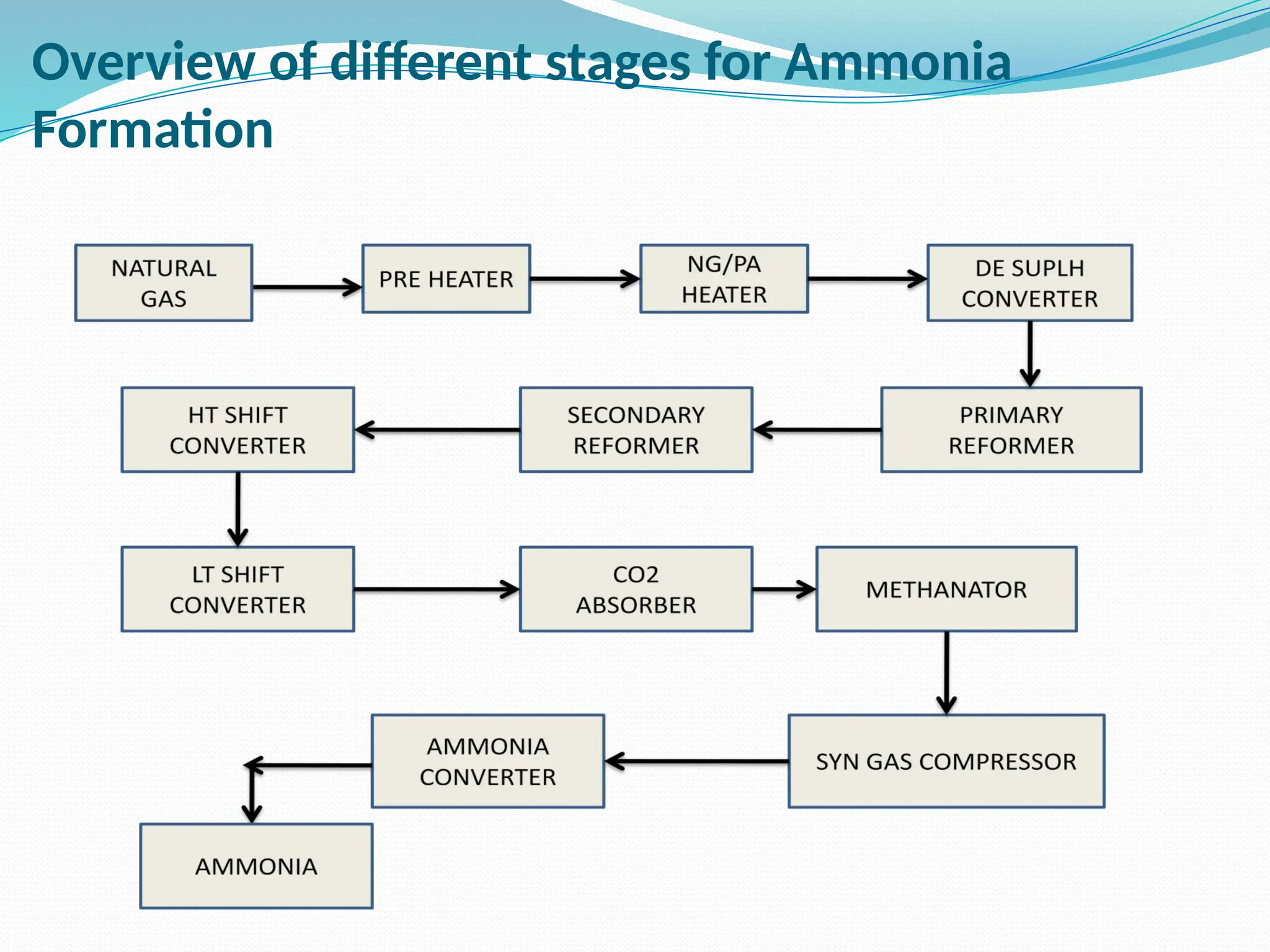
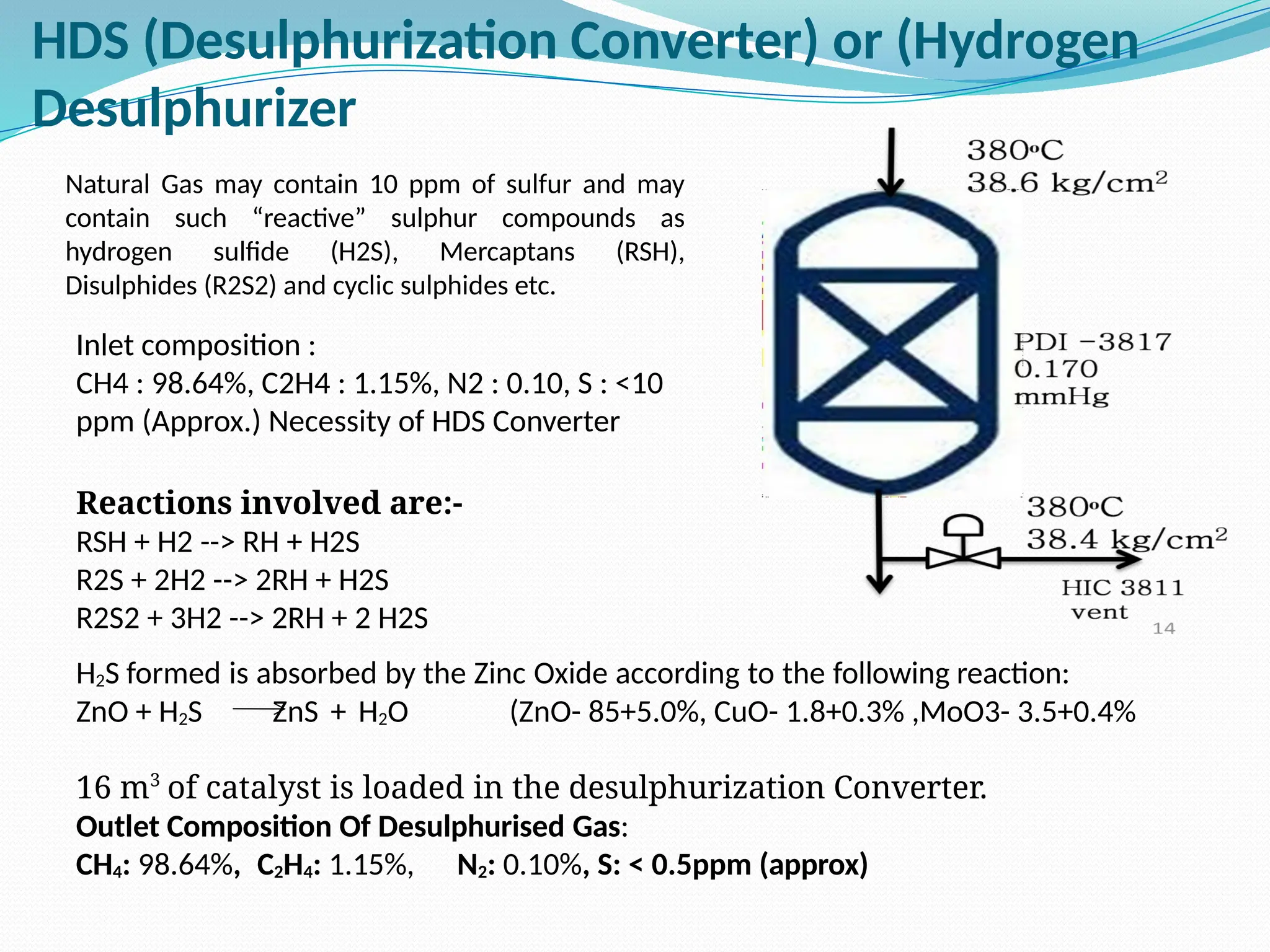
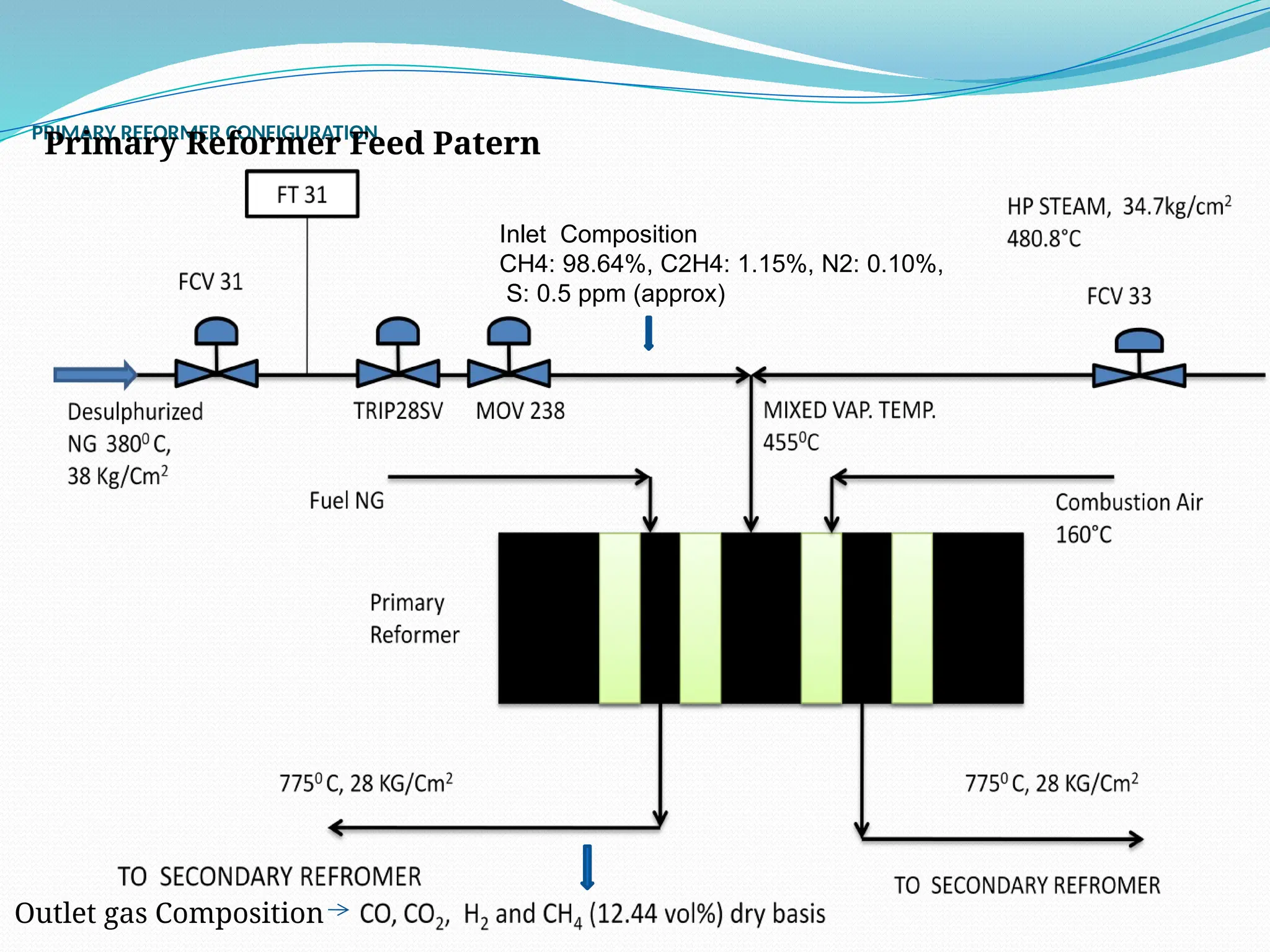
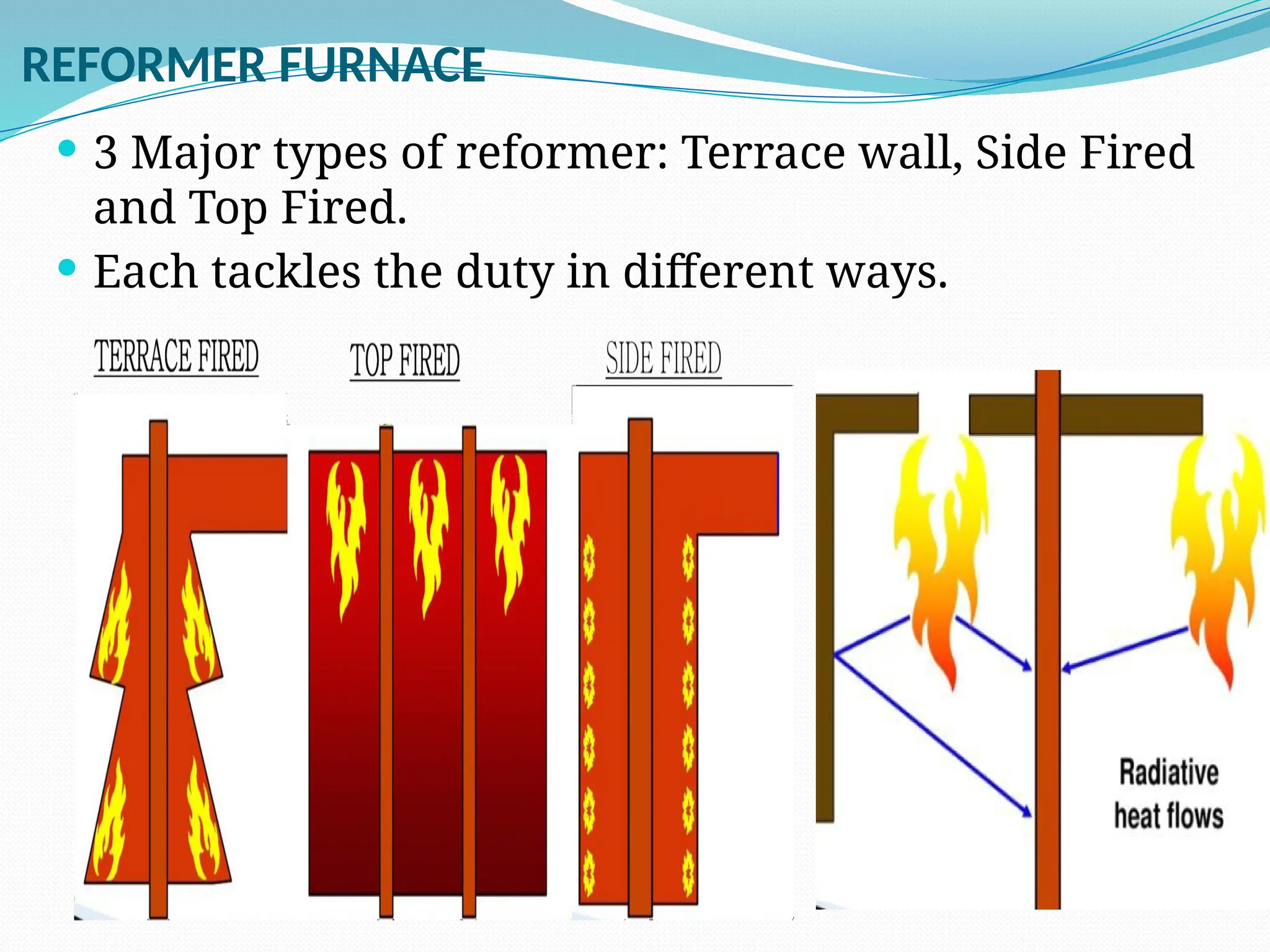
