This document discusses the development of an ISO technical report on e-portfolios for learning. It provides background on the consensus to develop the report in 2009-2010. The challenges of developing international standards are acknowledged. The report aims to provide guidance by 2012 on interoperability rather than prescriptive specifications. It defines e-portfolios and their uses from learner and assessor perspectives. Stakeholder use cases informed the development of categories and elements for e-portfolio composition. These include Identification, Synopsis, Education, Outcomes, Capability, Career, and Experience.















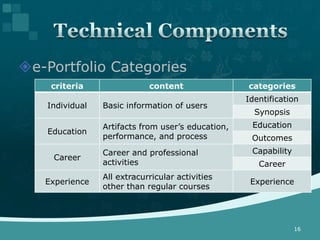

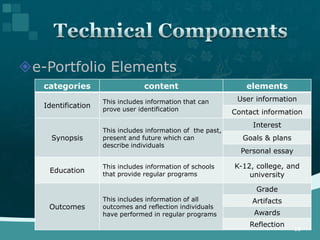
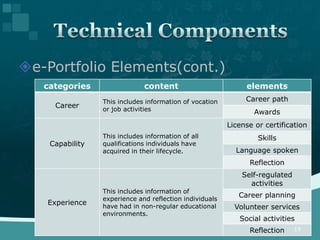


![[Figure]
Structure of the e-portfolio
reference model
<7 categories & 25 elements>
22](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20111017eac2011sswjm-111123220044-phpapp01/85/An-e-portfolio-reference-model-for-e-learning-22-320.jpg)


