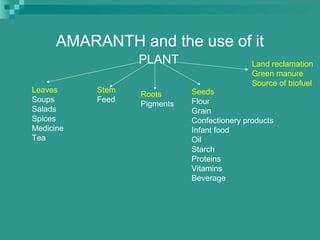
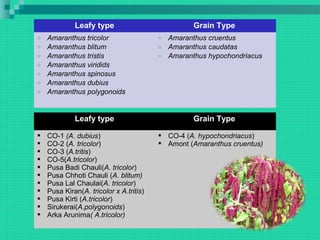
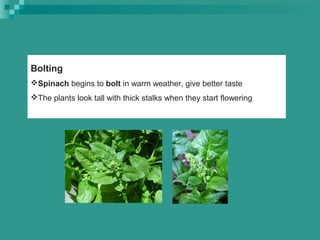
This document provides information about the production of amaranth, spinach, and basella vegetable crops. It discusses the botanical details, climate and soil requirements, varieties, sowing methods, fertilizer use, irrigation, and harvesting of these warm season crops. For amaranth, it highlights its use as a leafy green and grain crop. Several varieties are listed for both purposes. Spinach is described as an important cool season crop rich in nutrients, and ideal varieties for different regions of India are mentioned. Finally, basella is introduced as a summer vine crop with soft stems and leaves that can substitute for spinach, along with its cultivation practices.