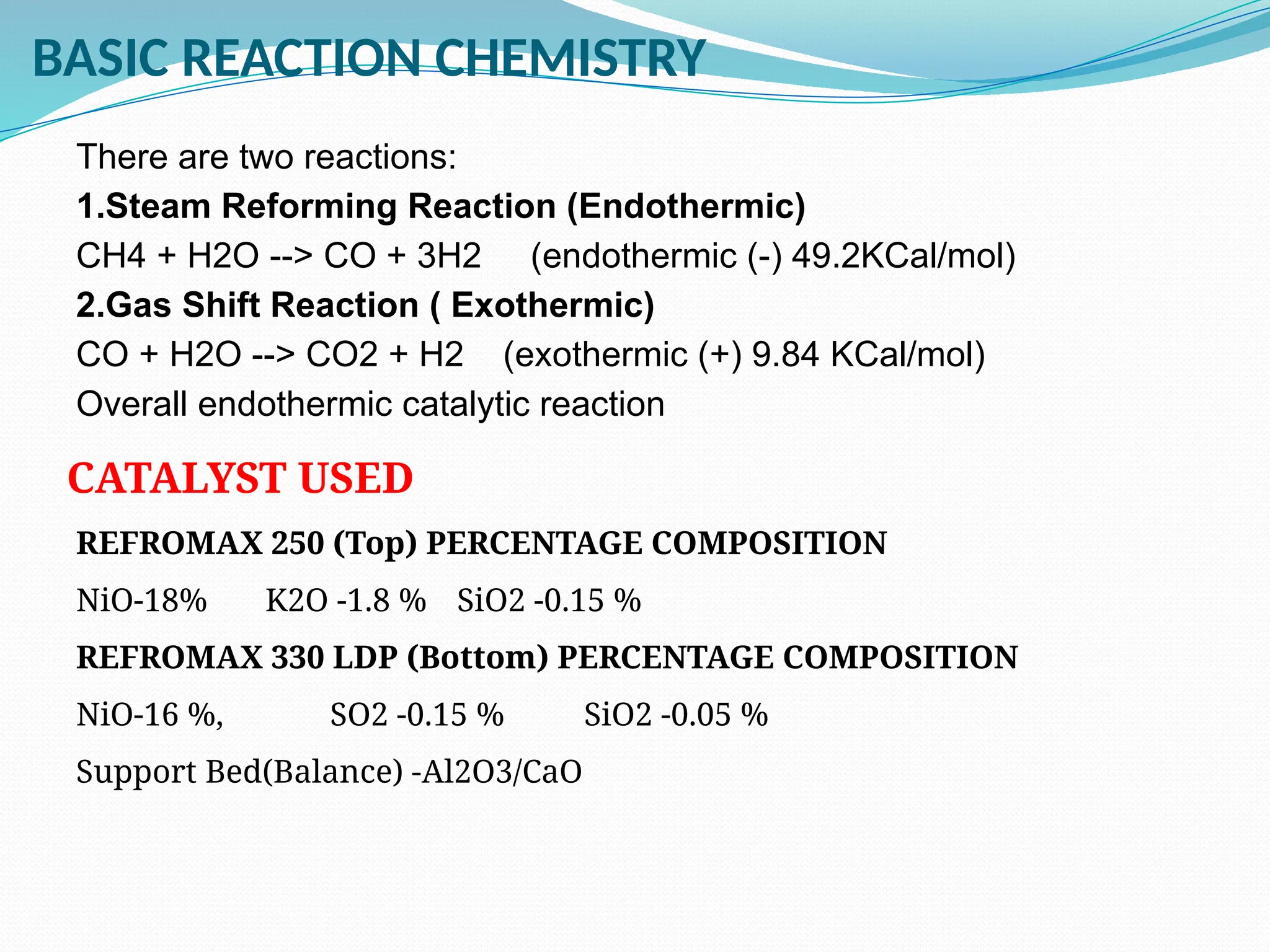
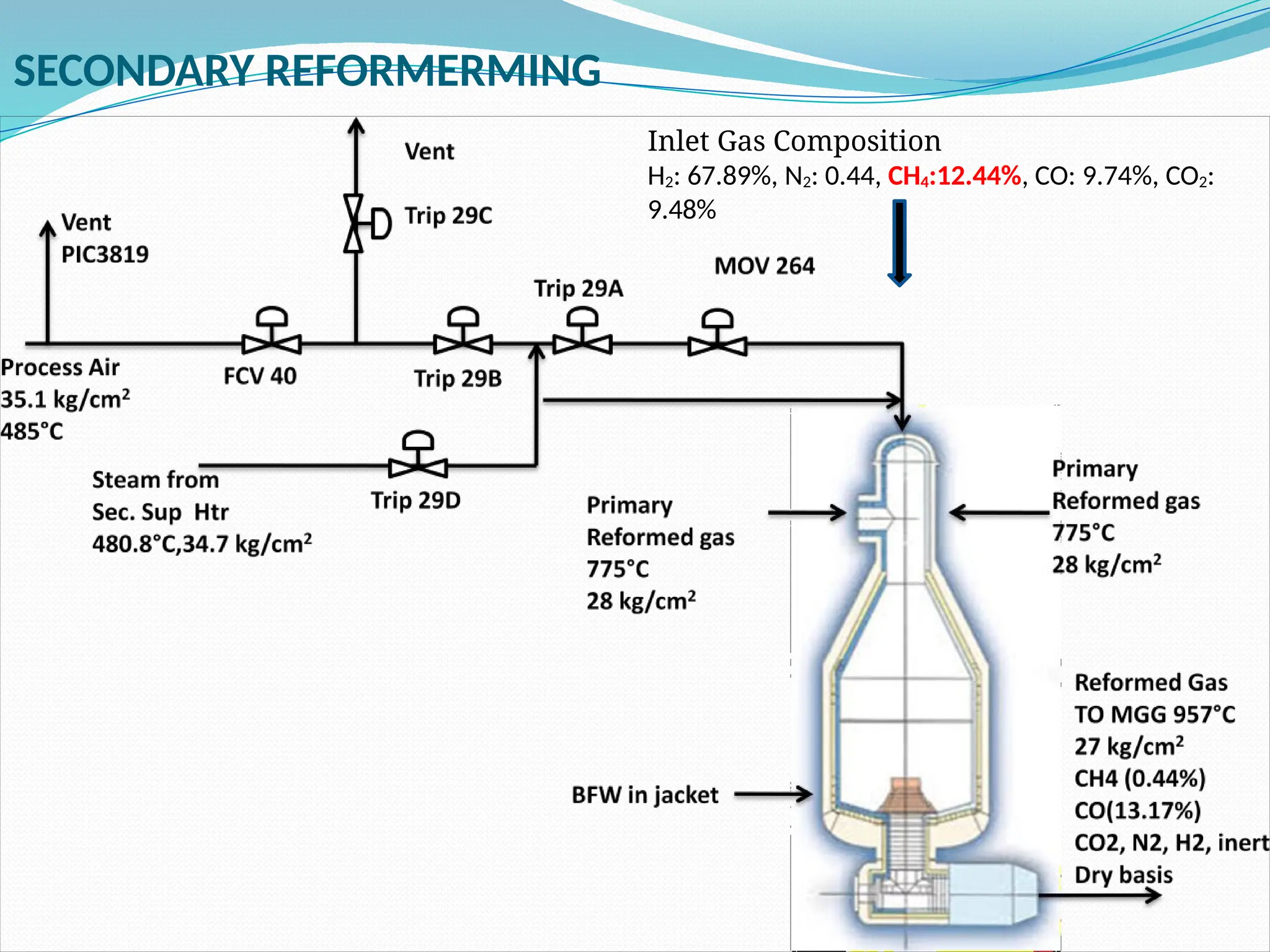
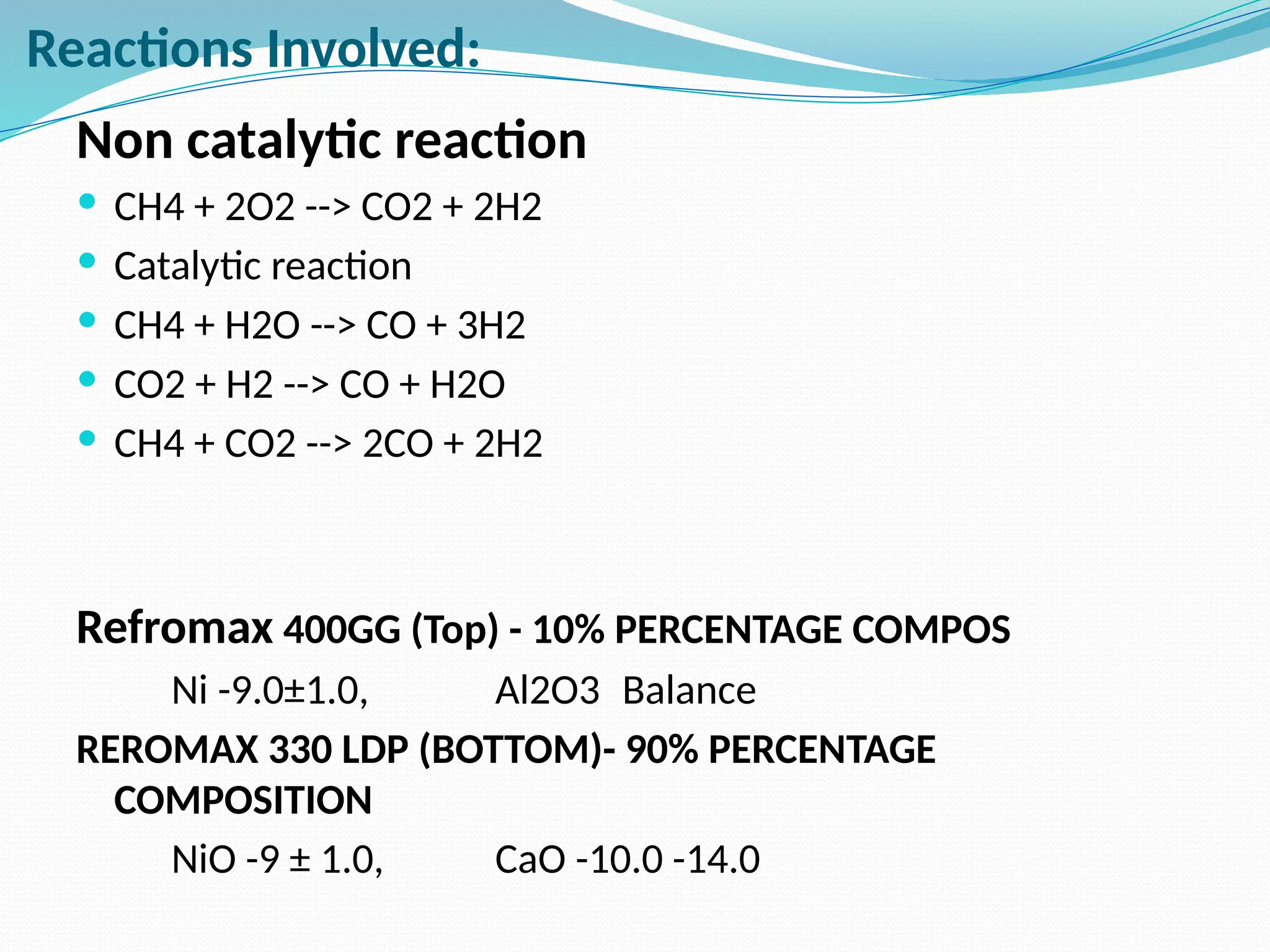
