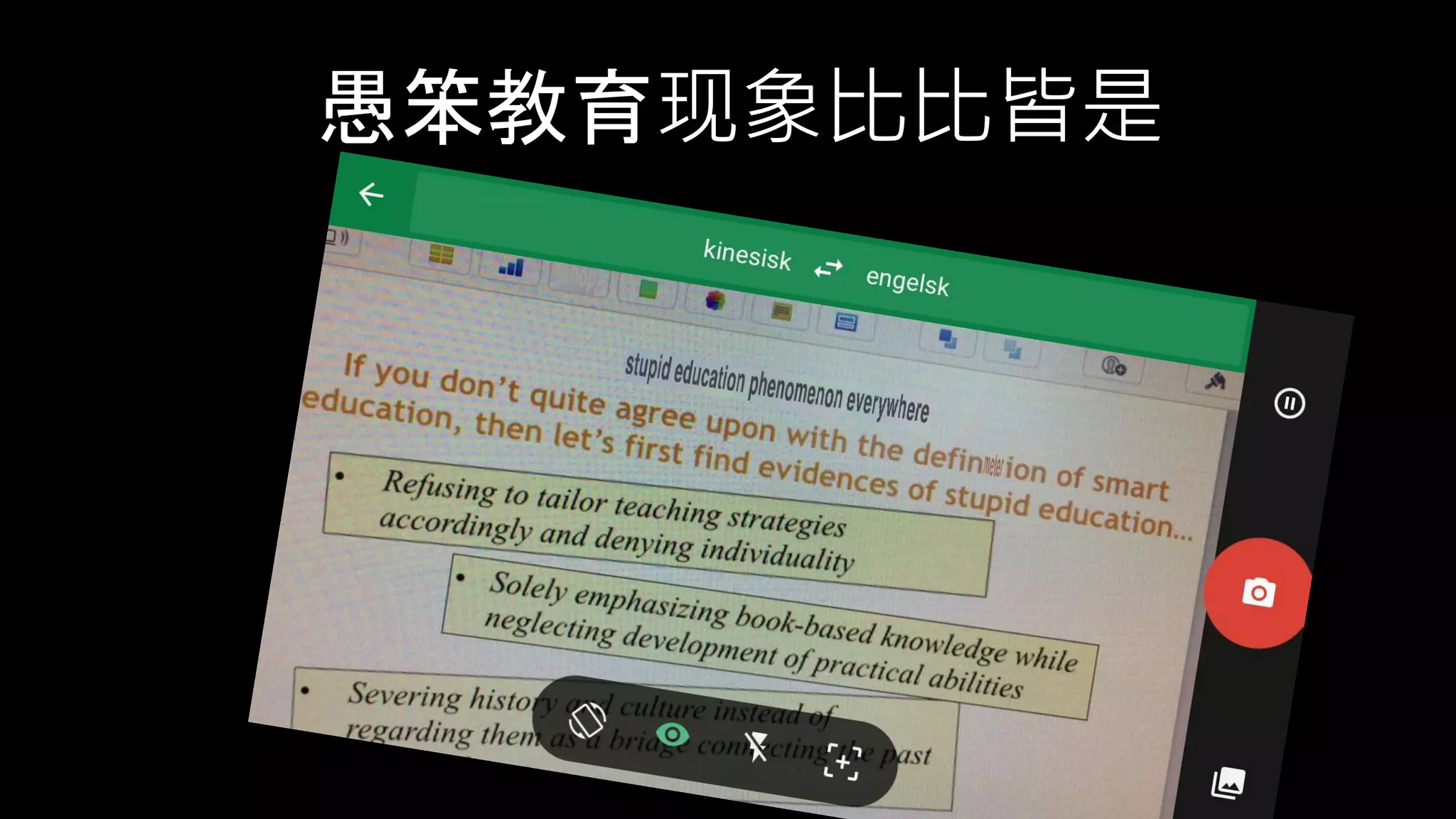
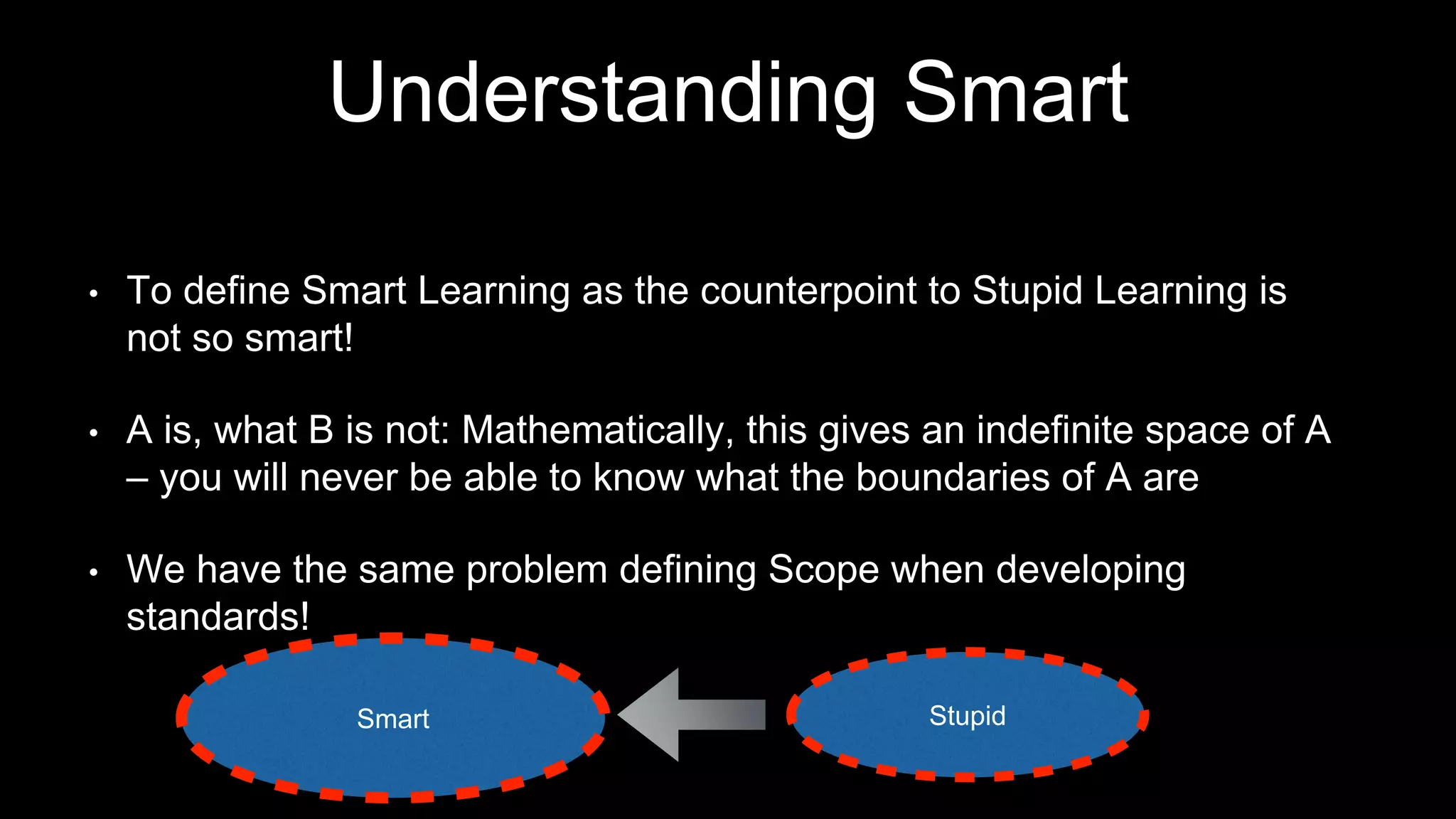
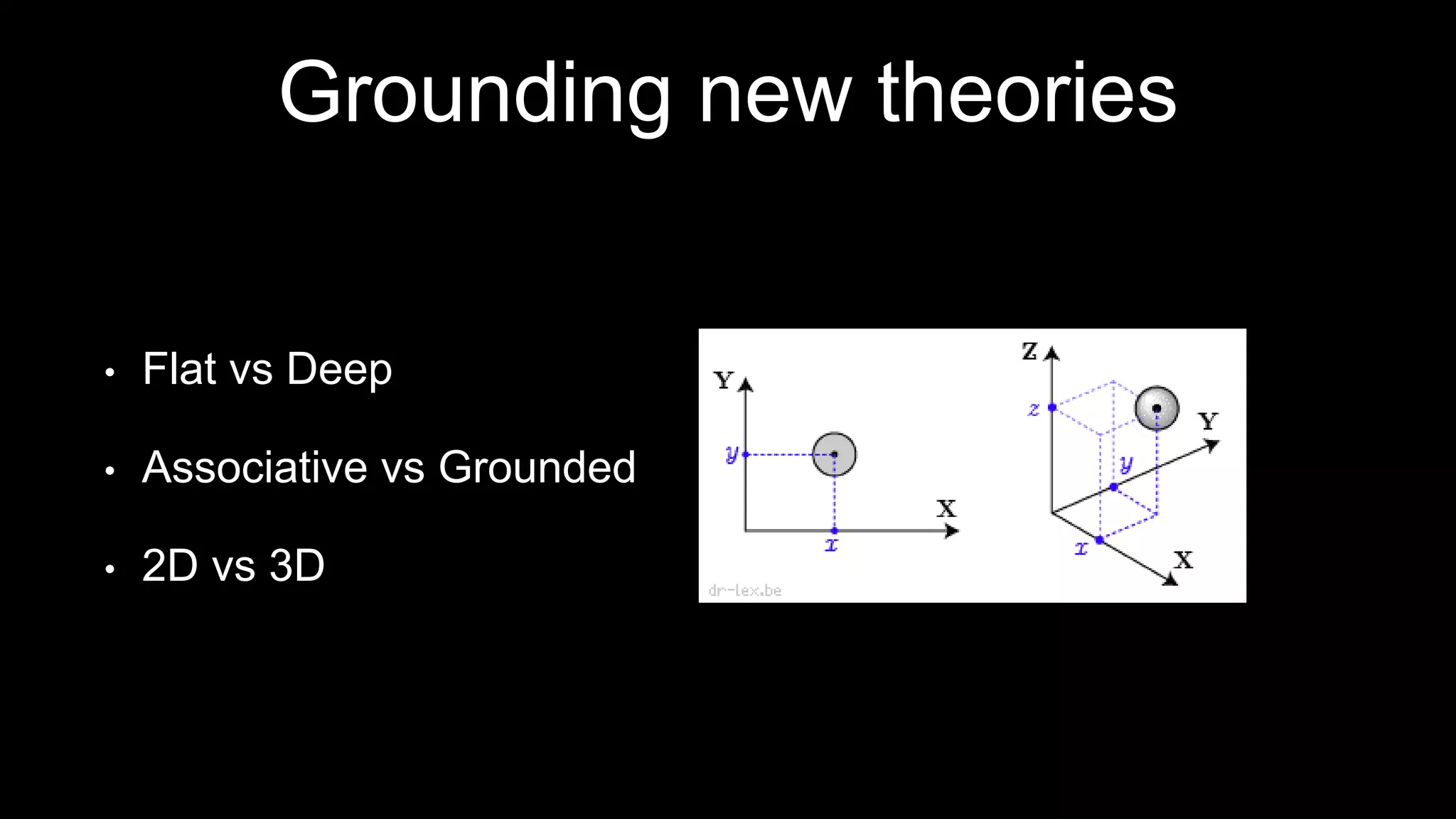
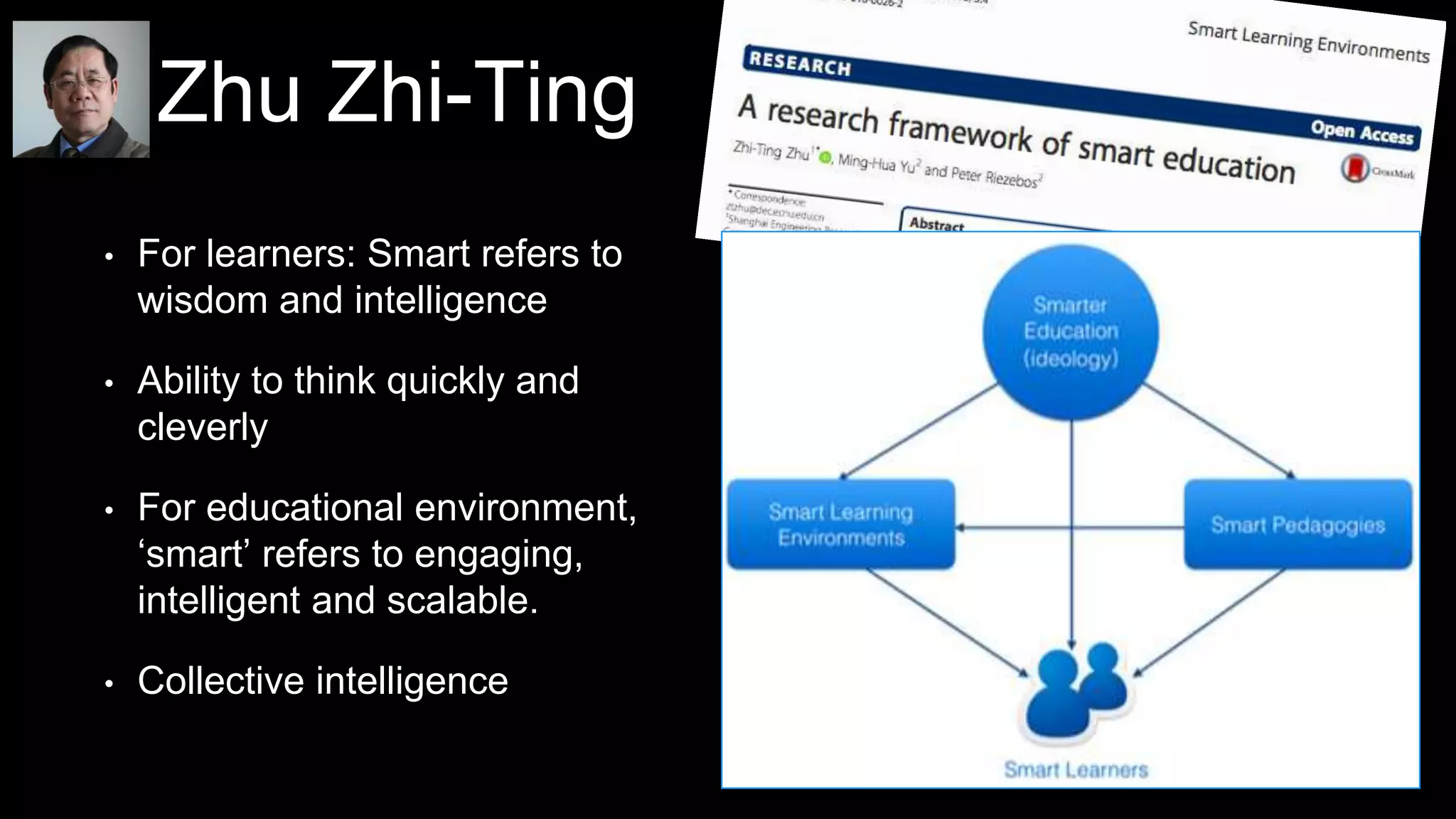
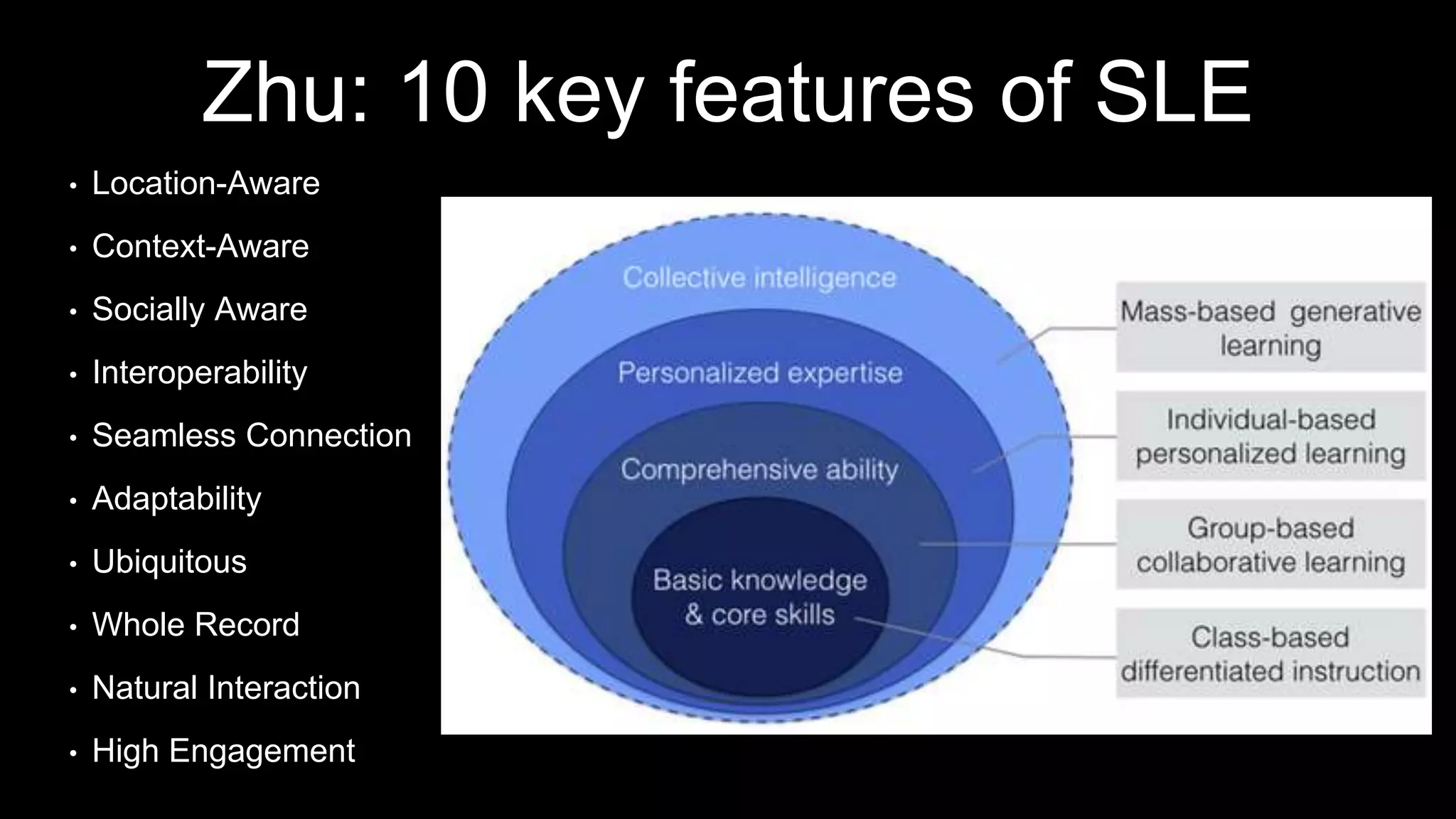
