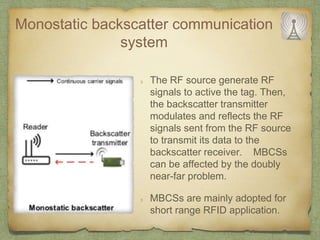
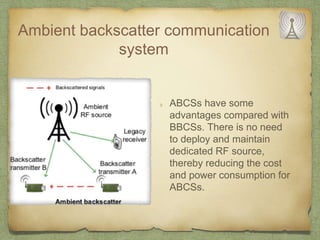
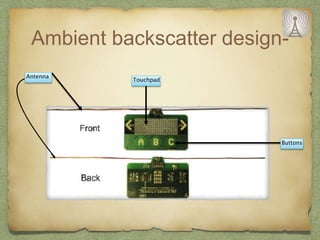
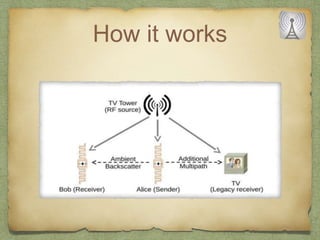
The document discusses ambient backscatter technology, which enables data transmission using existing radio frequency signals without needing batteries or grid connections. It introduces three types of backscatter communication systems: monostatic, bistatic, and ambient backscatter, each offering different advantages and use cases. Future applications include embedding backscatter devices in infrastructure for monitoring and assisting consumers in retail environments.