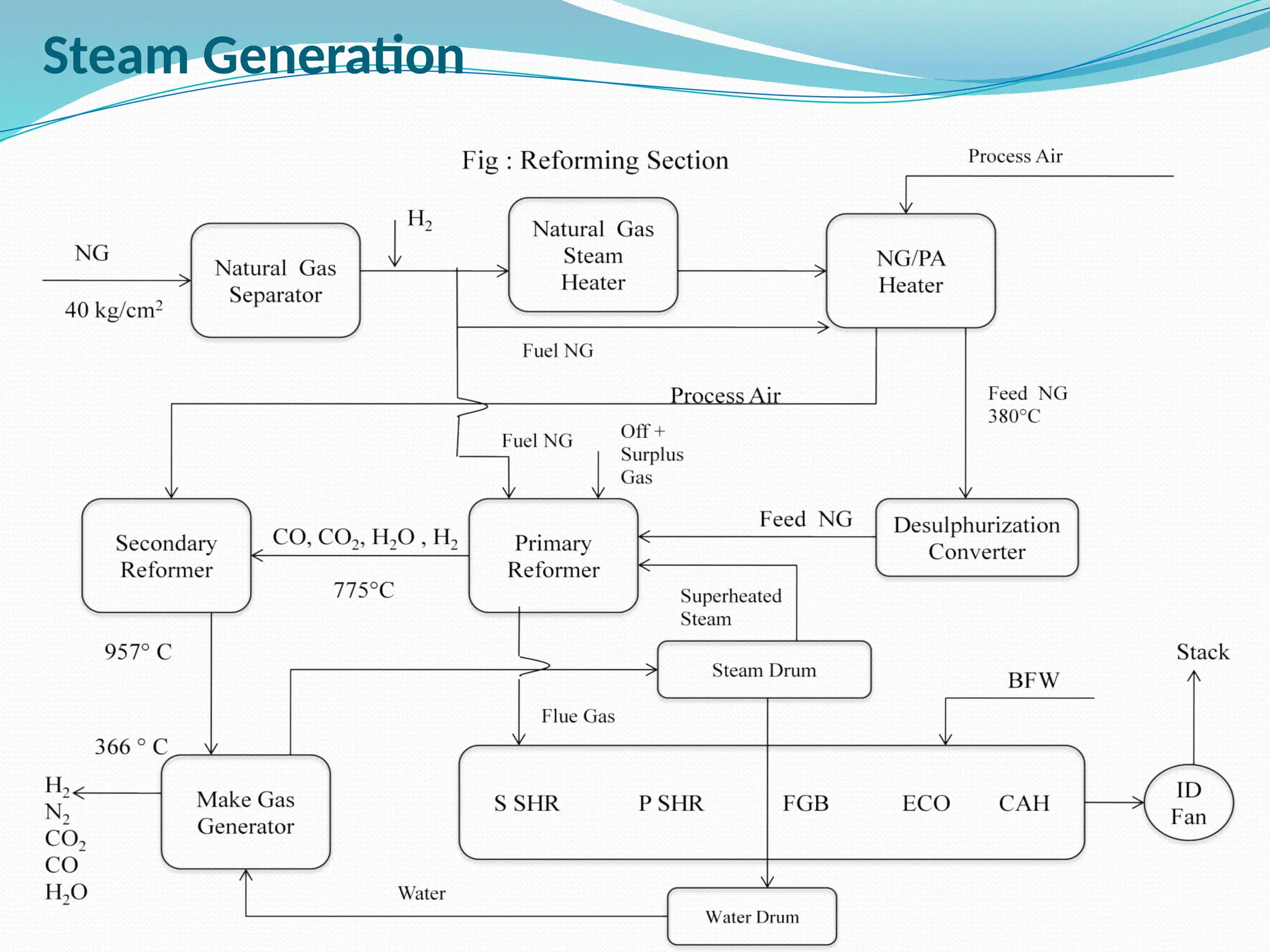
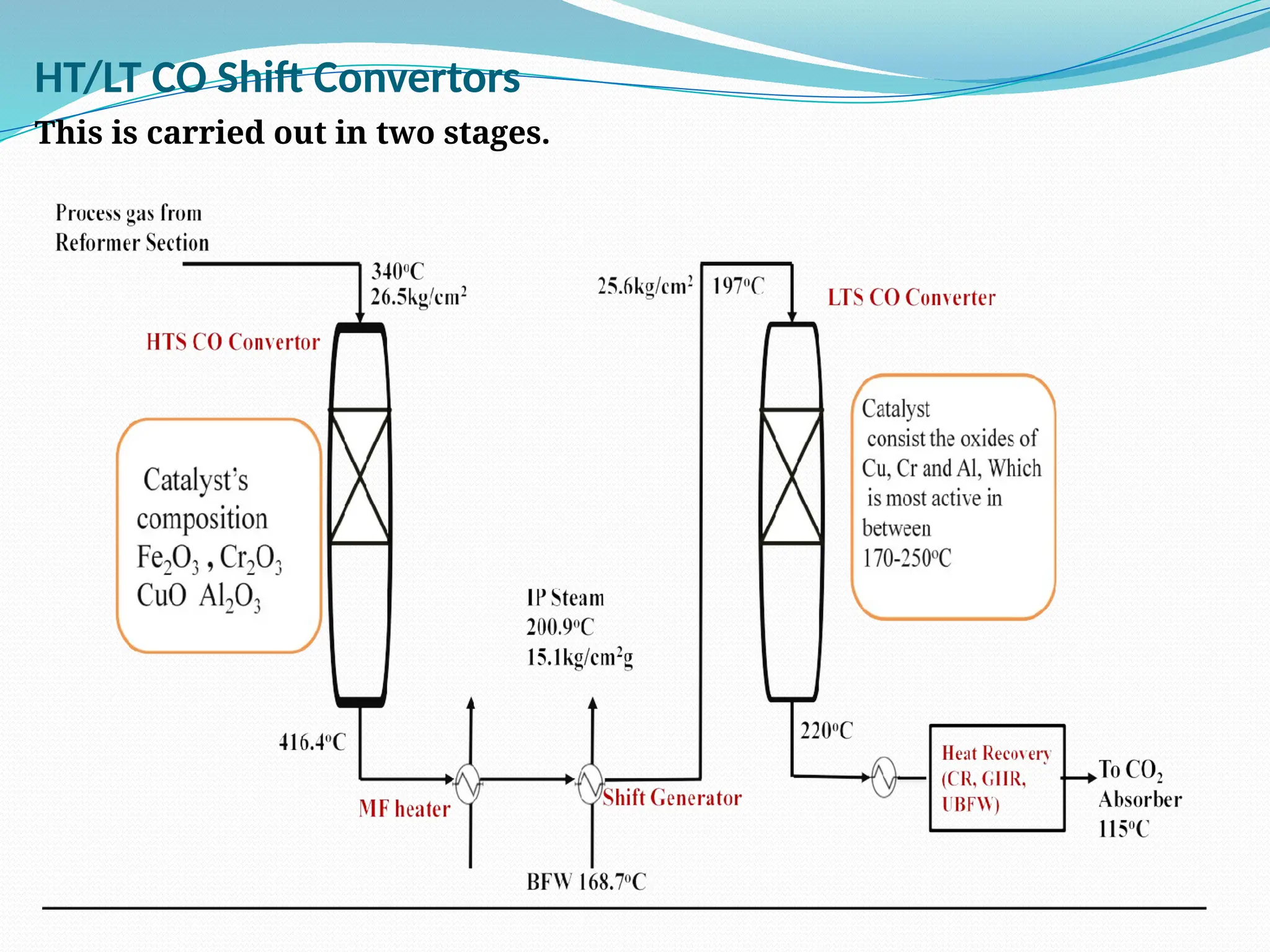
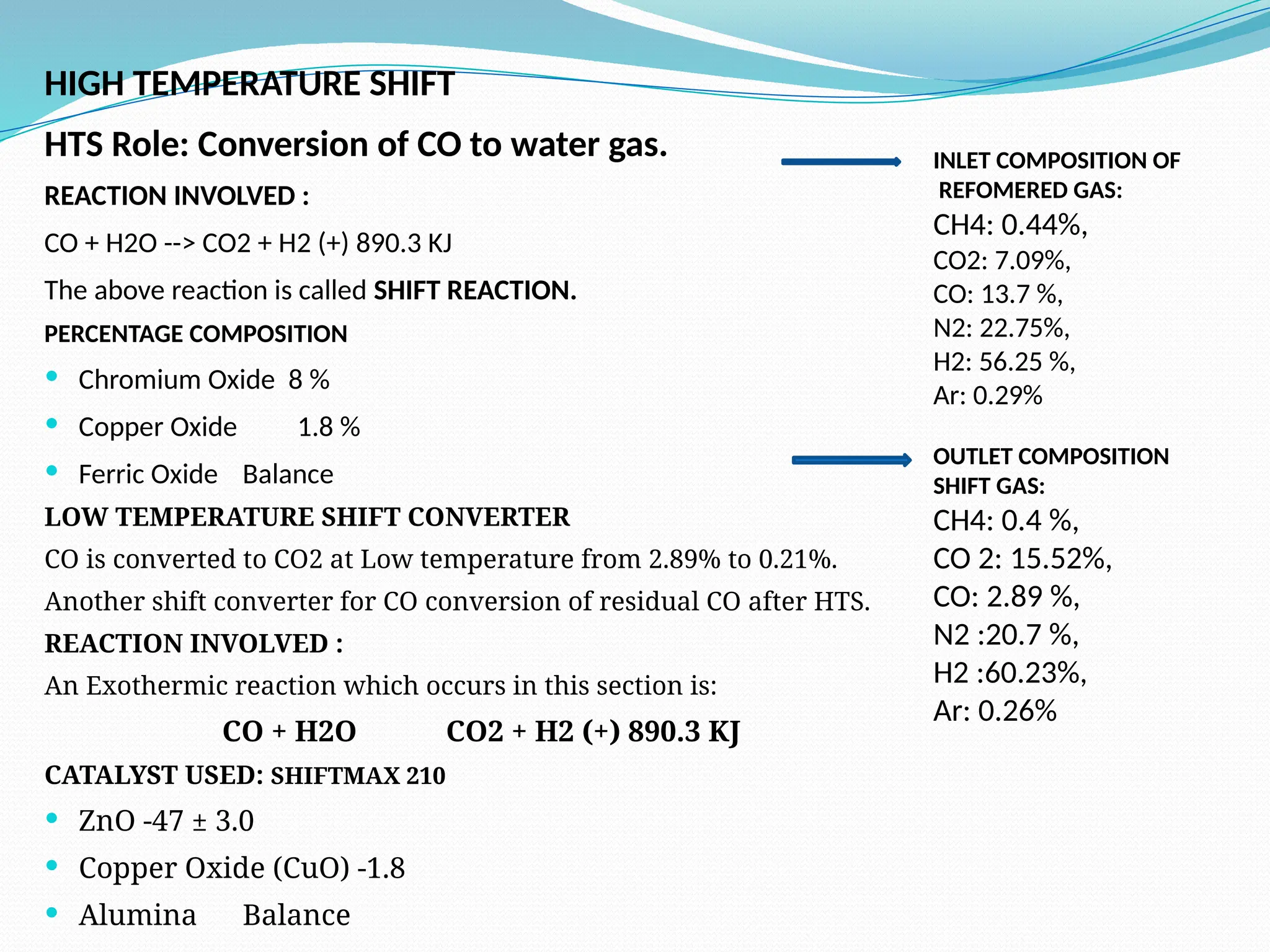
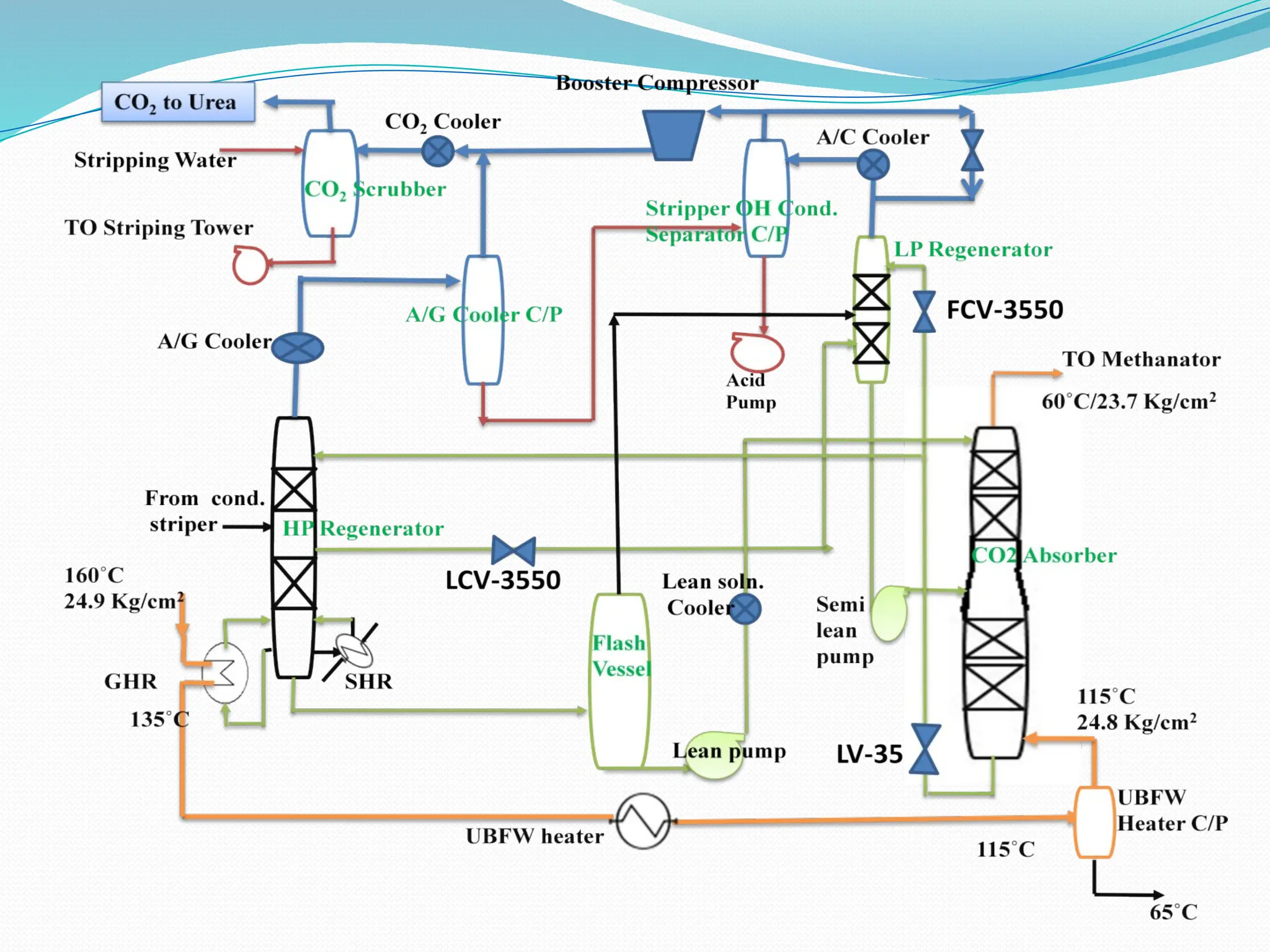