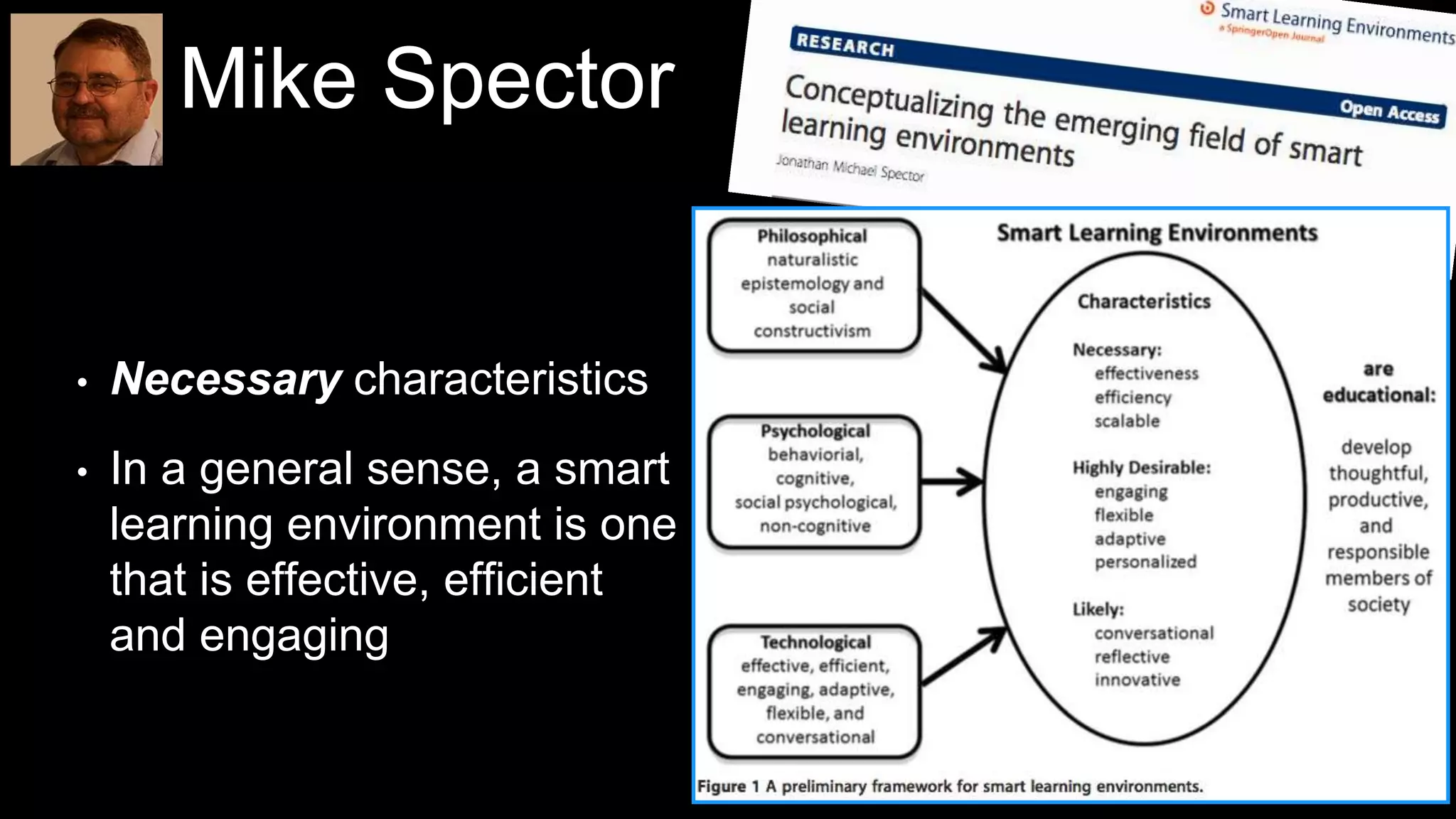
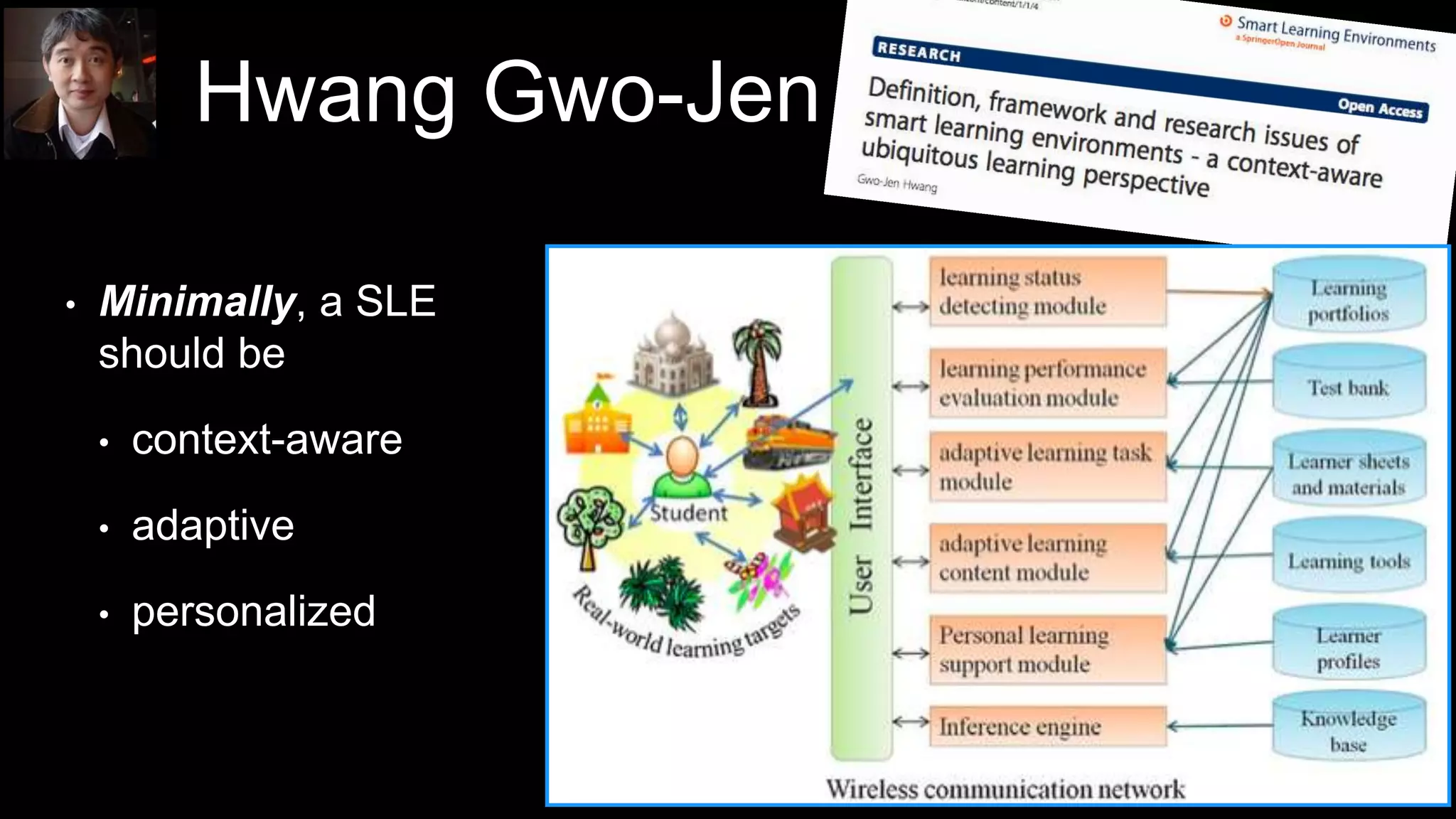
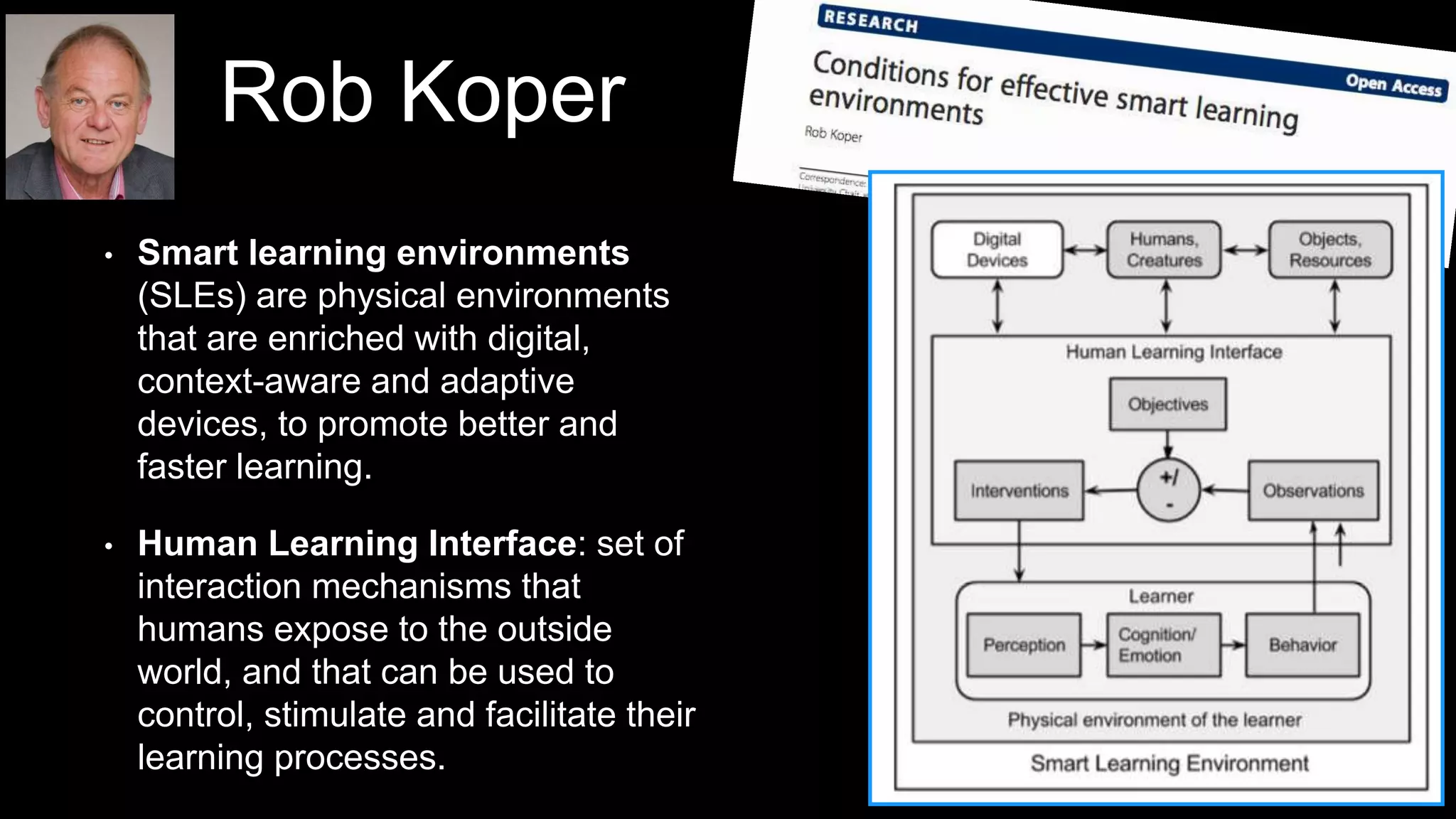
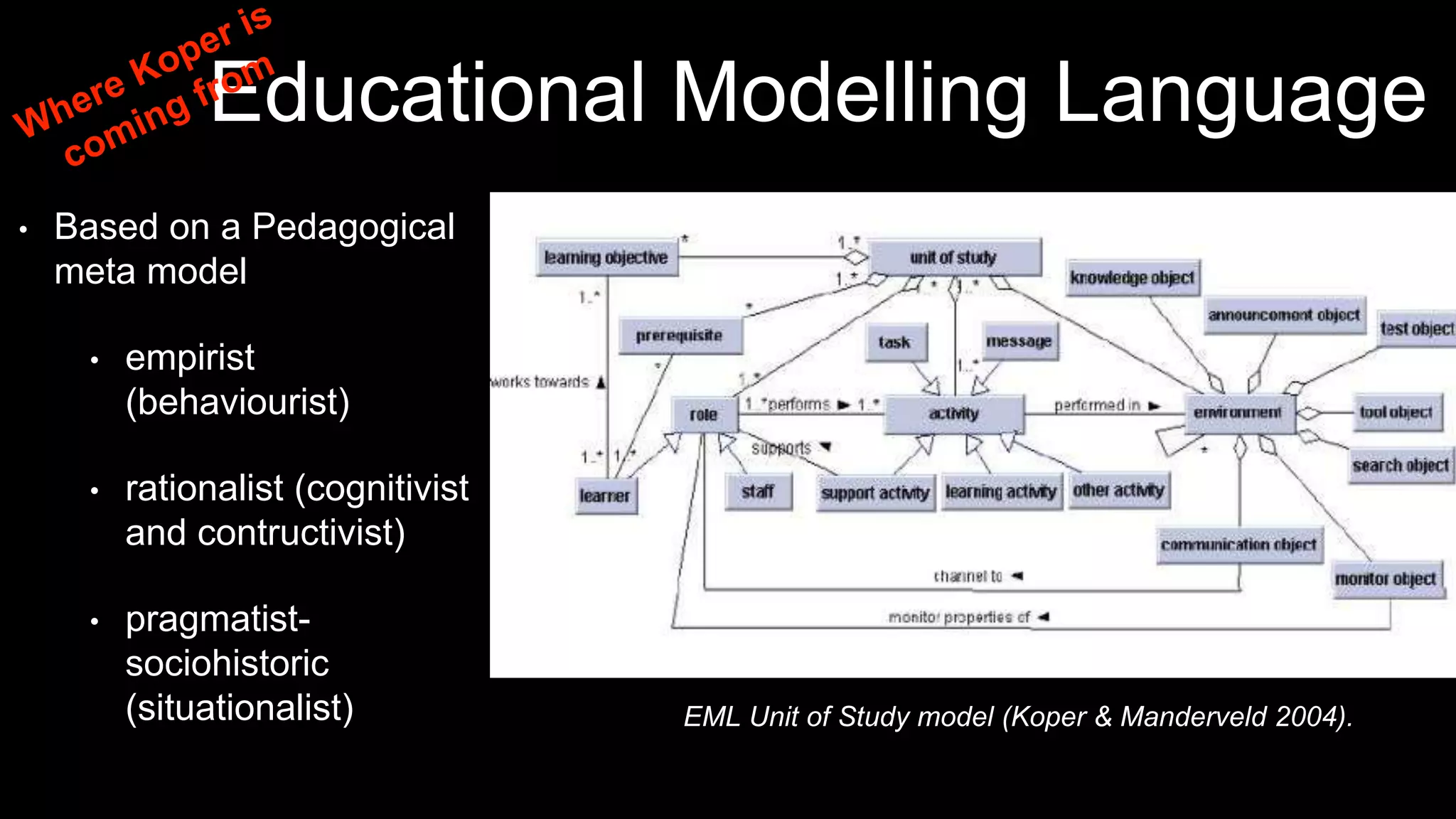
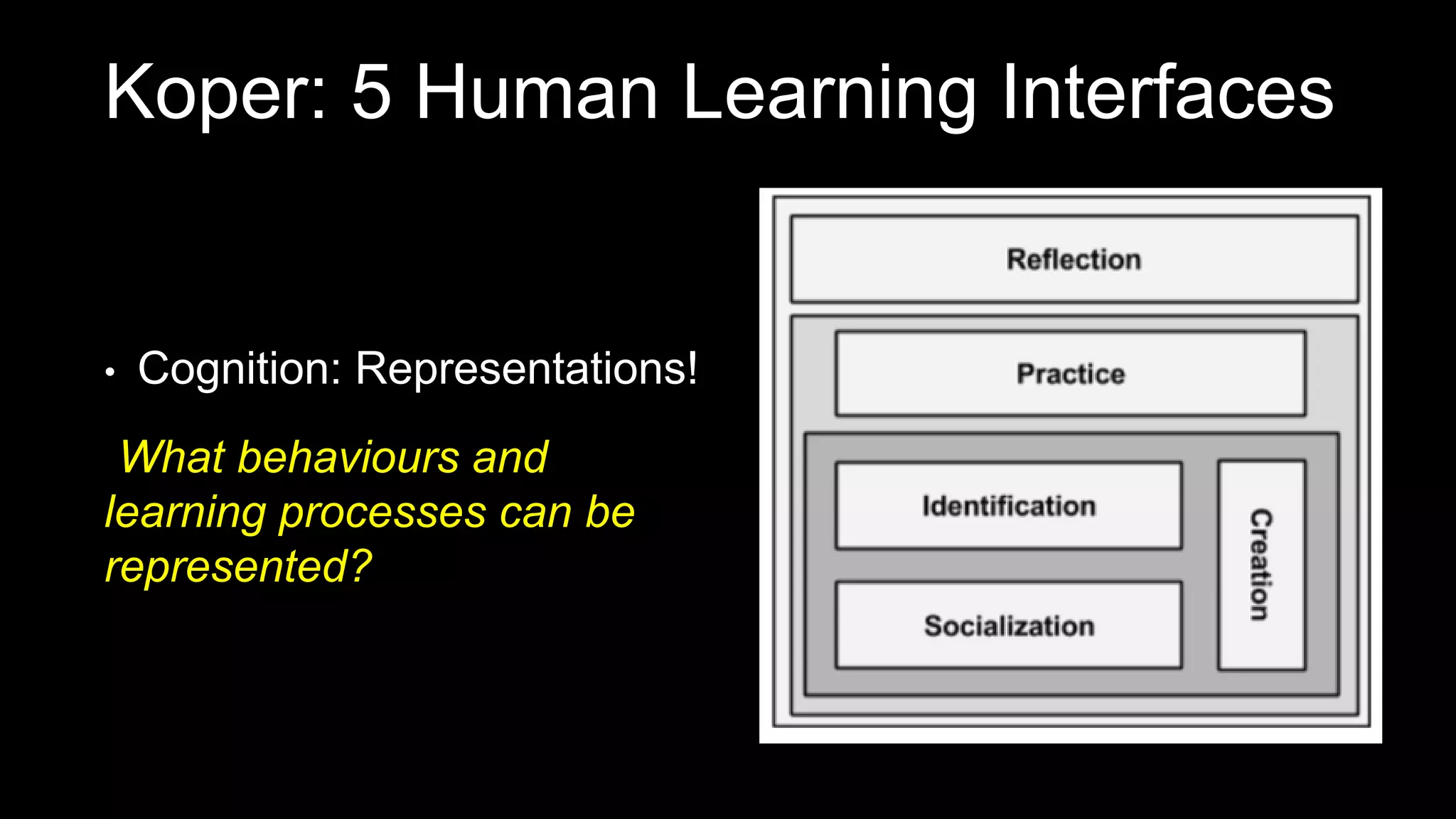
