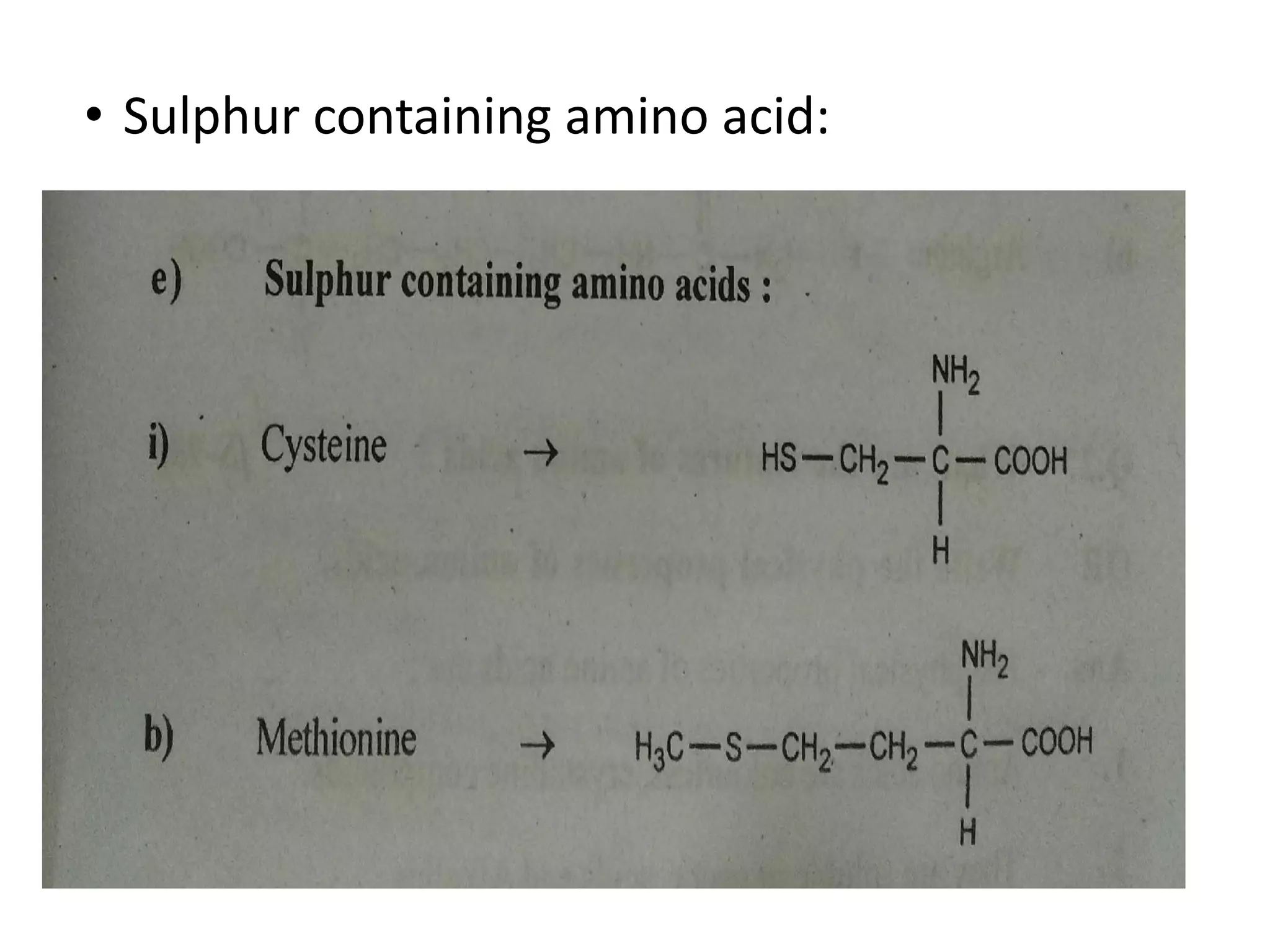
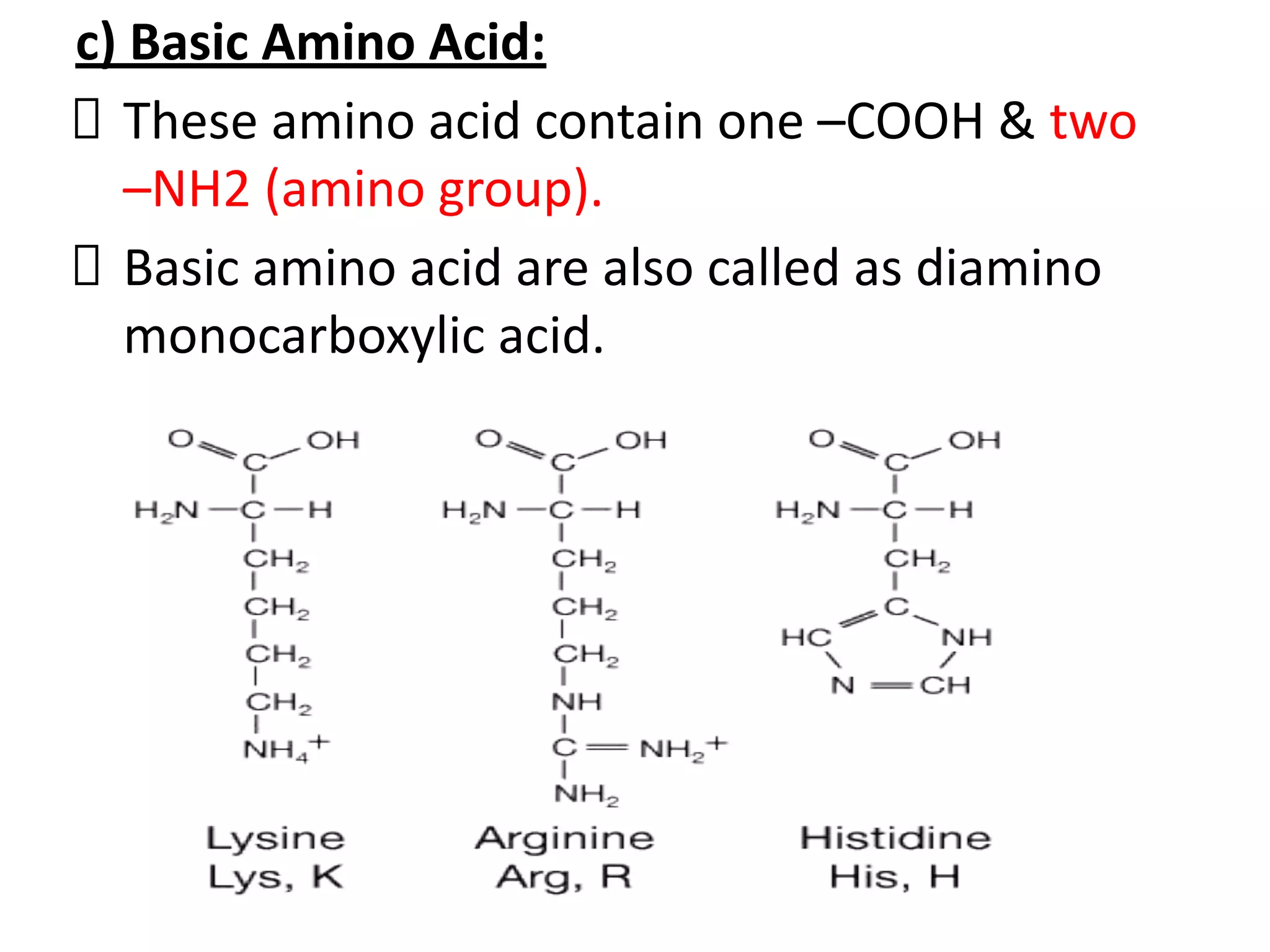
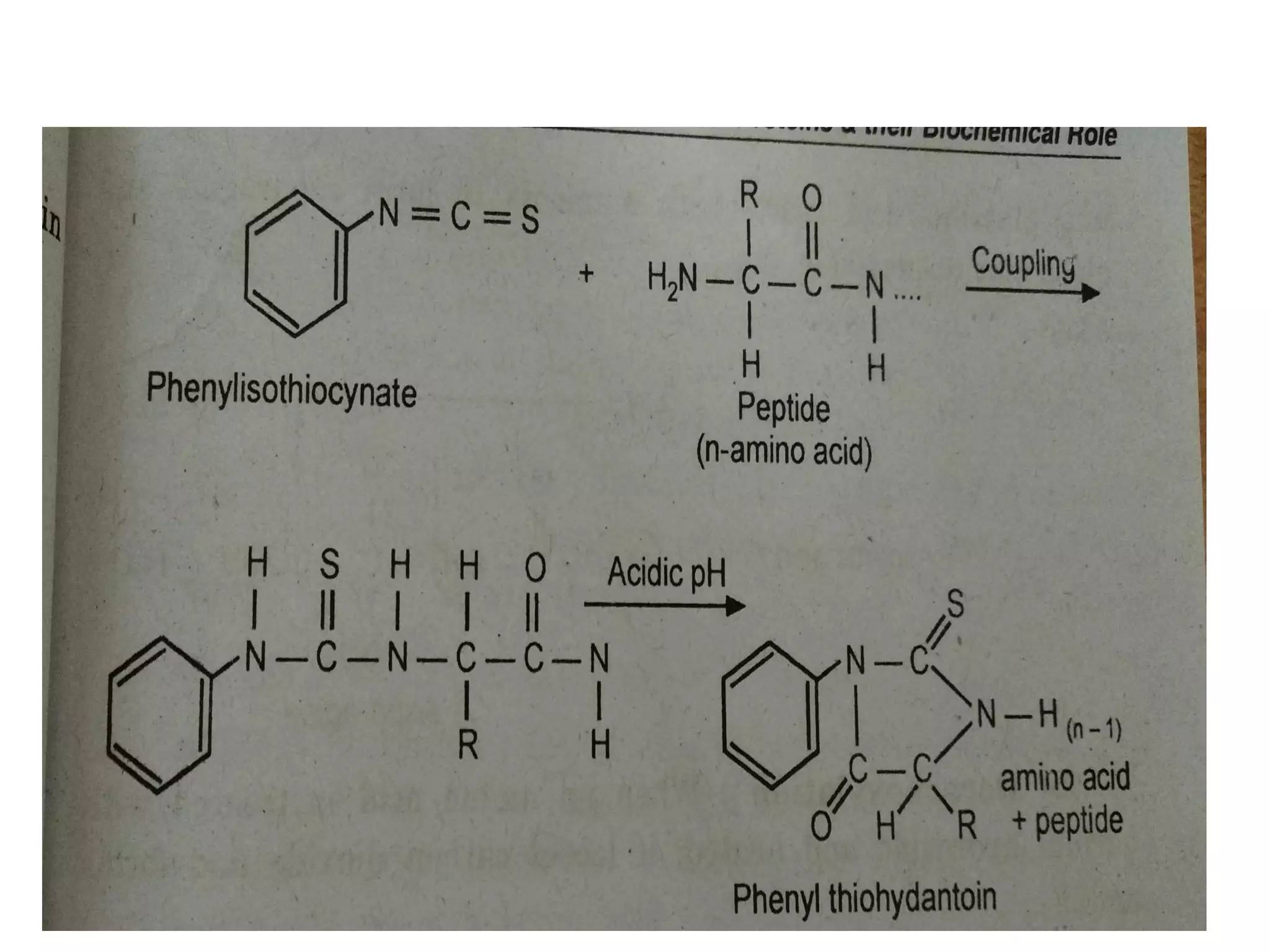
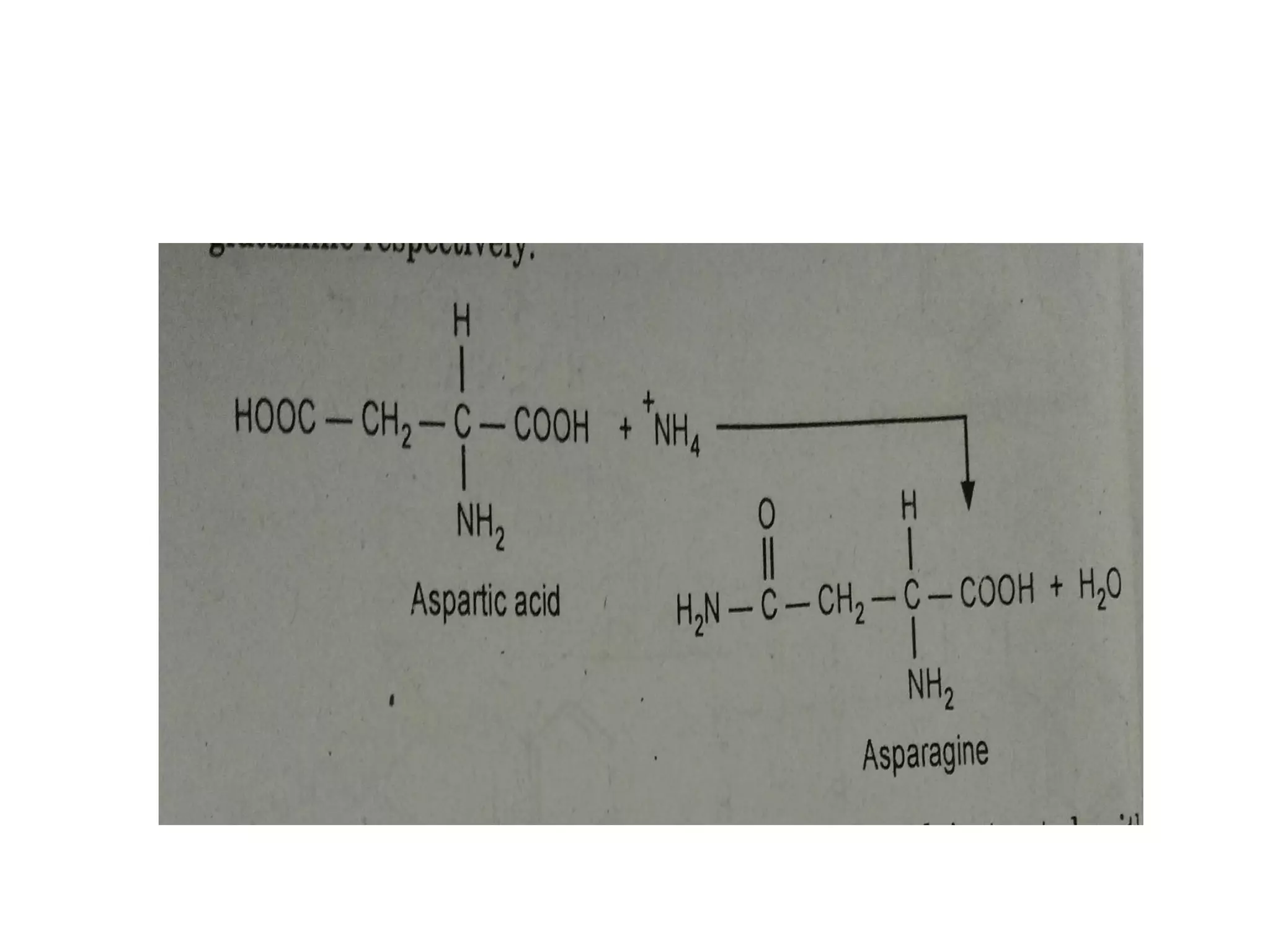
Proteins are made up of amino acids and perform important functions in the body. They can act as enzymes, hormones, antibodies, and structures. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, containing an amino group, a carboxyl group, and an R group that determines their properties. Amino acids can be classified based on their R group, charge, and essential/nonessential status. Key amino acid properties include acid-base behavior, isoelectric point, and ability to form zwitterions. Common reactions used to identify amino acids include ninhydrin, FDNB, Dansyl, and Edman reactions.

![• Protein:
• Proteins are naturally occurring nitrogen containing complex
substance that consist of large number of α amino acid residues
joined by peptide linkage (CO-NH) found in all living system.
• Function:
1. Some proteins act as hormones and hence regulate various
metabolic process e.g. insulin is responsible for maintaining blood
sugar level, hormones receptor, etc.
2. Some proteins act as catalyst for biological reaction.
3. Nucleoproteins act as carrier of genetic characters.
4. Proteins are responsible for transportation of metabolite or gases
(like oxygen, CO2
) are called transport protein.
5. Some blood proteins help to form antibodies which provide
resistance to disease so called as antibodies or defense proteins.
6. Protein Which are required to give strength to cell or tissues called
structural protein viz collagen in connective tissue,keratin in hair.
7. Protein which are required to carry out mechanical work are called
muscle protein. ]
8. Haemoglobin acts as a oxygen carrier in mammals.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/protein-210706133824/75/Amino-acids-its-basic-properties-2-2048.jpg)