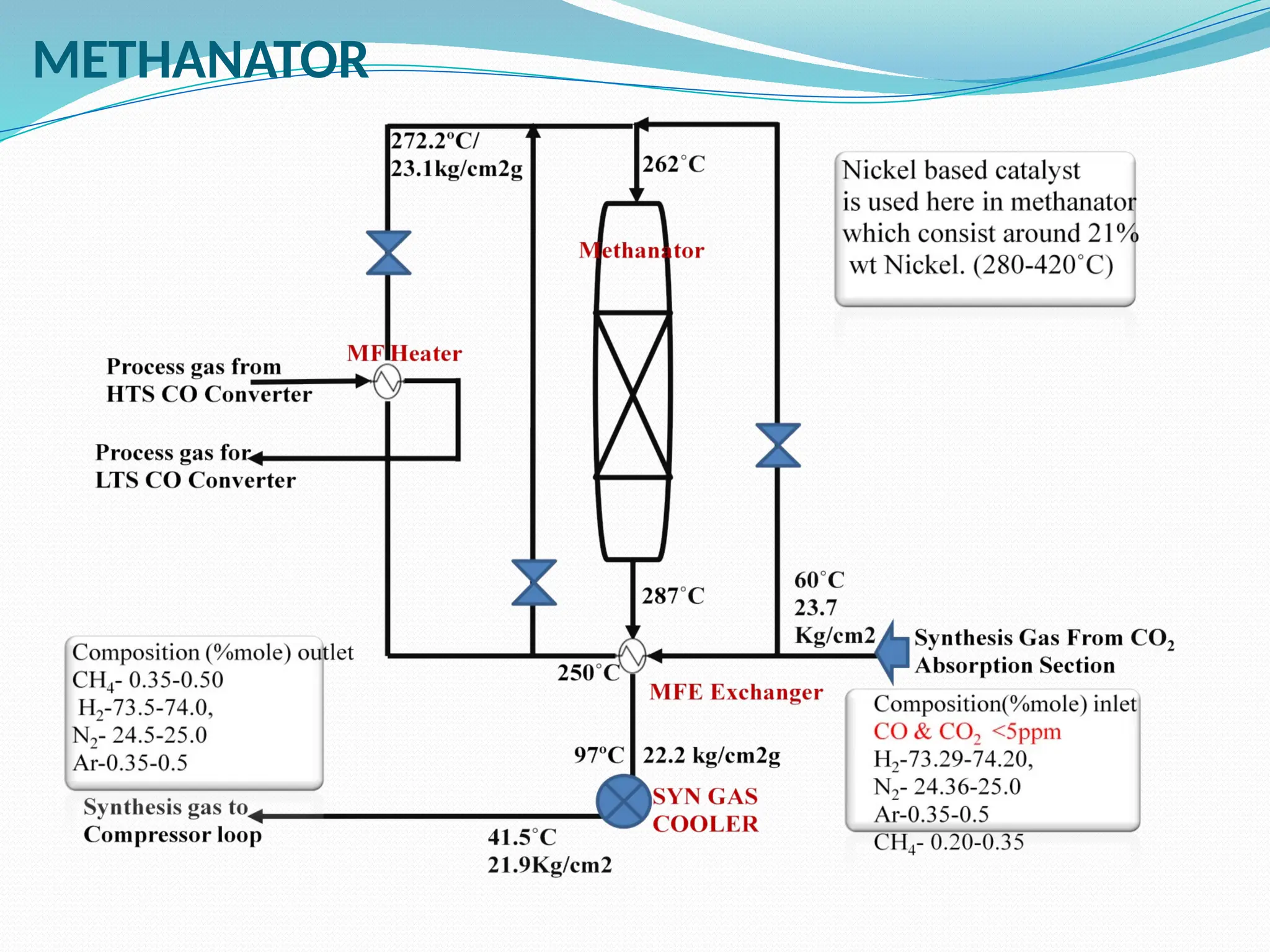
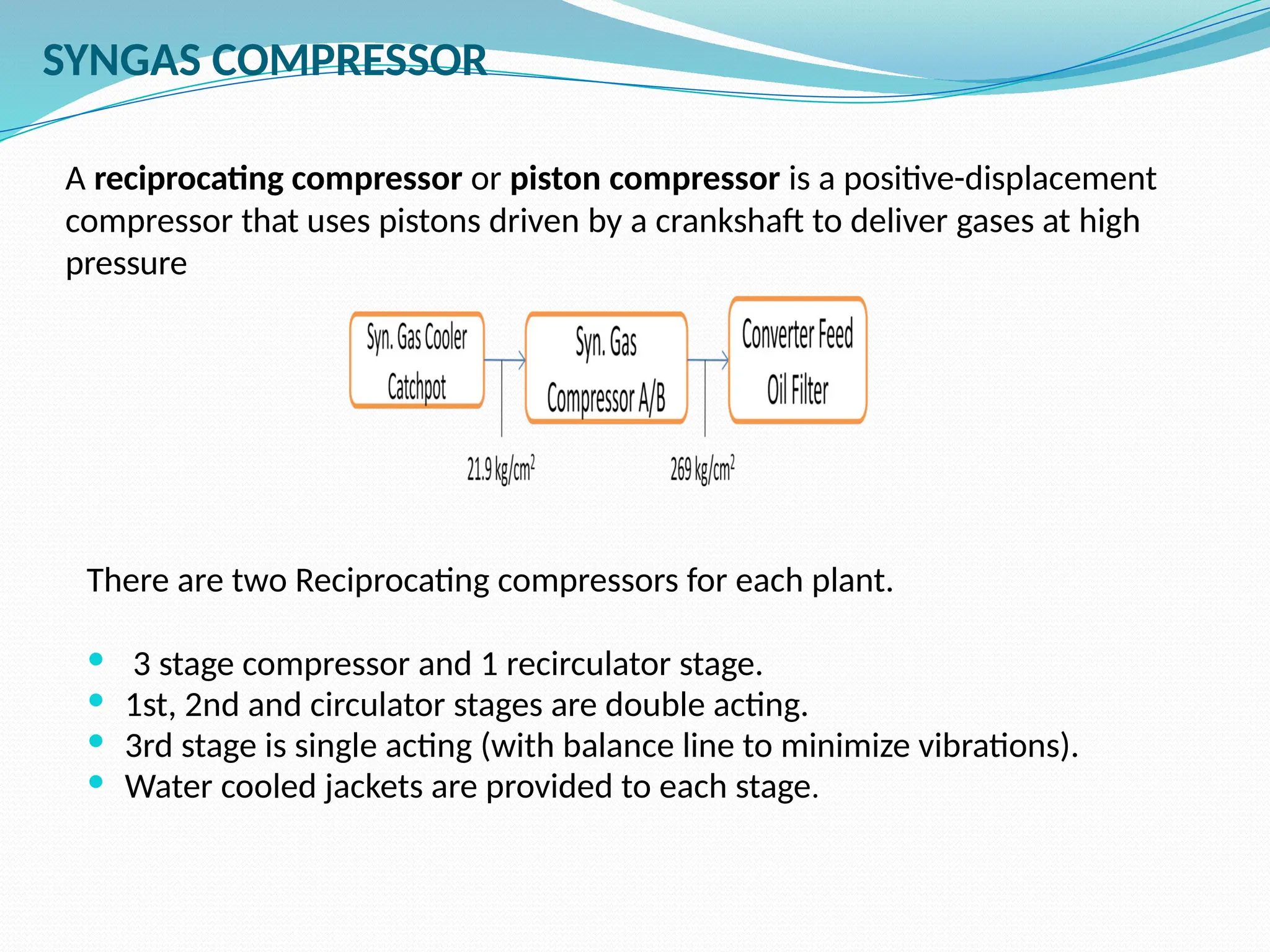
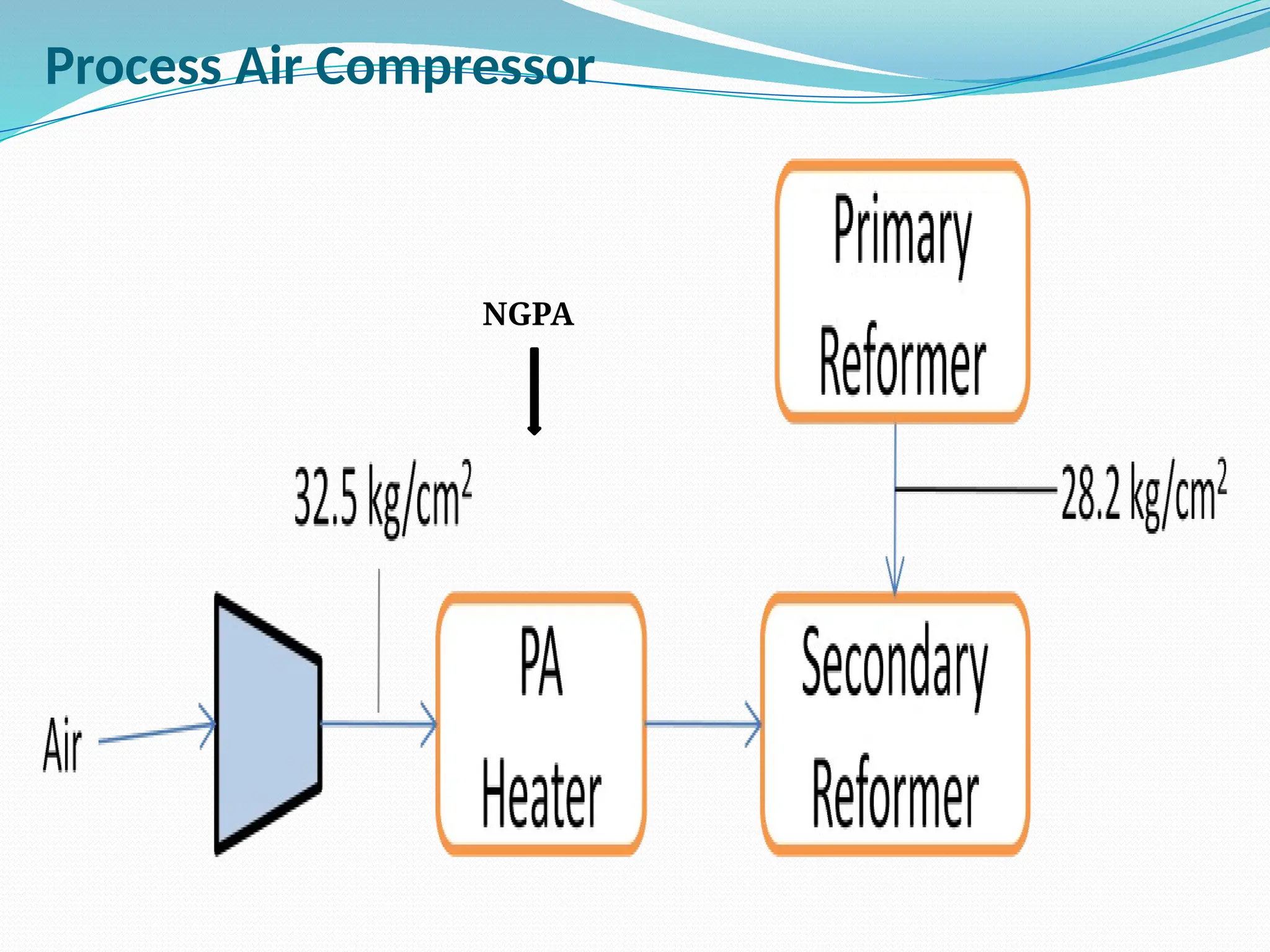
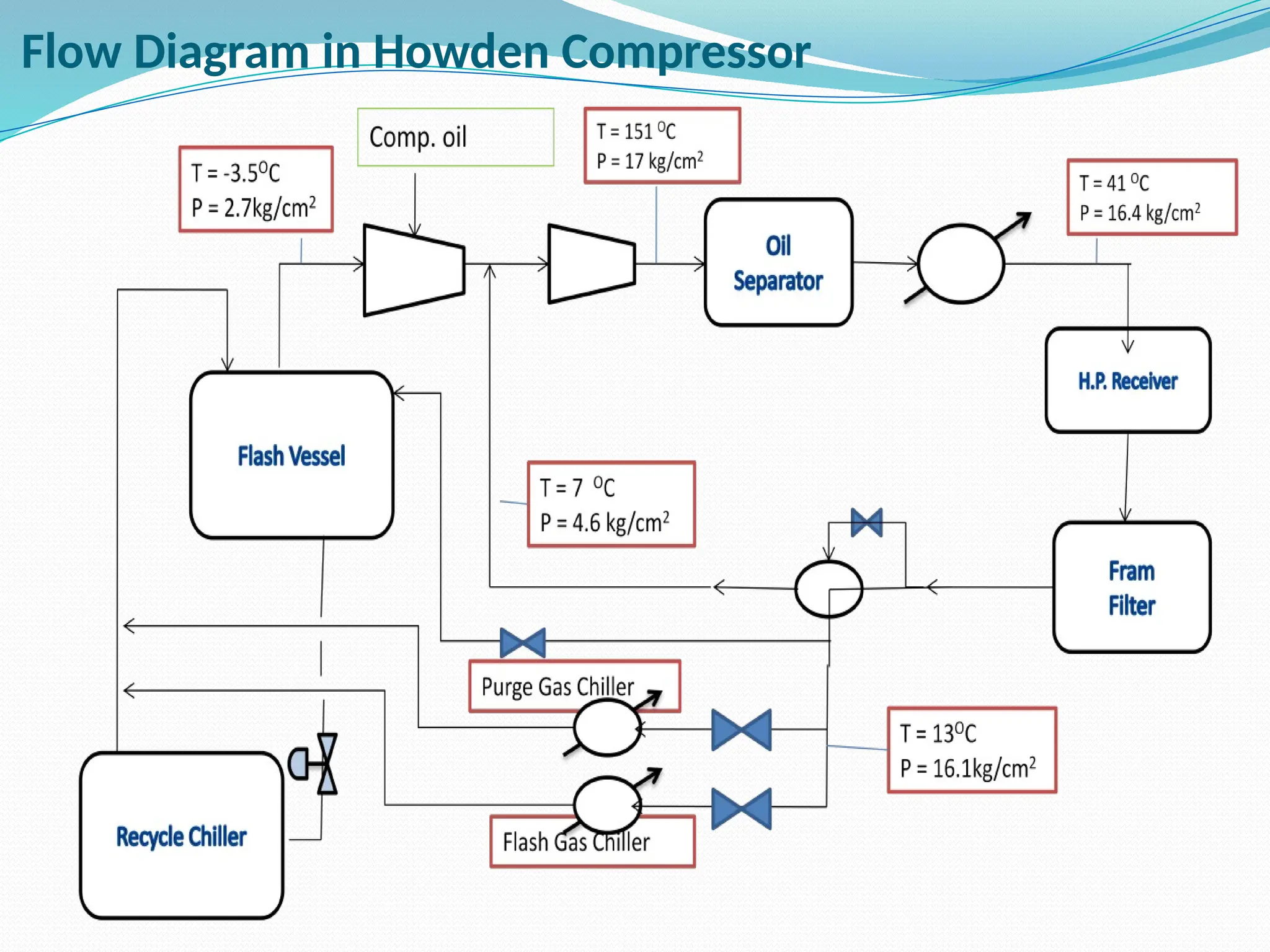