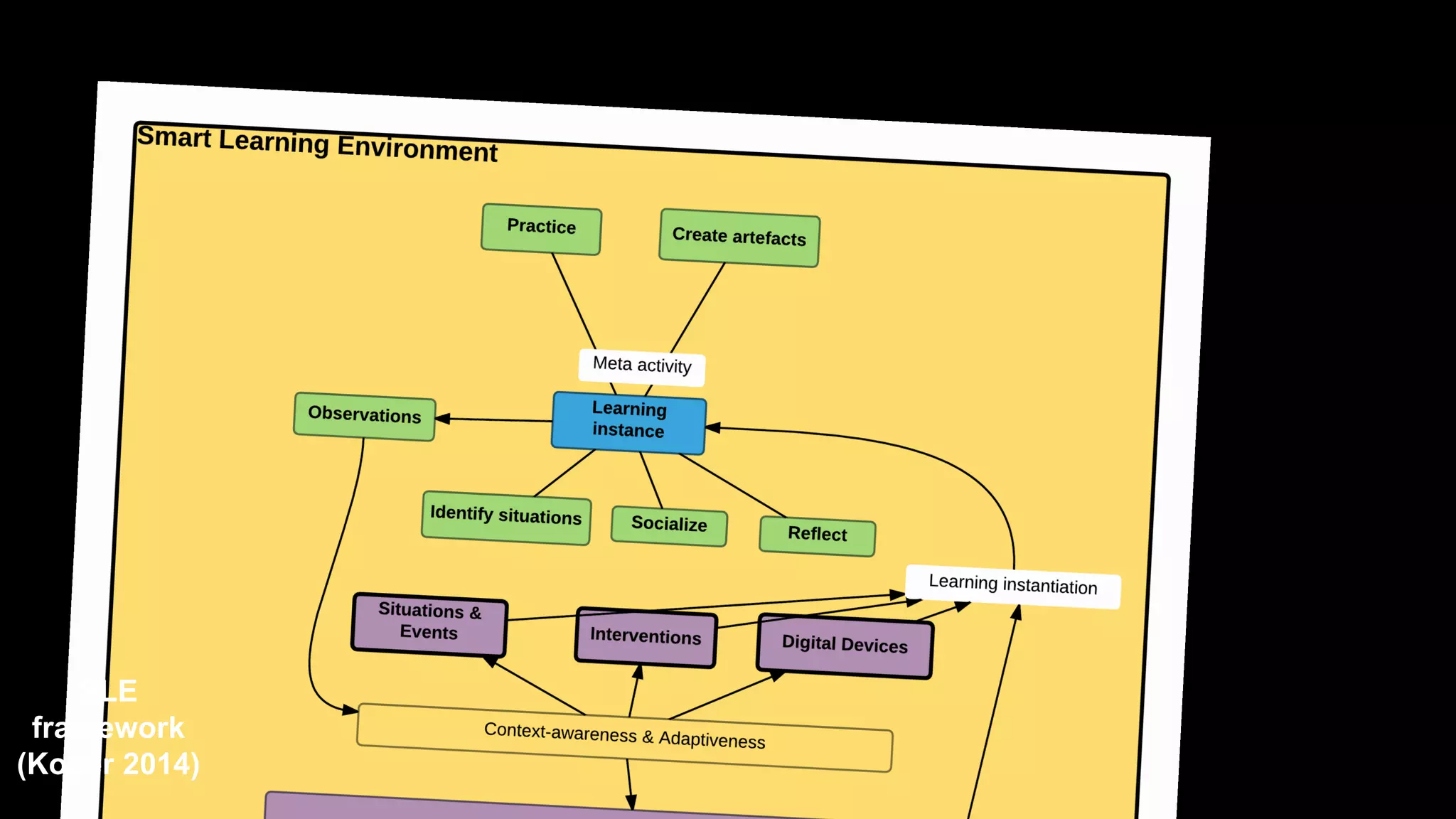
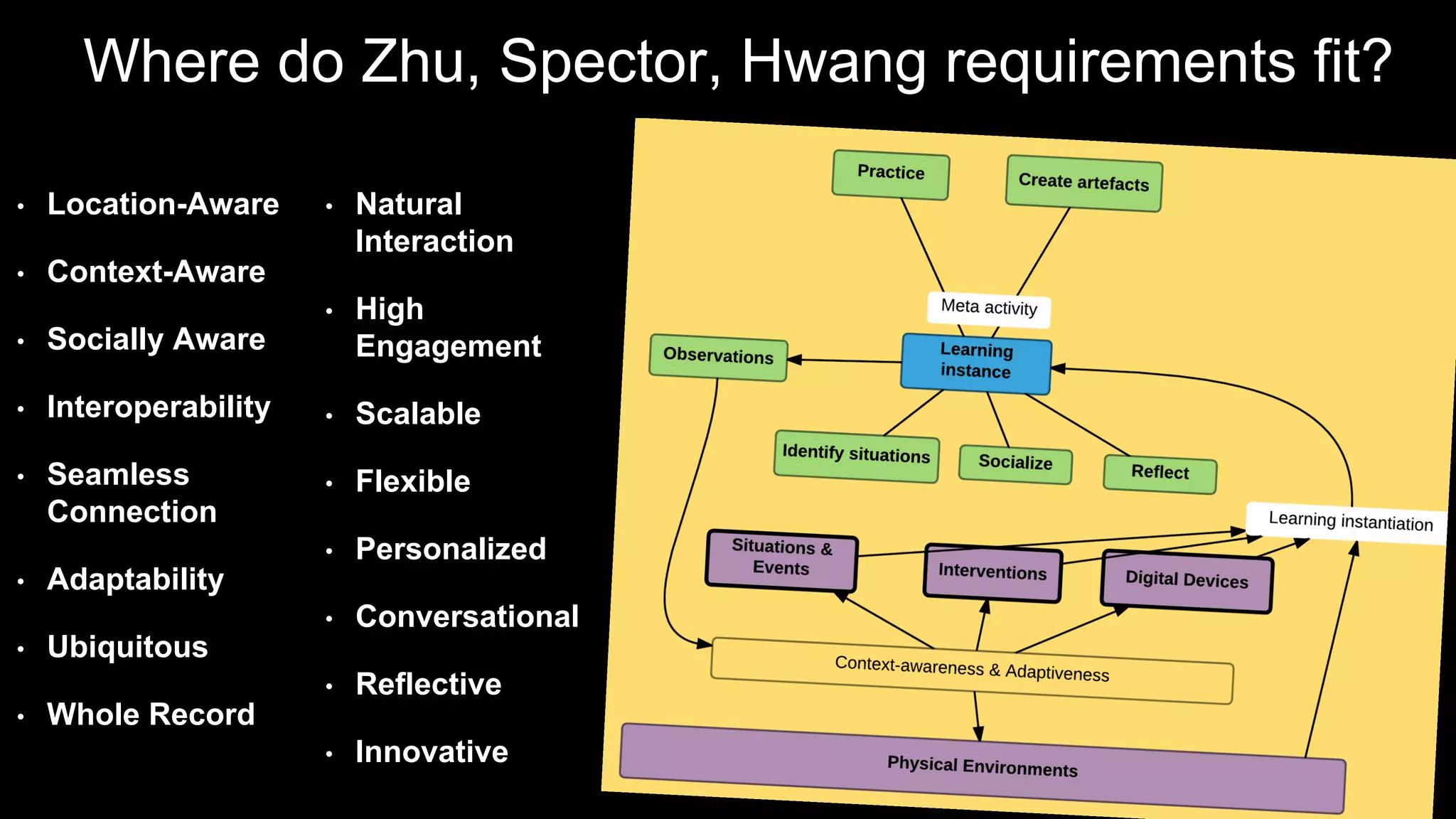
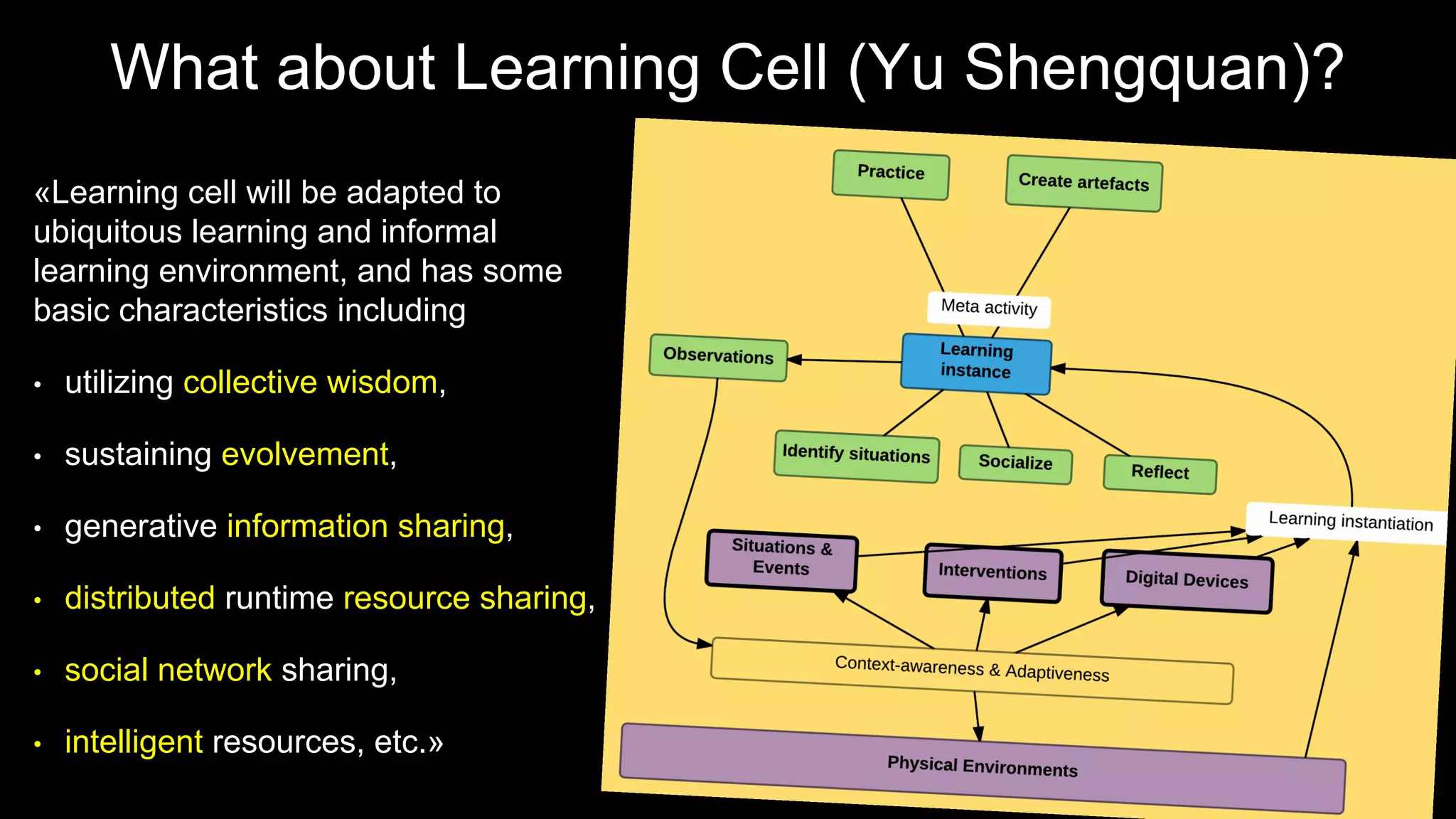
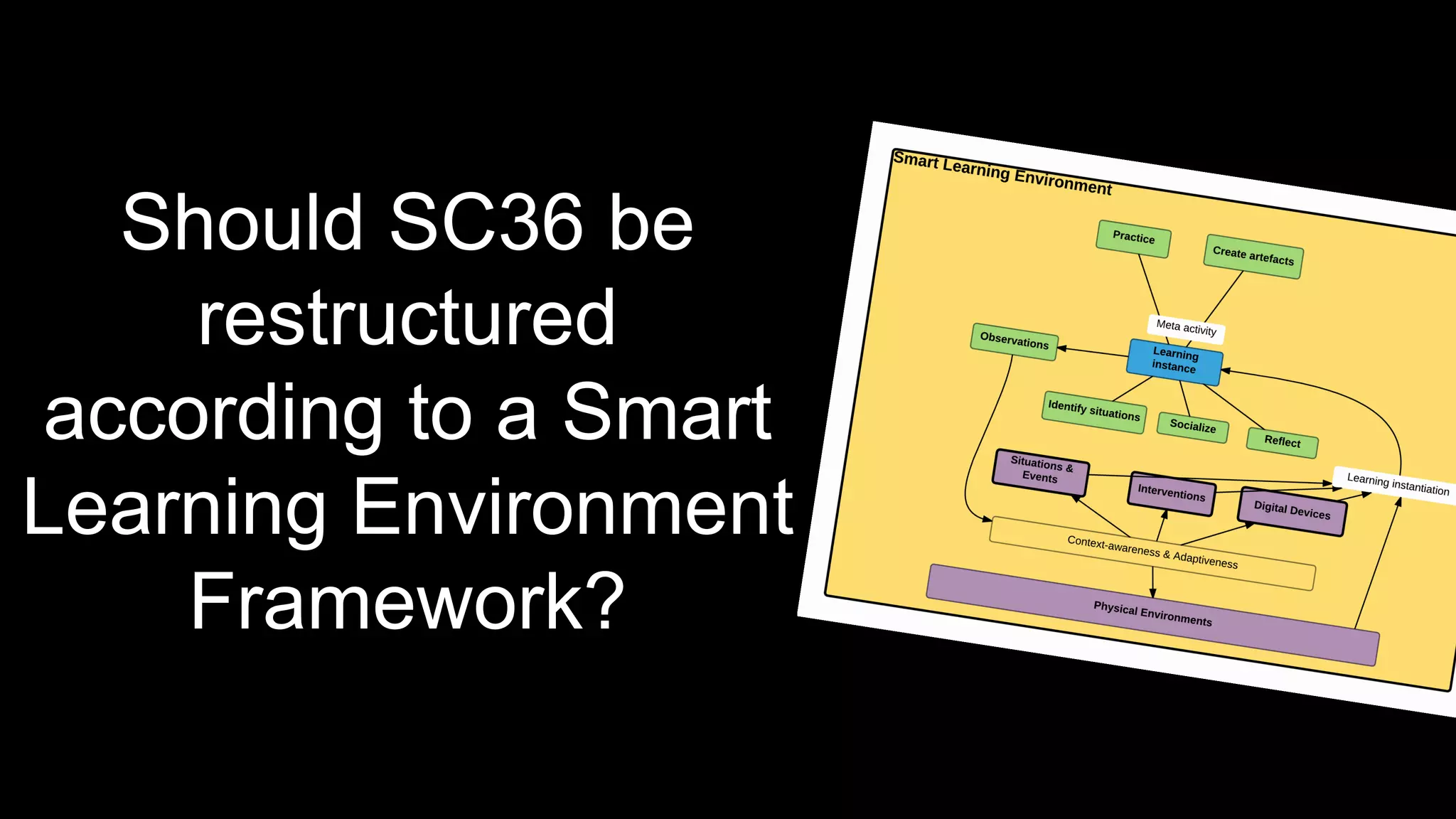
