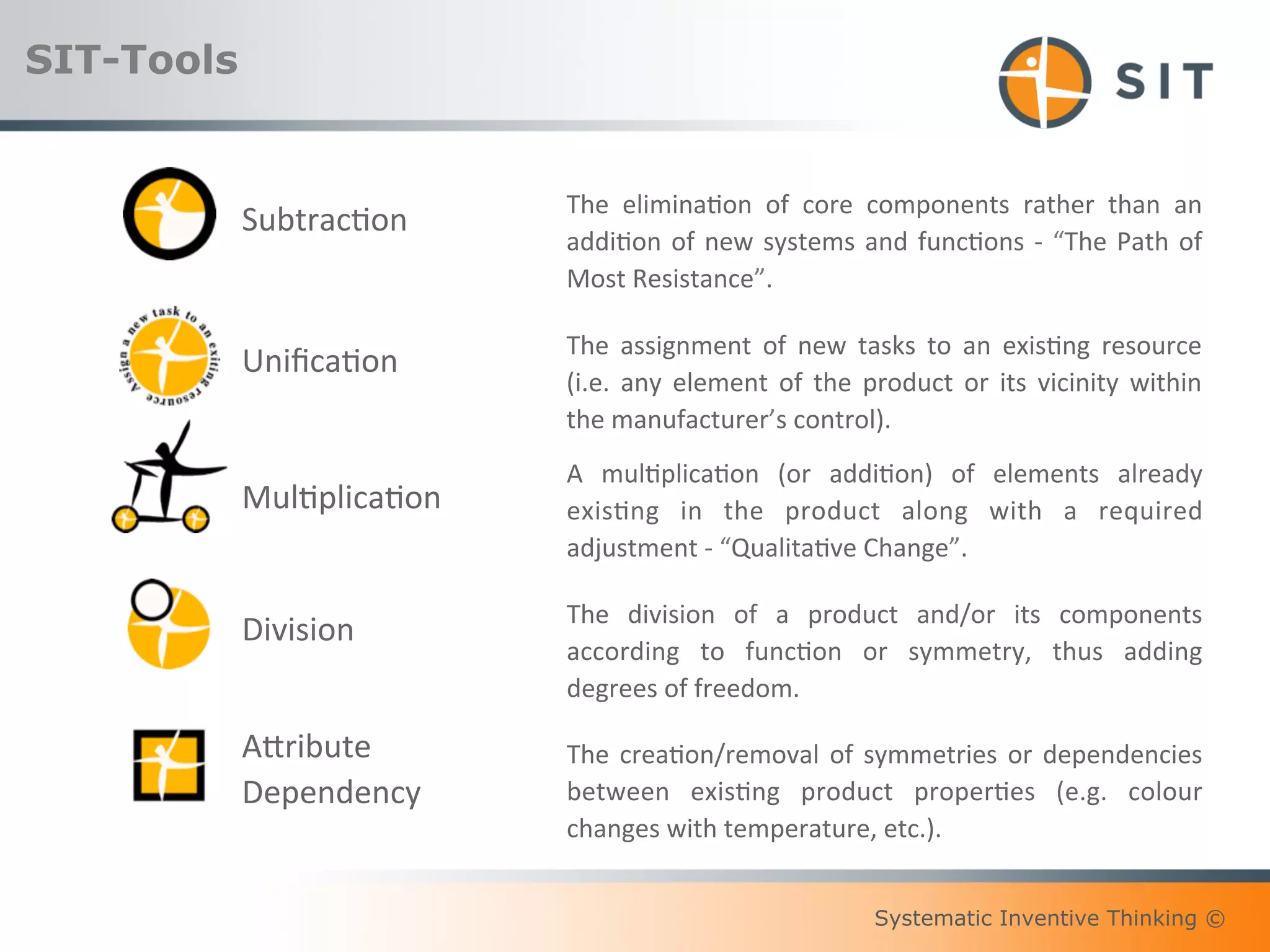
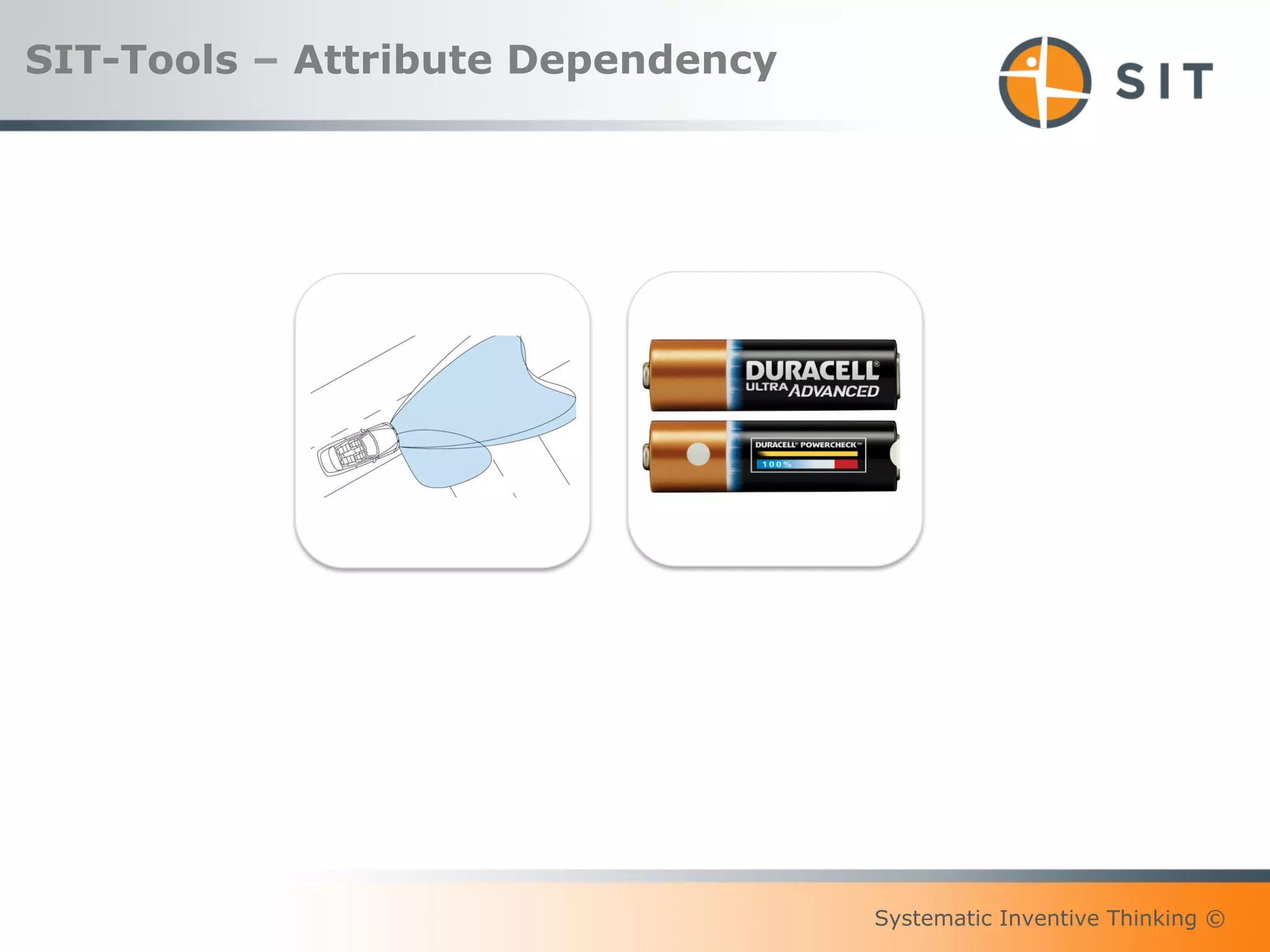
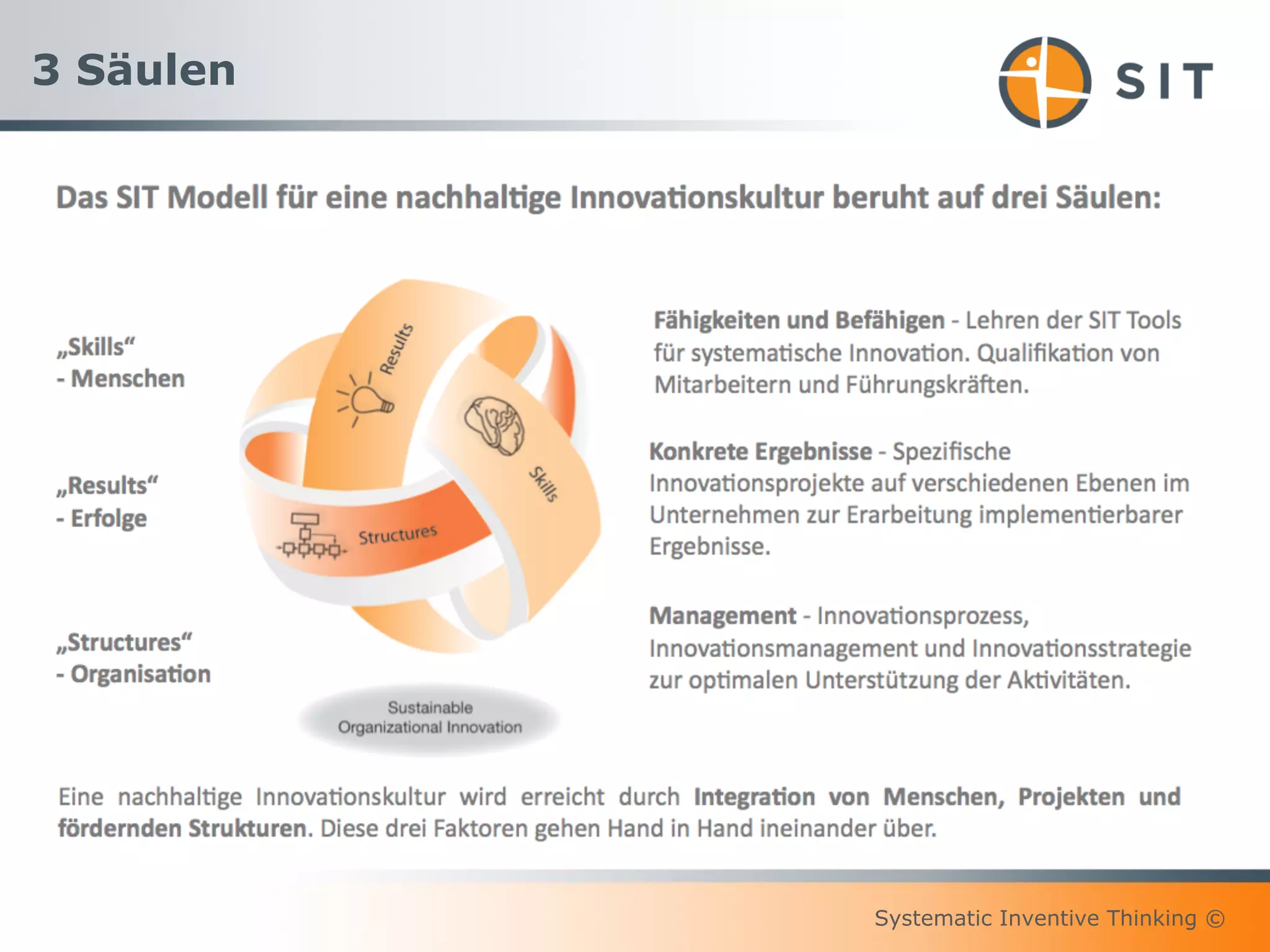
This document provides an overview of Systematic Inventive Thinking (SIT). SIT is a method for systematic innovation that utilizes a set of tools and principles. The document outlines the key SIT tools, which include subtraction, task unification, attribute dependency, multiplication, and division. It also discusses how SIT aims to push ideas towards an "innovation sweet spot" that is neither too close to existing solutions nor too far from realistic implementation. Additionally, the document references the three pillars of sustainable innovation culture and notes that SIT has been applied successfully by customers in various industries.