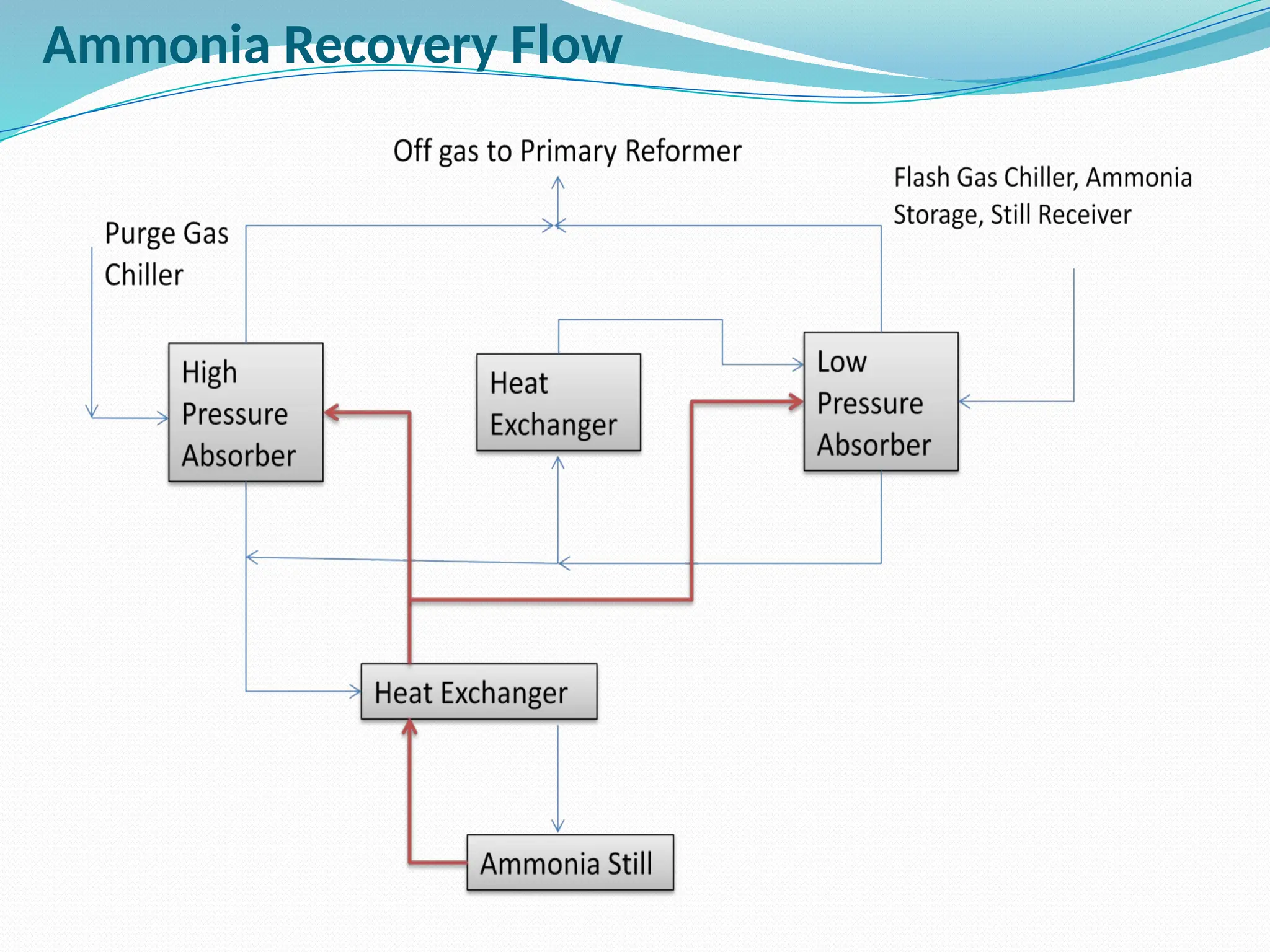
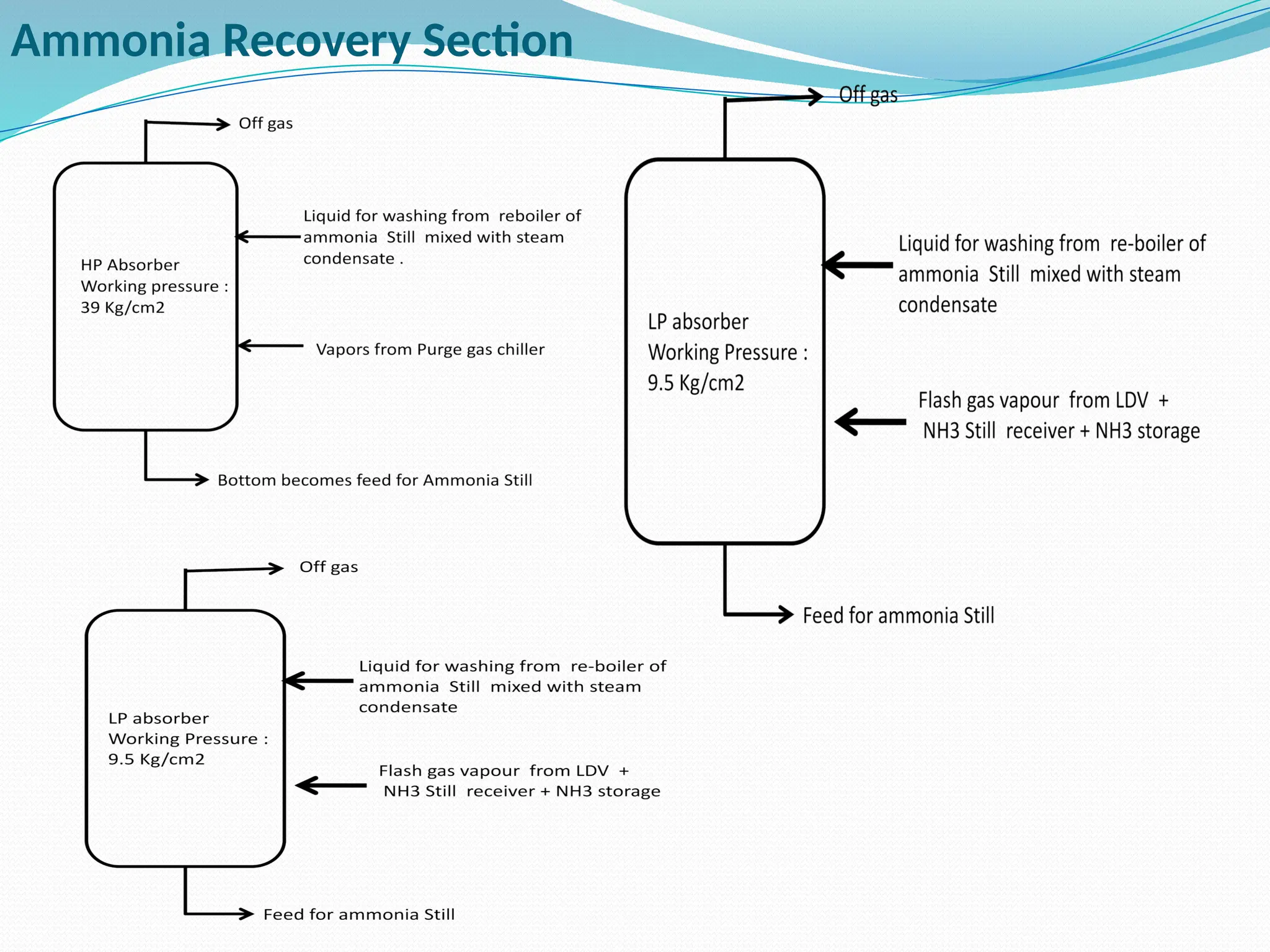
Kanpur Fertilizer & Chemical Ltd. has three ammonia plants with a total capacity of 1290 mtpd, which were re-commissioned in 2013 after switching from naphtha to natural gas. The ammonia production process involves the conversion of nitrogen and hydrogen from natural gas through several stages, including desulphurization, reforming, and methanation, utilizing various catalysts and heat recovery methods. The overall aim is to produce ammonia efficiently while managing by-products and maintaining catalyst integrity.