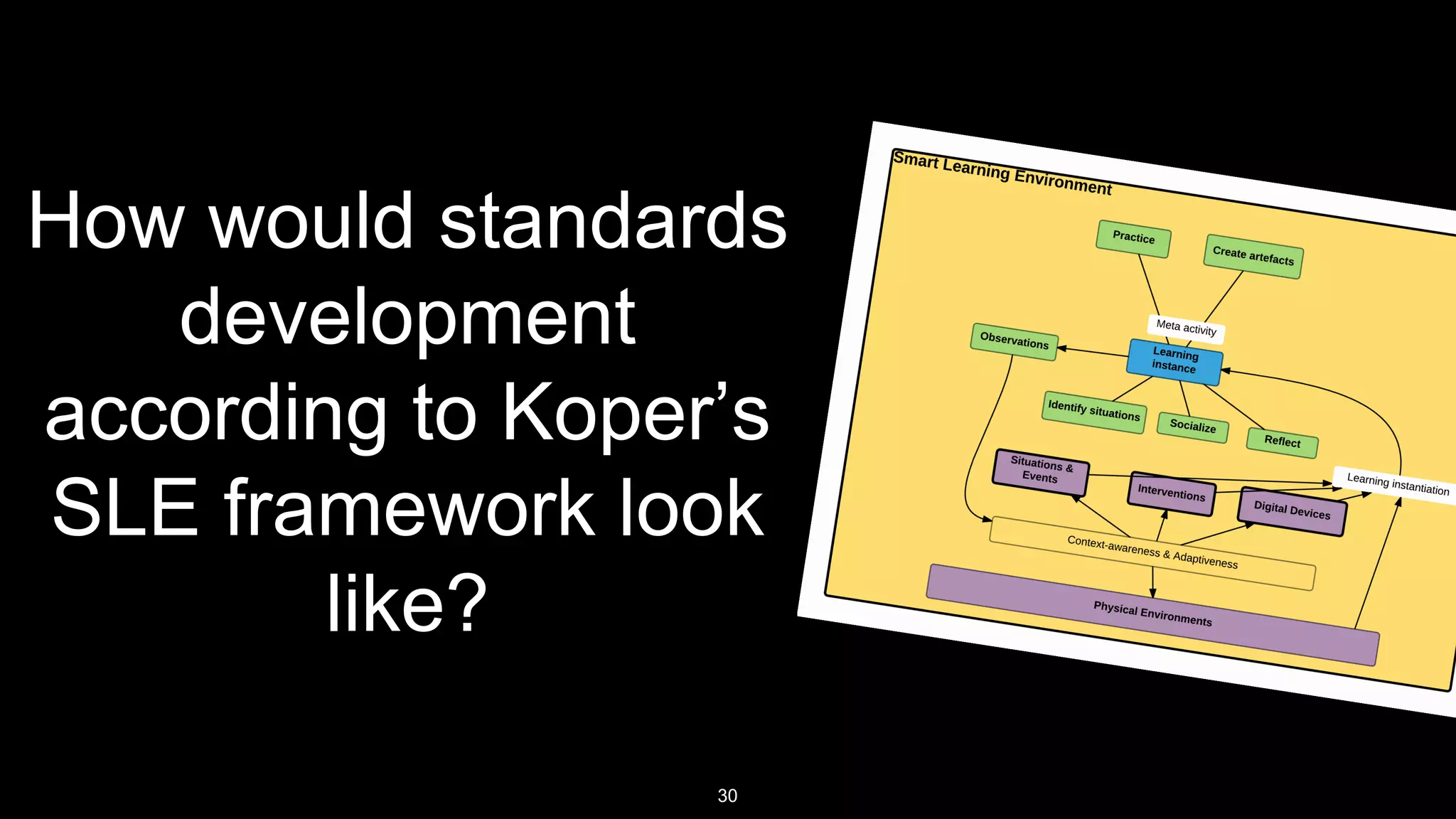
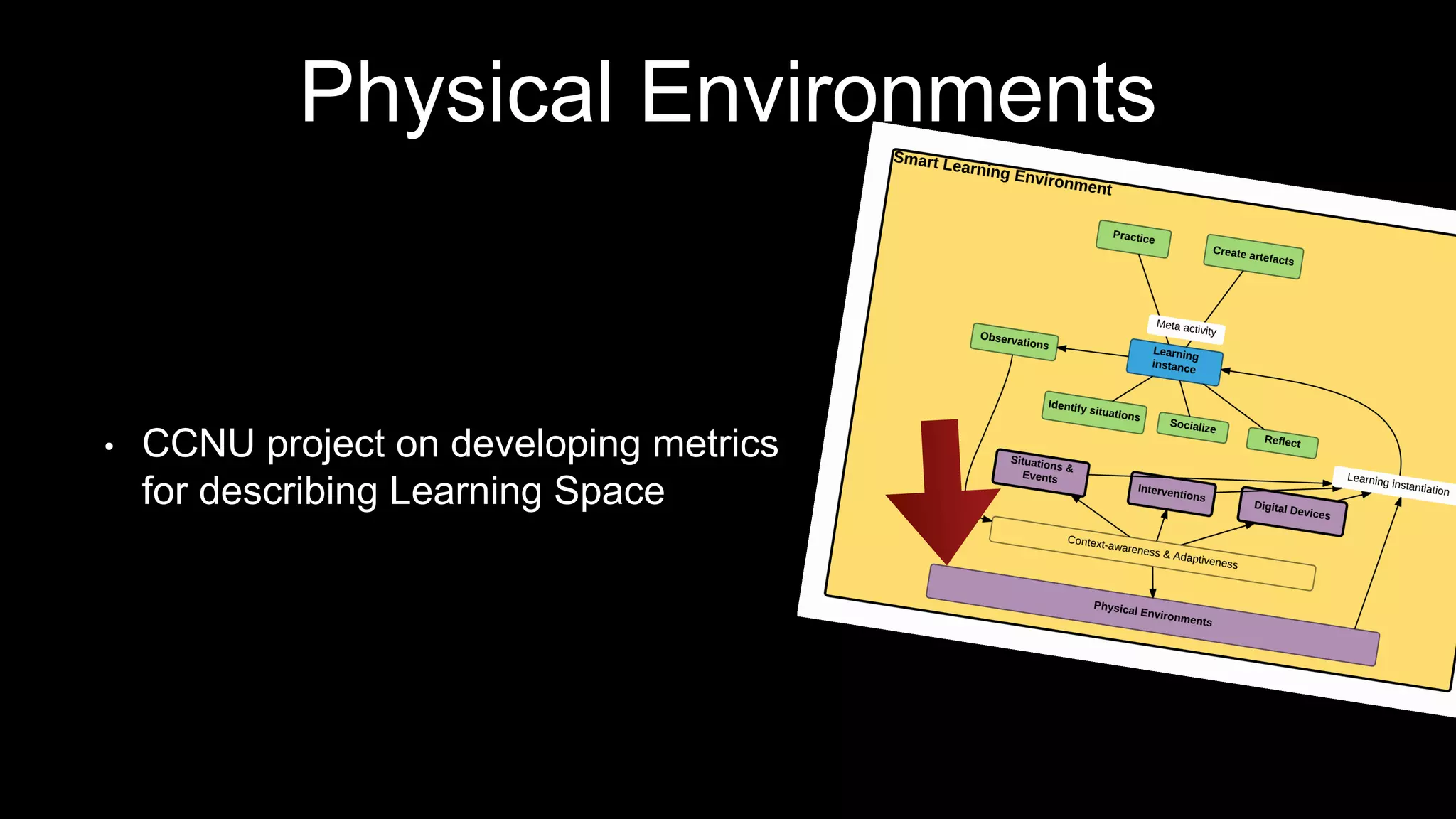
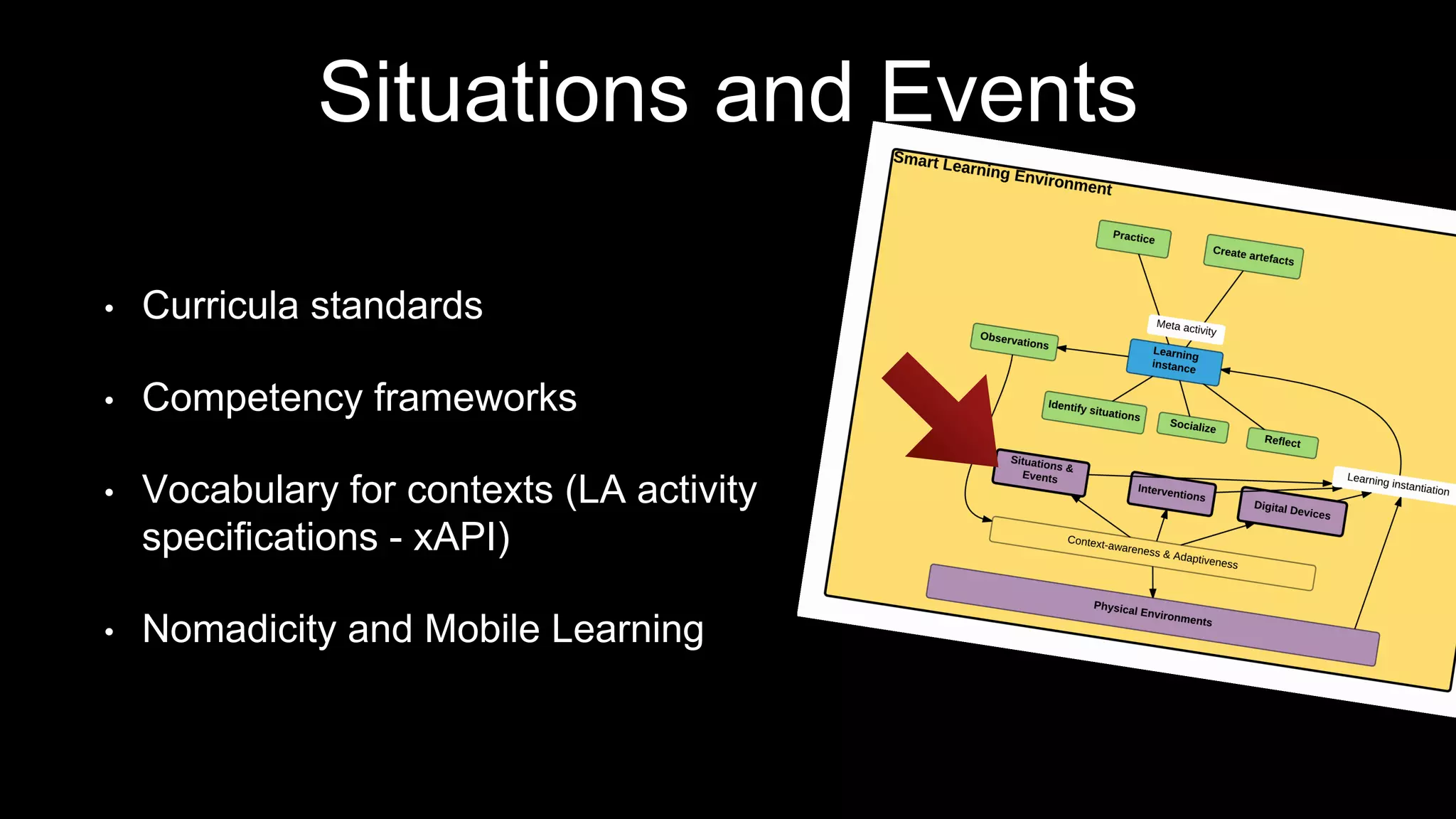
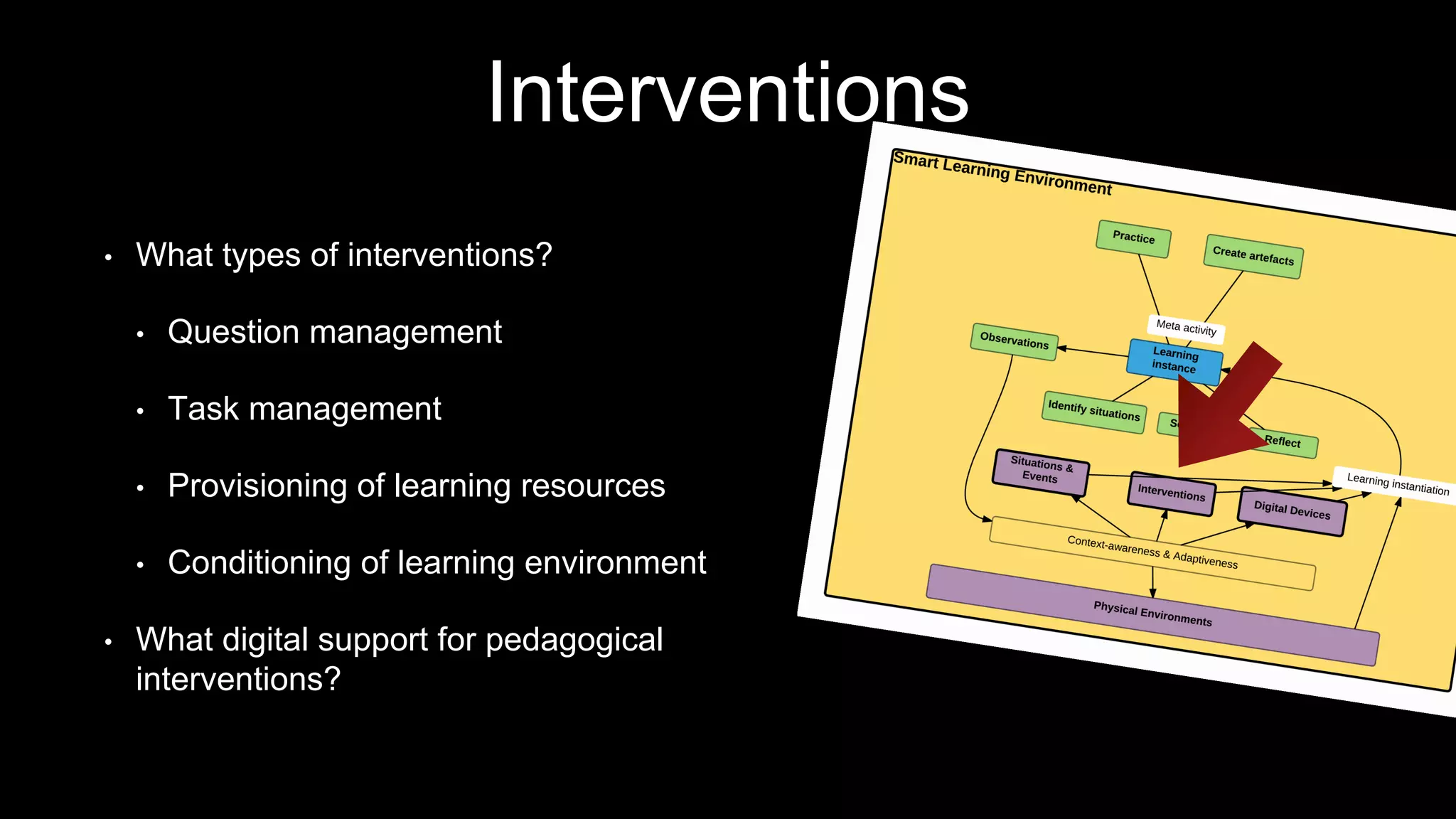
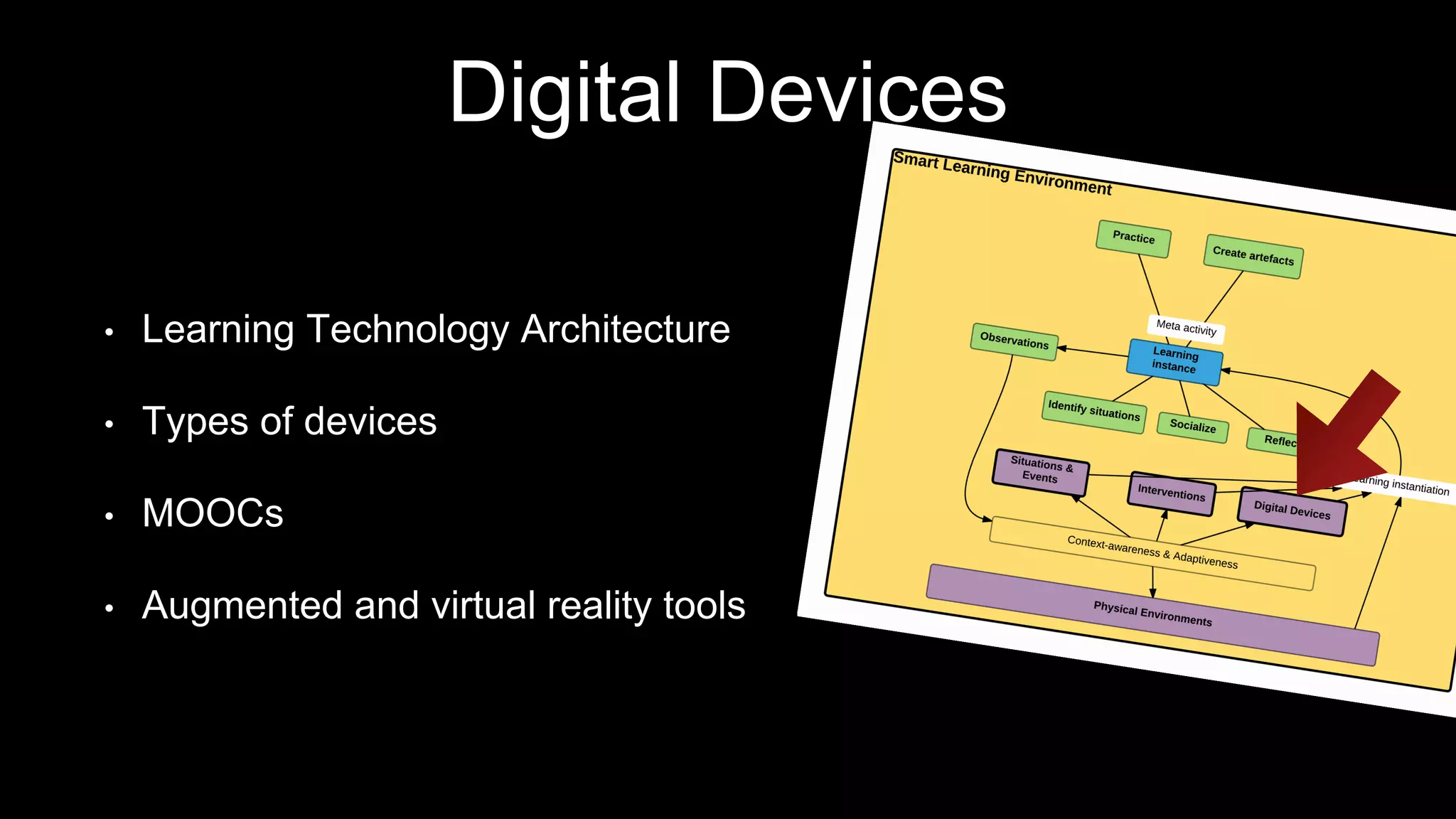
