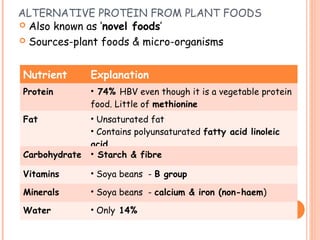
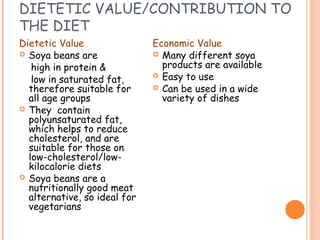
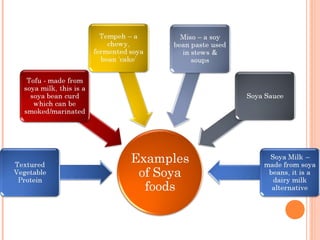
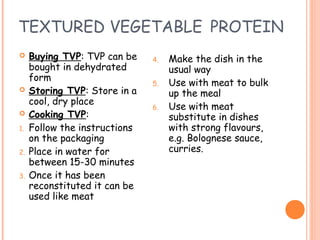
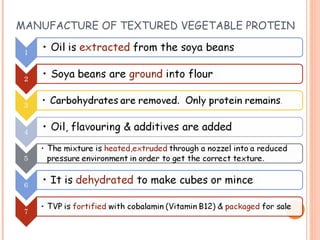
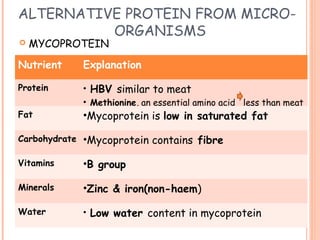
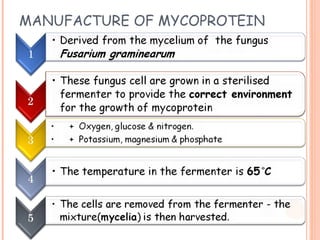
This document discusses alternative plant-based and microorganism-based sources of protein. It focuses on soybeans and textured vegetable protein (TVP) as plant-based options. Soybeans are high in protein and low in saturated fat, making them suitable for all ages. TVP is a dehydrated soybean product that can be rehydrated and used like meat to bulk up dishes. Mycoprotein, also known as Quorn, is a microorganism-based protein similar in nutrients to meat but lower in saturated fat. The document provides information on the manufacture and uses of these novel protein sources.