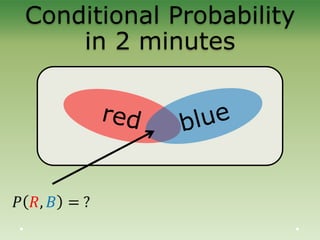
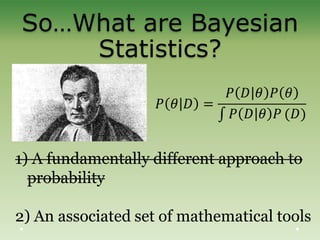
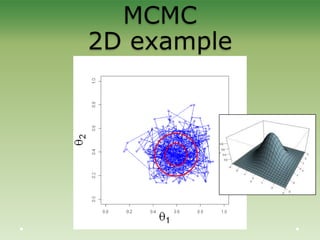
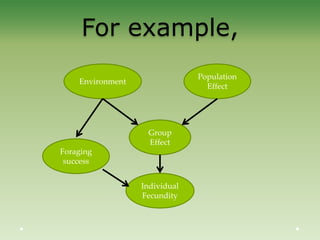
This document provides an introduction to Bayesian statistics. It discusses that Bayesian statistics takes a fundamentally different approach to probability than frequentist statistics by viewing parameters as random variables rather than fixed values. It also uses mathematical tools like Bayes' theorem, priors, posteriors, and Markov chain Monte Carlo simulations. The document explains Bayesian concepts and compares the Bayesian and frequentist perspectives. It argues that Bayesian methods are particularly useful for complex models with many interacting parameters.