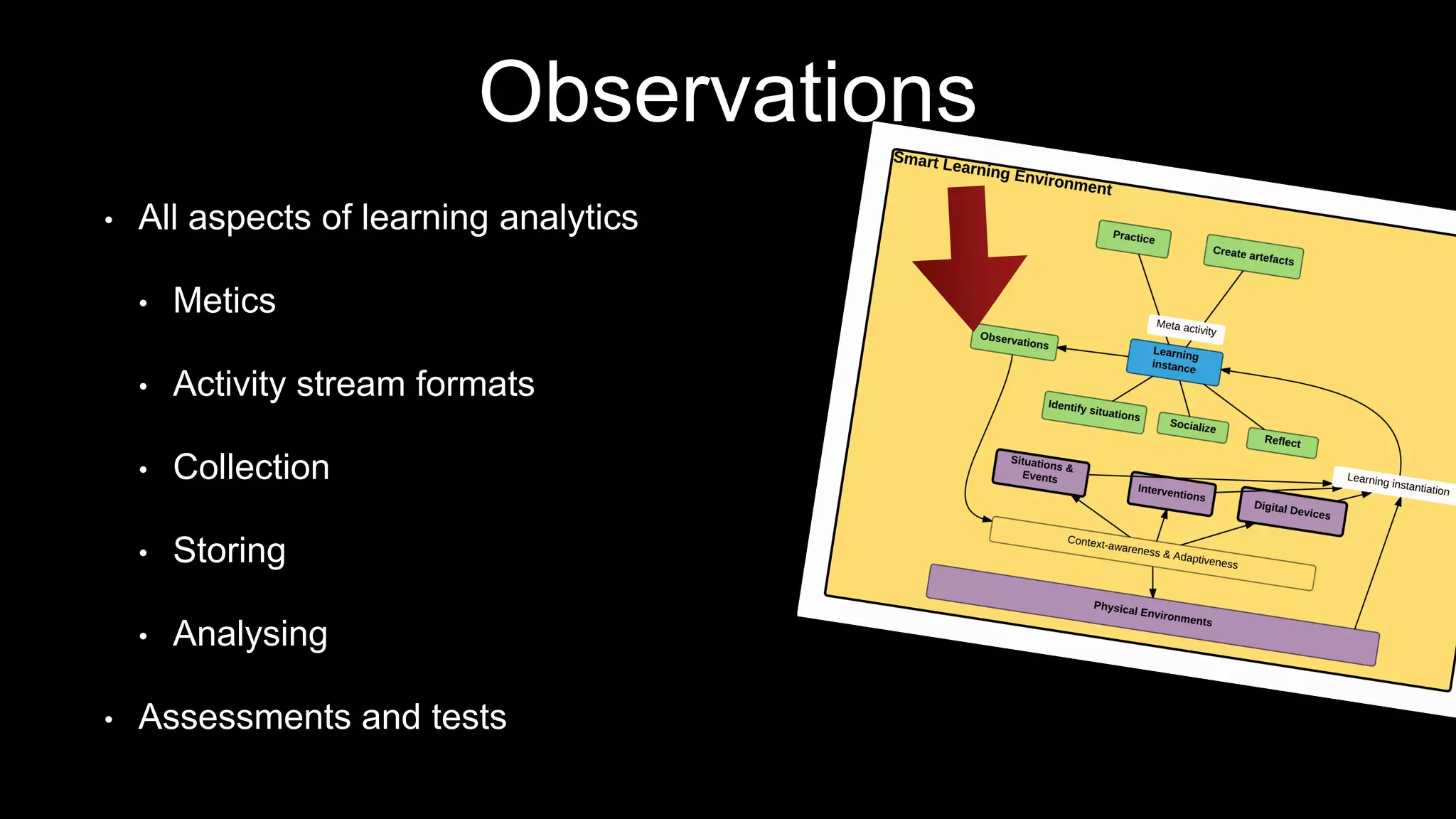
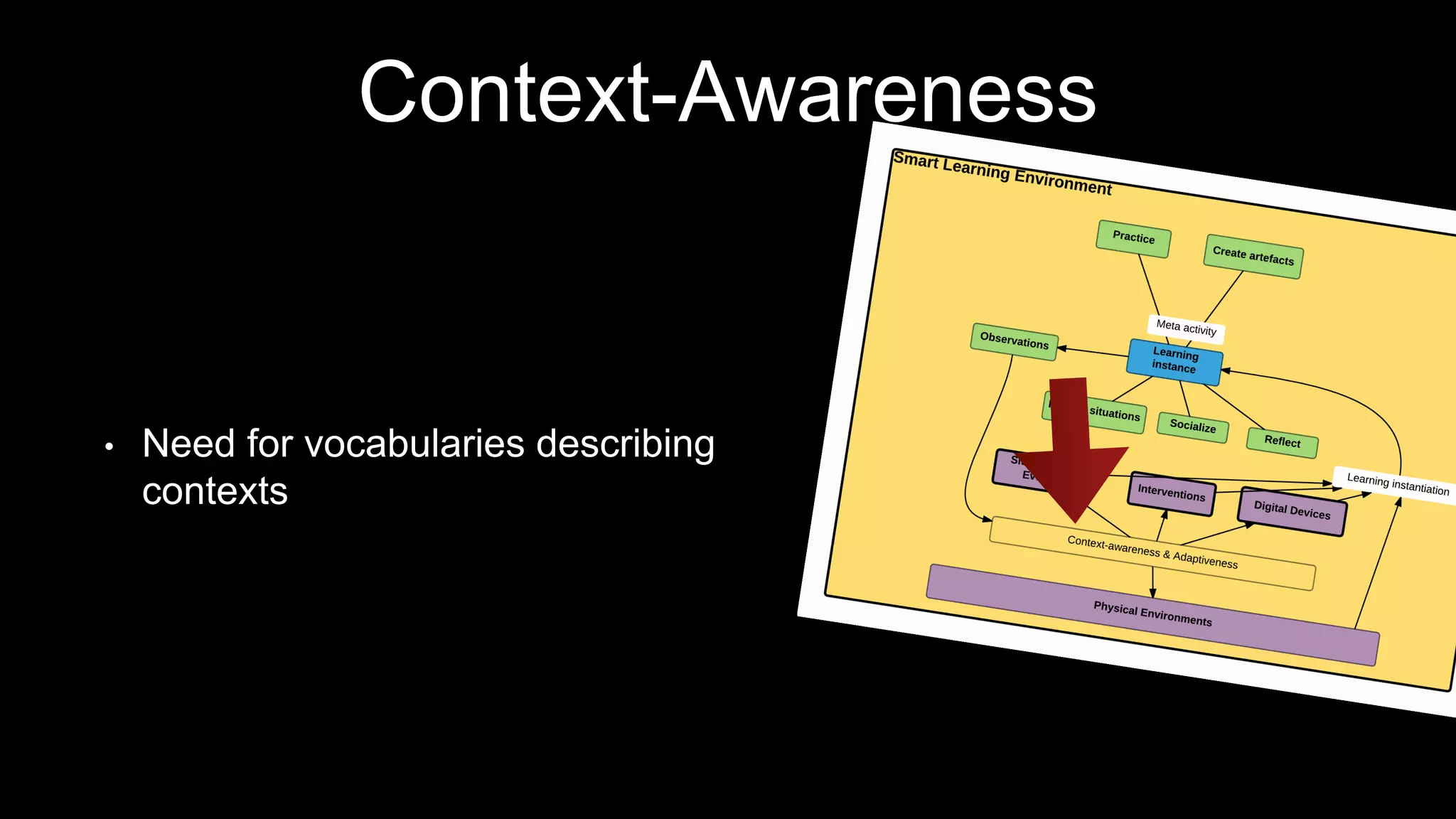
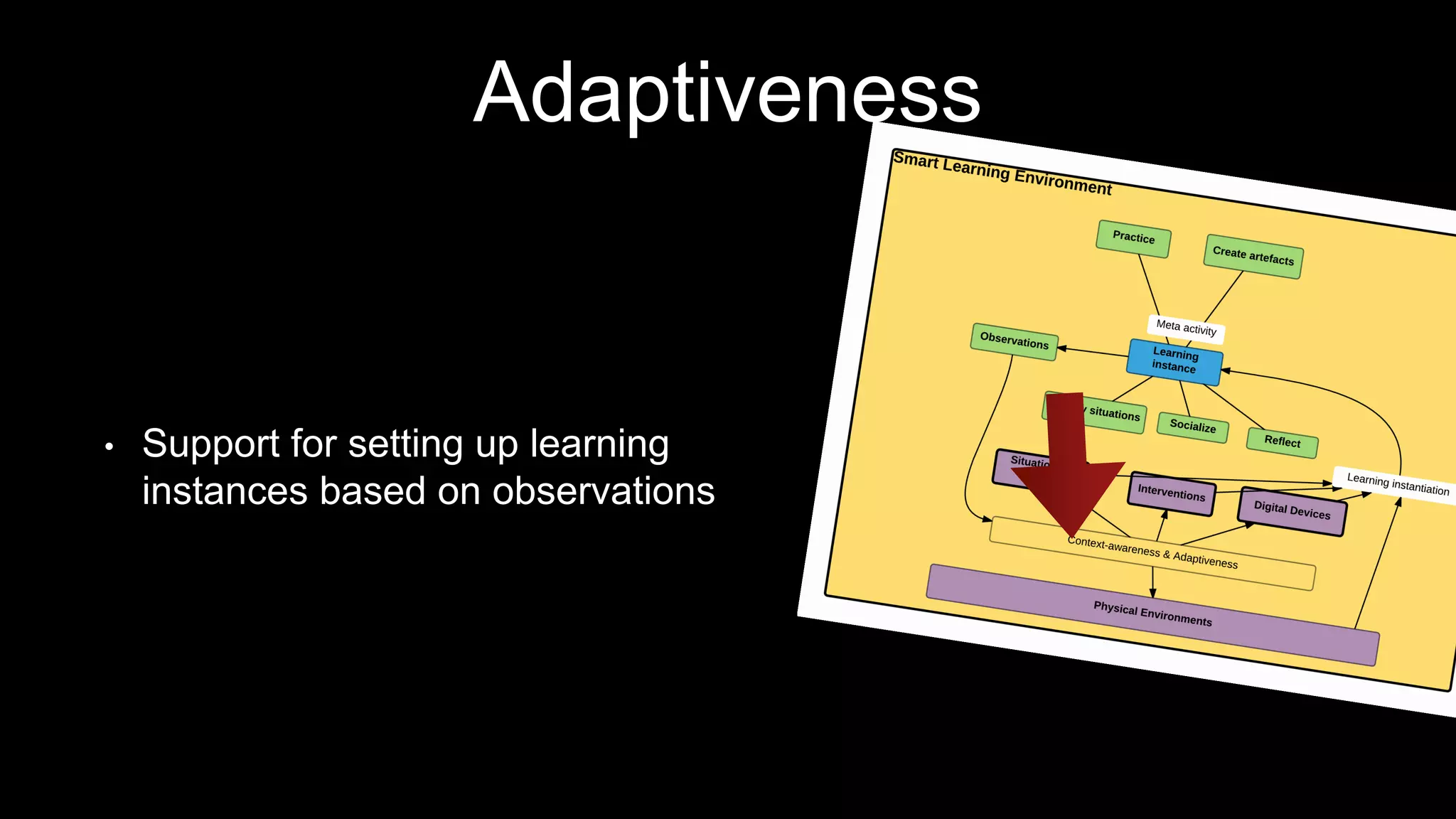
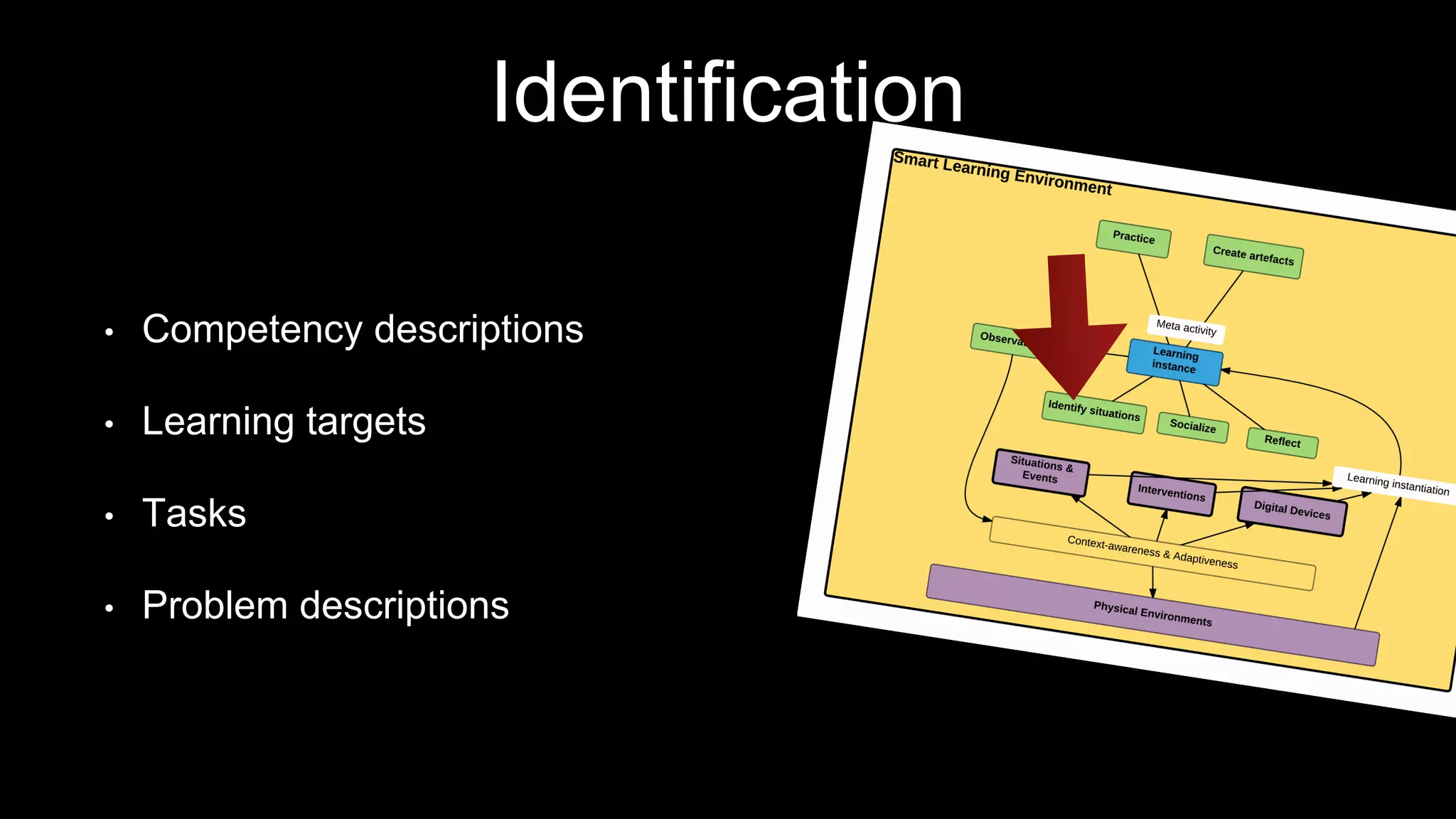
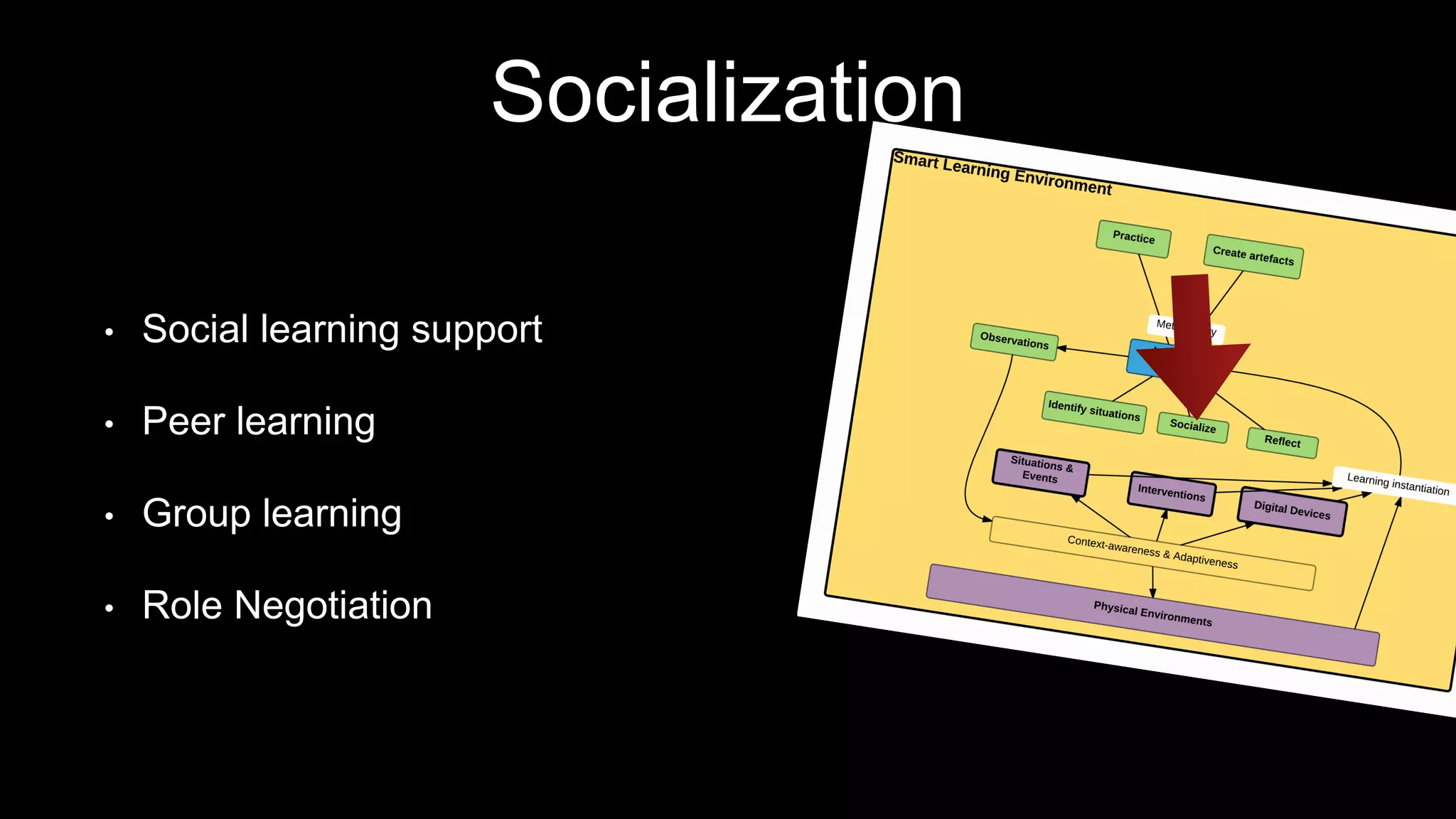
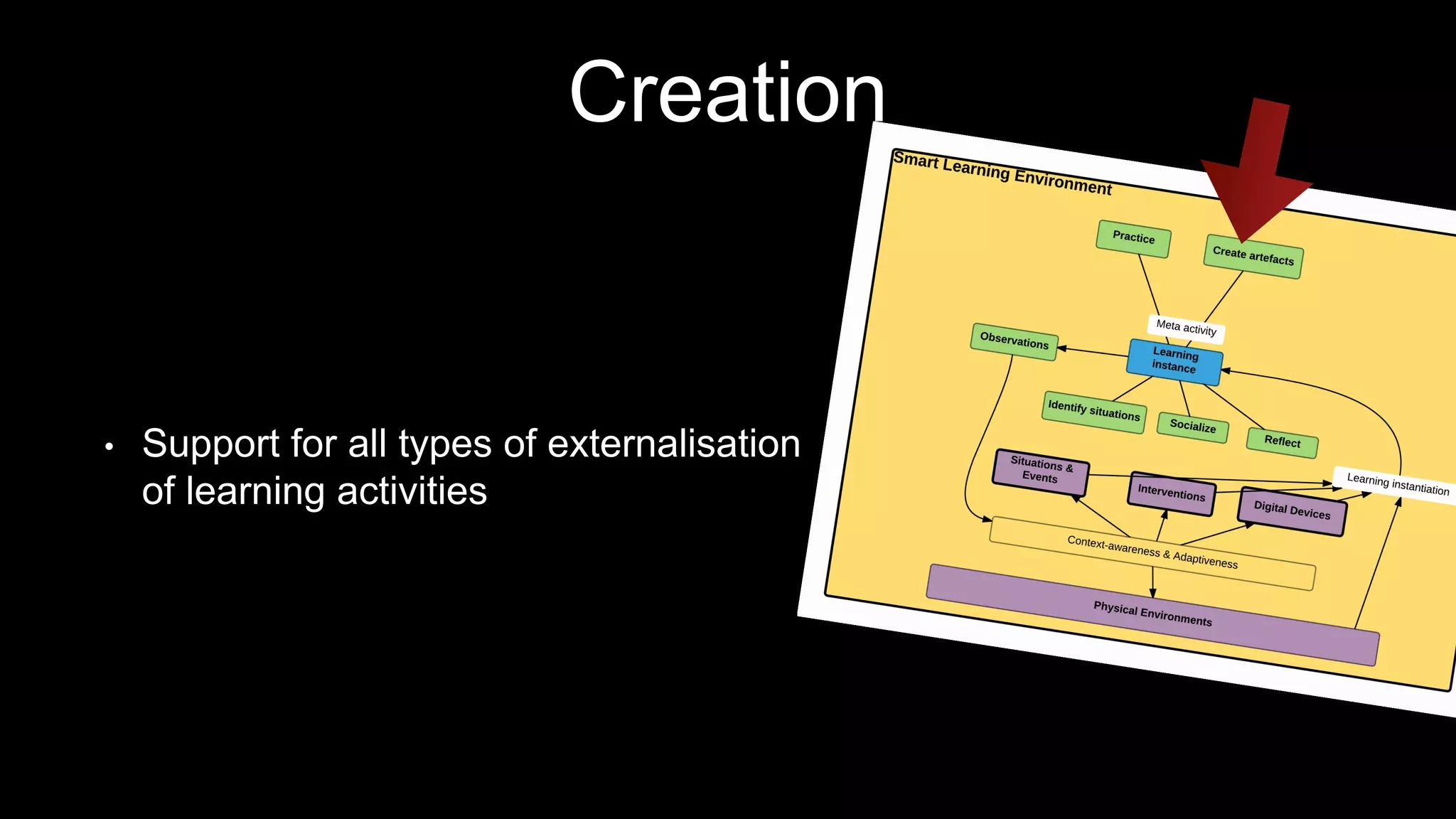
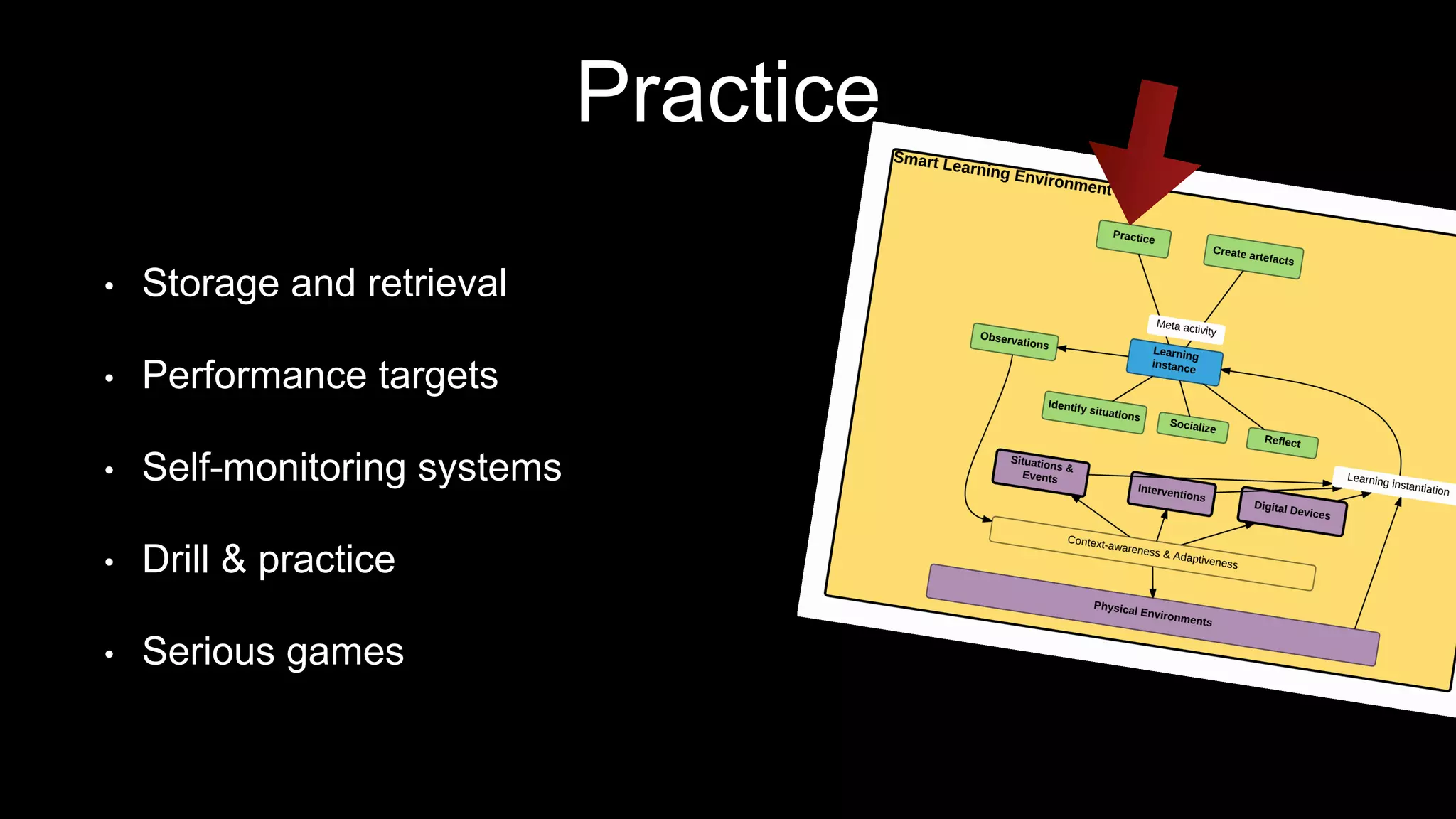
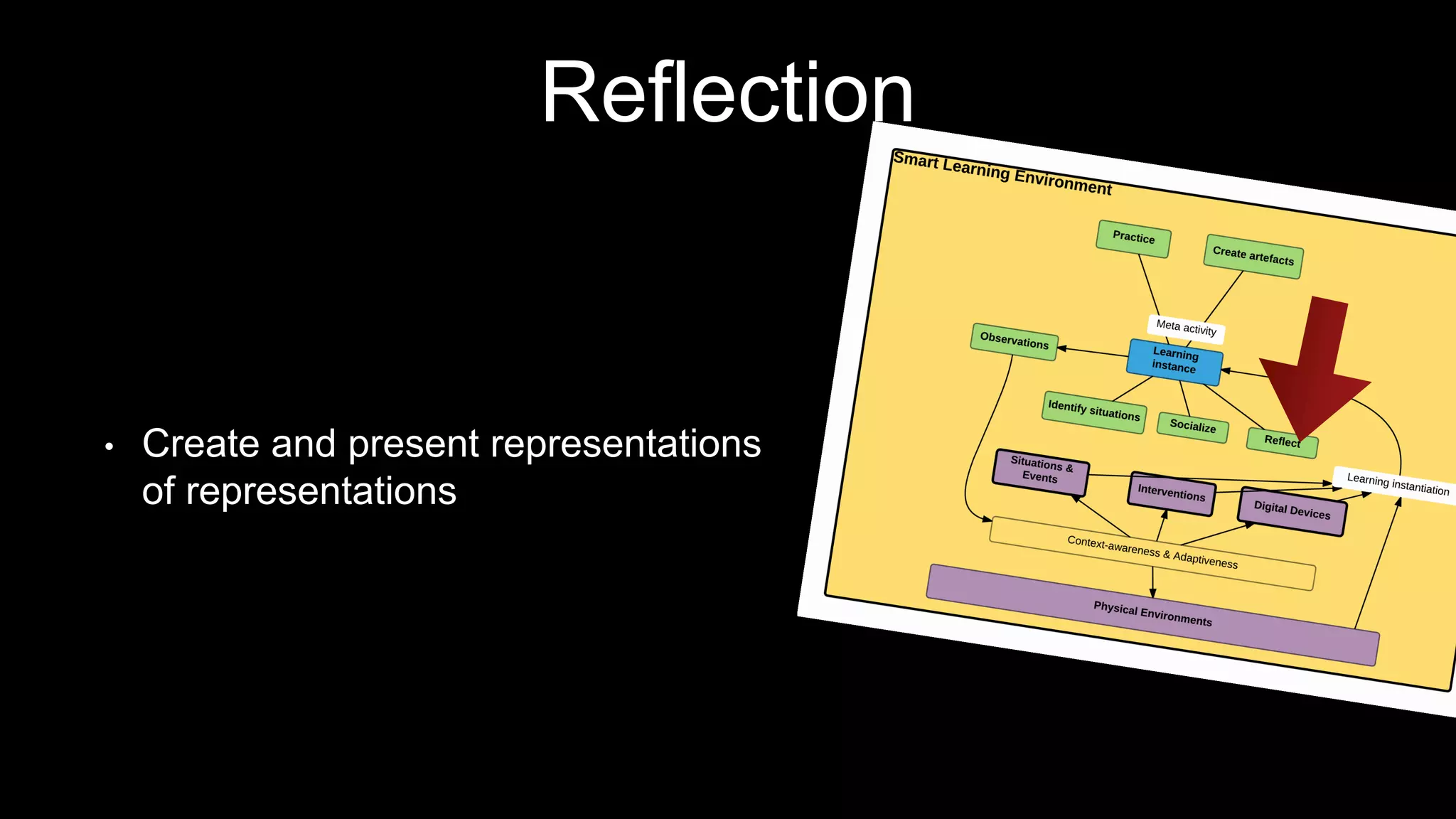
The document discusses the development of a framework for smart learning environments (SLEs), emphasizing their characteristics such as context-awareness, adaptability, and engagement. Various standards-setting organizations are involved in creating these frameworks to enhance educational practices through technology integration. The conclusion highlights the necessity for a coherent theoretical model to effectively guide the standardization of learning technologies.